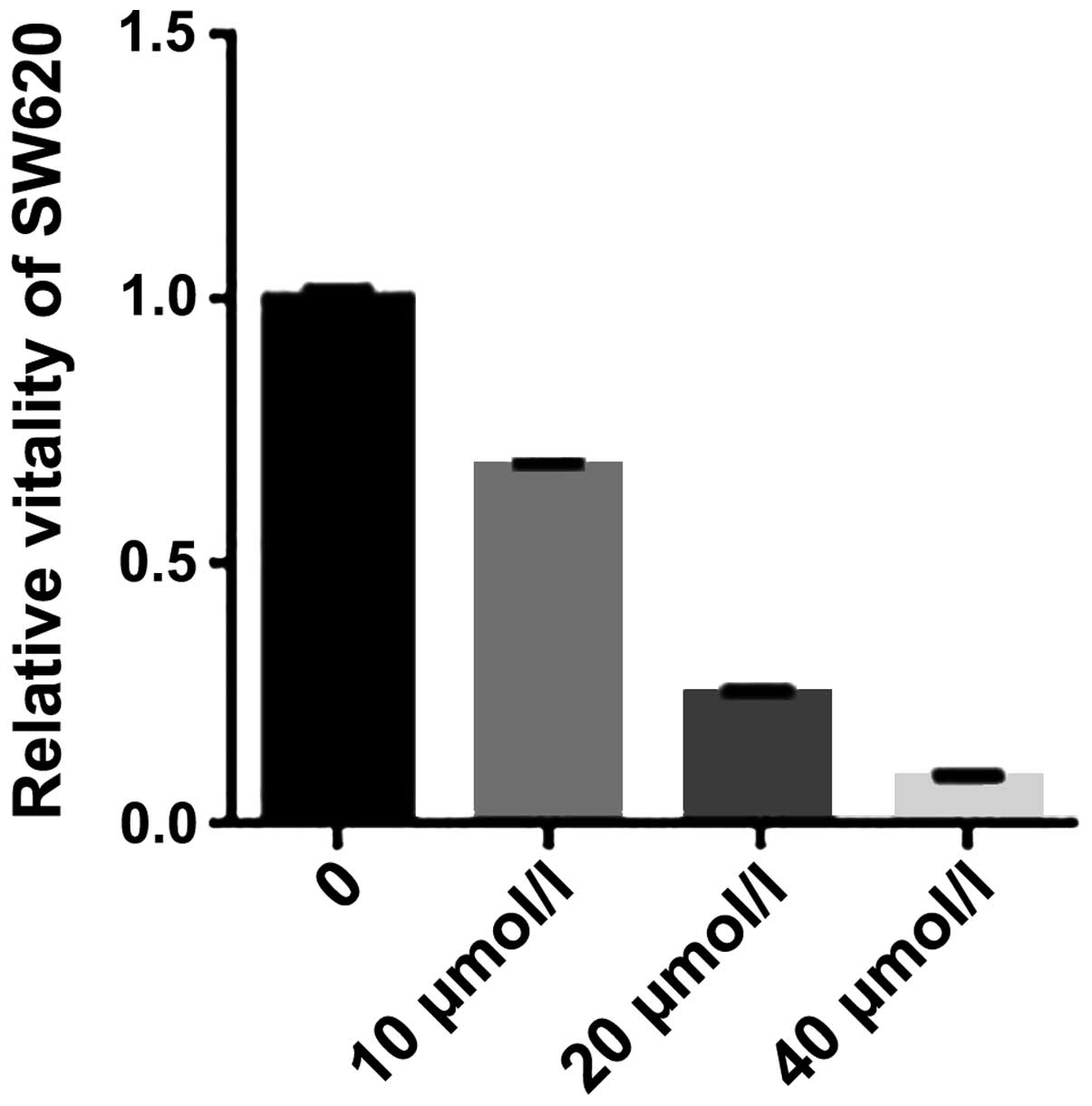
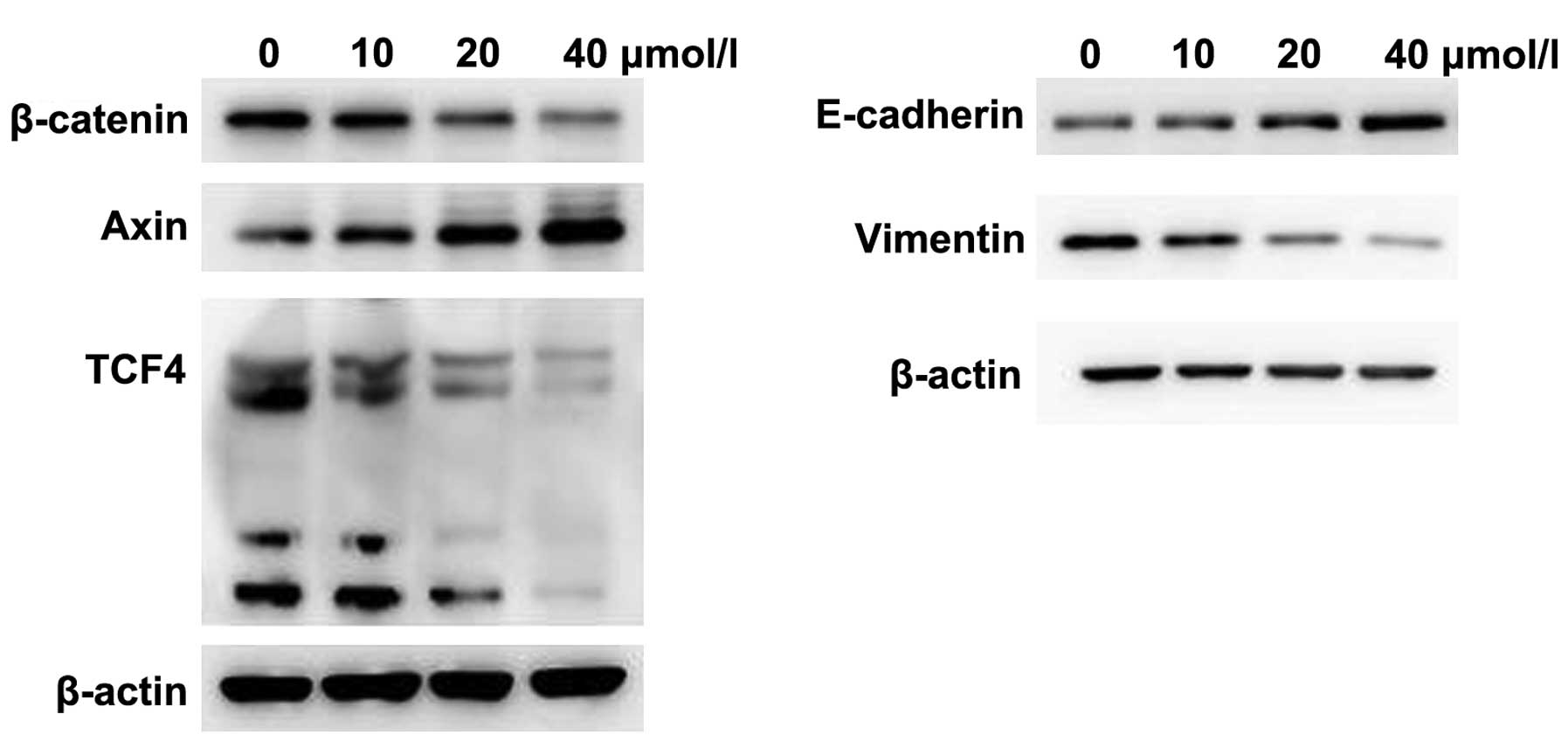
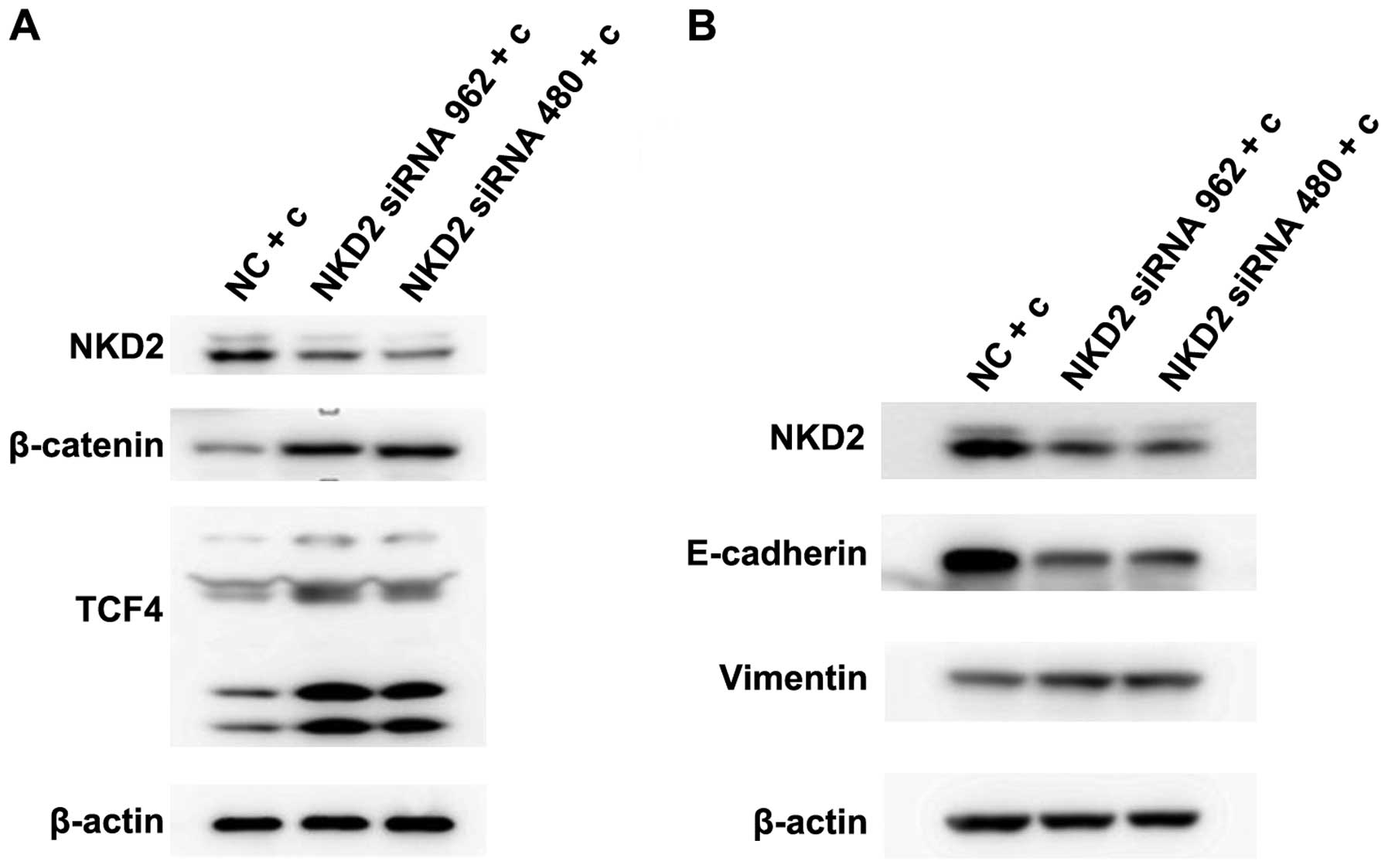
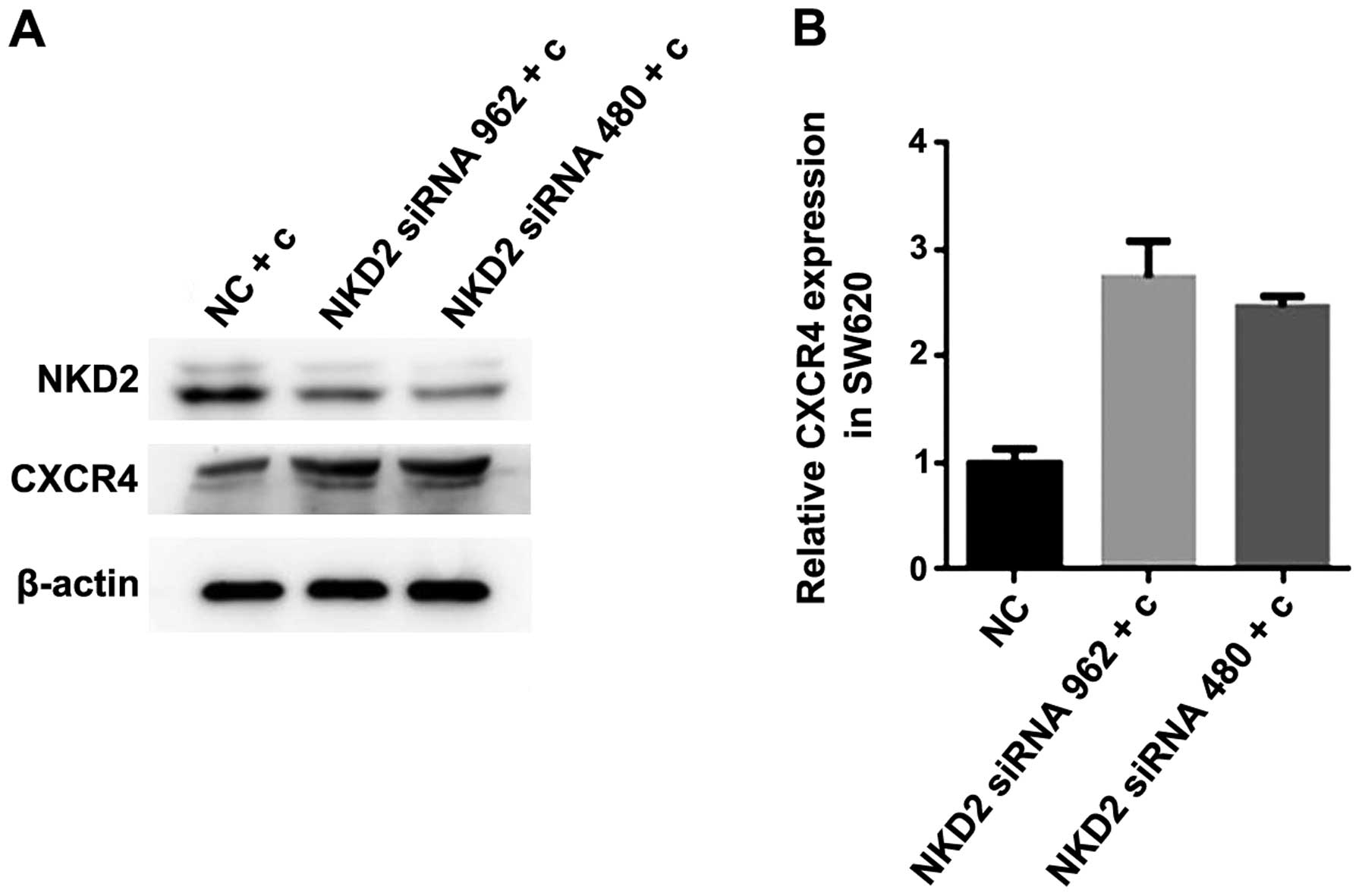
|
1
|
Noreen F, Röösli M, Gaj P, Pietrzak J,
Weis S, Urfer P, Regula J, Schär P and Truninger K: Modulation of
age- and cancer-associated DNA methylation change in the healthy
colon by aspirin and lifestyle. J Natl Cancer Inst. 106:1062014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pelser C, Arem H, Pfeiffer RM, Elena JW,
Alfano CM, Hollenbeck AR and Park Y: Prediagnostic lifestyle
factors and survival after colon and rectal cancer diagnosis in the
