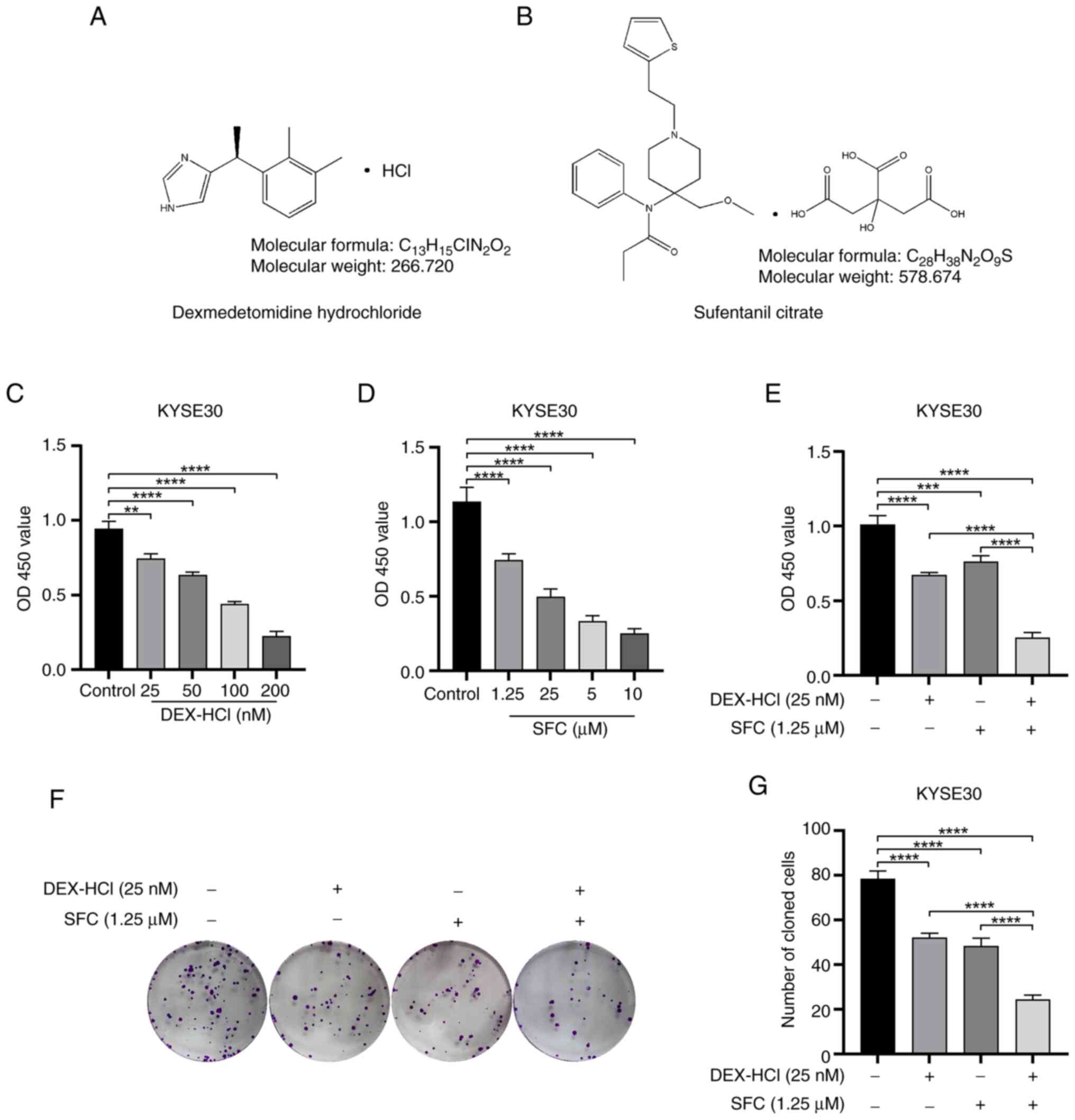
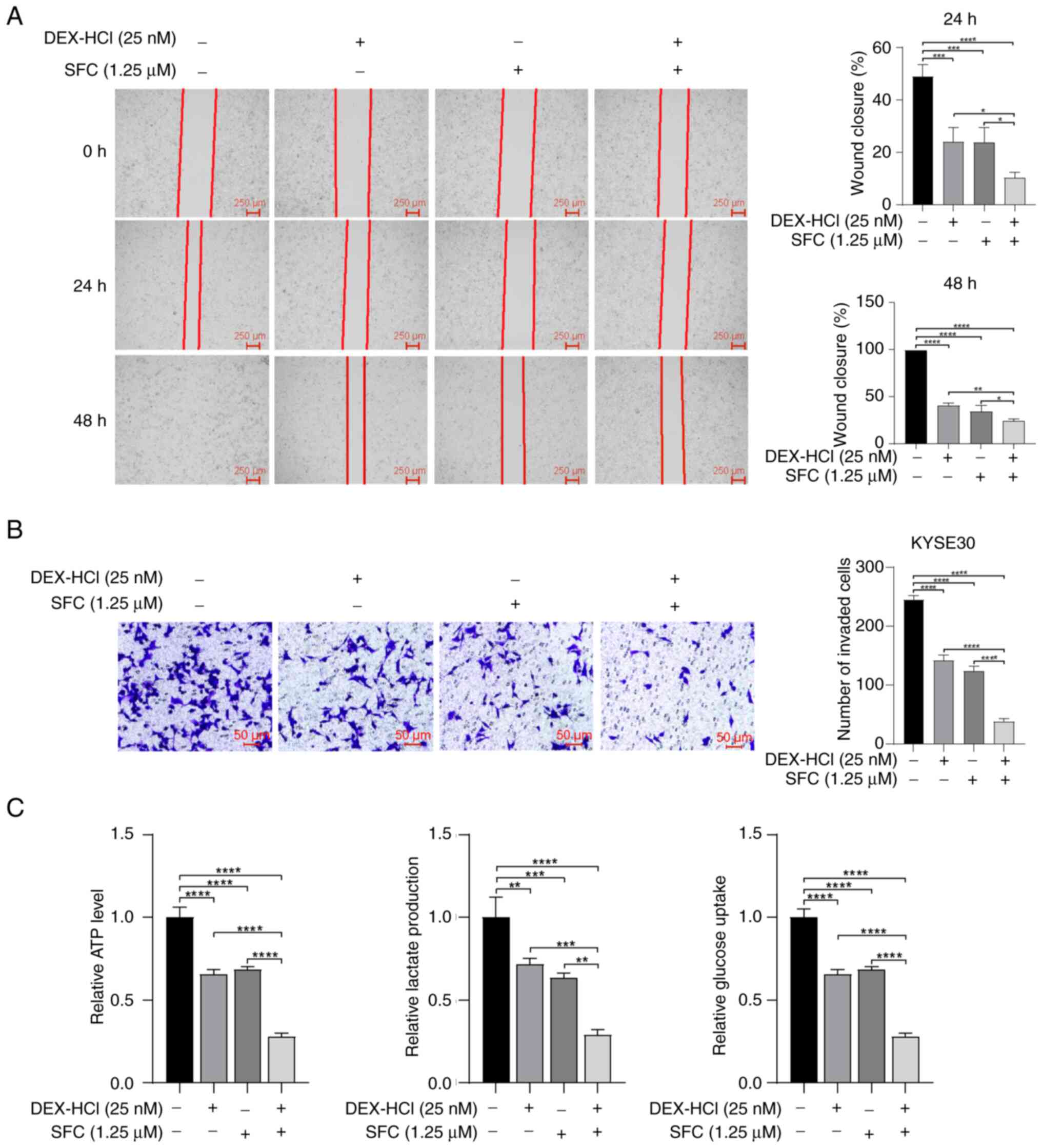
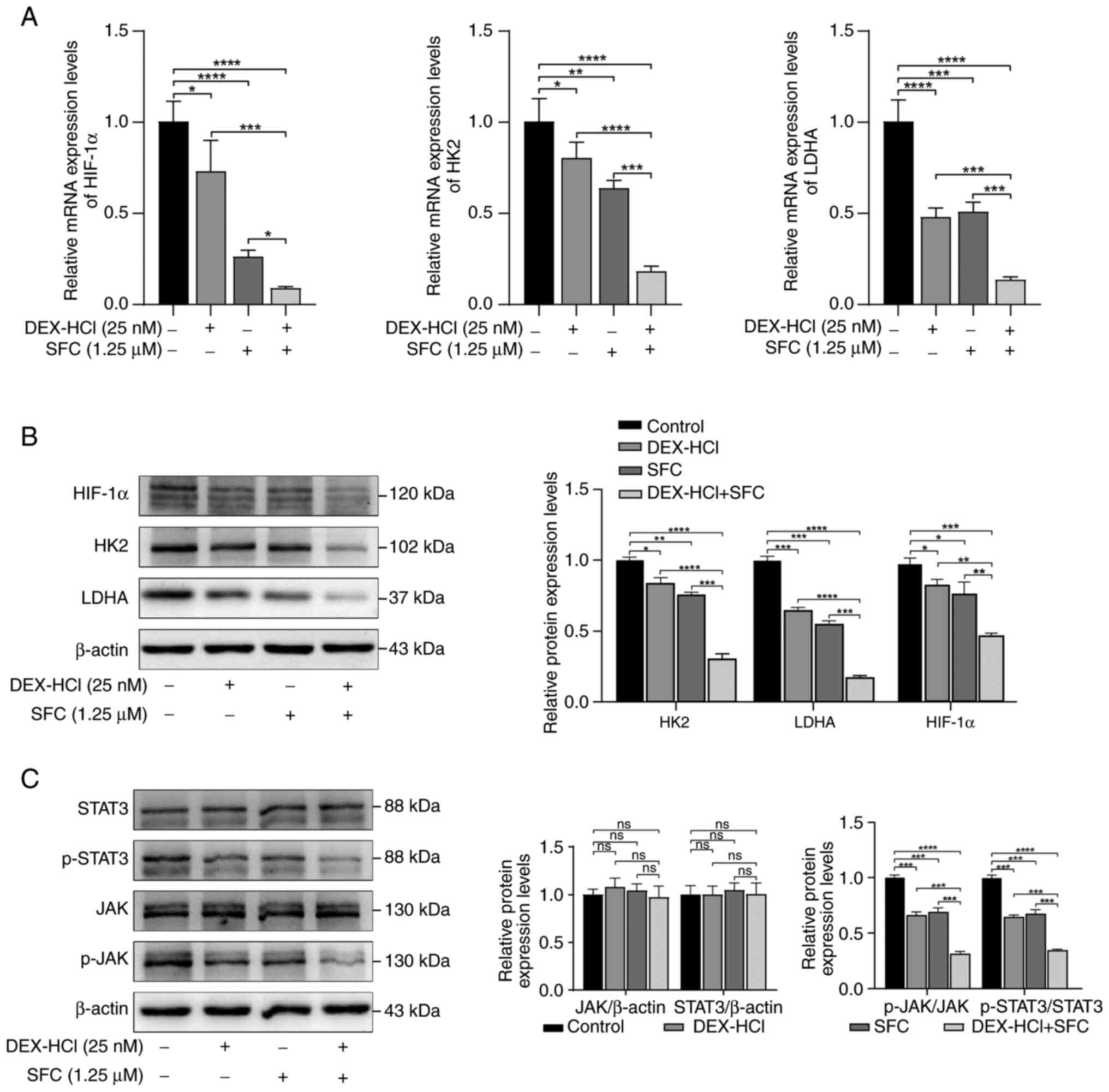
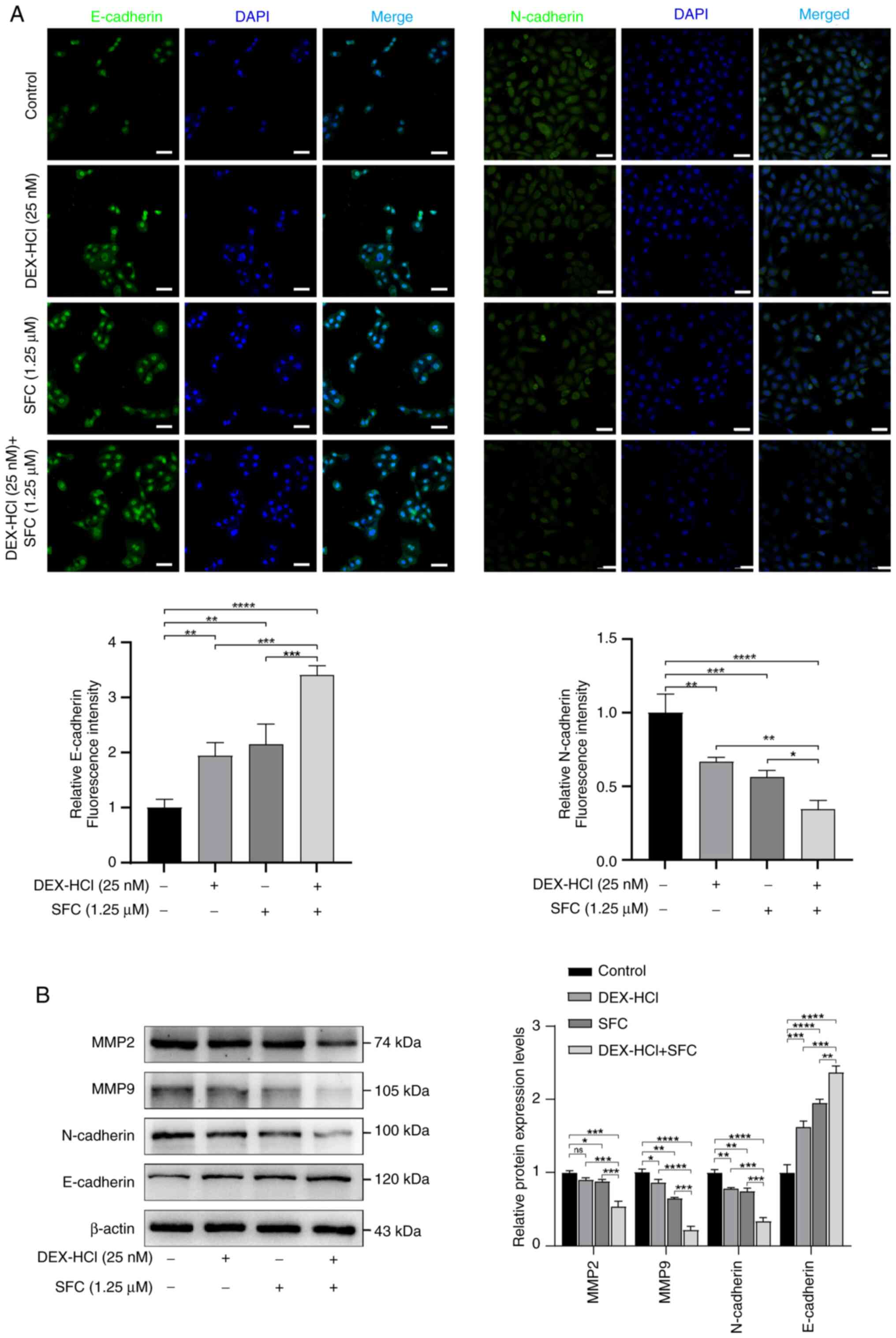
|
1
|
Liu CQ, Ma YL, Qin Q, Wang PH, Luo Y, Xu
PF and Cui Y: Epidemiology of esophageal cancer in 2020 and
projections to 2030 and 2040. Thorac Cancer. 14:3–11. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu Z, Zhao Y, Kong P, Liu Y, Huang J, Xu
E, Wei W, Li G, Cheng X, Xue L, et al: Integrated multi-omics
profiling yields a clinically relevant molecular classification for
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 41:181–195. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Morgan E, Soerjomataram I, Rumgay H,
Coleman HG, Thrift AP, Vignat J, Laversanne M, Ferlay J and Arnold
M: The global landscape of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and
esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality in 2020 and
projections to 2040: New estimates from GLOBOCAN 2020.
