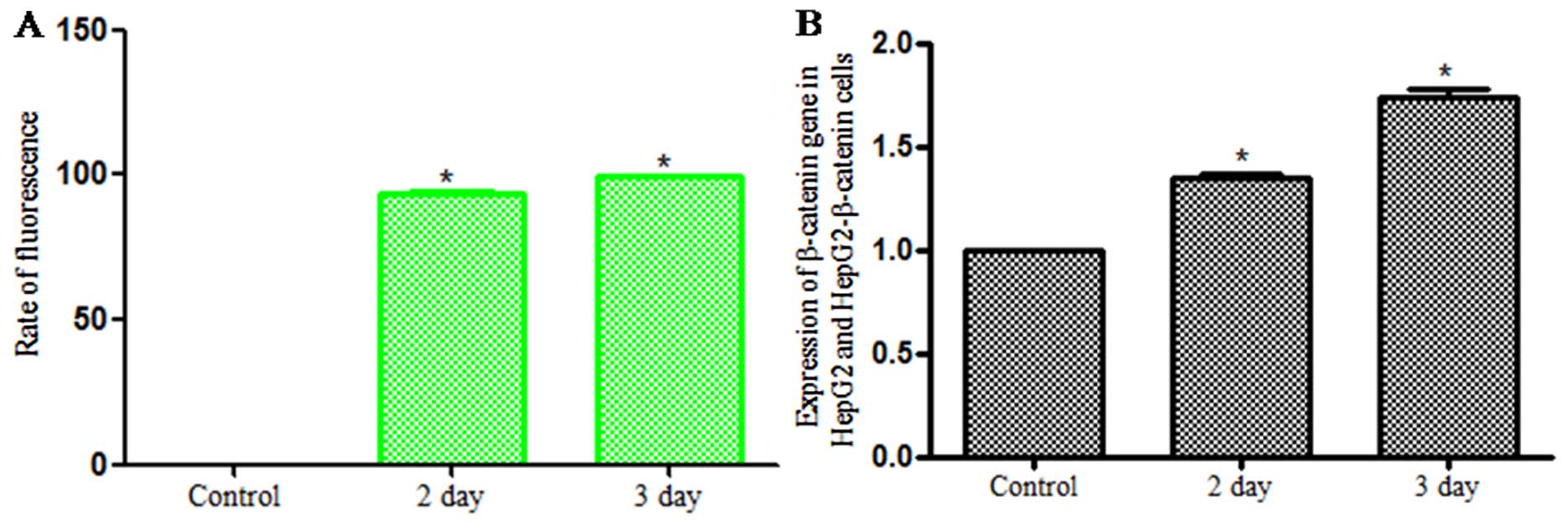
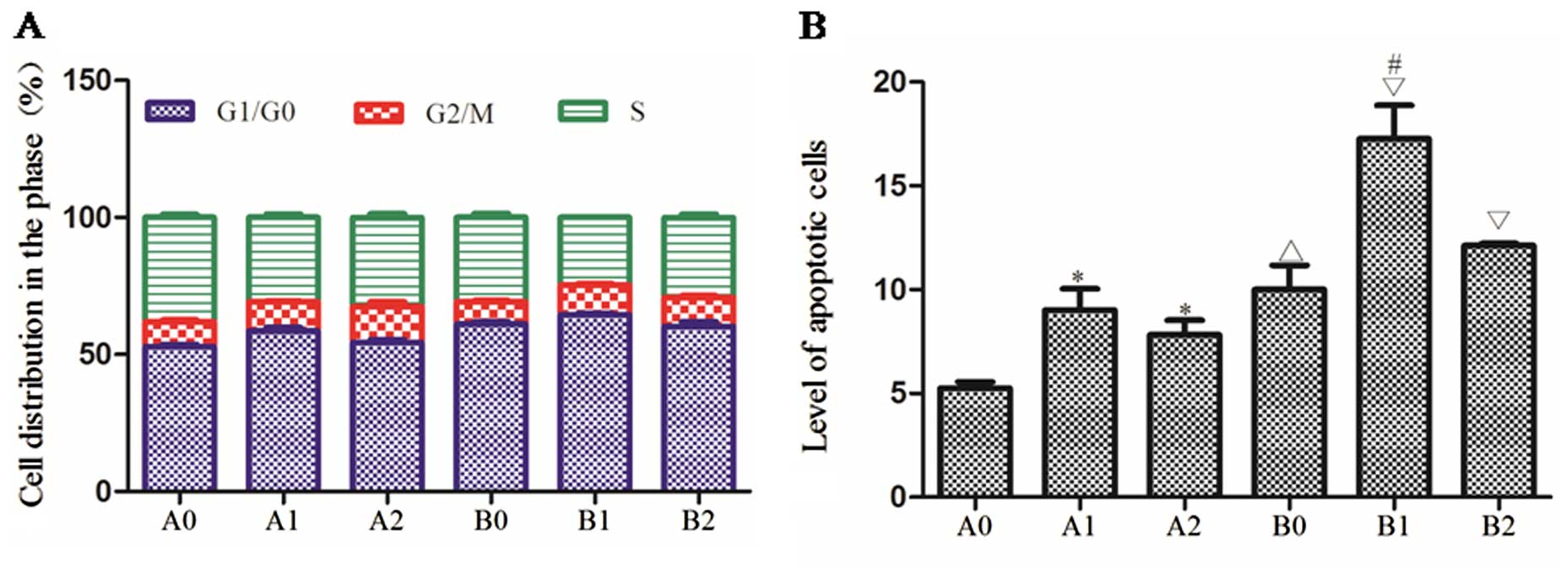
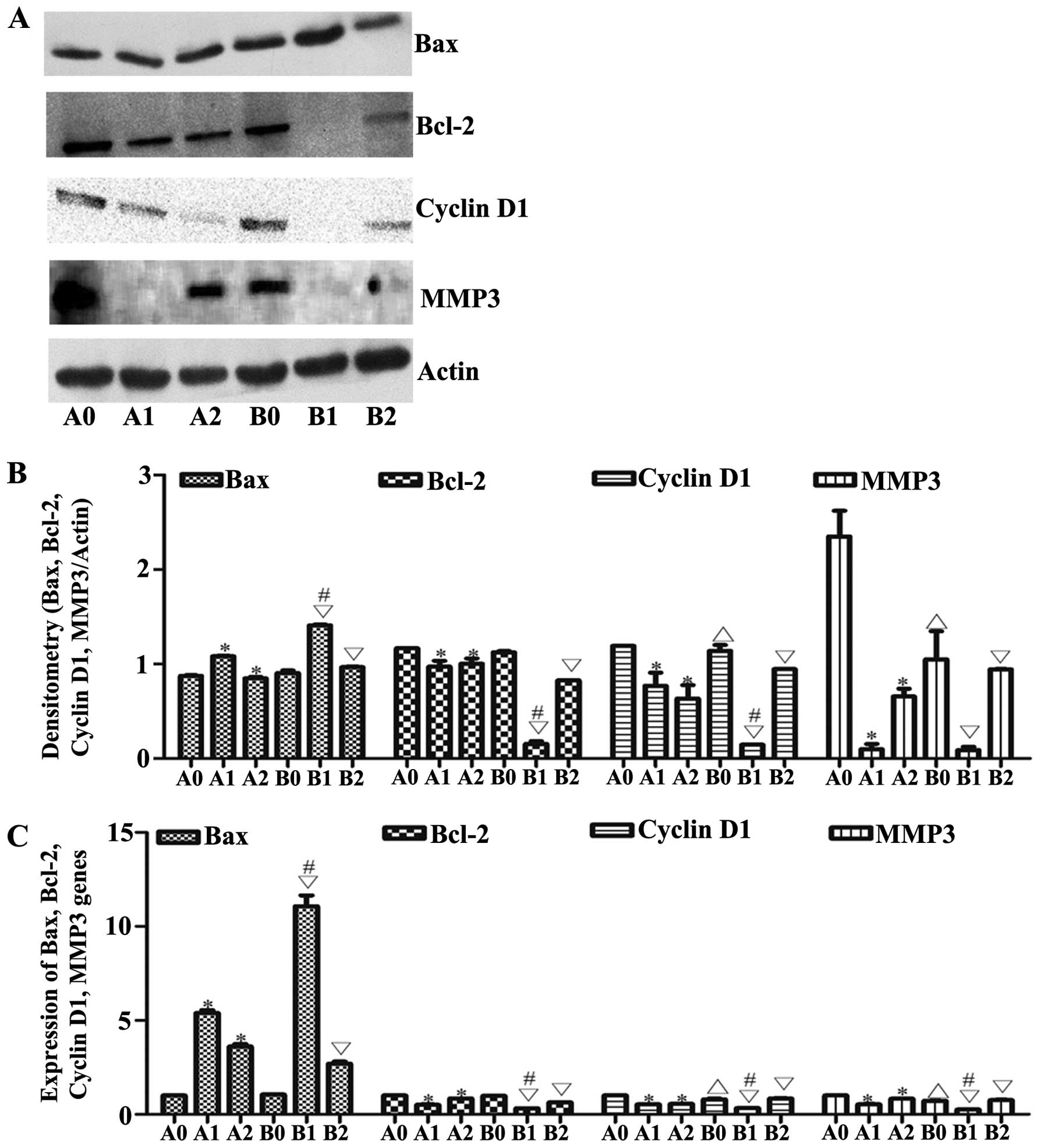
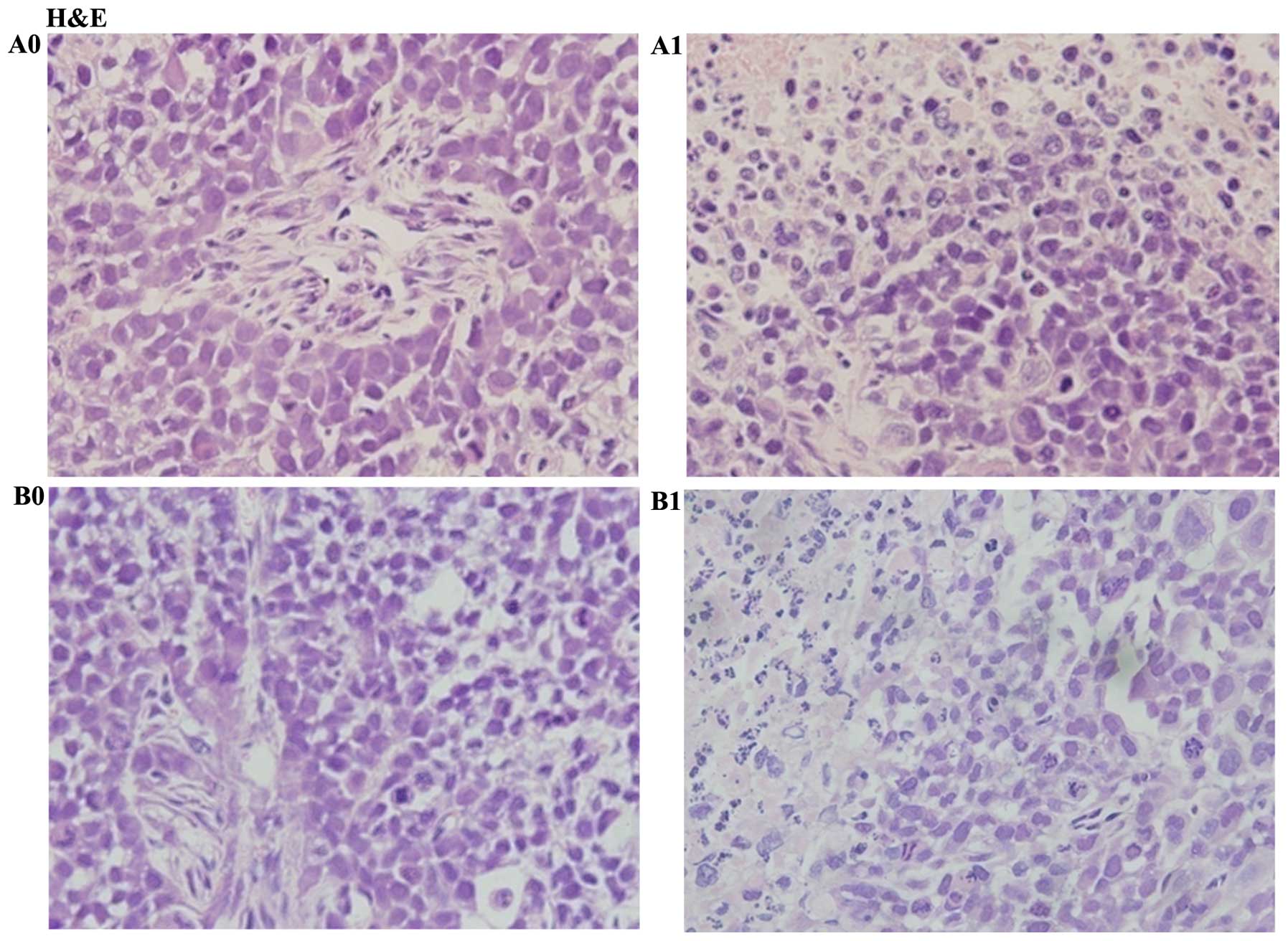
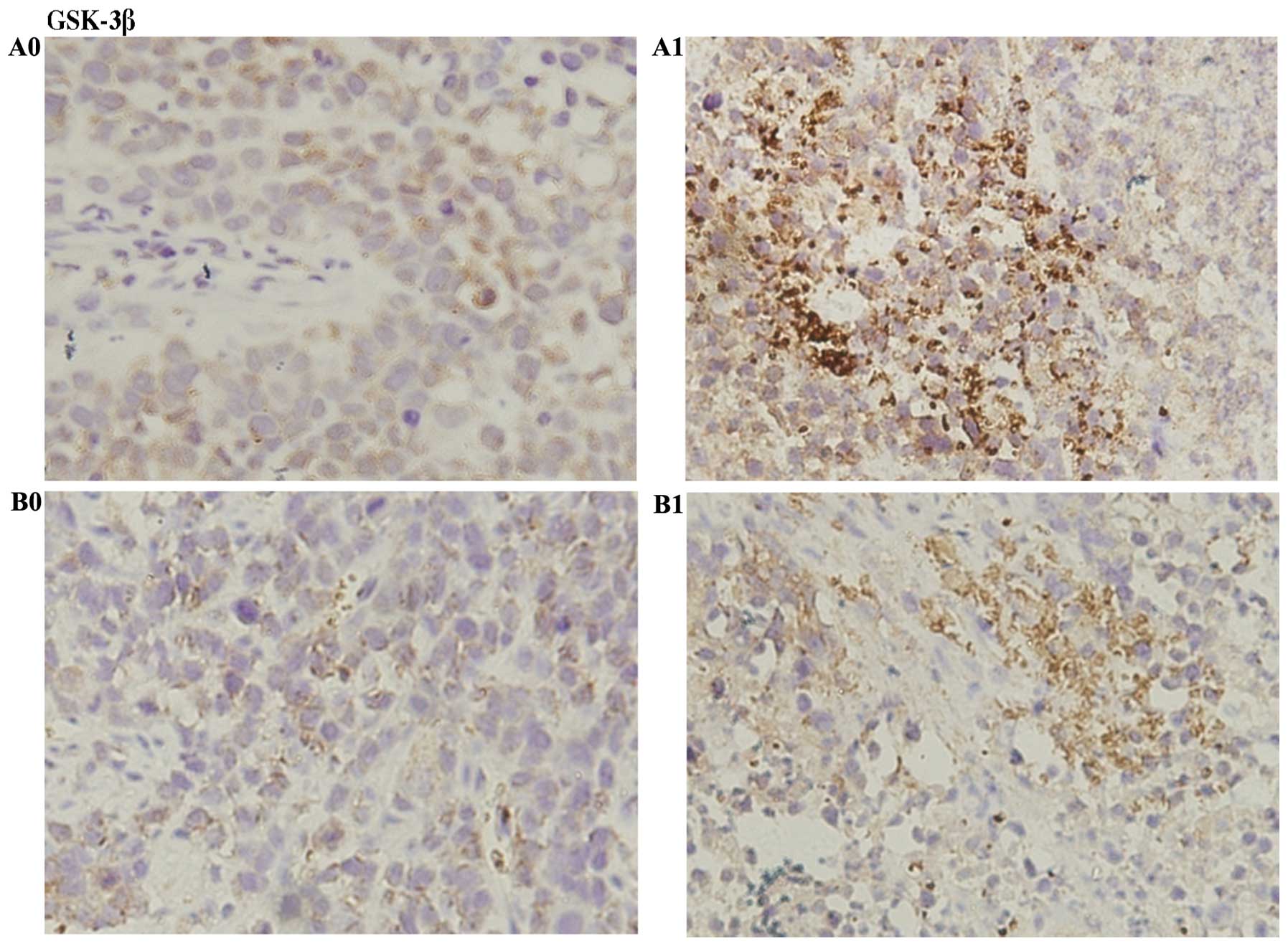
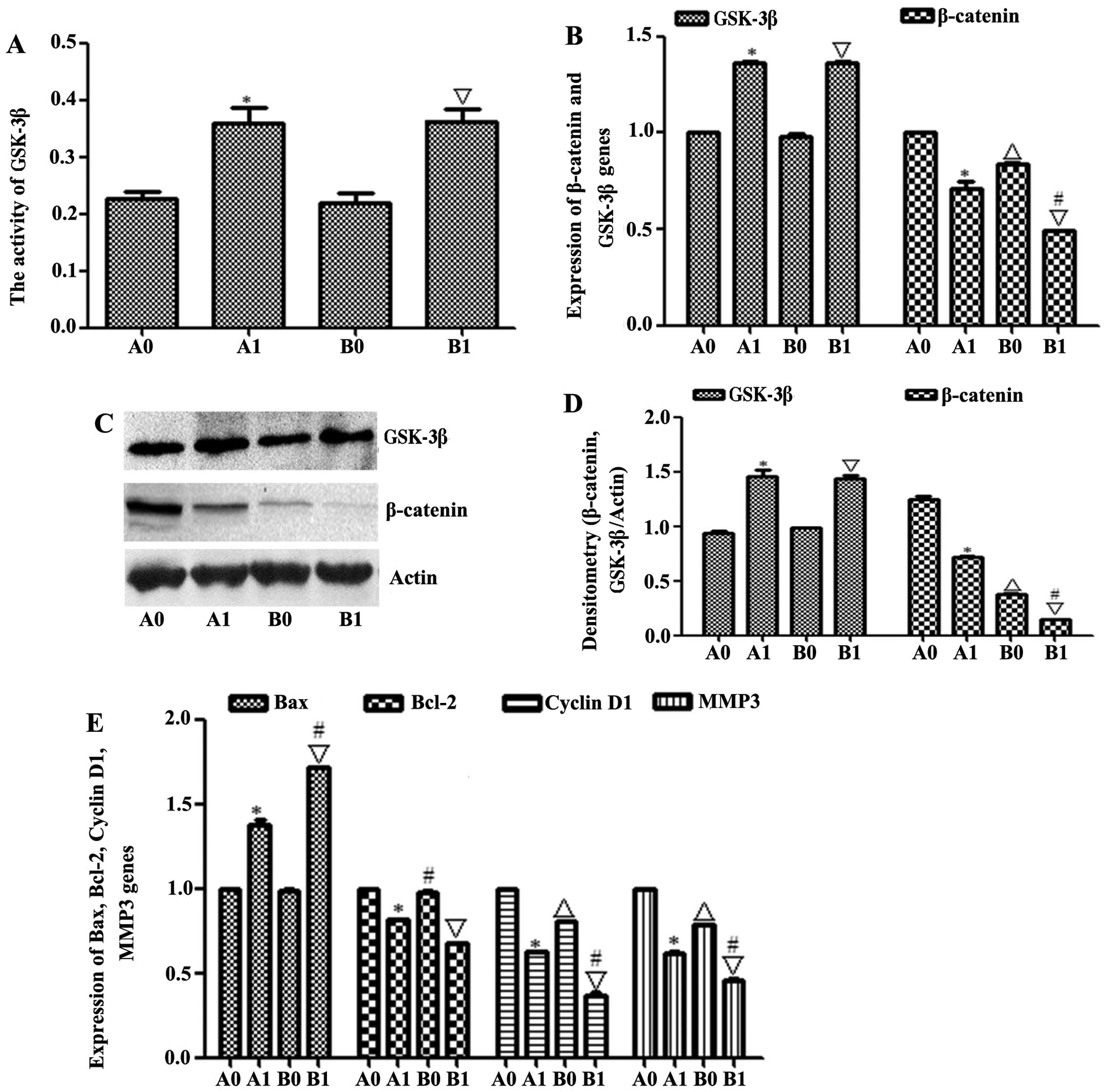
|
1
|
Tsai WL, Lai KH, Liang HL, Hsu PI, Chan
HH, Chen WC, Yu HC, Tsay FW, Wang HM, Tsai HC, et al: Hepatic
arterial infusion chemotherapy for patients with huge unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 9:e927842014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Page AJ, Cosgrove DC, Philosophe B and
Pawlik TM: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Diagnosis, management, and
prognosis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 23:289–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Scaggiante B, Kazemi M, Pozzato G, Dapas