National Institutes of Health (NIH)-AARP Diet and Health Study.
Cancer. 120:1540–1547. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Winkels RM, Heine-Bröring RC, van Zutphen
M, van Harten-Gerritsen S, Kok DE, van Duijnhoven FJ and Kampman E:
The COLON study: Colorectal cancer: Longitudinal, Observational
study on Nutritional and lifestyle factors that may influence
colorectal tumour recurrence, survival and quality of life. BMC
Cancer. 14:3742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sunkara V and Hébert JR: The colorectal
cancer mortality-to- incidence ratio as an indicator of global
cancer screening and care. Cancer. 121:1563–1569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang W, Liu Z, Zhou G, Tian A and Sun N:
Magnetic gold nanoparticle-mediated small interference RNA
silencing Bag-1 gene for colon cancer therapy. Oncol Rep.
35:978–984. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Heerboth S, Housman G, Leary M, Longacre
M, Byler S, Lapinska K, Willbanks A and Sarkar S: EMT and tumor
metastasis. Clin Transl Med. 4:62015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kabashima A, Higuchi H, Takaishi H,
Matsuzaki Y, Suzuki S, Izumiya M, Iizuka H, Sakai G, Hozawa S,
Azuma T, et al: Side population of pancreatic cancer cells
predominates in TGF-beta-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal
transition and invasion. Int J Cancer. 124:2771–2779. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsuji T, Ibaragi S and Hu GF:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell cooperativity in
metastasis. Cancer Res. 69:7135–7139. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hay ED: The mesenchymal cell, its role in
the embryo, and the remarkable signaling mechanisms that create it.
