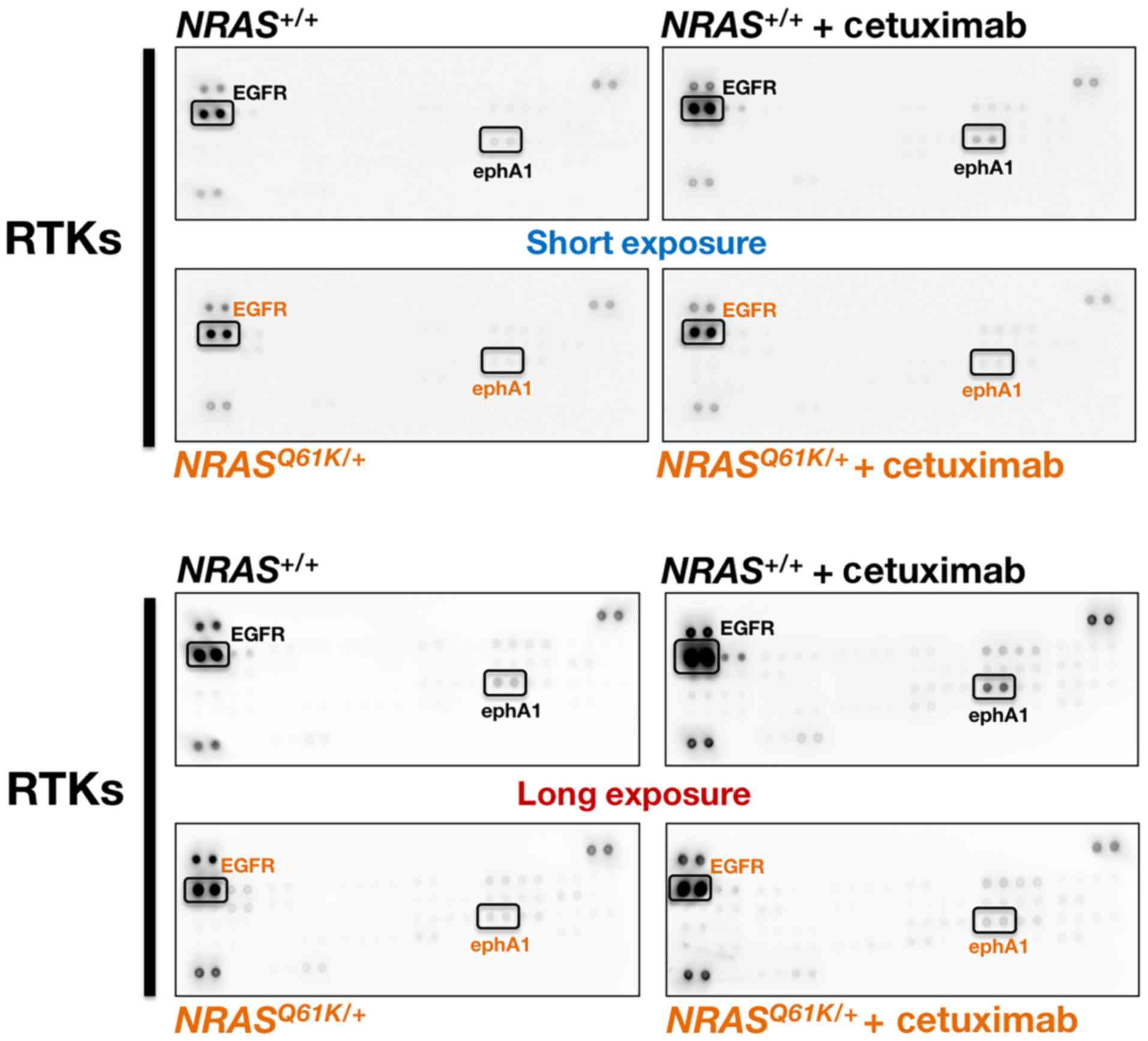
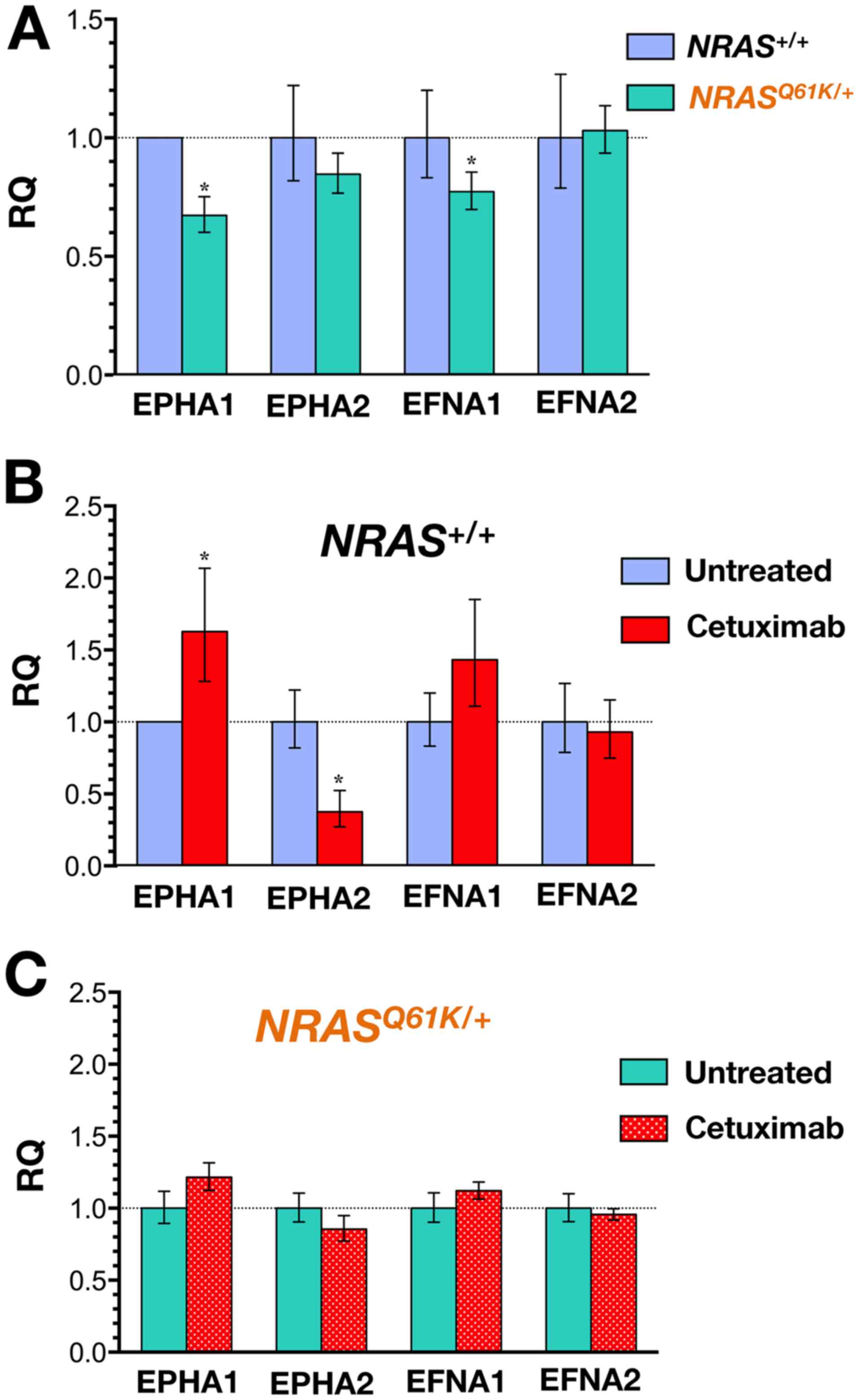
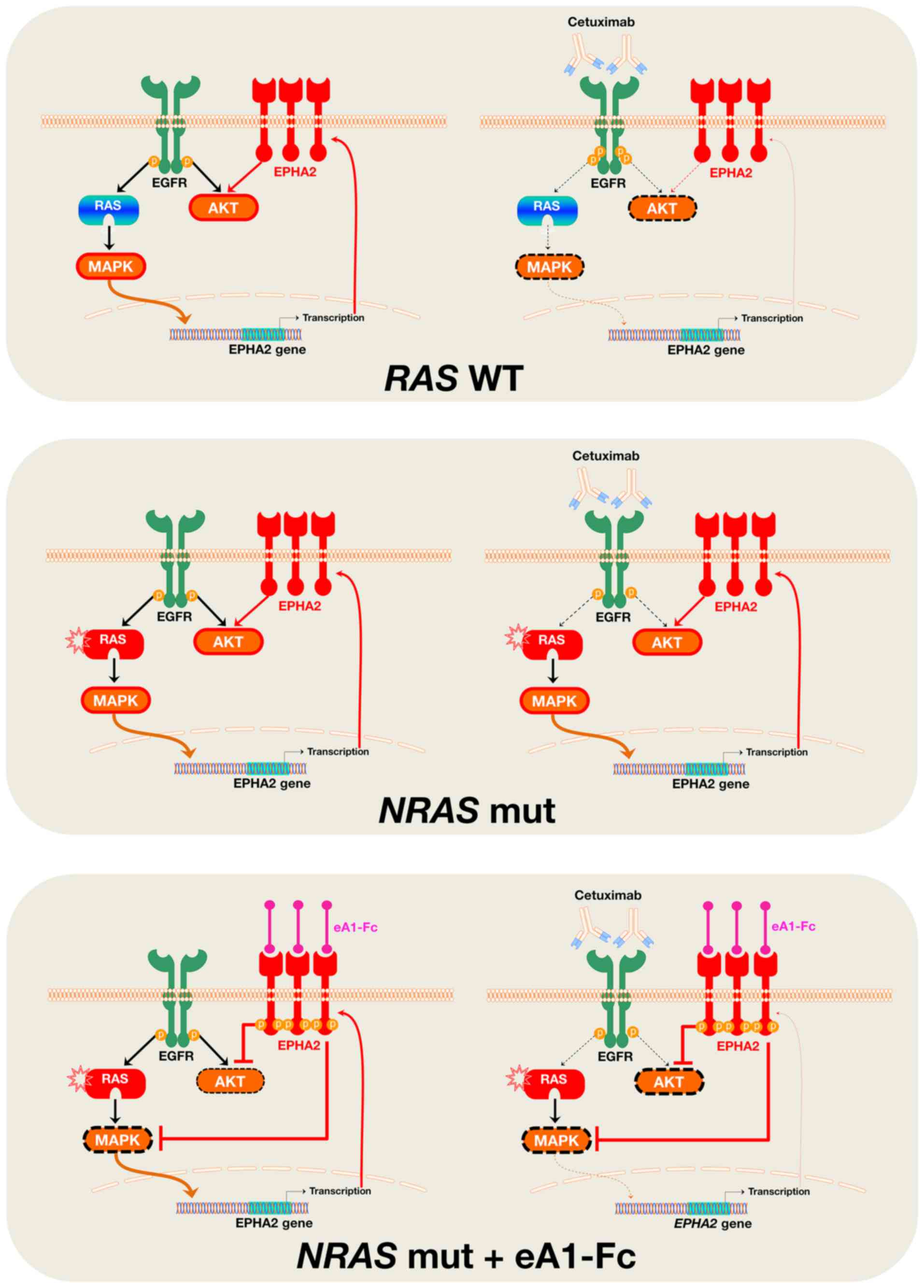
|
1
|
De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De
Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G, Kalogeras KT, Kotoula V,
Papamichael D, Laurent-Puig P, et al: Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS,
and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy
in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: A
retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol. 11:753–762. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peeters M, Oliner KS, Parker A, Siena S,
Van Cutsem E, Huang J, Humblet Y, Van Laethem JL, André T, Wiezorek
J, et al: Massively parallel tumor multigene sequencing to evaluate
response to panitumumab in a randomized phase III study of
metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 19:1902–1912. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Misale S, Di Nicolantonio F,
Sartore-Bianchi A, Siena S and Bardelli A: Resistance to anti-EGFR
therapy in colorectal cancer: From heterogeneity to convergent
evolution. Cancer Discov. 4:1269–1280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meriggi F, Vermi W, Bertocchi P and
