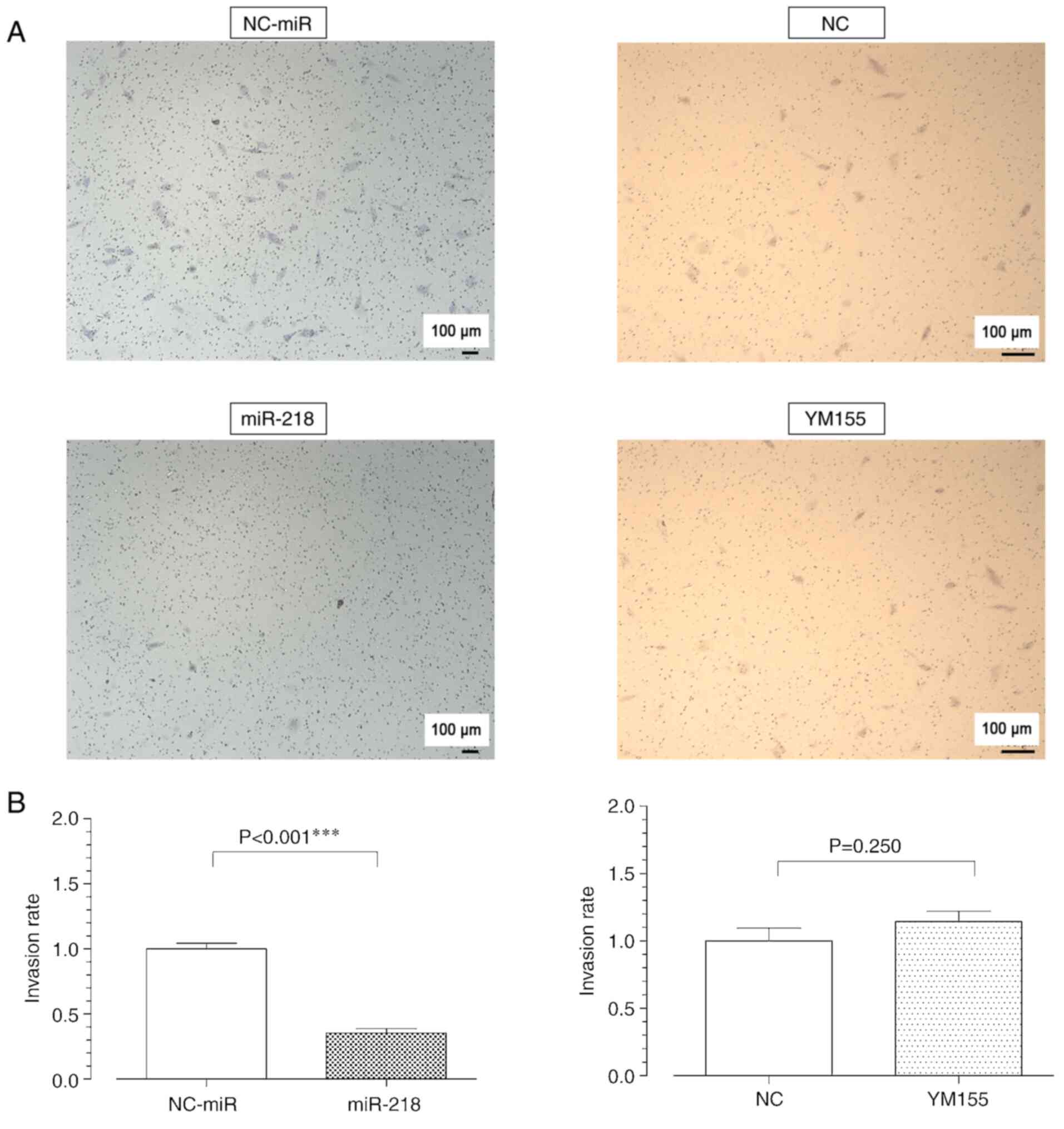
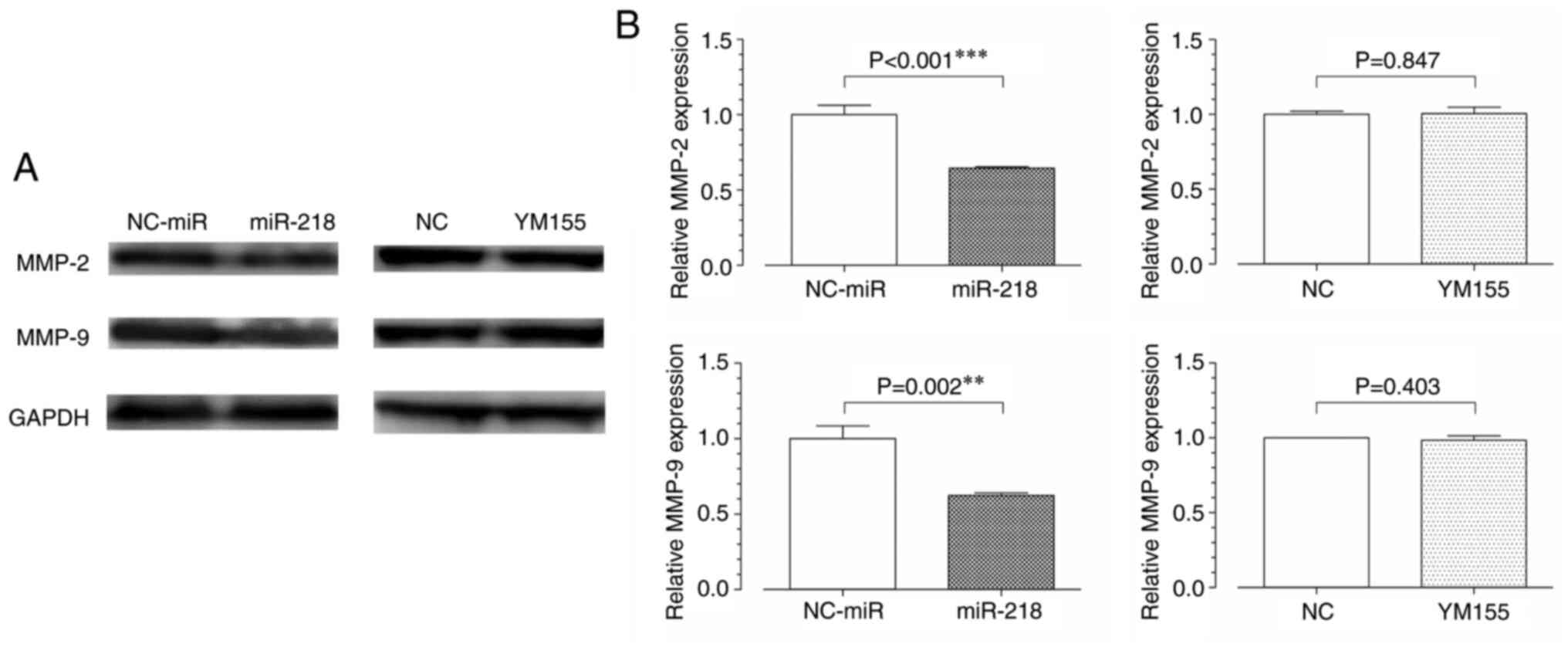
|
1
|
Eaton BR, Schwarz R, Vatner R, Yeh B,
Claude L, Indelicato DJ and Laack N: Osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood
Cancer. 68 (Suppl 2):e283522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bielack SS, Kempf-Bielack B, Delling G,
Exner GU, Flege S, Helmke K, Kotz R, Salzer-Kuntschik M, Werner M,
Winkelmann W, et al: Prognostic factors in high-grade osteosarcoma
of the extremities or trunk: An analysis of 1,702 patients treated
on neoadjuvant cooperative osteosarcoma study group protocols. J
Clin Oncol. 20:776–790. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kempf-Bielack B, Bielack SS, Jürgens H,
Branscheid D, Berdel WE, Exner GU, Göbel U, Helmke K, Jundt G,
Kabisch H, et al: Osteosarcoma relapse after combined modality
therapy: An analysis of unselected patients in the cooperative
osteosarcoma study group (COSS). J Clin Oncol. 23:559–568. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee YT, Tan YJ and Oon CE: Molecular
targeted therapy: Treating cancer with specificity. Eur J
Pharmacol. 834:188–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Szuhai K, Cleton-Jansen AM, Hogendoorn PC
and Bovée JV: Molecular pathology and its diagnostic use in bone
tumors. Cancer Genet. 205:193–204. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shaikh AB, Li F, Li M, He B, He X, Chen G,
Guo B, Li D, Jiang F, Dang L, et al: Present advances and future
perspectives of molecular targeted therapy for osteosarcoma. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:5062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Y, Teng Z, Wang Y, Gao P and Chen J:
Prognostic significance of survivin expression in osteosarcoma
patients: A meta-analysis. Med Sci Monit. 21:2877–2885. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: Key regulator of mitosis and apoptosis and novel
target for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Islam A, Kageyama H, Hashizume K, Kaneko Y
and Nakagawara A: Role of survivin, whose gene is mapped to 17q25,
in human neuroblastoma and identification of a novel
dominant-negative isoform, survivin-beta/2B. Med Pediatr Oncol.
