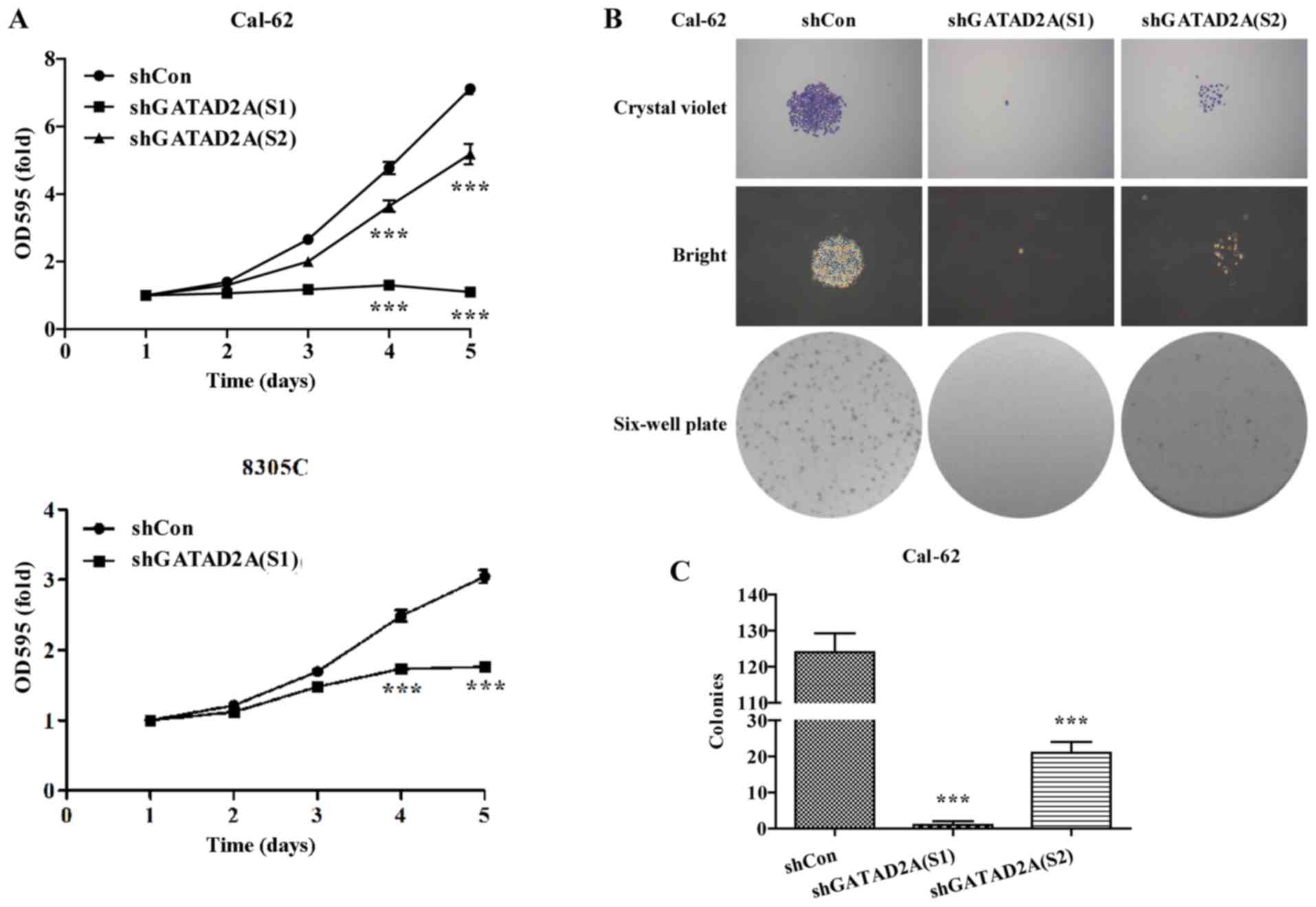
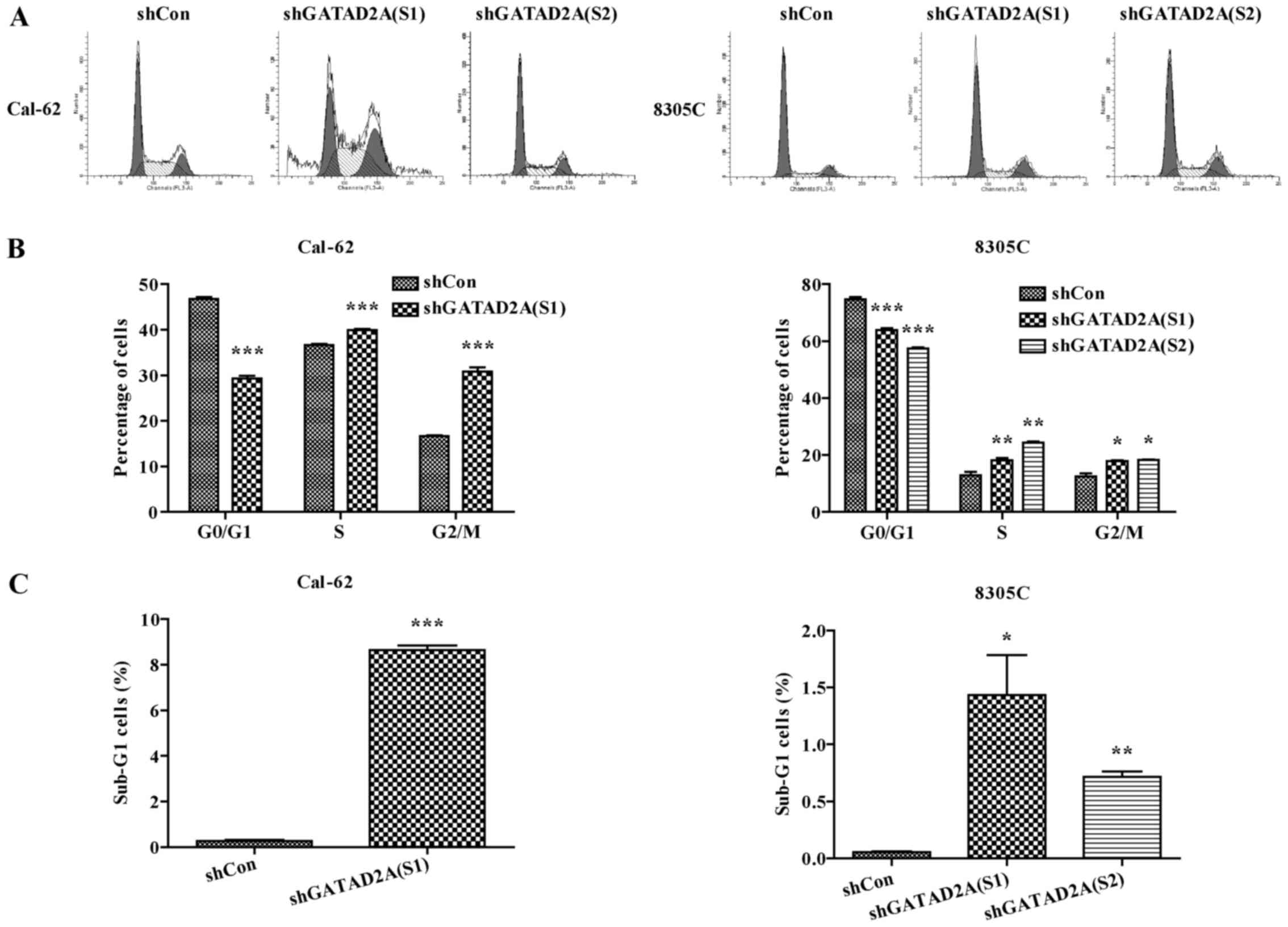
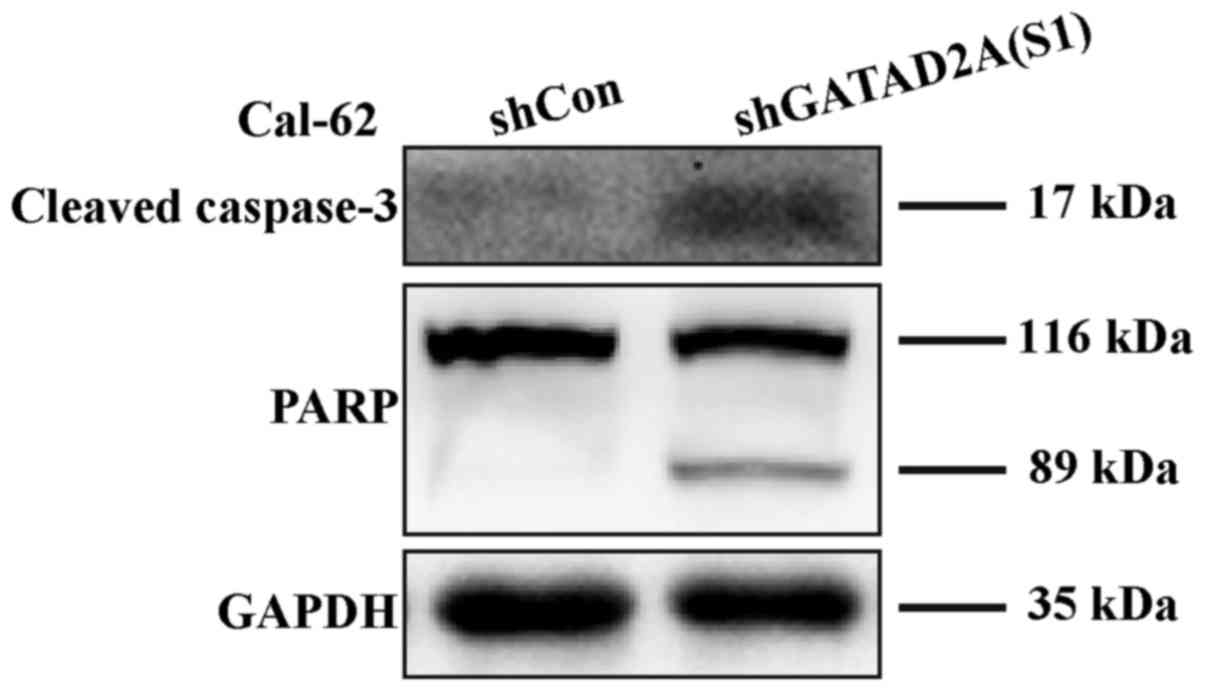
|
1
|
Weitzman SP and Cabanillas ME: The
treatment landscape in thyroid cancer: A focus on cabozantinib.