Zaniboni A: The emerging role of NRAS mutations in colorectal
cancer patients selected for anti-EGFR therapies. Rev Recent Clin
Trials. 9:8–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bronte G, Silvestris N, Castiglia M,
Galvano A, Passiglia F, Sortino G, Cicero G, Rolfo C, Peeters M,
Bazan V, et al: New findings on primary and acquired resistance to
anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: Do all roads
lead to RAS? Oncotarget. 6:24780–24796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hecht JR, Douillard JY, Schwartzberg L,
Grothey A, Kopetz S, Rong A, Oliner KS and Sidhu R: Extended RAS
analysis for anti-epidermal growth factor therapy in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 41:653–659. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schirripa M, Cremolini C, Loupakis F,
Morvillo M, Bergamo F, Zoratto F, Salvatore L, Antoniotti C,
Marmorino F, Sensi E, et al: Role of NRAS mutations as prognostic
and predictive markers in metastatic colorectal cancer. Int J
Cancer. 136:83–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsu HC, Thiam TK, Lu YJ, Yeh CY, Tsai WS,
You JF, Hung HY, Tsai CN, Hsu A, Chen HC, et al: Mutations of
KRAS/NRAS/BRAF predict cetuximab resistance in metastatic
colorectal cancer patients. Oncotarget. 7:22257–22270.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Taniguchi H, Yamazaki K, Yoshino T, Muro
K, Yatabe Y, Watanabe T, Ebi H, Ochiai A and Baba E; Tsuchihara K;
Japanese Society of Medical Oncology: Japanese Society of Medical
Oncology Clinical Guidelines: RAS (KRAS/NRAS) mutation testing in
colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 106:324–327. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Allegra CJ, Rumble RB, Hamilton SR, Mangu
PB, Roach N, Hantel A and Schilsky RL: Extended RAS gene mutation
testing in metastatic colorectal carcinoma to predict response to
anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody therapy:
American Society of Clinical Oncology Provisional Clinical Opinion
Update 2015. J Clin Oncol. 34:179–185. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Irahara N, Baba Y, Nosho K, Shima K, Yan
L, Dias-Santagata D, Iafrate AJ, Fuchs CS, Haigis KM and Ogino S:
NRAS mutations are rare in colorectal cancer. Diagn Mol Pathol.
19:157–163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Janakiraman M, Vakiani E, Zeng Z, Pratilas
CA, Taylor BS, Chitale D, Halilovic E, Wilson M, Huberman K, Filho
JC Ricarte, et al: Genomic and biological characterization of exon
4 KRAS mutations in human cancer. Cancer Res. 70:5901–5911. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Haigis KM, Kendall KR, Wang Y, Cheung A,
Haigis MC, Glickman JN, Niwa-Kawakita M, Sweet-Cordero A,
Sebolt-Leopold J, Shannon KM, et al: Differential effects of
oncogenic K-Ras and N-Ras on proliferation, differentiation and
tumor progression in the colon. Nat Genet. 40:600–608. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Velho S, Vakiani E, Peng S, Bass
AJ, Chu GC, Gierut J, Bugni JM, Der CJ, Philips M, et al: Mutant
N-RAS protects colorectal cancer cells from stress-induced
apoptosis and contributes to cancer development and progression.
Cancer Discov. 3:294–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Queralt B, Cuyàs E, Bosch-Barrera J,
Massaguer A, De Llorens R, Martin-Castillo B, Brunet J, Salazar R
and Menendez JA: Synthetic lethal interaction of cetuximab with
MEK1/2 inhibition in NRAS-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer.