35:550–553. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kami K, Doi R, Koizumi M, Toyoda E, Mori
T, Ito D, Fujimoto K, Wada M, Miyatake S and Imamura M: Survivin
expression is a prognostic marker in pancreatic cancer patients.
Surgery. 136:443–448. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kappler M, Köhler T, Kampf C,
Diestelkötter P, Würl P, Schmitz M, Bartel F, Lautenschläger C,
Rieber EP, Schmidt H, et al: Increased survivin transcript levels:
An independent negative predictor of survival in soft tissue
sarcoma patients. Int J Cancer. 95:360–363. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miyachi K, Sasaki K, Onodera S, Taguchi T,
Nagamachi M, Kaneko H and Sunagawa M: Correlation between survivin
mRNA expression and lymph node metastasis in gastric cancer.
Gastric Cancer. 6:217–224. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Monzó M, Rosell R, Felip E, Astudillo J,
Sánchez JJ, Maestre J, Martín C, Font A, Barnadas A and Abad A: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene: Re-expression of survivin messenger RNA
as a prognosis marker in non-small-cell lung cancers. J Clin Oncol.
17:2100–2104. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sarela AI, Macadam RC, Farmery SM, Markham
AF and Guillou PJ: Expression of the antiapoptosis gene, survivin,
predicts death from recurrent colorectal carcinoma. Gut.
46:645–650. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang H, Xi X, Kong X, Huang G and Ge G:
The expression and significance of survivin mRNA in urinary bladder
carcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 130:487–490. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Osaka E, Suzuki T, Osaka S, Yoshida Y,
Sugita H, Asami S, Tabata K, Sugitani M, Nemoto N and Ryu J:
Survivin expression levels as independent predictors of survival
for osteosarcoma patients. J Orthop Res. 25:116–121. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gao JZ, Chen FH, Wang L, Wei H and Meng
SL: YM155 inhibits tumor growth and enhances chemosensitivity to
cisplatin in osteosarcoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 19:2062–2069.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Clemens MR, Gladkov OA, Gartner E,
Vladimirov V, Crown J, Steinberg J, Jie F and Keating A: Phase II,
multicenter, open-label, randomized study of YM155 plus docetaxel
as first-line treatment in patients with HER2-negative metastatic
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 149:171–179. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Di Leva G, Garofalo M and Croce CM:
MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 9:287–314. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tutar L, Tutar E, Özgür A and Tutar Y:
Therapeutic targeting of microRNAs in cancer: Future perspectives.
Drug Dev Res. 76:382–388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang J, Lyu H, Wang J and Liu B: MicroRNA
regulation and therapeutic targeting of survivin in cancer. Am J
Cancer Res. 5:20–31. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu YF, Zhang L, Waye MM, Fu WM and Zhang
JF: MiR-218 mediates tumorigenesis and metastasis: Perspectives and
implications. Exp Cell Res. 334:173–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tong X, Yang P, Wang K, Liu Y, Liu X, Shan
X, Huang R, Zhang K and Wang J: Survivin is a prognostic indicator
in glioblastoma and may be a target of microRNA-218. Oncol Lett.
18:359–367. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kogo R, How C, Chaudary N, Bruce J, Shi W,
Hill RP, Zahedi P, Yip KW and Liu FF: The microRNA-218~survivin
axis regulates migration, invasion and lymph node metastasis in
cervical cancer. Oncotarget. 6:1090–1100. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zarogoulidis P, Petanidis S, Kioseoglou E,
Domvri K, Anestakis D and Zarogoulidis K: MiR-205 and miR-218
expression is associated with carboplatin chemoresistance and
regulation of apoptosis via Mcl-1 and survivin in lung cancer
cells. Cell Signal. 27:1576–1588. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai G, Zheng D, Guo W, Yang J and Cheng
AY: Cinobufagin induces apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells via the
mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem.
