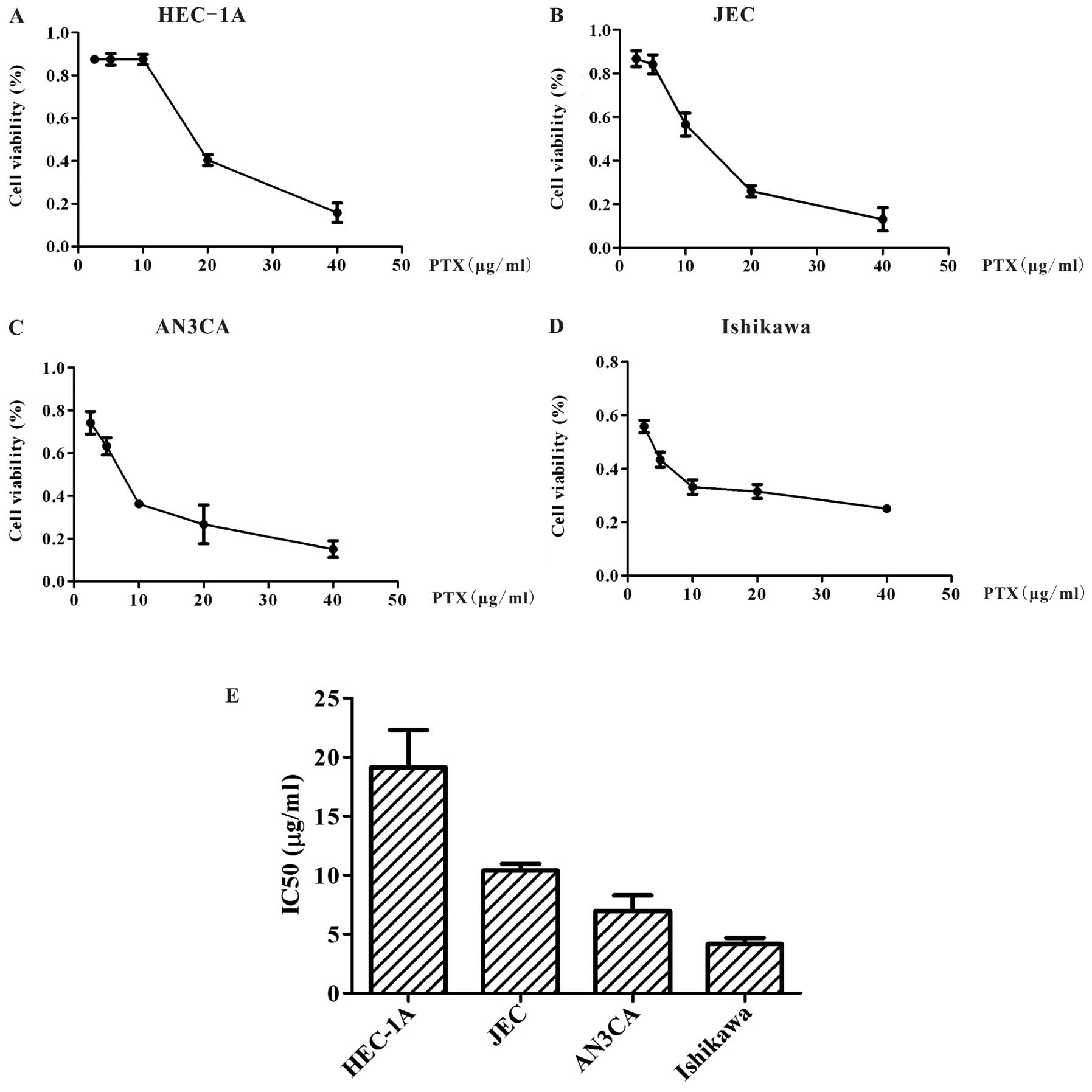
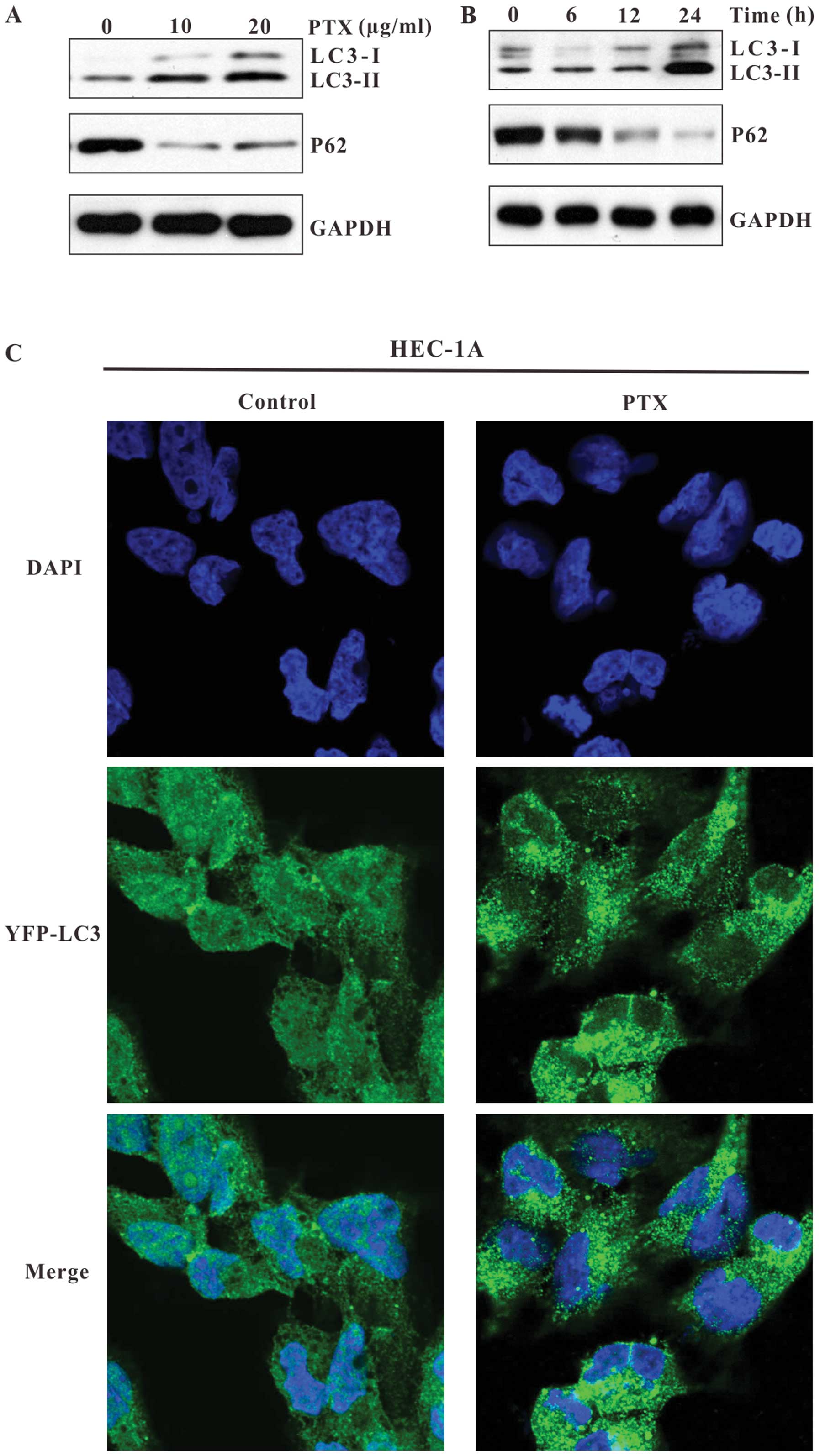
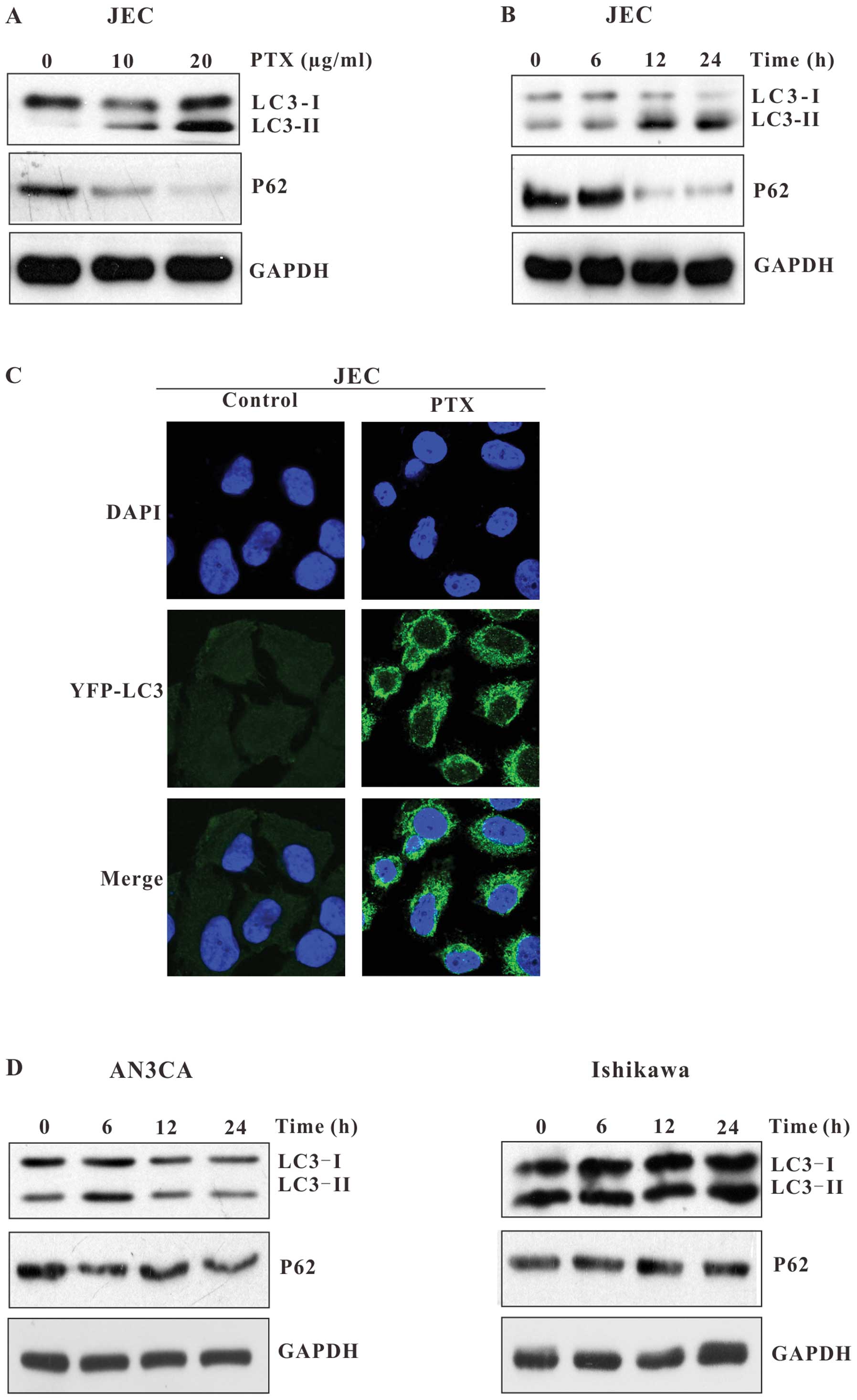
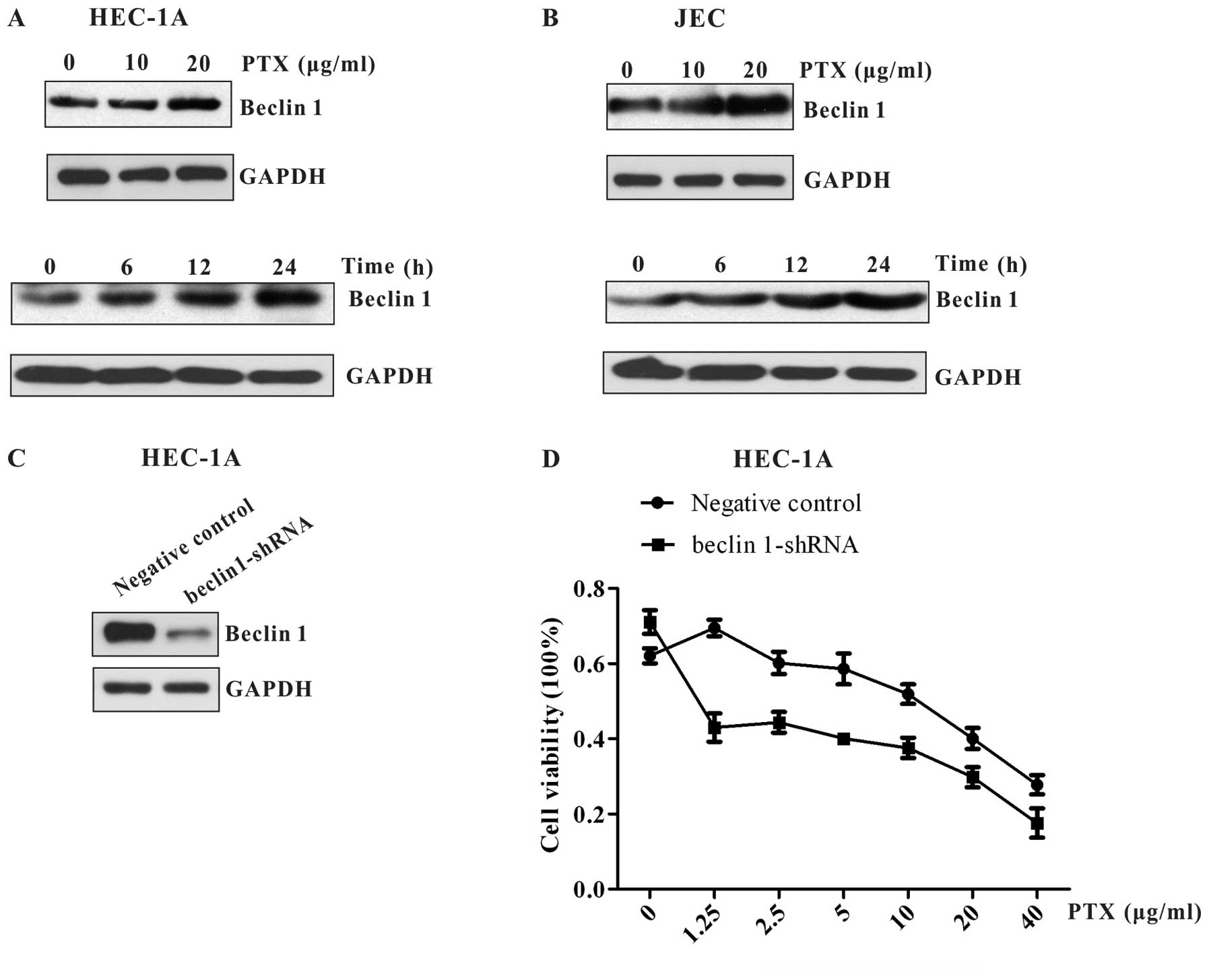
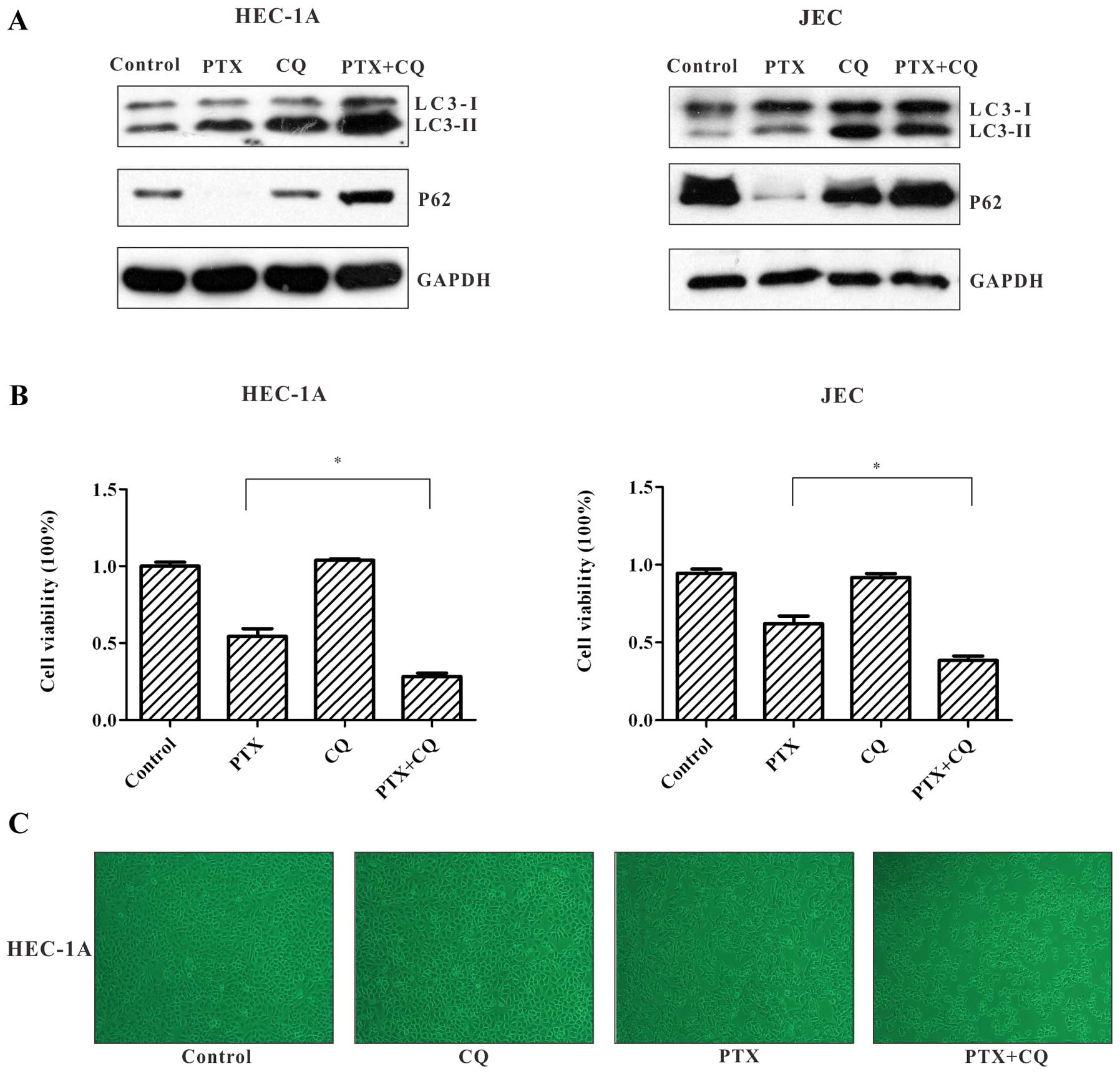
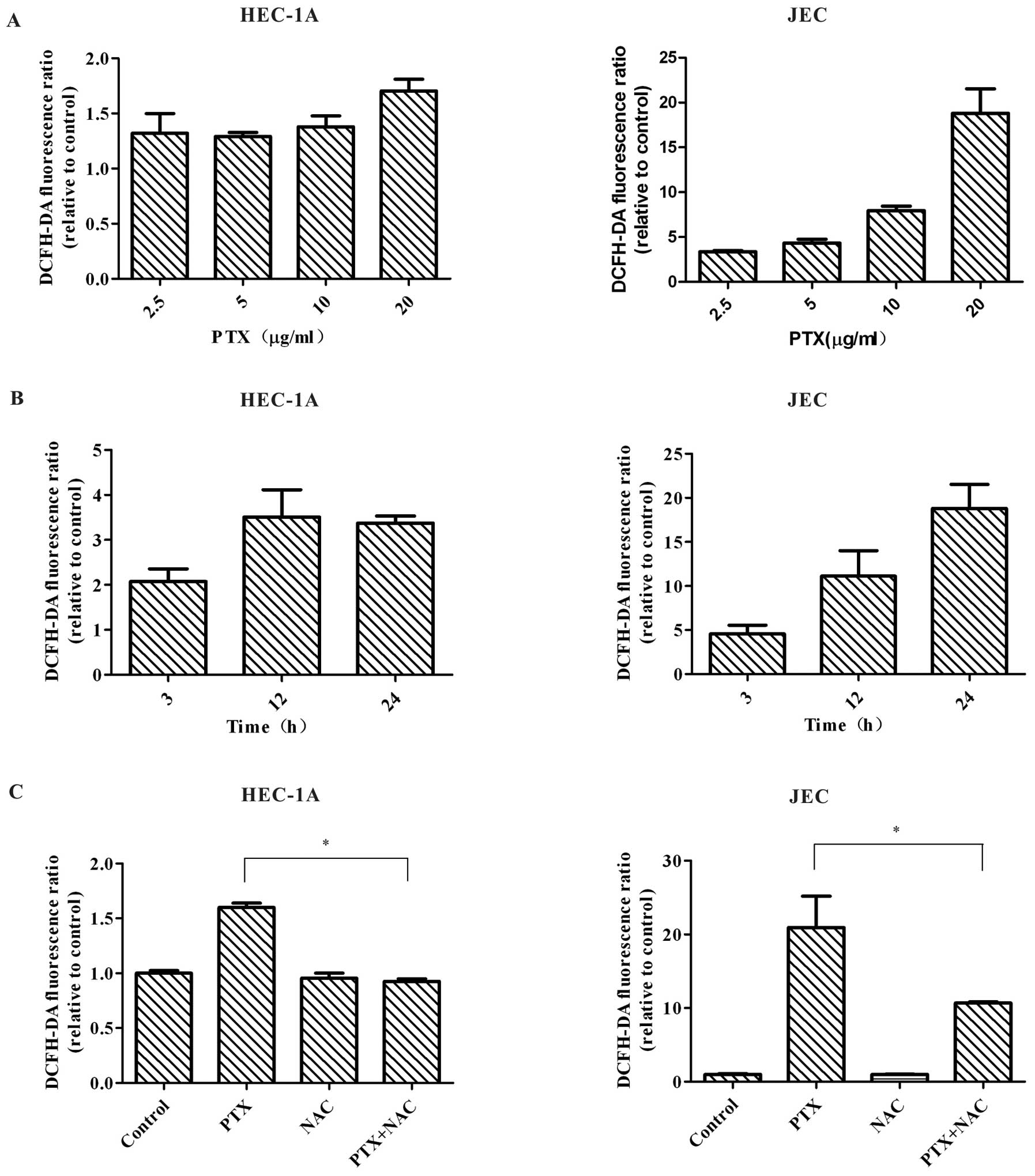
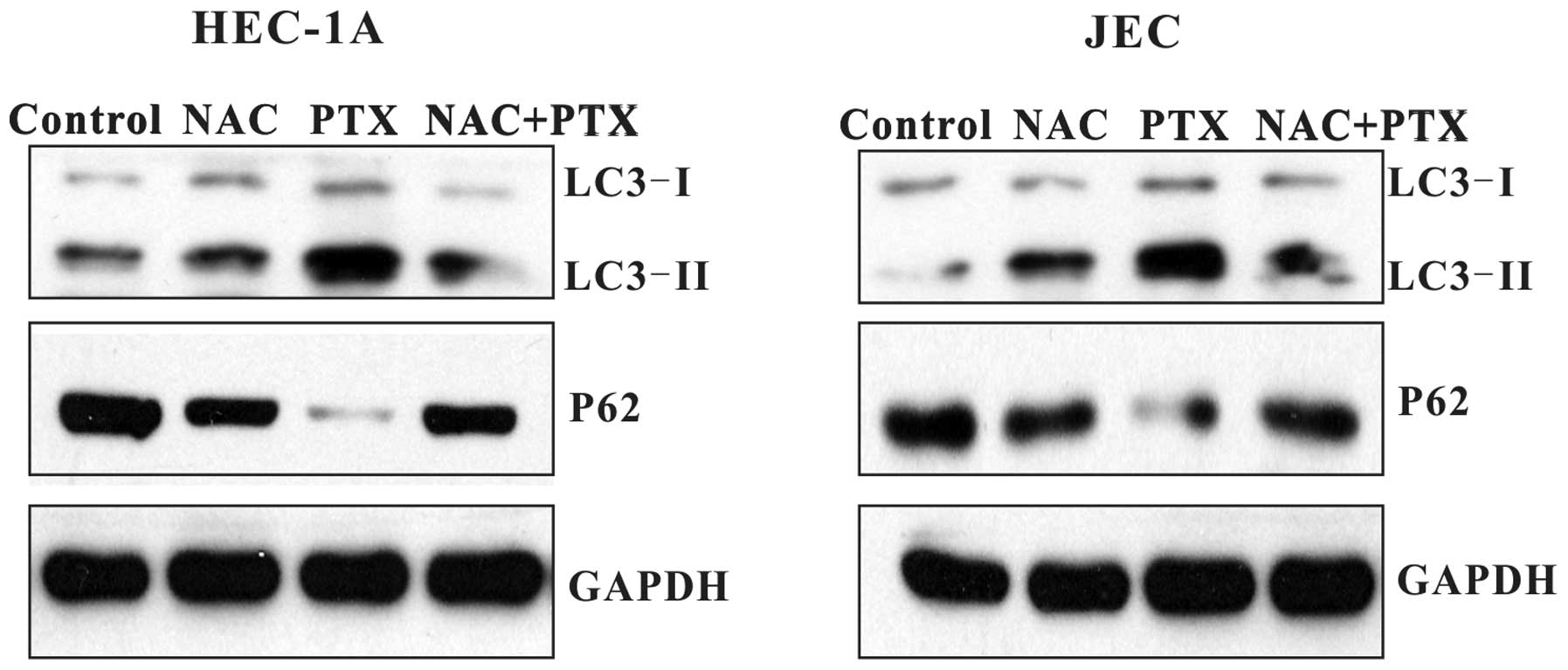
|
1
|
Mazgani M, Le N and Hoskins PJ; British
Columbia Cancer Agency. Reuse of carboplatin and paclitaxel in
patients with relapsed endometrial cancer - the British Columbia
Cancer Agency experience. Gynecol Oncol. 111:474–477. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pectasides D, Xiros N, Papaxoinis G,