B, Farra R, Grassi M, Zanconati F and Grassi G: Novel
hepatocellular carcinoma molecules with prognostic and therapeutic
potentials. World J Gastroenterol. 20:1268–1288. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanase A-M, Dumitrascu T, Dima S, Grigorie
R, Marchio A, Pineau P and Popescu I: Influence of hepatitis
viruses on clinicopathological profiles and long-term outcome in
patients undergoing surgery for hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 13:162–172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ji Z, Wang T, Shao Z, Huang D, Wang A, Guo
Z, Long Y, Zhang L, Su H, Zhang Q, et al: A population-based study
examining hepatitis B virus infection and immunization rates in
Northwest China. PLoS One. 9:e974742014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu L-B, Wang J, Liu C, Pang HW, Chen YJ,
Ou QJ and Chen JS: Staging systems for predicting survival of
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after surgery. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:5257–5262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Osaki A, Suda T, Kamimura K, Tsuchiya A,
Tamura Y, Takamura M, Igarashi M, Kawai H, Yamagiwa S and Aoyagi Y:
A safe and effective dose of cisplatin in hepatic arterial infusion
chemotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2:86–98.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ker CG, Chen JS, Kuo KK, Chuang SC, Wang
SJ, Chang WC, Lee KT, Chen HY and Juan CC: Liver surgery for
hepatocellular carcinoma: Laparoscopic versus open approach. Int J