46:1134–1147. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xuan C, Jin M, Gao Y, Xu S, Wang L, Wang
Y, Han R and An Q: miR-218 suppresses the proliferation of
osteosarcoma through downregulation of E2F2. Oncol Lett.
17:571–577. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Deng W, Fu M, Cao Y, Cao X, Wang M, Yang
Y, Qu R, Li J, Xu X and Yu J: Angelica sinensis polysaccharide
nanoparticles as novel non-viral carriers for gene delivery to
mesenchymal stem cells. Nanomedicine. 9:1181–1191. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Waller CF: Imatinib mesylate. Recent
Results Cancer Res. 212:1–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara
S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I,
et al: Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer
with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kataoka K, Osaka E, Shimizu T, Okamura Y,
Yoshida Y and Tokuhashi Y: Lung squamous cell carcinoma with
brachial soft tissue metastasis responsive to gefitinib: Report of
a rare case. Thorac Cancer. 7:676–680. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pakkala S and Ramalingam SS: Personalized
therapy for lung cancer: Striking a moving target. JCI Insight.
3:1208582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Italiano A, Mir O, Mathoulin-Pelissier S,
Penel N, Piperno-Neumann S, Bompas E, Chevreau C, Duffaud F,
Entz-Werlé N, Saada E, et al: Cabozantinib in patients with
advanced Ewing sarcoma or osteosarcoma (CABONE): A multicentre,
single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 21:446–455. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van Zandwijk N, Pavlakis N, Kao SC, Linton
A, Boyer MJ, Clarke S, Huynh Y, Chrzanowska A, Fulham MJ, Bailey
DL, et al: Safety and activity of microRNA-loaded minicells in
patients with recurrent malignant pleural mesothelioma: A
first-in-man, phase 1, open-label, dose-escalation study. Lancet
Oncol. 18:1386–1396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Janssen HL, Reesink HW, Lawitz EJ, Zeuzem
S, Rodriguez-Torres M, Patel K, van der Meer AJ, Patick AK, Chen A,
Zhou Y, et al: Treatment of HCV infection by targeting microRNA. N
Engl J Med. 368:1685–1694. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen X, Chen XG, Hu X, Song T, Ou X and
Zhang C, Zhang W and Zhang C: MiR-34a and miR-203 inhibit survivin
expression to control cell proliferation and survival in human
osteosarcoma cells. J Cancer. 7:1057–1065. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fernández JG, Rodríguez DA, Valenzuela M,
Calderon C, Urzúa U, Munroe D, Rosas C, Lemus D, Díaz N, Wright MC,
et al: Survivin expression promotes VEGF-induced tumor angiogenesis
via PI3K/Akt enhanced β-catenin/Tcf-Lef dependent transcription.
Mol Cancer. 13:2092014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu J, Luo B and Zhao M: Bmi-1-targeting
suppresses osteosarcoma aggressiveness through the NF-κB signaling
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 16:7949–7958. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li YJ, Zhang W, Xia H, Zhang BS, Chen P,
Zhao YL and Li J: miR-218 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by targeting Robo1 and Ecop in lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Future Oncol. 13:2571–2582. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lin CH, Ji T, Chen CF and Hoang BH: Wnt
signaling in osteosarcoma. Adv Exp Med Biol. 804:33–45. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang W, Liu Y, Li YF, Yue Y, Yang X and
Peng L: Targeting of survivin pathways by YM155 inhibits cell death
and invasion in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 38:2426–2437. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Z, Ma L and Wang J: YM155 exerts a
growth inhibitory effect on human osteosarcoma in vitro and
in vivo. Oncol Rep. 34:1074–1080. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Imai M, Muraki M, Takamatsu K, Saito H,
Seiki M and Takahashi Y: Spontaneous transformation of human
granulosa cell tumours into an aggressive phenotype: A metastasis
model cell line. BMC Cancer. 8:3192008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pautke C, Schieker M, Tischer T, Kolk A,
Neth P, Mutschler W and Milz S: Characterization of osteosarcoma
cell lines MG-63, Saos-2 and U-2 OS in comparison to human
osteoblasts. Anticancer Res. 24:3743–3748. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liu Y, Wang Q, Yu P, Miao W, Liu C, Pu Y
and Zhang C: Methylation of WWOX gene promotes proliferation of
osteosarcoma cells. J BUON. 25:2708–2713. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|