Gastroenterology. 163:649–658. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li P, Jing J, Liu W, Wang J, Qi X and
Zhang G: Spatiotemporal patterns of esophageal cancer burden
attributable to behavioral, metabolic, and dietary risk factors
from 1990 to 2019: Longitudinal observational study. JMIR Public
Health Surveill. 9:e460512023. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Codipilly DC and Wang KK: Squamous cell
carcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterol Clin North Am.
51:457–484. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu D, Wu X, Wu W, Wu S, Li H, Zhang Y, Yan
X, Zhai J, Dong X, Feng S, et al: Plasma cell-free DNA
5-hydroxymethylcytosine and whole-genome sequencing signatures for
early detection of esophageal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 14:8432023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang S, Zheng R, Arnold M, Abnet C, Zeng
H, Zhang S, Chen R, Sun K, Li L, An L, et al: Global and national
trends in the age-specific sex ratio of esophageal cancer and
gastric cancer by subtype. Int J Cancer. 151:1447–1461. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Manfioletti G and Fedele M:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Int J Mol Sci.
24:113862023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lu W and Kang Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in cancer progression and metastasis. Dev Cell.
49:361–374. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Counihan JL, Grossman EA and Nomura DK:
Cancer metabolism: Current understanding and therapies. Chem Rev.
118:6893–6923. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang M, Wei T, Zhang X and Guo D:
Targeting lipid metabolism reprogramming of immunocytes in response
to the tumor microenvironment stressor: A potential approach for
tumor therapy. Front Immunol. 13:9374062022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xin P, Xu X, Deng C, Liu S, Wang Y, Zhou
X, Ma H, Wei D and Sun S: The role of JAK/STAT signaling pathway
and its inhibitors in diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 80:1062102020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang P, Li Z and Yang G: Silencing of
ISLR inhibits tumour progression and glycolysis by inactivating the
IL-6/JAK/STAT3 pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Mol
Med. 48:2222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao C, Zhang W, Hua M, Chen H, Yang B,
Wang Y and Yang Q: RNF7 inhibits apoptosis and sunitinib
sensitivity and promotes glycolysis in renal cell carcinoma via the
SOCS1/JAK/STAT3 feedback loop. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 27:362022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lei K, Du W, Lin S, Yang L, Xu Y, Gao Y,
Xu B, Tan S, Xu Y, Qian X, et al: 3B, a novel photosensitizer,
inhibits glycolysis and inflammation via miR-155-5p and breaks the
JAK/STAT3/SOCS1 feedback loop in human breast cancer cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 82:141–150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
You Z, Xu D, Ji J, Guo W, Zhu W and He J:
JAK/STAT signal pathway activation promotes progression and
survival of human oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Transl
Oncol. 14:143–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao X, Tang YP, Wang CY, Wu JX and Ye F:
Prognostic values of STAT3 and HIF-1lα in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:3351–3357. 2019.
