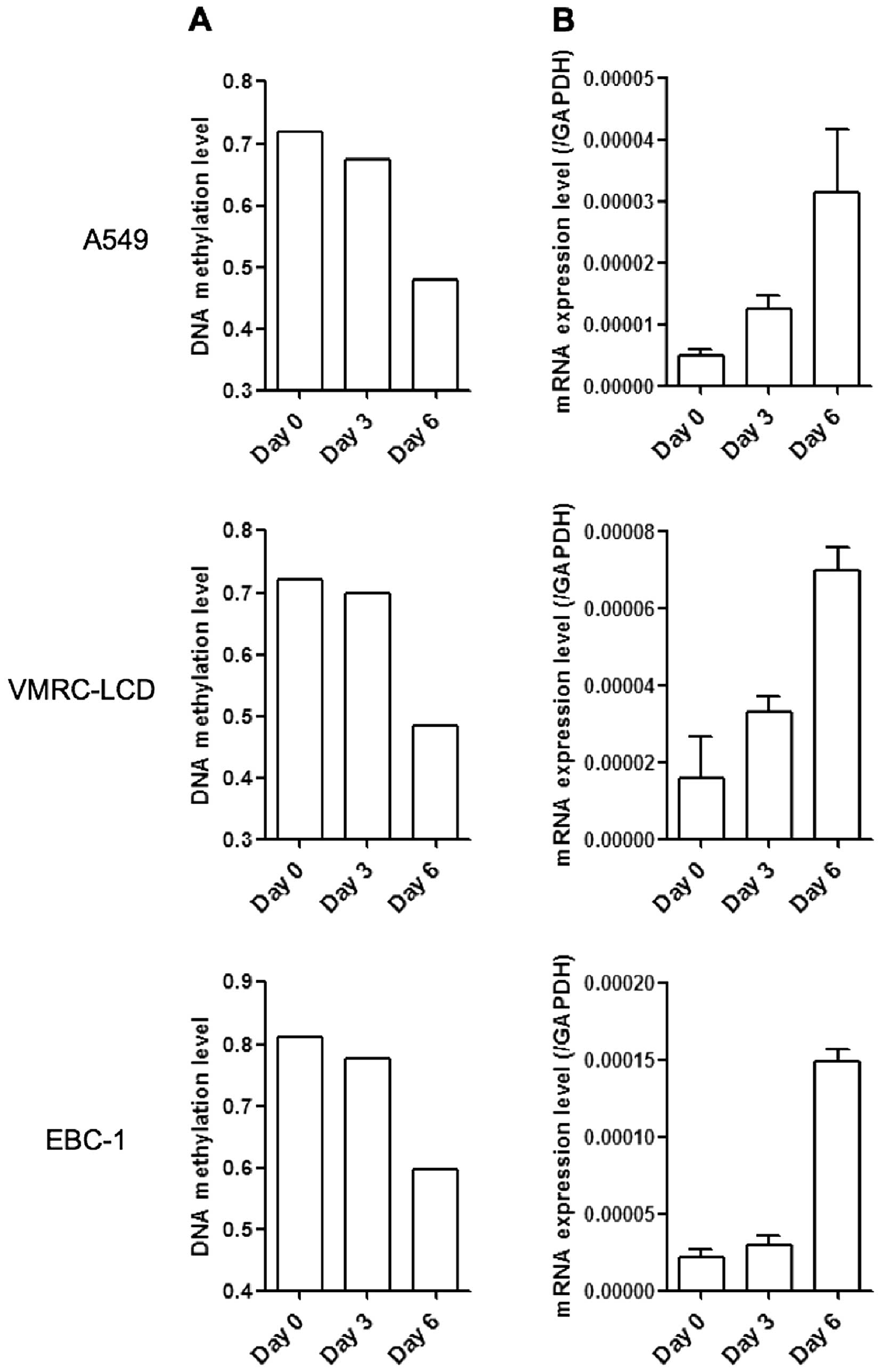
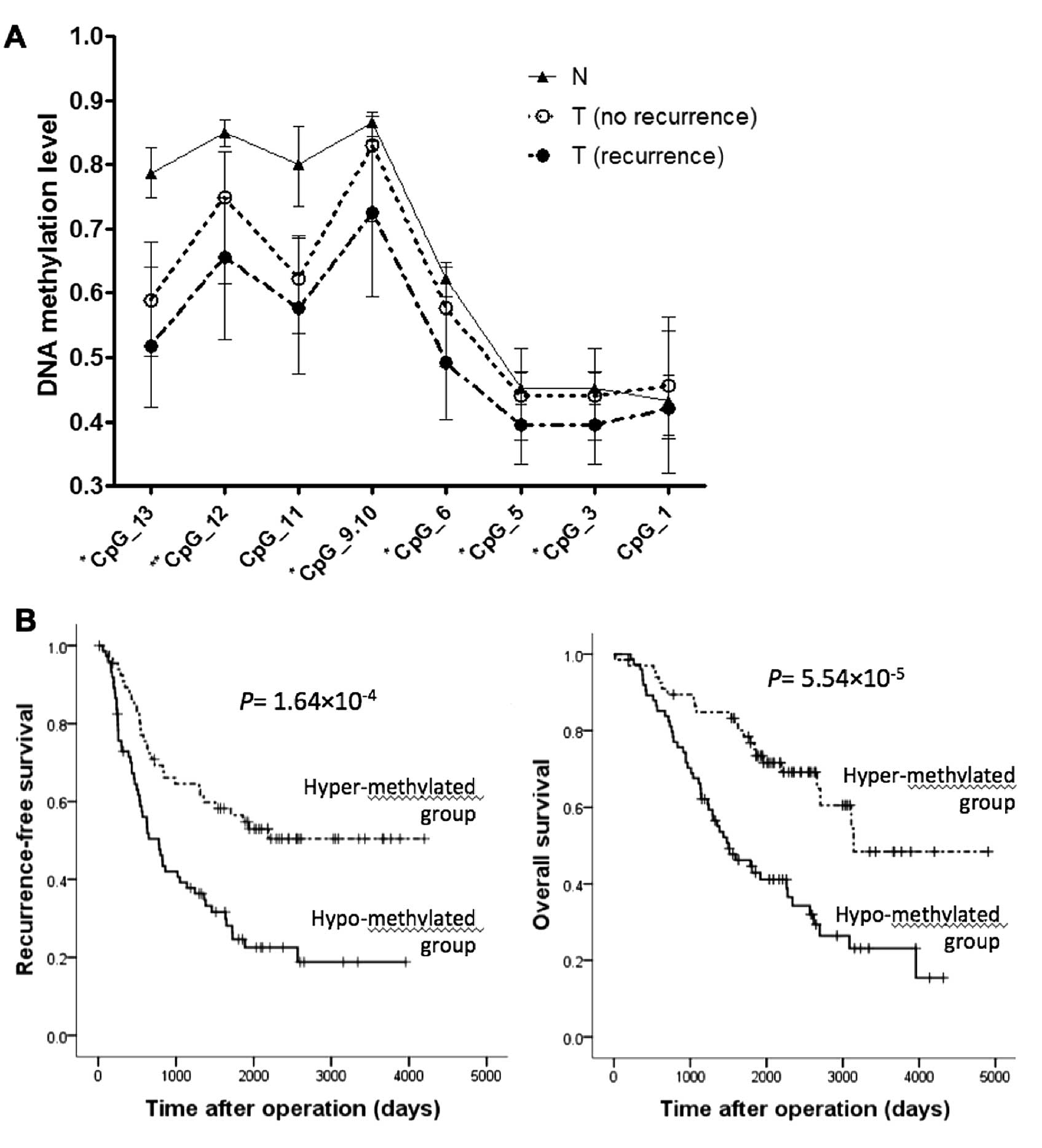
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu L, Zhao E, Li C, Huang L, Xiao L,
Cheng L, Huang X, Song Y and Xu D: TRIm28, a new molecular marker
predicting metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell
lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 37:71–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Julien SG, Dubé N, Hardy S and Tremblay
ML: Inside the human cancer tyrosine phosphatome. Nat Rev Cancer.
11:35–49. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Matozaki T, Suzuki T, Uchida T, Inazawa J,
Ariyama T, Matsuda K, Horita K, Noguchi H, Mizuno H, Sakamoto C, et
al: Molecular cloning of a human transmembrane-type protein
tyrosine phosphatase and its expression in gastrointestinal
cancers. J Biol Chem. 269:2075–2081. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matozaki T, Murata Y, Mori M, Kotani T,
Okazawa H and Ohnishi H: Expression, localization, and biological
function of the R3 subtype of receptor-type protein tyrosine
phosphatases in mammals. Cell Signal. 22:1811–1817. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sadakata H, Okazawa H, Sato T, Supriatna
Y, Ohnishi H, Kusakari S, Murata Y, Ito T, Nishiyama U, Minegishi
T, et al: SAP-1 is a microvillus-specific protein tyrosine
phosphatase that modulates intestinal tumorigenesis. Genes Cells.
14:295–308. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nagano H, Noguchi T, Inagaki K, Yoon S,
Matozaki T, Itoh H, Kasuga M and Hayashi Y: Downregulation of
stomach cancer-associated protein tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SAP-1) in
advanced human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 22:4656–4663.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Noguchi T, Tsuda M, Takeda H, Takada T,
Inagaki K, Yamao T, Fukunaga K, Matozaki T and Kasuga M: Inhibition
of cell growth and spreading by stomach cancer-associated
protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SAP-1) through dephosphorylation of
p130cas. J Biol Chem. 276:15216–15224. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Takada T, Noguchi T, Inagaki K, Hosooka T,
Fukunaga K, Yamao T, Ogawa W, Matozaki T and Kasuga M: Induction of
apoptosis by stomach cancer-associated protein-tyrosine
phosphatase-1. J Biol Chem. 277:34359–34366. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baylin SB and Jones PA: A decade of
exploring the cancer epigenome - biological and translational
implications. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:726–734. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Heller G, Zielinski CC and
Zöchbauer-Müller S: Lung cancer: From single-gene methylation to
methylome profiling. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:95–107. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arai E, Chiku S, Mori T, Gotoh M, Nakagawa
T, Fujimoto H and Kanai Y: Single-CpG-resolution methylome analysis
identifies clinicopathologically aggressive CpG island methylator
phenotype clear cell renal cell carcinomas. Carcinogenesis.