Oncotarget. 7:82185–82199. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mandic R, Rodgarkia-Dara CJ, Zhu L, Folz
BJ, Bette M, Weihe E, Neubauer A and Werner JA: Treatment of HNSCC
cell lines with the EGFR-specific inhibitor cetuximab (Erbitux)
results in paradox phosphorylation of tyrosine 1173 in the
receptor. FEBS Lett. 580:4793–4800. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshida T, Okamoto I, Okabe T, Iwasa T,
Satoh T, Nishio K, Fukuoka M and Nakagawa K: Matuzumab and
cetuximab activate the epidermal growth factor receptor but fail to
trigger downstream signaling by Akt or Erk. Int J Cancer.
122:1530–1538. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oliveras-Ferraros C, Vazquez-Martin A,
López-Bonet E, Martín-Castillo B, Del Barco S, Brunet J and
Menendez JA: Growth and molecular interactions of the anti-EGFR
antibody cetuximab and the DNA cross-linking agent cisplatin in
gefitinib-resistant MDA-MB-468 cells: New prospects in the
treatment of triple-negative/basal-like breast cancer. Int J Oncol.
33:1165–1176. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pasquale EB: Eph-ephrin bidirectional
signaling in physiology and disease. Cell. 133:38–52. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pasquale EB: Eph receptors and ephrins in
cancer: Bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:165–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wykosky J and Debinski W: The EphA2
receptor and ephrinA1 ligand in solid tumors: Function and
therapeutic targeting. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1795–1806. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beauchamp A and Debinski W: Ephs and
ephrins in cancer: ephrin-A1 signalling. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
23:109–115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miao H, Li DQ, Mukherjee A, Guo H, Petty
A, Cutter J, Basilion JP, Sedor J, Wu J, Danielpour D, et al: EphA2
mediates ligand-dependent inhibition and ligand-independent
promotion of cell migration and invasion via a reciprocal
regulatory loop with Akt. Cancer Cell. 16:9–20. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Petty A, Myshkin E, Qin H, Guo H, Miao H,
Tochtrop GP, Hsieh JT, Page P, Liu L, Lindner DJ, et al: A small
molecule agonist of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits tumor
cell migration in vitro and prostate cancer metastasis in vivo.
PLoS One. 7:e421202012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carter N, Nakamoto T, Hirai H and Hunter
T: EphrinA1-induced cytoskeletal re-organization requires FAK and
p130(cas). Nat Cell Biol. 4:565–573. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW
and Whang EE: Ligation of EphA2 by Ephrin A1-Fc inhibits pancreatic
adenocarcinoma cellular invasiveness. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
320:1096–1102. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wykosky J, Gibo DM, Stanton C and Debinski
W: EphA2 as a novel molecular marker and target in glioblastoma
multiforme. Mol Cancer Res. 3:541–551. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Walker-Daniels J, Riese DJ II and Kinch
MS: c-Cbl-dependent EphA2 protein degradation is induced by ligand
binding. Mol Cancer Res. 1:79–87. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramnarain DB, Park S, Lee DY, Hatanpaa KJ,
Scoggin SO, Otu H, Libermann TA, Raisanen JM, Ashfaq R, Wong ET, et
al: Differential gene expression analysis reveals generation of an
autocrine loop by a mutant epidermal growth factor receptor in
glioma cells. Cancer Res. 66:867–874. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Larsen AB, Pedersen MW, Stockhausen MT,
Grandal MV, van Deurs B and Poulsen HS: Activation of the EGFR gene
target EphA2 inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced cancer cell
motility. Mol Cancer Res. 5:283–293. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Larsen AB, Stockhausen MT and Poulsen HS:
Cell adhesion and EGFR activation regulate EphA2 expression in
cancer. Cell Signal. 22:636–644. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Koch H, Busto ME, Kramer K, Médard G and
Kuster B: Chemical proteomics uncovers EPHA2 as a mechanism of
acquired resistance to small molecule EGFR kinase inhibition. J
Proteome Res. 14:2617–2625. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Miao H, Wei BR, Peehl DM, Li Q, Alexandrou
T, Schelling JR, Rhim JS, Sedor JR, Burnett E and Wang B:
Activation of EphA receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits the Ras/MAPK
pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 3:527–530. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Macrae M, Neve RM, Rodriguez-Viciana P,
Haqq C, Yeh J, Chen C, Gray JW and McCormick F: A conditional
feedback loop regulates Ras activity through EphA2. Cancer Cell.
