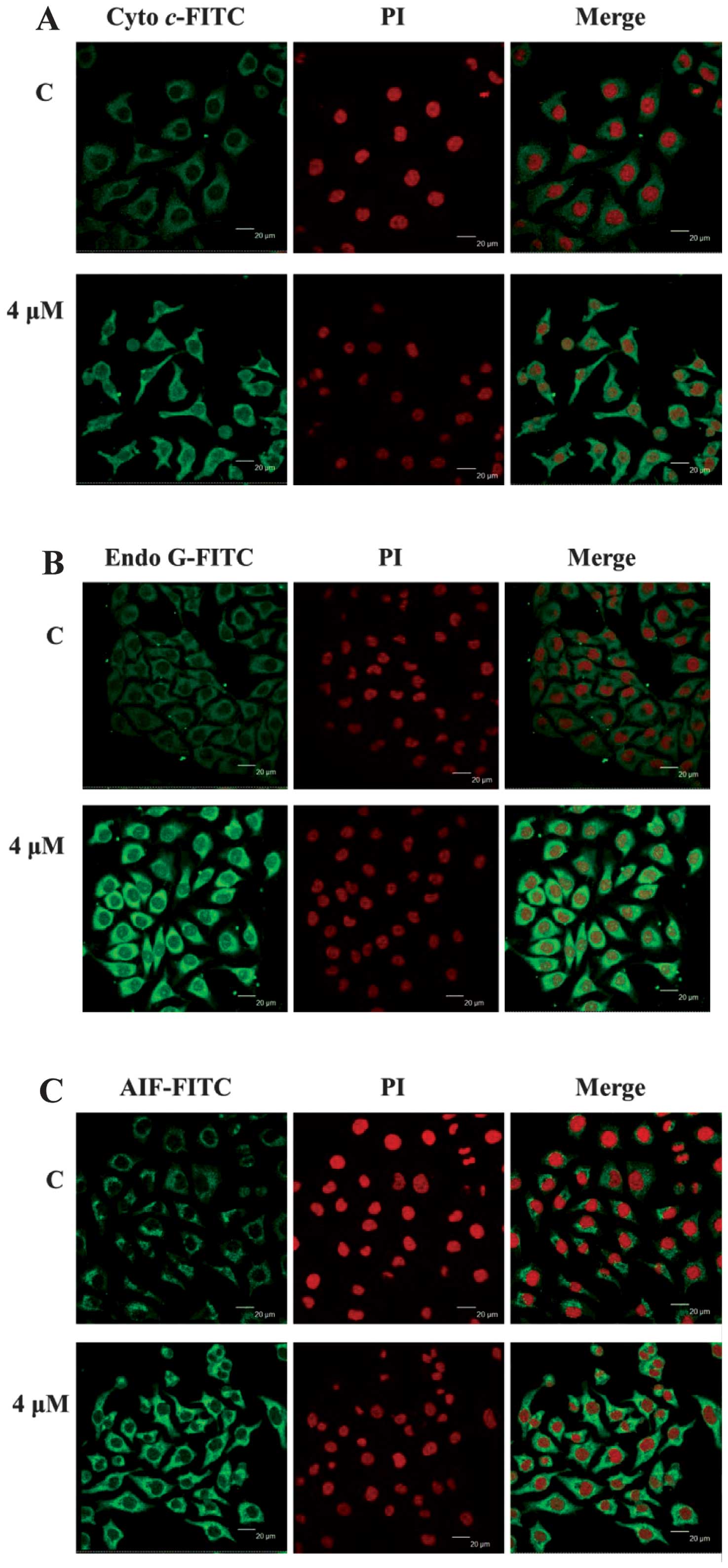
|
1
|
Postovit LM, Margaryan NV, Seftor EA and
Hendrix MJ: Role of nodal signaling and the microenvironment
underlying melanoma plasticity. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res.
21:348–357. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bergomi M, Pellacani G, Vinceti M, et al:
Trace elements and melanoma. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 19:69–73. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chudnovsky Y, Khavari PA and Adams AE:
Melanoma genetics and the development of rational therapeutics. J
Clin Invest. 115:813–824. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thompson JF, Scolyer RA and Kefford RF:
Cutaneous melanoma in the era of molecular profiling. Lancet.
374:362–365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller AJ and Mihm MC Jr: Melanoma. N Engl
J Med. 355:51–65. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bhatia S, Tykodi SS and Thompson JA:
Treatment of metastatic melanoma: an overview. Oncology (Williston
Park). 23:488–496. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Gava B, Zorzet S, Spessotto P, Cocchietto
M and Sava G: Inhibition of B16 melanoma metastases with the
ruthenium complex imidazolium
trans-imidazoledimethylsulfoxide-tetra-chlororuthenate and
down-regulation of tumor cell invasion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
317:284–291. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM and Snader KM: The
influence of natural products upon drug discovery. Nat Prod Rep.
17:215–234. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang GS: Medical uses of mylabris in
ancient China and recent studies. J Ethnopharmacol. 26:147–162.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu B: The inf luence of several anticancer
agents on cell proliferation, differentiation and the cell cycle of
murine erythroleukemia cells. Am J Chin Med. 9:268–276. 1981.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sagawa M, Nakazato T, Uchida H, Ikeda Y
and Kizaki M: Cantharidin induces apoptosis of human multiple
myeloma cells via inhibition of the JAK/STAT pathway. Cancer Sci.
