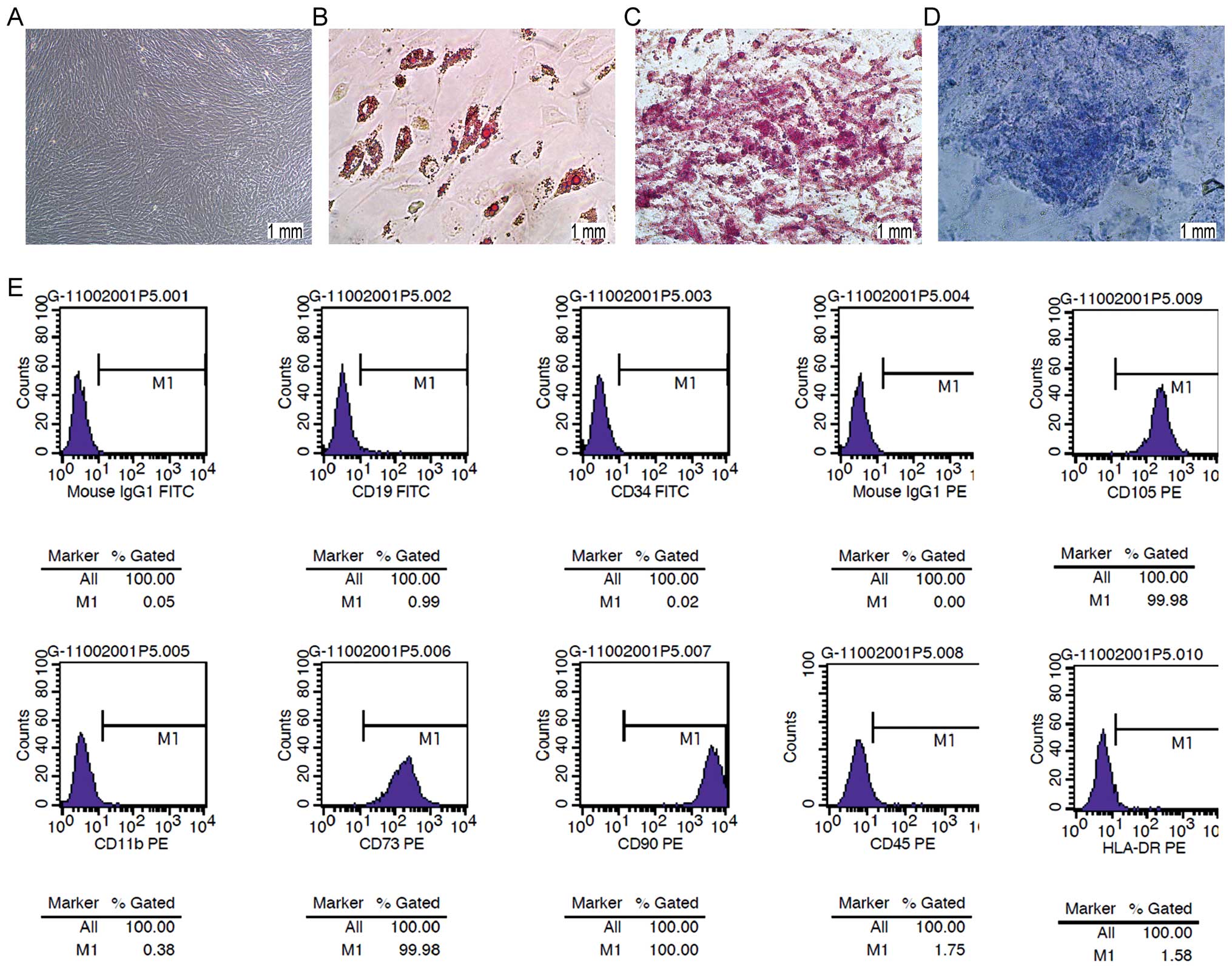
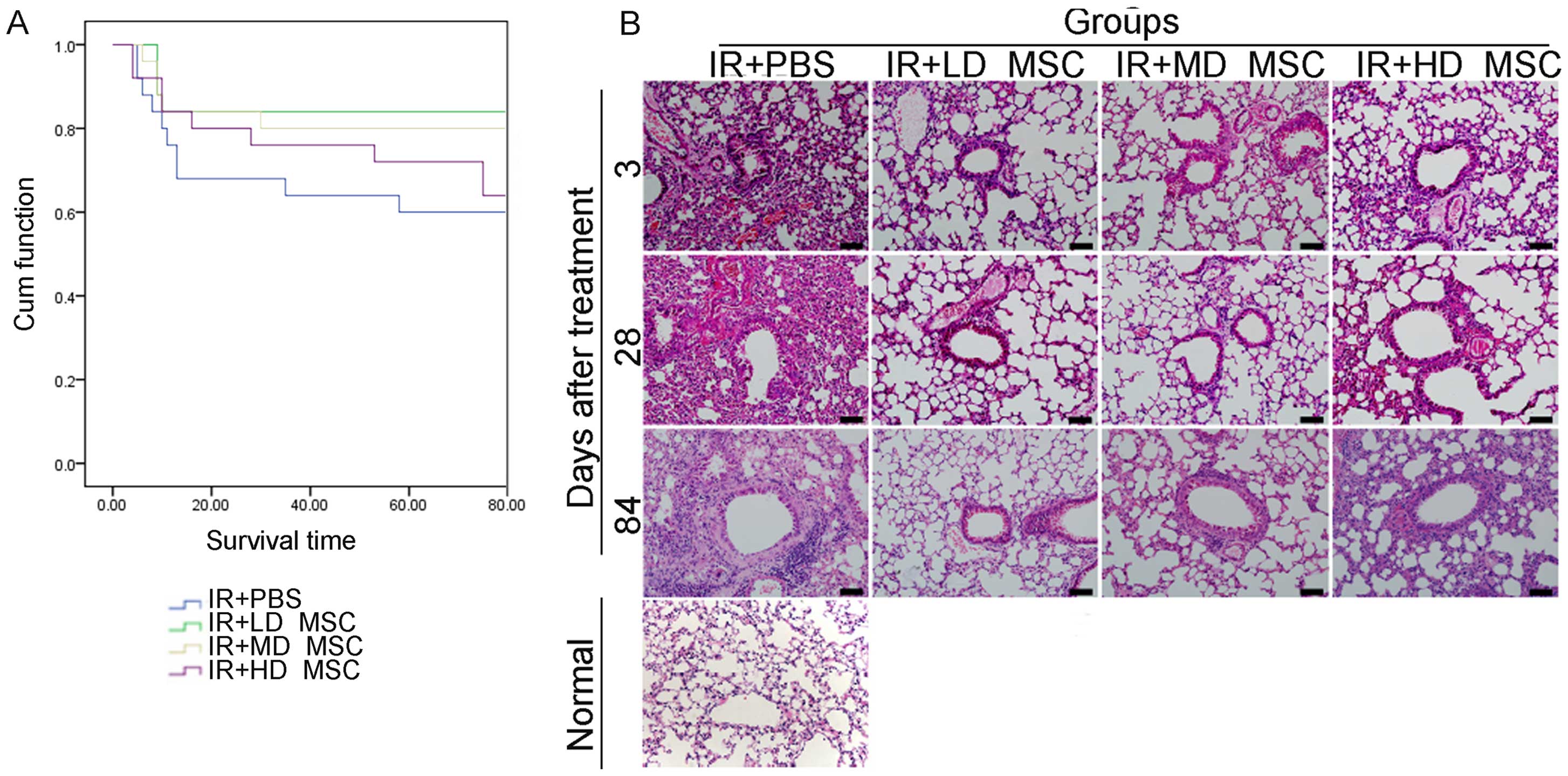
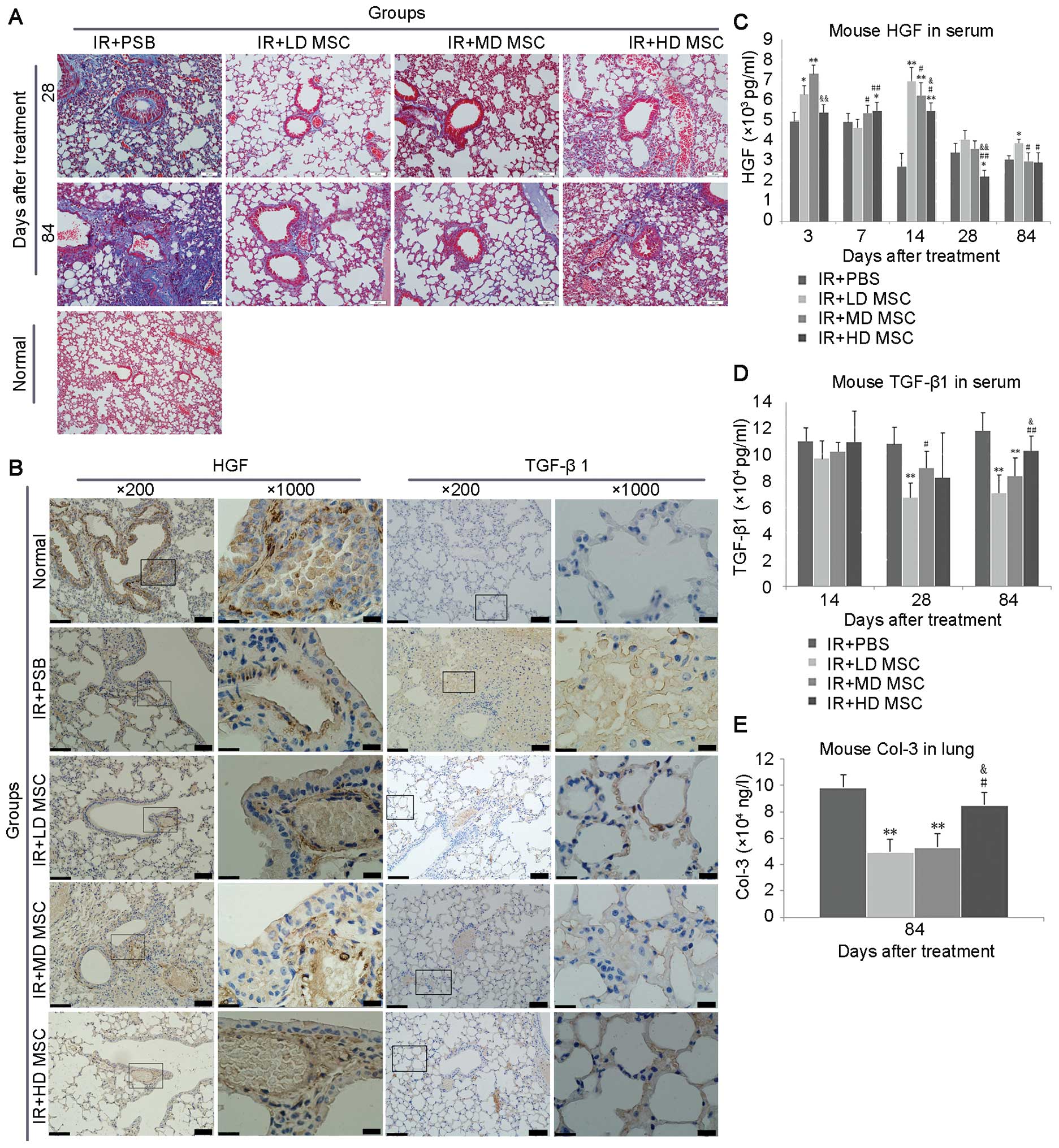
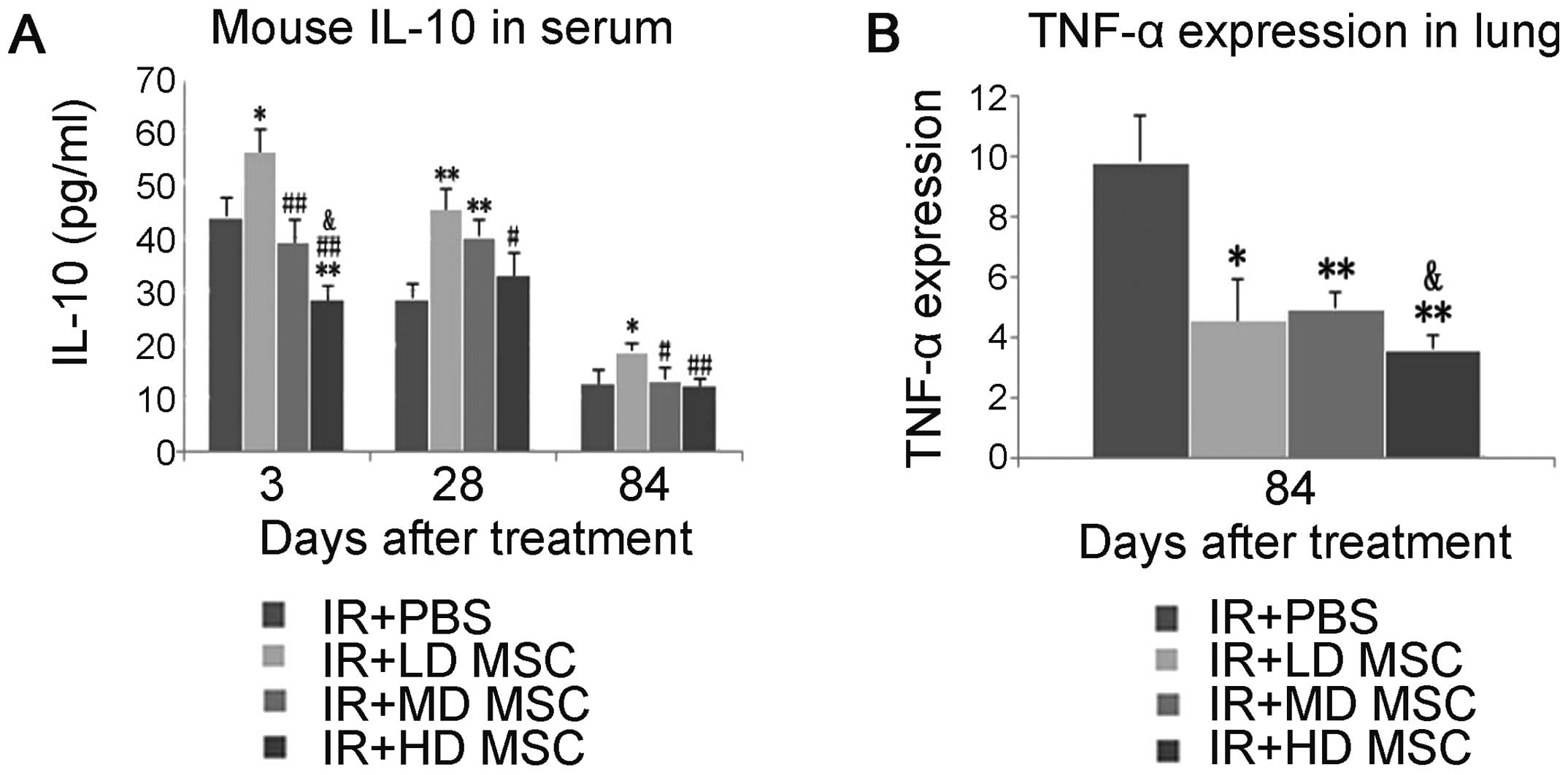
|
1
|
Mehta V: Radiation pneumonitis and
pulmonary fibrosis in non-small-cell lung cancer: Pulmonary
function, prediction, and prevention. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
63:5–24. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie L, Zhou J, Zhang S, Chen Q, Lai R,
Ding W, Song C, Meng X and Wu J: Integrating microRNA and mRNA
expression profiles in response to radiation-induced injury in rat
lung. Radiat Oncol. 9(111)2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rube CE, Uthe D, Schmid KW, Richter KD,
Wessel J, Schuck A, Willich N and Rube C: Dose-dependent induction
of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in the lung tissue of
fibrosis-prone mice after thoracic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 47:1033–1042. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arpin D, Perol D, Blay JY, Falchero L,
Claude L, Vuillermoz-Blas S, Martel-Lafay I, Ginestet C, Alberti L,
Nosov D, et al: Early variations of circulating interleukin-6 and
interleukin-10 levels during thoracic radiotherapy are predictive
for radiation pneumonitis. J Clin Oncol. 23:8748–8756. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chiang CS, Liu WC, Jung SM, Chen FH, Wu
CR, McBride WH, Lee CC and Hong JH: Compartmental responses after
thoracic irradiation of mice: Strain differences. Int J Radiat
oncolBiol Phys. 62:862–871. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rübe CE, Rodemann HP and Rübe C: The
relevance of cytokines in the radiation-induced lung reaction.