|
|
18
|
Fang J, Chu L, Li C, Chen Y, Hu F, Zhang
X, Zhao H, Liu Z and Xu Q: JAK2 inhibitor blocks the inflammation
and growth of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vitro through
the JAK/STAT3 pathway. Oncol Rep. 33:494–502. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang Y, Jin G, Liu H, Liu K, Zhao J, Chen
X, Wang D, Bai R, Li X, Jang Y, et al: Metformin inhibits
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma-induced angiogenesis by
suppressing JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 8:74673–74687.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Garcia SN, Guedes RC and Marques MM:
Unlocking the potential of HK2 in cancer metabolism and
therapeutics. Curr Med Chem. 26:7285–7322. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Jiang C, Zhong Y, Sun K, Jing H,
Song J, Xie J, Zhou Y, Tian M, Zhang C, et al: STING is a
cell-intrinsic metabolic checkpoint restricting aerobic glycolysis
by targeting HK2. Nat Cell Biol. 25:1208–1222. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xun S and Zheng R: Dexmedetomidine
alleviates neuropathic pain by regulating JAK/STAT pathway in rats.
J Cell Biochem. 121:2277–2283. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Si Y, Bao H, Han L, Shi H, Zhang Y, Xu L,
Liu C, Wang J, Yang X, Vohra A and Ma D: Dexmedetomidine protects
against renal ischemia and reperfusion injury by inhibiting the
JAK/STAT signaling activation. J Transl Med. 11:1412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Jiang W and Luo X: Remifentanil
combined with dexmedetomidine on the analgesic effect of breast
cancer patients undergoing modified radical mastectomy and the
influence of perioperative T lymphocyte subsets. Front Surg.
9:10166902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cai Q, Liu G, Huang L, Guan Y, Wei H, Dou
Z, Liu D, Hu Y and Gao M: The role of dexmedetomidine in
tumor-progressive factors in the perioperative period and cancer
recurrence: A narrative review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 16:2161–2175.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang H, Qu M, Guo K, Wang Y, Gu J, Wu H,
Zhu X, Sun Z, Cata JP, Chen W and Miao C: Intraoperative lidocaine
infusion in patients undergoing pancreatectomy for pancreatic
cancer: A mechanistic, multicentre randomised clinical trial. Br J
Anaesth. 129:244–253. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ruijter JM, Barnewall RJ, Marsh IB,
Szentirmay AN, Quinn JC, van Houdt R, Gunst QD and van den Hoff
MJB: Efficiency correction is required for accurate quantitative
PCR analysis and reporting. Clin Chem. 67:829–842. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 70:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meng J, Zhang C, Zhu N, Zhang C, Liu M,
Han Z and Li Y: EPN3 plays oncogenic role in non-small cell lung
cancer by activating the JAK1/2-STAT3 pathway. Environ Toxicol.
38:1968–1979. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gundamaraju R, Lu W, Paul MK, Jha NK,
Gupta PK, Ojha S, Chattopadhyay I, Rao PV and Ghavami S: Autophagy
and EMT in cancer and metastasis: Who controls whom? Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1868:1664312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang X, Shi G, Gao F, Liu P, Wang H and
Tan X: TSPAN1 upregulates MMP2 to promote pancreatic cancer cell
migration and invasion via PLCγ. Oncol Rep. 41:2117–2125.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang L, Xi RX and Zhang XZ: Matrix
metalloproteinase variants associated with risk and clinical
outcome of esophageal cancer. Genet Mol Res. 14:4616–4624. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu XL, Ling ZQ, Chen SZ, Li B, Ji WH and
Mao WM: The impact of E-cadherin expression on the prognosis of
esophageal cancer: A meta-analysis. Dis Esophagus. 27:79–86. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu S, Liu J, Min L, Sun X, Guo Q, Li H,
Zhang Z, Zhao Y, Gu J and Zhang S: Cadherin expression shift could
well distinguish esophageal squamous cell carcinoma from non-
cancerous esophageal tissues. Oncol Res Treat. 41:380–385. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mendonsa AM, Na TY and Gumbiner BM:
E-cadherin in contact inhibition and cancer. Oncogene.