Pectasides E, Sykiotis C, Koumarianou A, Psyrri A, Gaglia A,
Kassanos D, Gouveris P, et al: Carboplatin and paclitaxel in
advanced or metastatic endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
109:250–254. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sorbe B, Andersson H, Boman K, Rosenberg P
and Kalling M: Treatment of primary advanced and recurrent
endometrial carcinoma with a combination of carboplatin and
paclitaxel-long-term follow-up. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 18:803–808.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vandenput I, Vergote I, Leunen K,
Berteloot P, Neven P and Amant F: Leuven dose-dense
paclitaxel/carboplatin regimen in patients with primary advanced or
recurrent endometrial carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
19:1147–1151. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lefranc F, Facchini V and Kiss R:
Proautophagic drugs: A novel means to combat apoptosis-resistant
cancers, with a special emphasis on glioblastomas. Oncologist.
12:1395–1403. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mathew R, Karantza-Wadsworth V and White
E: Role of autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:961–967. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morselli E, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Vicencio
JM, Criollo A, Maiuri MC and Kroemer G: Anti- and pro-tumor
functions of autophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1793:1524–1532. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Q, Si S, Schoen S, Chen J, Jin XB
and Wu G: Suppression of autophagy enhances preferential toxicity
of paclitaxel to folliculin-deficient renal cancer cells. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 32:992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim HJ, Lee SG, Kim YJ, Park JE, Lee KY,