Experimental basis and clinical significance. Strahlenther Onkol.
180:541–549. 2004.In German.
|
|
7
|
Dhainaut JF, Charpentier J and Chiche JD:
Transforming growth factor-beta: A mediator of cell regulation in
acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 31(Suppl 4):
S258–S264. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim JY, Kim YS, Kim YK, Park HJ, Kim SJ,
Kang JH, Wang YP, Jang HS, Lee SN and Yoon SC: The TGF-β1 dynamics
during radiation therapy and its correlation to symptomatic
radiation pneumonitis in lung cancer patients. Radiat Oncol.
4(59)2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chung EJ, Hudak K, Horton JA, White A,
Scroggins BT, Vaswani S and Citrin D: Transforming growth factor
alpha is a critical mediator of radiation lung injury. Radiat Res.
182:350–362. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Németh K, Leelahavanichkul A, Yuen PS,
Mayer B, Parmelee A, Doi K, Robey PG, Leelahavanichkul K, Koller
BH, Brown JM, et al: Bone marrow stromal cells attenuate sepsis via
prostaglandin E(2)-dependent reprogramming of host macrophages to
increase their interleukin-10 production. Nat Med. 15:42–49. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Shi Y, Hu G, Su J, Li W, Chen Q, Shou P,
Xu C, Chen X, Huang Y, Zhu Z, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells: A new
strategy for immunosuppression and tissue repair. Cell Res.
20:510–518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Yang YF, Zhao L, Xiao FJ, Zhang
QW, Wen ML, Wu CT, Peng RY and Wang LS: Hepatocyte growth factor
gene-modified mesenchymal stem cells reduce radiation-induced lung
injury. Hum Gene Ther. 24:343–353. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Asmussen S, Ito H, Traber DL, Lee JW, Cox
RA, Hawkins HK, McAuley DF, McKenna DH, Traber LD, Zhuo H, et al:
Human mesenchymal stem cells reduce the severity of acute lung
injury in a sheep model of bacterial pneumonia. Thorax. 69:819–825.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Devaney J, Horie S, Masterson C, Elliman
S, Barry F, O'Brien T, Curley GF, O'Toole D and Laffey JG: Human
mesenchymal stromal cells decrease the severity of acute lung
injury induced by E. coli in the Rat. Thorax. 70:625–635. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rao X, huang X, Zhou Z and Lin X: An
improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative
real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat
Bioinforma Biomath. 3:71–85. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Saether EE, Chamberlain CS, Leiferman EM,
Kondratko-Mittnacht JR, Li WJ, Brickson SL and Vanderby R: Enhanced
medial collateral ligament healing using mesenchymal stem cells:
Dosage effects on cellular response and cytokine profile. Stem Cell
Rev. 10:86–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Yavagal DR, Lin B, Raval AP, Garza PS,
Dong C, Zhao W, Rangel EB, Mcniece I, Rundek T, Sacco RL, et al:
Efficacy and dose-dependent safety of intra-arterial delivery of
mesenchymal stem cells in a rodent stroke model. PLoS One.