Cancer Manag Res. 7:265–278. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grande C and Brose MS: The evolving
treatment landscape for metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer. J
Adv Pract Oncol. 5:461–465. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
LiVolsi VA: The pathology of autoimmune
thyroid disease: a review. Thyroid. 4:333–339. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Aschebrook-Kilfoy B, Ward MH, Sabra MM and
Devesa SS: Thyroid cancer incidence patterns in the United States
by histologic type, 1992–2006. Thyroid. 21:125–134. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Moley JF: Medullary thyroid carcinoma.
Curr Treat Options Oncol. 4:339–347. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carling T and Udelsman R: Thyroid cancer.
Annu Rev Med. 65:125–137. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Enewold L, Zhu K, Ron E, Marrogi AJ,
Stojadinovic A, Peoples GE and Devesa SS: Rising thyroid cancer
incidence in the United States by demographic and tumor
characteristics, 1980–2005. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
18:784–791. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Torchy MP, Hamiche A and Klaholz BP:
Structure and function insights into the NuRD chromatin remodeling
complex. Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:2491–2507. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Smits AH, Jansen PW, Poser I, Hyman AA and
Vermeulen M: Stoichiometry of chromatin-associated protein
complexes revealed by label-free quantitative mass
spectrometry-based proteomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 41:e282013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brackertz M, Boeke J, Zhang R and
Renkawitz R: Two highly related p66 proteins comprise a new family
of potent transcriptional repressors interacting with MBD2 and
MBD3. J Biol Chem. 277:40958–40966. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brackertz M, Gong Z, Leers J and Renkawitz
R: p66alpha and p66beta of the Mi-2/NuRD complex mediate MBD2 and
histone interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 34:397–406. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marino S and Nusse R: Mutants in the mouse
NuRD/Mi2 component P66alpha are embryonic lethal. PLoS One.
2:e5192007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lai AY and Wade PA: Cancer biology and
NuRD: A multifaceted chromatin remodelling complex. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:588–596. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Feng Q, Cao R, Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H,
Tempst P and Zhang Y: Identification and functional
characterization of the p66/p68 components of the MeCP1 complex.
Mol Cell Biol. 22:536–546. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Umansky SR, Korol' BA and Nelipovich PA:
In vivo DNA degradation in thymocytes of gamma-irradiated or
hydrocortisone-treated rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 655:9–17. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gong J, Traganos F and Darzynkiewicz Z: A
selective procedure for DNA extraction from apoptotic cells
applicable for gel electrophoresis and flow cytometry. Anal
Biochem. 218:314–319. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Darzynkiewicz Z, Juan G, Li X, Gorczyca W,
Murakami T and Traganos F: Cytometry in cell necrobiology: Analysis
of apoptosis and accidental cell death (necrosis). Cytometry.
27:1–20. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nagata S, Nagase H, Kawane K, Mukae N and
Fukuyama H: Degradation of chromosomal DNA during apoptosis. Cell
Death Differ. 10:108–116. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nagata S: Apoptotic DNA fragmentation. Exp
Cell Res. 256:12–18. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heller B, Wang ZQ, Wagner EF, Radons J,
Bürkle A, Fehsel K, Burkart V and Kolb H: Inactivation of the
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase gene affects oxygen radical and nitric
oxide toxicity in islet cells. J Biol Chem. 270:11176–11180. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Karabay AZ, Aktan F, Sunguroğlu A and
Buyukbingol Z: Methylsulfonylmethane modulates apoptosis of
LPS/IFN-γ-activated RAW 264.7 macrophage-like cells by targeting
p53, Bax, Bcl-2, cytochrome c and PARP proteins. Immunopharmacol
Immunotoxicol. 36:379–389. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kaufmann SH: Induction of endonucleolytic
DNA cleavage in human acute myelogenous leukemia cells by
etoposide, camptothecin, and other cytotoxic anticancer drugs: A
cautionary note. Cancer Res. 49:5870–5878. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Olsen JV, Vermeulen M, Santamaria A, Kumar
C, Miller ML, Jensen LJ, Gnad F, Cox J, Jensen TS, Nigg EA, et al:
Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals widespread full
phosphorylation site occupancy during mitosis. Sci Signal.
3:ra32010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Polo SE, Kaidi A, Baskcomb L, Galanty Y
and Jackson SP: Regulation of DNA-damage responses and cell-cycle
progression by the chromatin remodelling factor CHD4. EMBO J.
29:3130–3139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|