Hepatol. 2011:5967922011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miyahara K, Nouso K and Yamamoto K:
Chemotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in the sorafenib
age. World J Gastroenterol. 20:4151–4159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song SB, Tung NH, Quang TH, Ngan NT, Kim
KE and Kim YH: Inhibition of TNF-α-mediated NF-κB transcriptional
activity in HepG2 cells by dammarane-type saponins from Panax
ginseng leaves. J Ginseng Res. 36:146–152. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Guo XX, Guo Q, Li Y, Lee SK, Wei XN and
Jin YH: Ginsenoside Rh2 induces human hepatoma cell apoptosisvia
bax/bak triggered cytochrome C release and caspase-9/caspase-8
activation. Int J Mol Sci. 13:15523–15535. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang Z, Zheng Q, Liu K, Li G and Zheng R:
Ginsenoside Rh(2) enhances antitumour activity and decreases
genotoxic effect of cyclophosphamide. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
98:411–415. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ho YL, Li KC, Chao W, Chang YS and Huang
GJ: Korean red ginseng suppresses metastasis of human hepatoma
SK-Hep1 cells by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 and
urokinase plasminogen activator. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2012:9658462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chung KS, Cho SH, Shin JS, Kim DH, Choi
JH, Choi SY, Rhee YK, Hong HD and Lee KT: Ginsenoside Rh2 induces
cell cycle arrest and differentiation in human leukemia cells by
upregulating TGF-β expression. Carcinogenesis. 34:331–340. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yan XJ, Gong LH, Zheng FY, Cheng KJ, Chen
ZS and Shi Z: Triterpenoids as reversal agents for anticancer drug
resistance treatment. Drug Discov Today. 19:482–488. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li S, Gao Y, Ma W, Guo W, Zhou G, Cheng T
and Liu Y: EGFR signaling-dependent inhibition of glioblastoma
growth by ginsenoside Rh2. Tumour Biol. 35:5593–5598. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Park EK, Lee EJ, Lee SH, Koo KH, Sung JY,
Hwang EH, Park JH, Kim CW, Jeong KC, Park BK, et al: Induction of
apoptosis by the ginsenoside Rh2 by internalization of lipid rafts
and caveolae and inactivation of Akt. Br J Pharmacol.