9:e937352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fukuda Y, Horie N, Satoh K, Yamaguchi S,
Morofuji Y, Hiu T, Izumo T, Hayashi K, Nishida N and Nagata I:
Intra-arterial transplantation of low-dose stem cells provides
functional recovery without adverse effects after stroke. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 35:399–406. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kean TJ, Lin P, Caplan AI and Dennis JE:
MSCs: Delivery routes and engraftment, cell-targeting strategies,
and immune modulation. Stem Cells Int. 2013(732742)2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Z, Hu X, Mao J, Liu X, Zhang L, Liu J,
Li D and Shan H: Optimization of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs)
delivery dose and route in mice with acute liver injury by
bioluminescence imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 17:185–194. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Song YS, Lee HJ, Doo SH, Lee SJ, Lim I,
Chang KT and Kim SU: Mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing
hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) inhibit collagen deposit and improve
bladder function in rat model of bladder outlet obstruction. Cell
Transplant. 21:1641–1650. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang K, Yang S, Zhu Y, Mo A, Zhang D and
Liu L: Protection against acute radiation-induced lung injury: A
novel role for the anti-angiogenic agent Endostar. Mol Med Rep.
6:309–315. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim MD, Kim SS, Cha HY, Jang SH, Chang DY,
Kim W, Suh-Kim H and Lee JH: Therapeutic effect of hepatocyte
growth factor-secreting mesenchymal stem cells in a rat model of
liver fibrosis. Exp Mol Med. 46:e1102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ortiz LA, Gambelli F, McBride C, Gaupp D,
Baddoo M, Kaminski N and Phinney DG: Mesenchymal stem cell
engraftment in lung is enhanced in response to bleomycin exposure
and ameliorates its fibrotic effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:8407–8411. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ooi YY, Dheen ST and Tay SS: Paracrine
effects of mesenchymal stem cells-conditioned medium on microglial
cytokines expression and nitric oxide production.
Neuroimmunomodulation. 22:233–242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cho KS, Park MK, Kang SA, Park HY, Hong
SL, Park HK, Yu HS and Roh HJ: Adipose-derived stem cells
ameliorate allergic airway inflammation by inducing regulatory T
cells in a mouse model of asthma. Mediators Inflamm.
2014(436476)2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Curley GF, Hayes M, Ansari B, Shaw G, Ryan
A, Barry F, O'Brien T, O'Toole D and Laffey JG: Mesenchymal stem
cells enhance recovery and repair following ventilator-induced lung
injury in the rat. Thorax. 67:496–501. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhao MM, Cui JZ, Cui Y, Li R, Tian YX,
Song SX, Zhang J and Gao JL: Therapeutic effect of exogenous bone
marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on silicosis
via paracrine mechanisms in rats. Mol Med Rep. 8:741–746.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee JW, Krasnodembskaya A, McKenna DH,
Song Y, Abbott J and Matthay MA: Therapeutic effects of human
mesenchymal stem cells in ex vivo human lungs injured with live
bacteria. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 187:751–760. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kotton DN, Ma By, Cardoso WV, Sanderson
EA, Summer RS, Williams MC and Fine A: Bone marrow-derived cells as
progenitors of lung alveolar epithelium. Development.
128:5181–5188. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Prockop DJ: Marrow stromal cells as stem
cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 276:71–74. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ye J and Gimble JM: Regulation of stem
cell differentiation in adipose tissue by chronic inflammation.
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 38:872–878. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
François S, Bensidhoum M, Mouiseddine M,
Mazurier C, Allenet B, Semont A, Frick J, Saché A, Bouchet S,
Thierry D, et al: Local irradiation not only induces homing of
human mesenchymal stem cells at exposed sites but promotes their
widespread engraftment to multiple organs: A study of their
quantitative distribution after irradiation damage. Stem Cells.
24:1020–1029. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|