8:111–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pratt RL and Kinch MS: Ligand binding
up-regulates EphA2 messenger RNA through the mitogen-activated
protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Mol Cancer
Res. 1:1070–1076. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu F, Park PJ, Lai W, Maher E,
Chakravarti A, Durso L, Jiang X, Yu Y, Brosius A, Thomas M, et al:
A genome-wide screen reveals functional gene clusters in the cancer
genome and identifies EphA2 as a mitogen in glioblastoma. Cancer
Res. 66:10815–10823. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Carles-Kinch K, Kilpatrick KE, Stewart JC
and Kinch MS: Antibody targeting of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase
inhibits malignant cell behavior. Cancer Res. 62:2840–2847.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shao H, Pandey A, O'Shea KS, Seldin M and
Dixit VM: Characterization of B61, the ligand for the Eck receptor
protein-tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 270:5636–5641. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Miao H, Gale NW, Guo H, Qian J, Petty A,
Kaspar J, Murphy AJ, Valenzuela DM, Yancopoulos G, Hambardzumyan D,
et al: EphA2 promotes infiltrative invasion of glioma stem cells in
vivo through cross-talk with Akt and regulates stem cell
properties. Oncogene. 34:558–567. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Amato KR, Wang S, Tan L, Hastings AK, Song
W, Lovly CM, Meador CB, Ye F, Lu P, Balko JM, et al: EPHA2 blockade
overcomes acquired resistance to EGFR kinase inhibitors in lung
cancer. Cancer Res. 76:305–318. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miao B, Ji Z, Tan L, Taylor M, Zhang J,
Choi HG, Frederick DT, Kumar R, Wargo JA, Flaherty KT, et al: EPHA2
is a mediator of vemurafenib resistance and a novel therapeutic
target in melanoma. Cancer Discov. 5:274–287. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhuang G, Brantley-Sieders DM, Vaught D,
Yu J, Xie L, Wells S, Jackson D, Muraoka-Cook R, Arteaga C and Chen
J: Elevation of receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 mediates resistance
to trastuzumab therapy. Cancer Res. 70:299–308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Menyhárt O, Santarpia L and Győrffy B: A
comprehensive outline of trastuzumab resistance biomarkers in HER2
overexpressing breast cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 15:665–683.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Youngblood VM, Kim LC, Edwards DN, Hwang
Y, Santapuram PR, Stirdivant SM, Lu P, Ye F, Brantley-Sieders DM
and Chen J: The ephrin-A1/EPHA2 signaling axis regulates glutamine
metabolism in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res.
76:1825–1836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
De Robertis M, Loiacono L, Fusilli C,
Poeta ML, Mazza T, Sanchez M, Marchionni L, Signori E, Lamorte G,
Vescovi AL, et al: Dysregulation of EGFR pathway in EphA2 cell
subpopulation significantly associates with poor prognosis in
colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 23:159–170. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pentheroudakis G, Kotoula V, De Roock W,
Kouvatseas G, Papakostas P, Makatsoris T, Papamichael D, Xanthakis
I, Sgouros J, Televantou D, et al: Biomarkers of benefit from
cetuximab-based therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer:
Interaction of EGFR ligand expression with RAS/RAF, PIK3CA
genotypes. BMC Cancer. 13:492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Strimpakos A, Pentheroudakis G, Kotoula V,
De Roock W, Kouvatseas G, Papakostas P, Makatsoris T, Papamichael
D, Andreadou A, Sgouros J, et al: The prognostic role of ephrin A2
and endothelial growth factor receptor pathway mediators in
patients with advanced colorectal cancer treated with cetuximab.
Clin Colorectal Cancer. 12:267–274.e2. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dong Y, Wang J, Sheng Z, Li G, Ma H, Wang
X, Zhang R, Lu G, Hu Q, Sugimura H, et al: Downregulation of EphA1
in colorectal carcinomas correlates with invasion and metastasis.
Mod Pathol. 22:151–160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|