Yoo YH and Kim JM: Cytoprotective role of autophagy during
paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in Saos-2 osteosarcoma cells. Int J
Oncol. 42:1985–1992. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xi G, Hu X, Wu B, Jiang H, Young CY, Pang
Y and Yuan H: Autophagy inhibition promotes paclitaxel-induced
apoptosis in cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 307:141–148. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ajabnoor GM, Crook T and Coley HM:
Paclitaxel resistance is associated with switch from apoptotic to
autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis.
3:e2602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Eum KH and Lee M: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis in the regulation of paclitaxel-induced
cell death in v-Ha-ras-transformed fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem.
348:61–68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Veldhoen RA, Banman SL, Hemmerling DR,
Odsen R, Simmen T, Simmonds AJ, Underhill DA and Goping IS: The
chemotherapeutic agent paclitaxel inhibits autophagy through two
distinct mechanisms that regulate apoptosis. Oncogene. 32:736–746.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mizushima N and Yoshimori T: How to
interpret LC3 immunoblotting. Autophagy. 3:542–545. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H,
Abraham RT, Acevedo-Arozena A, Adeli K, Agholme L, Agnello M,
Agostinis P, Aguirre-Ghiso JA, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy.
8:445–544. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A,
Bruun JA, Outzen H, Overvatn A, Bjorkoy G and Johansen T:
p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of
ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem.