Dev Dyn. 233:706–720. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ombrato L and Malanchi I: The EMT
universe: Space between cancer cell dissemination and metastasis
initiation. Crit Rev Oncog. 19:349–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zheng H and Kang Y: Multilayer control of
the EMT master regulators. Oncogene. 33:1755–1763. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Guarino M: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and tumour invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:2153–2160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Natalwala A, Spychal R and Tselepis C:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition mediated tumourigenesis in the
gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol. 14:3792–3797. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y and Zhou BP: Epithelial-mesenchymal
Transition-A Hall mark of Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Hallm.
1:38–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gonzalez EJ, Arms L and Vizzard MA: The
role(s) of cytokines/chemokines in urinary bladder inflammation and
dysfunction. BioMed Res Int. 2014:1205252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sallusto F and Baggiolini M: Chemokines
and leukocyte traffic. Nat Immunol. 9:949–952. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu XM, Liu YN, Zhang HL, Cao SB, Zhang T,
Chen LP and Shen W: CXCL12/CXCR4 chemokine signaling in spinal glia
induces pain hypersensitivity through MAPKs-mediated
neuro-inflammation in bone cancer rats. J Neurochem. 132:452–463.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Batsi O, Giannopoulou I, Nesseris I,
Valavanis C, Gakiopoulou H, Patsouris ES, Arapandoni-Dadioti P and
Lazaris AC: Immunohistochemical evaluation of CXCL12-CXCR4 axis and
VEGFR3 expression in primary urothelial cancer and its recurrence.
Anticancer Res. 34:3537–3542. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cojoc M, Peitzsch C, Trautmann F,
Polishchuk L, Telegeev GD and Dubrovska A: Emerging targets in
cancer management: Role of the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis. Onco Targets
Ther. 6:1347–1361. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Z, Ni C, Chen W, Wu P, Wang Z, Yin
J, Huang J and Qiu F: Expression of CXCR4 and breast cancer
prognosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer.
14:492014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sahebkar A: Dual effect of curcumin in
preventing atherosclerosis: The potential role of
pro-oxidant-antioxidant mechanisms. Nat Prod Res. 29:491–492. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Maheshwari RK, Singh AK, Gaddipati J and
Srimal RC: Multiple biological activities of curcumin: A short
review. Life Sci. 78:2081–2087. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang X, Chen Q, Wang Y, Peng W and Cai H:
Effects of curcumin on ion channels and transporters. Front
Physiol. 5:942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang GM, Xie WY, Wang HS, Du J, Wu BP, Xu
W, Liu HF, Xiao P, Liu ZG, Li HY, Liu SQ, Yin WJ, Zhang QG, Liang
JP and Huang HJ: Curcumin combined with FAPalphac vaccine elicits
effective antitumor response by targeting
indolamine-2,3-dioxygenase and inhibiting EMT induced by TNF-alpha
in melanoma. Oncotarget. 6:25932–25942. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sherwood V: WNT signaling: An emerging
mediator of cancer cell metabolism? Mol Cell Biol. 35:2–10. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Tan CW, Gardiner BS, Hirokawa Y, Smith DW
and Burgess AW: Analysis of Wnt signaling β-catenin spatial
dynamics in HEK293T cells. BMC Syst Biol. 8:442014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen J, Xu L, Hu X, Zhang J, Xu C, Li G
and Jiang H: Curcumin regulates VSMC phenotype transition via
modulation of Notch and Wnt signaling pathways. Drug Dev Res.
74:252–258. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim HJ, Park SY, Park OJ and Kim YM:
Curcumin suppresses migration and proliferation of Hep3B
hepatocarcinoma cells through inhibition of the Wnt signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 8:282–286. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Van Raay TJ, Coffey RJ and Solnica-Krezel
L: Zebrafish Naked1 and Naked2 antagonize both canonical and
non-canonical Wnt signaling. Dev Biol. 309:151–168. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi YJ and Huo K: Nkd2, a negative
regulator of Wnt pathway, delays mitotic exit in Hela cell. Genes
Genomics. 35:569–573. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Diagaradjane P, Anand P,
Harikumar KB, Deorukhkar A, Gelovani J, Guha S, Krishnan S and
Aggarwal BB: Curcumin sensitizes human colorectal cancer to
capecitabine by modulation of cyclin D1, COX-2, MMP-9, VEGF and
CXCR4 expression in an orthotopic mouse model. Int J Cancer.