37:4769–4780. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Parker J, Hockney S, Blaschuk OW and Pal
D: Targeting N-cadherin (CDH2) and the malignant bone marrow
microenvironment in acute leukaemia. Expert Rev Mol Med.
25:e162023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lou C, Wu K, Shi J, Dai Z and Xu Q:
N-cadherin protects oral cancer cells from NK cell killing in the
circulation by inducing NK cell functional exhaustion via the KLRG1
receptor. J Immunother Cancer. 10:e0050612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mariotti A, Perotti A, Sessa C and Rüegg
C: N-cadherin as a therapeutic target in cancer. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 16:451–465. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yoshio T, Ishiyama A, Tsuchida T,
Yoshimizu S, Horiuchi Y, Omae M, Hirasawa T, Yamamoto Y, Sano H,
Yokota M and Fujisaki J: Efficacy of novel sedation using the
combination of dexmedetomidine and midazolam during endoscopic
submucosal dissection for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Esophagus. 16:285–291. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Che J, Liu M and Lv H: Dexmedetomidine
disrupts esophagus cancer tumorigenesis by modulating
circ_0003340/miR-198/HMGA2 axis. Anticancer Drugs. 33:448–458.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tang H, Li C, Wang Y and Deng L:
Sufentanil inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of esophageal
cancer by inhibiting the NF-κB and snail signaling pathways.
J Oncol. 2021:75861002021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kocianova E, Piatrikova V and Golias T:
Revisiting the warburg effect with focus on lactate. Cancers
(Basel). 14:60282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhong X, He X, Wang Y, Hu Z, Huang H, Zhao
S, Wei P and Li D: Warburg effect in colorectal cancer: The
emerging roles in tumor microenvironment and therapeutic
implications. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1602022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Chelakkot C, Chelakkot VS, Shin Y and Song
K: Modulating glycolysis to improve cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
24:26062023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhang K, Zhang T, Yang Y, Tu W, Huang H,
Wang Y, Chen Y, Pan K and Chen Z: N(6)-methyladenosine-mediated
LDHA induction potentiates chemoresistance of colorectal cancer
cells through metabolic reprogramming. Theranostics. 12:4802–4817.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Jacquet P and Stephanou A: Searching for
the metabolic signature of cancer: A review from warburg's time to
now. Biomolecules. 12:14122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Brand A, Singer K, Koehl GE, Kolitzus M,
Schoenhammer G, Thiel A, Matos C, Bruss C, Klobuch S, Peter K, et
al: LDHA-associated lactic acid production blunts tumor
immunosurveillance by T and NK cells. Cell Metab. 24:657–671. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dinakar YH, Kumar H, Mudavath SL, Jain R,
Ajmeer R and Jain V: Role of STAT3 in the initiation, progression,
proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer and strategies to
deliver JAK and STAT3 inhibitors. Life Sci. 309:1209962022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Malekan M, Ebrahimzadeh MA and Sheida F:
The role of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1alpha and its signaling in
melanoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 141:1118732021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hu L, Liu R and Zhang L: Advance in bone
destruction participated by JAK/STAT in rheumatoid arthritis and
therapeutic effect of JAK/STAT inhibitors. Int Immunopharmacol.
111:1090952022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Hu X, Yuan L and Ma T: Mechanisms of
JAK-STAT signaling pathway mediated by CXCL8 gene silencing on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human cutaneous melanoma
cells. Oncol Lett. 20:1973–1981. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Li J, Shen J, Wang Z, Xu H, Wang Q, Chai
S, Fu P, Huang T, Anas O, Zhao H, et al: ELTD1 facilitates glioma
proliferation, migration and invasion by activating
JAK/STAT3/HIF-1alpha signaling axis. Sci Rep. 9:139042019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|