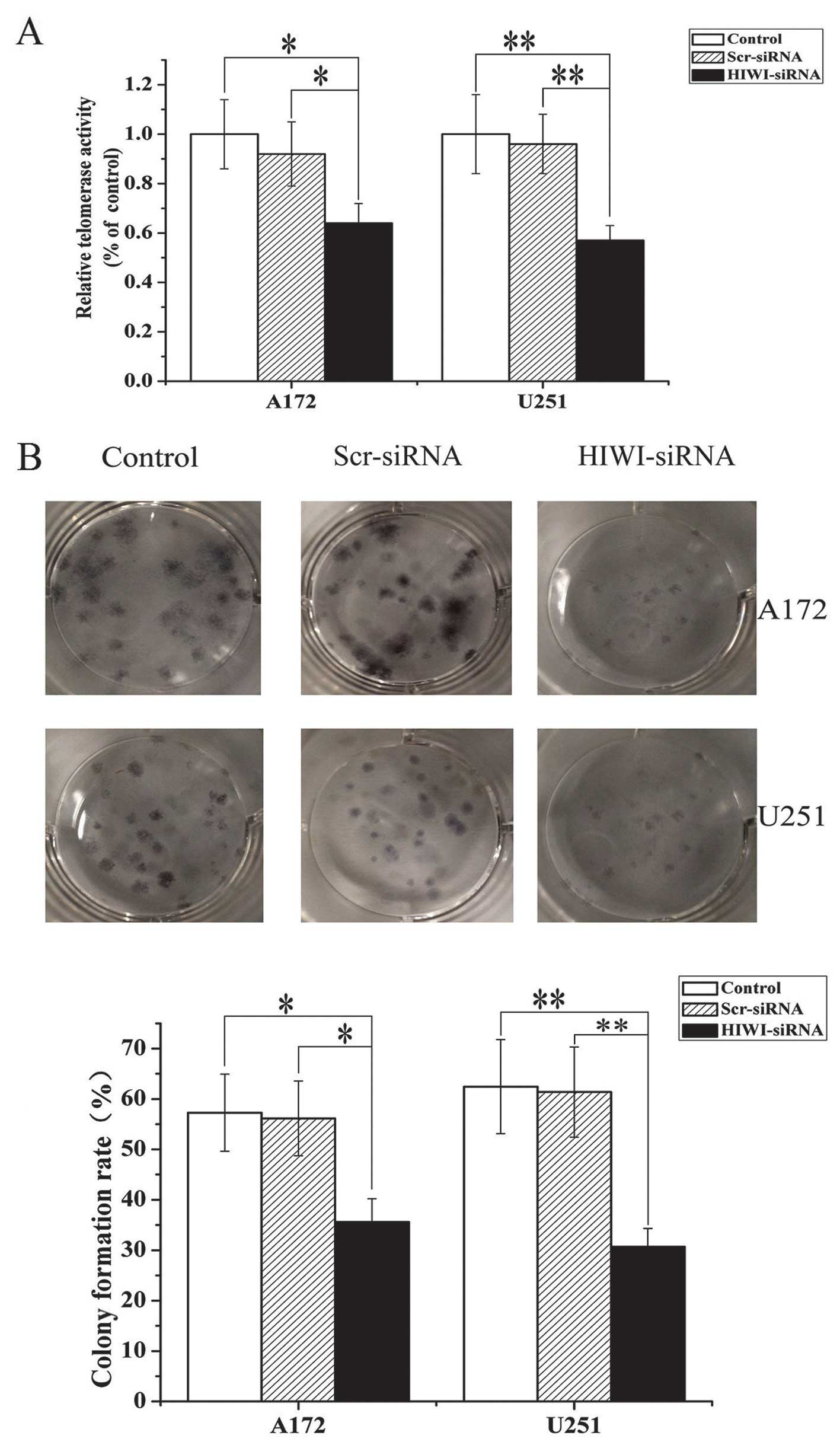
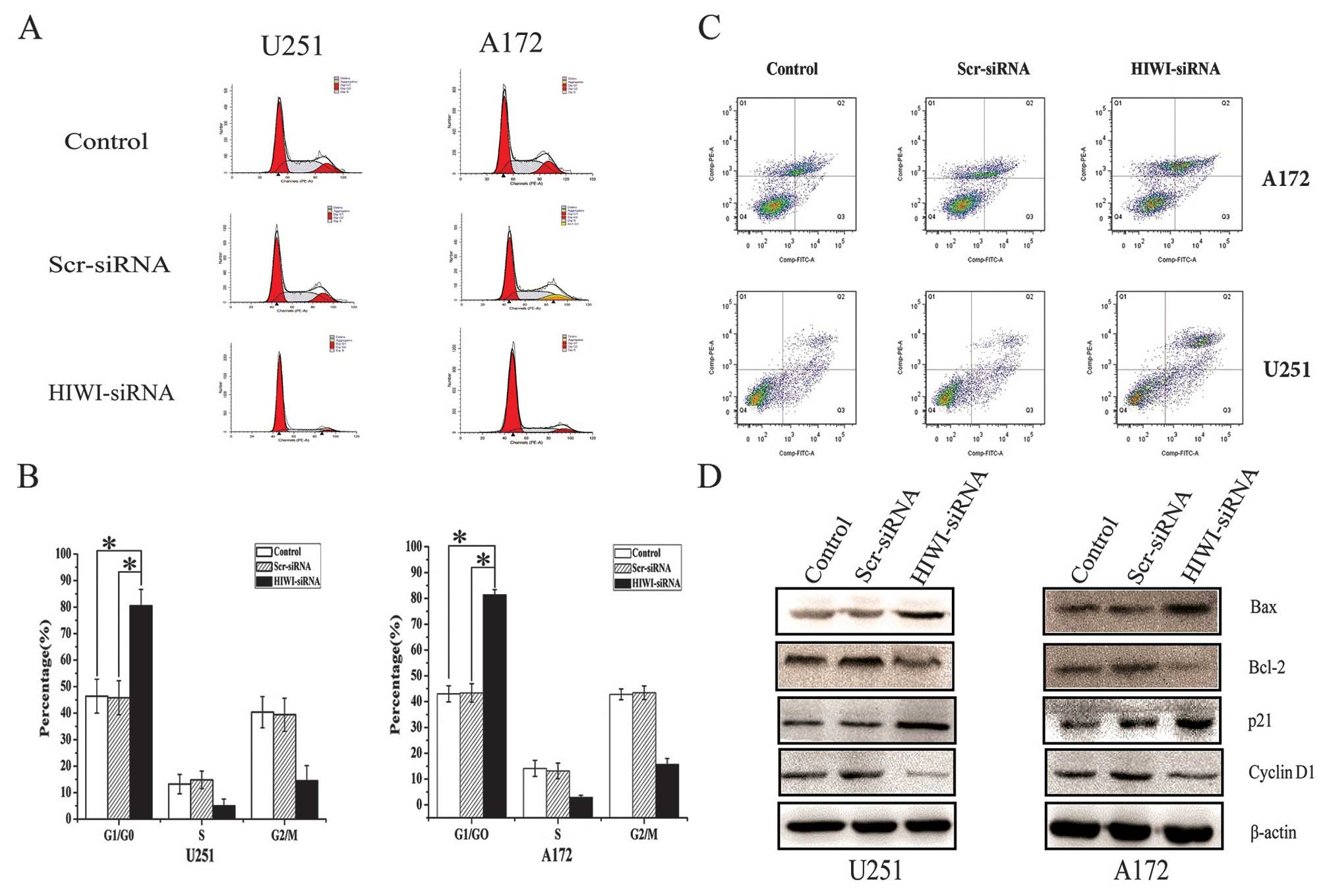
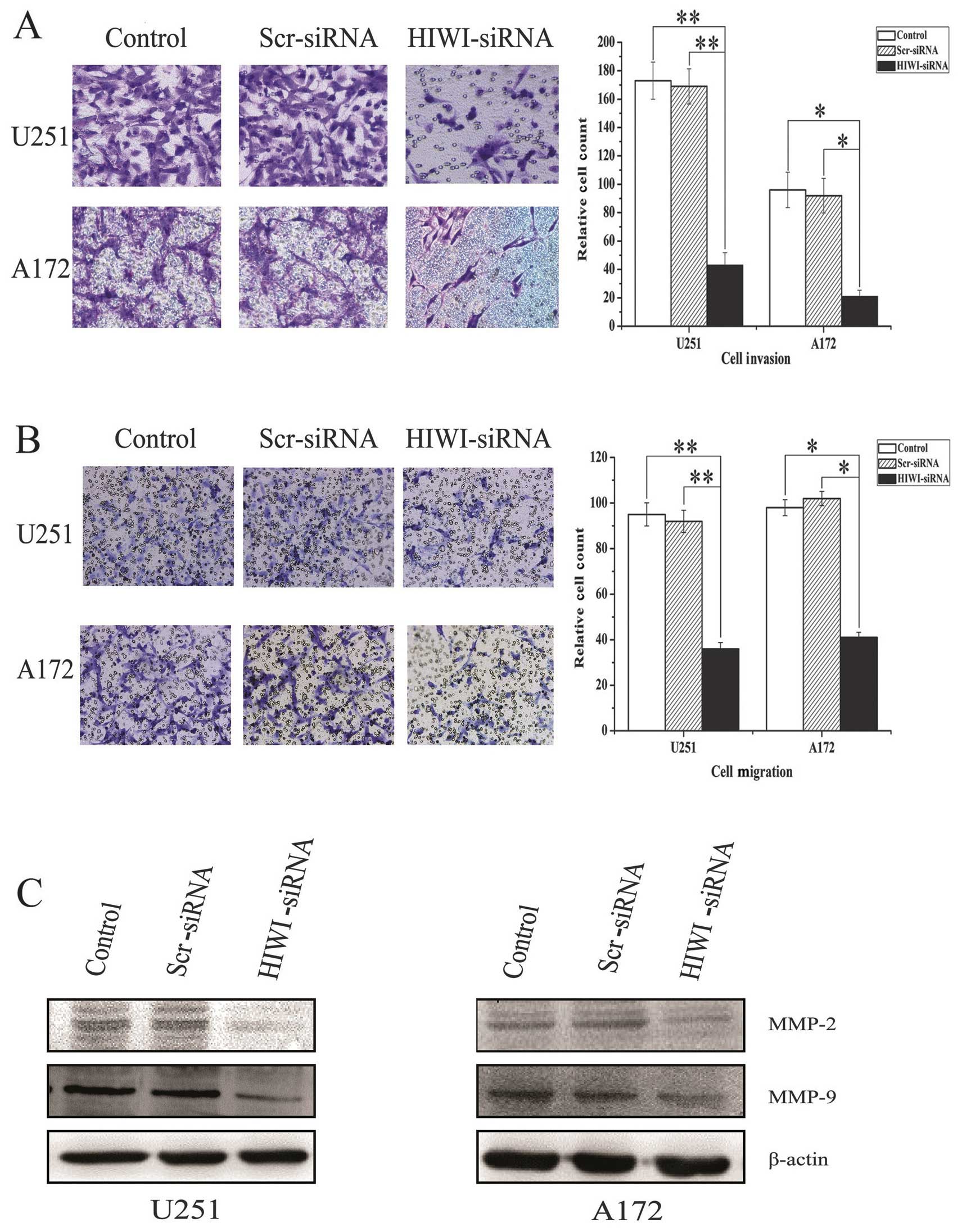
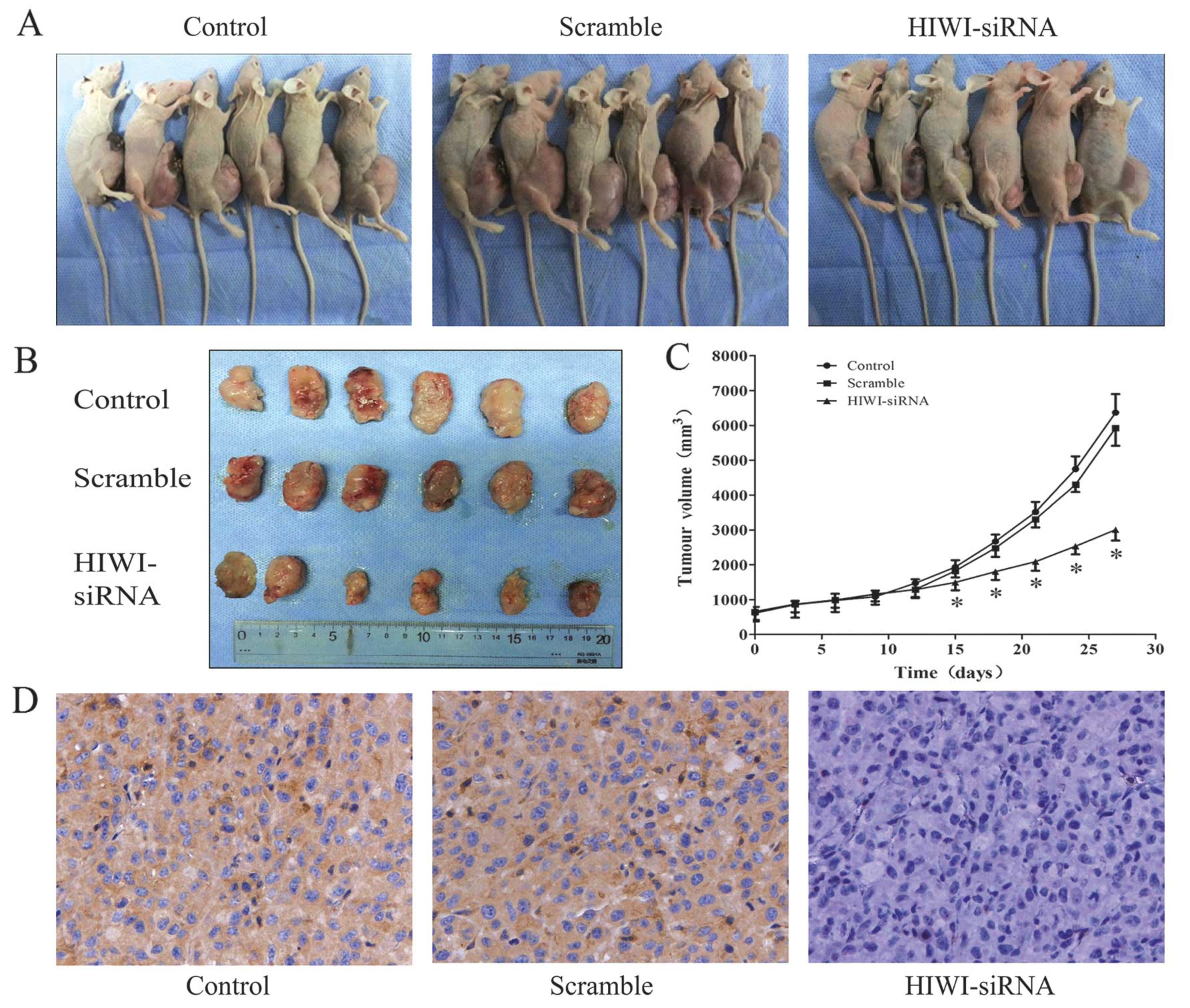
|
1
|
Maher EA, Furnari FB, Bachoo RM, et al:
Malignant glioma: genetics and biology of a grave matter. Genes
Dev. 15:1311–1333. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Stupp R and Roila F; ESMO Guidelines
Working Group. Malignant glioma: ESMO clinical recommendations for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 20(Suppl 4):
S126–S128. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Argyriou AA and Kalofonos HP: Molecularly
targeted therapies for malignant gliomas. Mol Med. 15:115–122.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cox DN, Chao A, Baker J, Chang L, Qiao D
and Lin H: A novel class of evolutionarily conserved genes defined
by piwi are essential for stem cell self-renewal. Gen Dev.
12:3715–3727. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sasaki T, Shiohama A, Minoshima S and
Shimizu N: Identification of eight members of the Argonaute family
in the human genome. Genomics. 82:323–330. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hutvagner G and Simard MJ: Argonaute
proteins: key players in RNA silencing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
9:22–32. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Siddiqi S, Terry M and Matushansky I: Hiwi
mediated tumorigenesis is associated with DNA hypermethylation.
PLoS One. 7:e337112012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Shen X, et al: The PIWI
protein acts as a predictive marker for human gastric cancer. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 5:315–325. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grochola LF, Greither T, Taubert H, et al:
The stem cell-associated Hiwi gene in human adenocarcinoma of the
pancreas: expression and risk of tumour-related death. Br J Cancer.