125:2187–2197. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Skommer J, Wlodkowic D and Pelkonen J:
Gene-expression profiling during curcumin-induced apoptosis reveals
downregulation of CXCR4. Exp Hematol. 35:84–95. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hu TH, Yao Y, Yu S, Han LL, Wang WJ, Guo
H, Tian T, Ruan ZP, Kang XM, Wang J, et al: SDF-1/CXCR4 promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression of colorectal
cancer by activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer
Lett. 354:417–426. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chaw SY, Majeed AA, Dalley AJ, Chan A,
Stein S and Farah CS: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
biomarkers-E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and Vimentin-in oral
squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol.
48:997–1006. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tacchelly-Benites O, Wang Z, Yang E, Lee E
and Ahmed Y: Toggling a conformational switch in Wnt/β-catenin
signaling: Regulation of Axin phosphorylation. The phosphorylation
state of Axin controls its scaffold function in two Wnt pathway
protein complexes. Bioessays. 35:1063–1070. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gupta A, Verma A, Mishra AK, Wadhwa G,
Sharma SK and Jain CK: The Wnt pathway: Emerging anticancer
strategies. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug Discov. 7:138–147.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dong Y, Cao B, Zhang M, Han W, Herman JG,
Fuks F, Zhao Y and Guo M: Epigenetic silencing of NKD2, a major
component of Wnt signaling, promotes breast cancer growth.
Oncotarget. 6:22126–22138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu C, Zhao H, Chen H and Yao Q: CXCR4 in
breast cancer: Oncogenic role and therapeutic targeting. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 9:4953–4964. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu JH, Yang HP, Zhou XD, Wang HJ, Gong L
and Tang CL: Role of wnt inhibitory factor-1 in inhibition of
bisdemethoxycurcumin mediated Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition
in highly metastatic lung cancer 95D cells. Chin Med J (Engl).
128:1376–1383. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Buhrmann C, Kraehe P, Lueders C, Shayan P,
Goel A and Shakibaei M: Curcumin suppresses crosstalk between colon
cancer stem cells and stromal fibroblasts in the tumor micro-
environment: potential role of EMT. PLoS One. 9:e1075142014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Braendegaard WS, Baatrup G, Pfeiffer P and
Qvortrup C: Trends in colorectal cancer in the elderly in Denmark,
1980–2012. Acta Oncol. 55(Suppl 1): 29–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Tiwari N, Gheldof A, Tatari M and
Christofori G: EMT as the ultimate survival mechanism of cancer
cells. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:194–207. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hu T and Li C: Convergence between
Wnt-β-catenin and EGFR signaling in cancer. Mol Cancer. 9:2362010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Deng Y, Su Q, Mo J, Fu X, Zhang Y and Lin
EH: Celecoxib downregulates CD133 expression through inhibition of
the Wnt signaling pathway in colon cancer cells. Cancer Invest.
31:97–102. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Jagtap S, Meganathan K, Wagh V, Winkler J,
Hescheler J and Sachinidis A: Chemoprotective mechanism of the
natural compounds, epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate, quercetin and
curcumin against cancer and cardiovascular diseases. Curr Med Chem.
16:1451–1462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen QY, Jiao DM, Wang LF, Wang L, Hu HZ,
Song J, Yan J, Wu LJ and Shi JG: Curcumin inhibits
proliferation-migration of NSCLC by steering crosstalk between a
Wnt signaling pathway and an adherens junction via EGR-1. Mol
Biosyst. 11:859–868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Leow PC, Bahety P, Boon CP, Lee CY, Tan
KL, Yang T and Ee PL: Functionalized curcumin analogs as potent
modulators of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur J Med Chem.
71:67–80. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: WNT signaling pathway
and stem cell signaling network. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4042–4045.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hu T, Li C, Cao Z, Van Raay TJ, Smith JG,
Willert K, Solnica-Krezel L and Coffey RJ: Myristoylated Naked2
anta-go nizes Wnt-beta-catenin activity by degrading Dishevelled-1
at the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 285:13561–13568. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ben-Baruch A: The multifaceted roles of
chemokines in malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:357–371. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Choe Y and Pleasure SJ: Wnt signaling
regulates intermediate precursor production in the postnatal
dentate gyrus by regulating CXCR4 expression. Dev Neurosci.
34:502–514. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao S, Wang J and Qin C: Blockade of
CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling inhibits intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
progression and metastasis via inactivation of canonical Wnt
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:1032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang J, Cai J, Han F, Yang C, Tong Q, Cao
T, Wu L and Wang Z: Silencing of CXCR4 blocks progression of
ovarian cancer and depresses canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Int J
Gynecol Cancer. 21:981–987. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|