99:1820–1826. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuo JH, Chu YL, Yang JS, et al:
Cantharidin induces apoptosis in human bladder cancer TSGH 8301
cells through mitochondria-dependent signal pathways. Int J Oncol.
37:1243–1250. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Williams LA, Möller W, Merisor E, Kraus W
and Rösner H: In vitro anti-proliferation/cytotoxic activity of
cantharidin (Spanish Fly) and related derivatives. West Indian Med
J. 52:10–13. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang WW, Ko SW, Tsai HY, et al:
Cantharidin induces G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis in human
colorectal cancer colo 205 cells through inhibition of CDK1
activity and caspase-dependent signaling pathways. Int J Oncol.
38:1067–1073. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Wang CC, Wu CH, Hsieh KJ, Yen KY and Yang
LL: Cytotoxic effects of cantharidin on the growth of normal and
carcinoma cells. Toxicology. 147:77–87. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li W, Chen Z, Zong Y, et al: PP2A
inhibitors induce apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cell line PANC-1
through persistent phosphorylation of IKKα and sustained activation
of the NF-κB pathway. Cancer Lett. 304:117–127. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Hsia TC, Yu CC, Hsu SC, et al: Cantharidin
induces apoptosis of H460 human lung cancer cells through
mitochondria-dependent pathways. Int J Oncol. 45:245–254. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Kim YM, Ku MJ, Son YJ, Yun JM, Kim SH and
Lee SY: Anti-metastatic effect of cantharidin in A549 human lung
cancer cells. Arch Pharm Res. 36:479–484. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hsia TC, Lin JH, Hsu SC, et al:
Cantharidin induces DNA damage and inhibits DNA repair-associated
protein levels in NCI-H460 human lung cancer cells. Environ
Toxicol. Mar 17–2014.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
20
|
Huang SH, Hsu MH, Hsu SC, et al: Phenethyl
isothiocyanate triggers apoptosis in human malignant melanoma A375.
S2 cells through reactive oxygen species and the
mitochondria-dependent pathways. Hum Exp Toxicol. 33:270–283. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chang Y-M, Velmurugan BK, Kuo W-W, et al:
Inhibitory effect of alpinate Oxyphyllae fructus extracts on Ang
II-induced cardiac pathological remodeling-related pathways in H9c2
cardiomyoblast cells. BioMedicine. 3:148–152. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lin M-C, Tsai S-Y, Wang F-Y, Liu F-H, Syu
J-N and Tang F-Y: Leptin induces cell invasion and the upregulation
of matrilysin in human colon cancer cells. BioMedicine. 3:174–180.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Das KC and Ravi D: Altered expression of
cyclins and cdks in premature infant baboon model of
bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Antioxid Redox Signal. 6:117–127. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee KH: Anticancer drug design based on
plant-derived natural products. J Biomed Sci. 6:236–250.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Das KC and Wasnick JD: Biphasic response
of checkpoint control proteins in hyperoxia: exposure to lower
levels of oxygen induces genome maintenance genes in experimental
baboon BPD. Mol Cell Biochem. 395:187–198. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Salameh A, Galvagni F, Anselmi F, De
Clemente C, Orlandini M and Oliviero S: Growth factor stimulation
induces cell survival by c-Jun. ATF2-dependent activation of
Bcl-XL. J Biol Chem. 285:23096–23104. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shirali S, Aghaei M, Shabani M, Fathi M,
Sohrabi M and Moeinifard M: Adenosine induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis via cyclinD1/Cdk4 and Bcl-2/Bax pathways in human ovarian
cancer cell line OVCAR-3. Tumour Biol. 34:1085–1095. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kelly PN and Strasser A: The role of Bcl-2
and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer
therapy. Cell Death Differ. 18:1414–1424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Strasser A, Cory S and Adams JM:
Deciphering the rules of programmed cell death to improve therapy
of cancer and other diseases. EMBO J. 30:3667–3683. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Laurent A, Nicco C, Chéreau C, et al:
Controlling tumor growth by modulating endogenous production of
reactive oxygen species. Cancer Res. 65:948–956. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gillies LA and Kuwana T: Apoptosis
regulation at the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Cell Biochem.
115:632–640. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Z, Cai F, Chen X, Luo M, Hu L and Lu
Y: The role of mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species in
hyperthermia-induced platelet apoptosis. PLoS One. 8:e750442013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Crompton M: The mitochondrial permeability
transition pore and its role in cell death. Biochem J. 341:233–249.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Murphy MP: How mitochondria produce
reactive oxygen species. Biochem J. 417:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Korsmeyer SJ, Shutter JR, Veis DJ, Merry
DE and Oltvai ZN: Bcl-2/Bax: a rheostat that regulates an
anti-oxidant pathway and cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. 4:327–332.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lindsay J, Esposti MD and Gilmore AP:
Bcl-2 proteins and mitochondria - specificity in membrane targeting
for death. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1813:532–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guha M, Kumar S, Choubey V, Maity P and
Bandyopadhyay U: Apoptosis in liver during malaria: role of
oxidative stress and implication of mitochondrial pathway. FASEB J.
20:1224–1226. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, et al:
Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: recommendations of
the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ.
19:107–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L and Brenner C:
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev.
87:99–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|