99:1083–1088. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li S, Meng L, Zhu C, et al: The universal
overexpression of a cancer testis antigen hiwi is associated with
cancer angiogenesis. Oncol Rep. 23:1063–1068. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zeng Y, Qu LK, Meng L, et al: HIWI
expression profile in cancer cells and its prognostic value for
patients with colorectal cancer. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:2144–2149.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang D, Fang Z, Dong M, et al: Effect of
RNA interference-related HiWi gene expression on the proliferation
and apoptosis of lung cancer stem cells. Oncol Lett. 4:146–150.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu C, Qu L, Dong B, et al: Combined
phenotype of 4 markers improves prognostic value of patients with
colon cancer. Am J Med Sci. 343:295–302. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun G, Wang Y, Sun L, et al: Clinical
significance of Hiwi gene expression in gliomas. Brain Res.
1373:183–188. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao YM, Zhou JM, Wang LR, et al: HIWI is
associated with prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
after curative resection. Cancer. 118:2708–2717. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou X, Ren Y, Moore L, et al:
Downregulation of miR-21 inhibits EGFR pathway and suppresses the
growth of human glioblastoma cells independent of PTEN status. Lab
Invest. 90:144–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hahnfeldt P, Panigrahy D, Folkman J and
Hlatky L: Tumor development under angiogenic signaling: a dynamical
theory of tumor growth, treatment response, and postvascular
dormancy. Cancer Res. 59:4770–4775. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu WK, Jiang XY and Zhang ZX: Expression
of PSCA, PIWIL1 and TBX2 and its correlation with HPV16 infection
in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded cervical squamous cell
carcinoma specimens. Arch Virol. 155:657–663. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li L, Yu C, Gao H and Li Y: Argonaute
proteins: potential biomarkers for human colon cancer. BMC Cancer.
10:382010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jiang J, Zhang H, Tang Q, Hao B and Shi R:
Expression of HIWI in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 61:53–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu X, Sun Y, Guo J, et al: Expression of
hiwi gene in human gastric cancer was associated with proliferation
of cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 118:1922–1929. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sharma AK, Nelson MC, Brandt JE, et al:
Human CD34(+) stem cells express the hiwi gene, a human homologue
of the Drosophila gene piwi. Blood. 97:426–434. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Janssen A and Medema RH: Mitosis as an
anti-cancer target. Oncogene. 30:2799–2809. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cornils H, Kohler RS, Hergovich A and
Hemmings BA: Human NDR kinases control G(1)/S cell cycle transition
by directly regulating p21 stability. Mol Cell Biol. 31:1382–1395.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ghate NB, Chaudhuri D, Sarkar R, et al: An
antioxidant extract of tropical lichen, Parmotrema
reticulatum, induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in breast
carcinoma cell line MCF-7. PLoS One. 8:e822932013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nakada M, Nakada S, Demuth T, Tran NL,
Hoelzinger DB and Berens ME: Molecular targets of glioma invasion.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:458–478. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Itoh Y, Palmisano R, Anilkumar N, Nagase
H, Miyawaki A and Seiki M: Dimerization of MT1-MMP during cellular
invasion detected by fluorescence resonance energy transfer.
Biochem J. 440:319–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kargiotis O, Chetty C, Gondi CS, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated transfer of siRNA against MMP-2 mRNA results in
impaired invasion and tumor-induced angiogenesis, induces apoptosis
in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo in glioblastoma.
Oncogene. 27:4830–4840. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhou X, Ma L, Li J, Gu J, Shi Q and Yu R:
Effects of SEMA3G on migration and invasion of glioma cells. Oncol
Rep. 28:269–275. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Munaut C, Noël A, Hougrand O, Foidart JM,
Boniver J and Deprez M: Vascular endothelial growth factor
expression correlates with matrix metalloproteinases MT1-MMP, MMP-2
and MMP-9 in human glioblastomas. Int J Cancer. 106:848–855. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yoshida D, Watanabe K, Noha M, Takahashi
H, Teramoto A and Sugisaki Y: Anti-invasive effect of an
anti-matrix metalloproteinase agent in a murine brain slice model
using the serial monitoring of green fluorescent protein-labeled
glioma cells. Neurosurgery. 52:187–197. 2003.
|
|
33
|
Bellail AC, Hunter SB, Brat DJ, Tan C and
Van Meir EG: Microregional extracellular matrix heterogeneity in
brain modulates glioma cell invasion. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:1046–1069. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|