282:24131–24145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ichimura Y and Komatsu M: Selective
degradation of p62 by autophagy. Semin Immunopathol. 32:431–436.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luiken JJ, Aerts JM and Meijer AJ: The
role of the intralysosomal pH in the control of autophagic
proteolytic flux in rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 235:564–573.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Amaravadi RK, Yu D, Lum JJ, Bui T,
Christophorou MA, Evan GI, Thomas-Tikhonenko A and Thompson CB:
Autophagy inhibition enhances therapy-induced apoptosis in a
Myc-induced model of lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 117:326–336. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maclean KH, Dorsey FC, Cleveland JL and
Kastan MB: Targeting lysosomal degradation induces p53-dependent
cell death and prevents cancer in mouse models of lymphomagenesis.
J Clin Invest. 118:79–88. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Alexandre J, Batteux F, Nicco C, Chéreau
C, Laurent A, Guillevin L, Weill B and Goldwasser F: Accumulation
of hydrogen peroxide is an early and crucial step for
paclitaxel-induced cancer cell death both in vitro and in vivo. Int
J Cancer. 119:41–48. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ramanathan B, Jan KY, Chen CH, Hour TC, Yu
HJ and Pu YS: Resistance to paclitaxel is proportional to cellular
total antioxidant capacity. Cancer Res. 65:8455–8460. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lyle PA, Mitsopoulos P and Suntres ZE:
N-acetyl cysteine modulates the cytotoxic effects of Paclitaxel.
Chemotherapy. 57:298–304. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Dewaele M, Maes H and Agostinis P:
ROS-mediated mechanisms of autophagy stimulation and their
relevance in cancer therapy. Autophagy. 6:838–854. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miki H, Uehara N, Kimura A, Sasaki T, Yuri
T, Yoshizawa K and Tsubura A: Resveratrol induces apoptosis via
ROS-triggered autophagy in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
40:1020–1028. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim JY, Cho TJ, Woo BH, Choi KU, Lee CH,
Ryu MH and Park HR: Curcumin-induced autophagy contributes to the
decreased survival of oral cancer cells. Arch Oral Biol.
57:1018–1025. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang L, Yang M, Zhang H, Wang Z, Yu Y, Xie
M, Zhao M, Liu L and Cao L: S100A8-targeting siRNA enhances arsenic
trioxide-induced myeloid leukemia cell death by down-regulating
autophagy. Int J Mol Med. 29:65–72. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Lin CJ, Lee CC, Shih YL, Lin TY, Wang SH,
Lin YF and Shih CM: Resveratrol enhances the therapeutic effect of
temozolomide against malignant glioma in vitro and in vivo by
inhibiting autophagy. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:377–391. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cheng P, Ni Z, Dai X, Wang B, Ding W, Rae
Smith A, Xu L, Wu D, He F and Lian J: The novel BH-3 mimetic
apogossypolone induces Beclin-1- and ROS-mediated autophagy in
human hepatocellular carcinoma [corrected] cells. Cell Death Dis.
4:e4892013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kanzawa T, Zhang L, Xiao L, Germano IM,
Kondo Y and Kondo S: Arsenic trioxide induces autophagic cell death
in malignant glioma cells by upregulation of mitochondrial cell
death protein BNIP3. Oncogene. 24:980–991. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chinnadurai G, Vijayalingam S and Gibson
SB: BNIP3 subfamily BH3-only proteins: Mitochondrial stress sensors
in normal and pathological functions. Oncogene. 27(Suppl 1):
S114–S127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bellodi C, Lidonnici MR, Hamilton A,
Helgason GV, Soliera AR, Ronchetti M, Galavotti S, Young KW, Selmi
T, Yacobi R, et al: Targeting autophagy potentiates tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-induced cell death in Philadelphia chromosome-positive
cells, including primary CML stem cells. J Clin Invest.
119:1109–1123. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ni Z, Wang B, Dai X, Ding W, Yang T, Li X,
Lewin S, Xu L, Lian J and He F: HCC cells with high levels of Bcl-2
are resistant to ABT-737 via activation of the ROS-JNK-autophagy
pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 70:194–203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sun K, Xie X, Liu Y, Han Z, Zhao X, Cai N,
Zhang S, Song J and Wei L: Autophagy lessens ischemic liver injury
by reducing oxidative damage. Cell Biosci. 3:262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guo XL, Li D, Hu F, Song JR, Zhang SS,
Deng WJ, Sun K, Zhao QD, Xie XQ, Song YJ, et al: Targeting
autophagy potentiates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and
proliferation inhibition in hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
320:171–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|