160:1212–1223. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maurer U, Preiss F, Brauns-Schubert P,
Schlicher L and Charvet C: GSK-3 - at the crossroads of cell death
and survival. J Cell Sci. 127:1369–1378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang JS, Herreros-Villanueva M, Koenig A,
Deng Z, de Narvajas AA, Gomez TS, Meng X, Bujanda L, Ellenrieder V,
Li XK, et al: Differential activity of GSK-3 isoforms regulates
NF-κB and TRAIL- or TNFα induced apoptosis in pancreatic cancer
cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11422014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gao Y, Liu Z, Zhang X, He J, Pan Y, Hao F,
Xie L, Li Q, Qiu X and Wang E: Inhibition of cytoplasmic GSK-3β
increases cisplatin resistance through activation of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in A549/DDP cells. Cancer Lett. 336:231–239. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee H, Bae S, Kim YS and Yoon Y:
WNT/β-catenin pathway mediates the anti-adipogenic effect of
platycodin D, a natural compound found in Platycodon grandiflorum.
Life Sci. 89:388–394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Thompson MD and Monga SP: WNT/beta-catenin
signaling in liver health and disease. Hepatology. 45:1298–1305.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mosimann C, Hausmann G and Basler K:
Beta-catenin hits chromatin: Regulation of Wnt target gene
activation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 10:276–286. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ying Y and Tao Q: Epigenetic disruption of
the WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human cancers.
Epigenetics. 4:307–312. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen L, Dai J, Wang Z, Zhang H, Huang Y
and Zhao Y: Ginseng total saponins reverse corticosterone-induced
changes in depression-like behavior and hippocampal
plasticity-related proteins by interfering with GSK-3 β-CREB
signaling pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014:5067352014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fu M, Wang C, Rao M, Wu X, Bouras T, Zhang
X, Li Z, Jiao X, Yang J, Li A, et al: Cyclin D1 represses p300
transactivation through a cyclin-dependent kinase-independent
mechanism. J Biol Chem. 280:29728–29742. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dahmani R, Just PA and Perret C: The
Wnt/β-catenin pathway as a therapeutic target in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol.
35:709–713. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Debeb BG, Lacerda L, Xu W, Larson R,
Solley T, Atkinson R, Sulman EP, Ueno NT, Krishnamurthy S, Reuben
JM, et al: Histone deacetylase inhibitors stimulate
dedifferentiation of human breast cancer cells through
WNT/β-catenin signaling. Stem Cells. 30:2366–2377. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Correia AL, Mori H, Chen EI, Schmitt FC
and Bissell MJ: The hemopexin domain of MMP3 is responsible for
mammary epithelial invasion and morphogenesis through extracellular
interaction with HSP90β. Genes Dev. 27:805–817. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Li F, Fan C, Wang C and Ruan H:
Effects and relationship of ERK1 and ERK2 in interleukin-1β-induced
alterations in MMP3, MMP13, type II collagen and aggrecan
expression in human chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 27:583–589.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Konstantinopoulos PA, Karamouzis MV,
Papatsoris AG and Papavassiliou AG: Matrix metalloproteinase
inhibitors as anticancer agents. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
40:1156–1168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|