33:1487–1493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sato T, Arai E, Kohno T, Tsuta K, Watanabe
S, Soejima K, Betsuyaku T and Kanai Y: DNA methylation profiles at
precancerous stages associated with recurrence of lung
adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 8:e594442013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sato T, Arai E, Kohno T, Takahashi Y,
Miyata S, Tsuta K, Watanabe S, Soejima K, Betsuyaku T and Kanai Y:
Epigenetic clustering of lung adenocarcinomas based on DNA
methylation profiles in adjacent lung tissue: Its correlation with
smoking history and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J
Cancer. 135:319–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jurinke C, Denissenko MF, Oeth P, Ehrich
M, van den Boom D and Cantor CR: A single nucleotide polymorphism
based approach for the identification and characterization of gene
expression modulation using MassARRAY. Mutat Res. 573:83–95. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fan J, Upadhye S and Worster A:
Understanding receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves. CJEM.
8:19–20. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Seo Y, Matozaki T, Tsuda M, Hayashi Y,
Itoh H and Kasuga M: Overexpression of SAP-1, a transmembrane-type
protein tyrosine phosphatase, in human colorectal cancers. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 231:705–711. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Motiwala T, Majumder S, Kutay H, Smith DS,
Neuberg DS, Lucas DM, Byrd JC, Grever M and Jacob ST: Methylation
and silencing of protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type O in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 13:3174–3181. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Motiwala T, Kutay H, Ghoshal K, Bai S,
Seimiya H, Tsuruo T, Suster S, Morrison C and Jacob ST: Protein
tyrosine phosphatase receptor-type O (PTPRO) exhibits
characteristics of a candidate tumor suppressor in human lung
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:13844–13849. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Veeriah S, Brennan C, Meng S, Singh B,
Fagin JA, Solit DB, Paty PB, Rohle D, Vivanco I, Chmielecki J, et
al: The tyrosine phosphatase PTPRD is a tumor suppressor that is
frequently inactivated and mutated in glioblastoma and other human
cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:9435–9440. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van Doorn R, Zoutman WH, Dijkman R, de
Menezes RX, Commandeur S, Mulder AA, van der Velden PA, Vermeer MH,
Willemze R, Yan PS, et al: Epigenetic profiling of cutaneous T-cell
lymphoma: Promoter hypermethylation of multiple tumor suppressor
genes including BCL7a, PTPRG, and p73. J Clin Oncol. 23:3886–3896.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang JF and Dai DQ: metastatic suppressor
genes inactivated by aberrant methylation in gastric cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 13:5692–5698. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oka T, Ouchida M, Koyama M, Ogama Y,
Takada S, Nakatani Y, Tanaka T, Yoshino T, Hayashi K, Ohara N, et
al: Gene silencing of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP1 gene by
aberrant methylation in leukemias/lymphomas. Cancer Res.
62:6390–6394. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Koyama M, Oka T, Ouchida M, Nakatani Y,
Nishiuchi R, Yoshino T, Hayashi K, Akagi T and Seino Y: Activated
proliferation of B-cell lymphomas/leukemias with the SHP1 gene
silencing by aberrant CpG methylation. Lab Invest. 83:1849–1858.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Reddy J, Shivapurkar N, Takahashi T,
Parikh G, Stastny V, Echebiri C, Crumrine K, Zöchbauer-Müller S,
Drach J, Zheng Y, et al: Differential methylation of genes that
regulate cytokine signaling in lymphoid and hematopoietic tumors.
Oncogene. 24:732–736. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yeh SH, Wu DC, Tsai CY, Kuo TJ, Yu WC,
Chang YS, Chen CL, Chang CF, Chen DS and Chen PJ: Genetic
characterization of fas-associated phosphatase-1 as a putative
tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 4q21.3 in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:1097–1108. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jacob ST and Motiwala T: Epigenetic
regulation of protein tyrosine phosphatases: Potential molecular
targets for cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 12:665–672. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wälchli S, Espanel X and Hooft van
Huijsduijnen R: Sap-1/PTPRH activity is regulated by reversible
dimerization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 331:497–502. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sakuraba J, Shintani T, Tani S and Noda M:
Substrate specificity of R3 receptor-like protein-tyrosine
phosphatase subfamily toward receptor protein-tyrosine kinases. J
Biol Chem. 288:23421–23431. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|