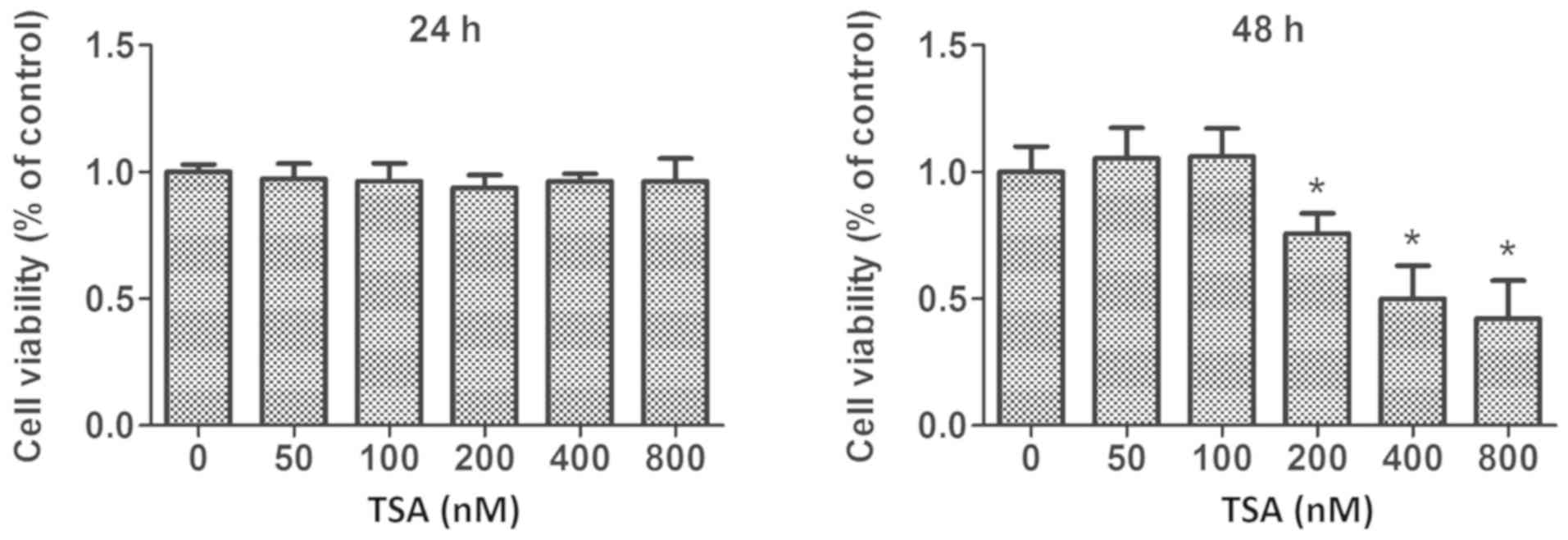
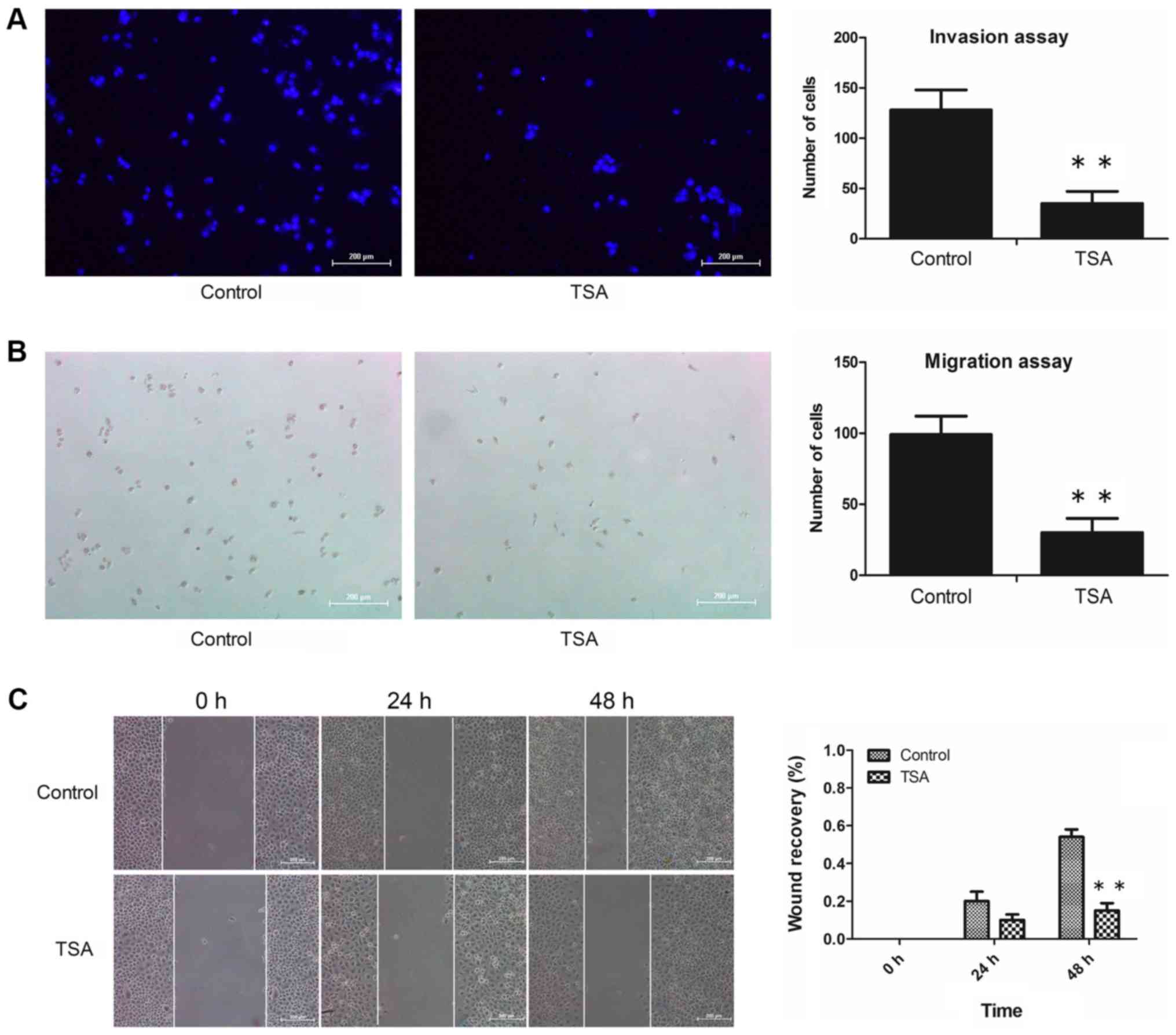
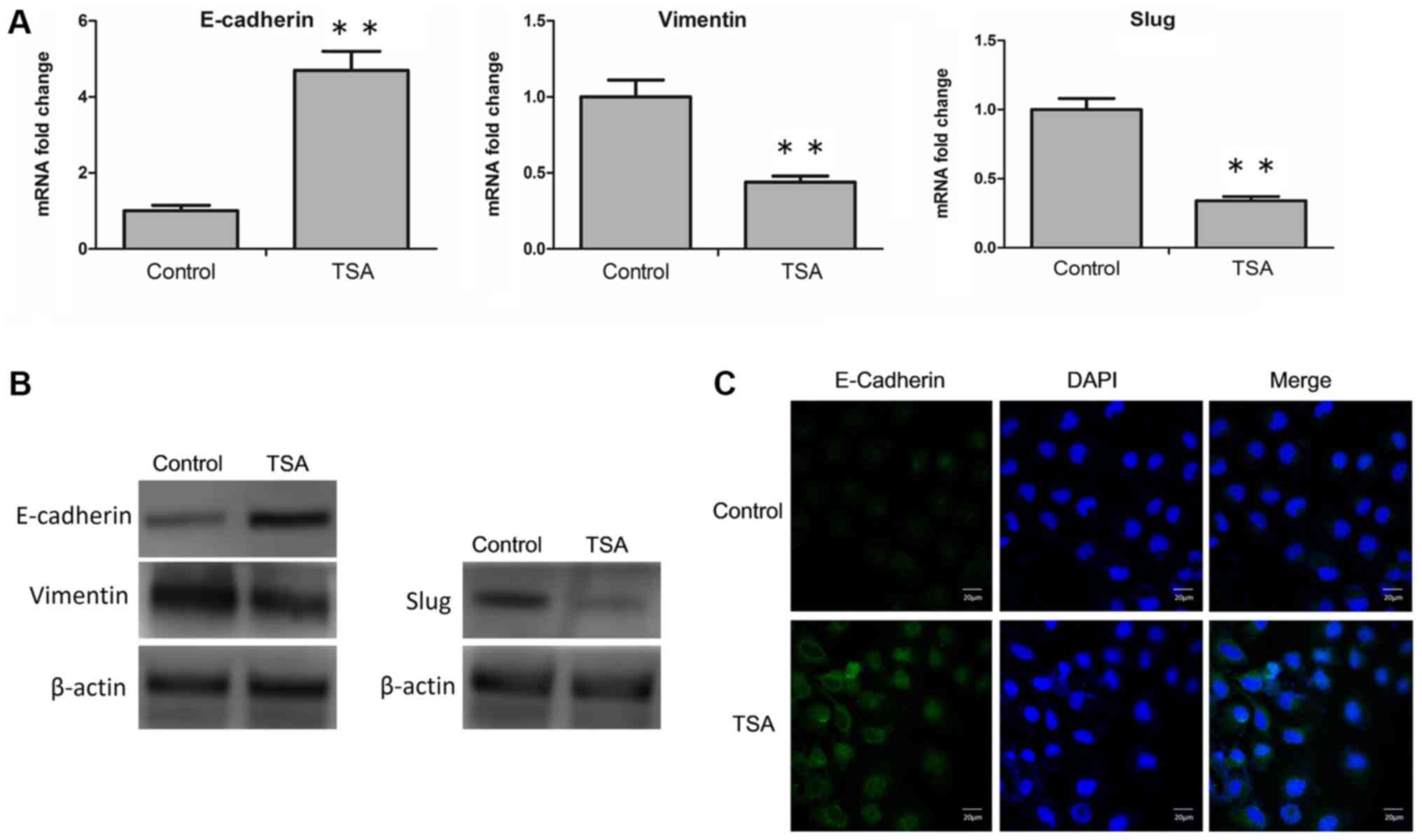
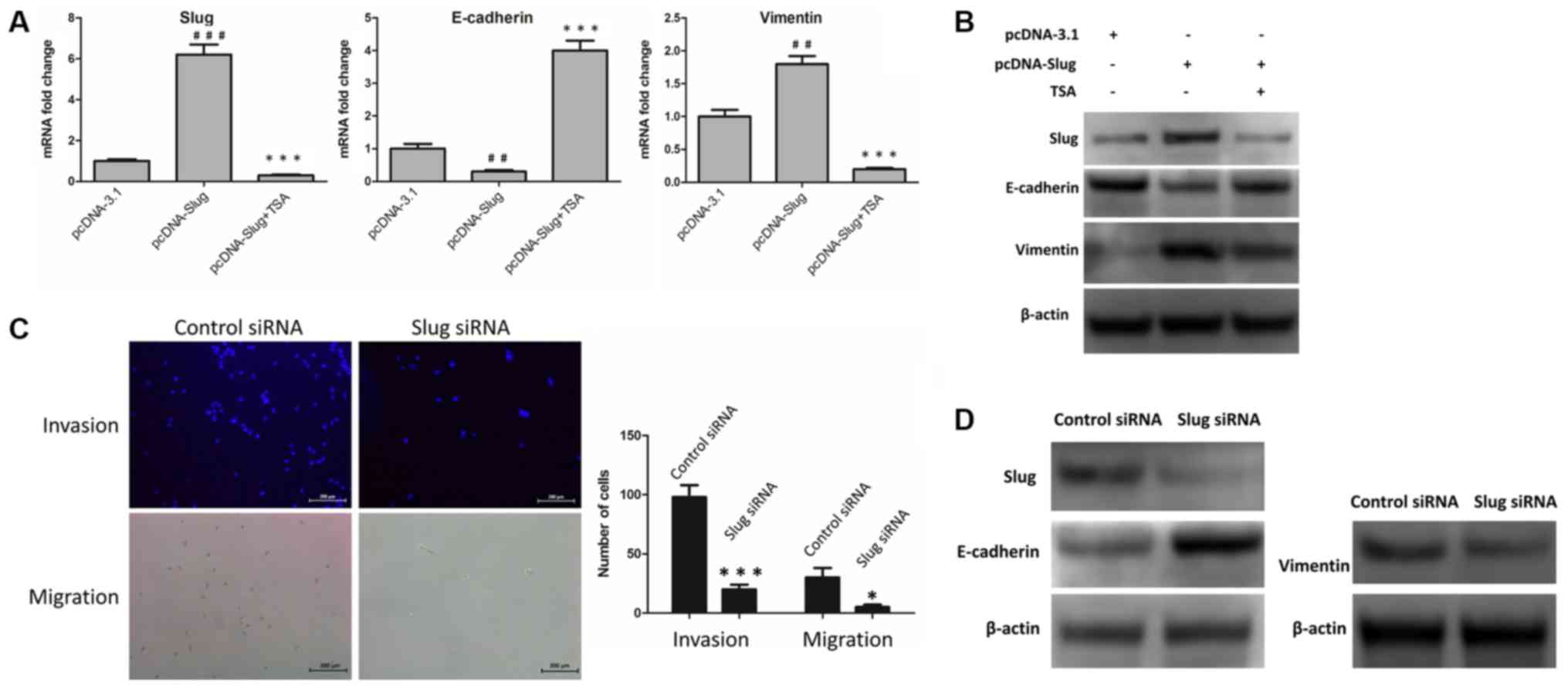
|
1
|
Lee YT: Breast carcinoma: Pattern of
metastasis at autopsy. J Surg Oncol. 23:175–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Weil RJ, Palmieri DC, Bronder JL, Stark AM
and Steeg PS: Breast cancer metastasis to the central nervous
system. Am J Pathol. 167:913–920. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vaidya JS, Keshtgar M and Baum M: Diseases
of the breast. Br J Cancer. 83:1769–1770. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Behrens J, Mareel MM, Van Roy FM and
Birchmeier W: Dissecting tumor cell invasion: Epithelial cells
acquire invasive properties after the loss of uvomorulin-mediated
cell-cell adhesion. J Cell Biol. 108:2435–2447. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chengsen X, David P, Christo V, Carol X
and Neilson EG: The gatekeeper effect of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition regulates the frequency of breast cancer metastasis.
Cancer Res. 63:3386–3394. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thompson EW, Newgreen DF and David T:
Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: A role for
epithelial-mesenchymal transition? Cancer Res. 65:5991–5995. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Felipe Lima J, Nofech-Mozes S, Bayani J
and Bartlett JM: EMT in breast carcinoma-a review. J Clin Med.
5(pii): E652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jean Paul T and Sleeman JP: Complex
networks orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Michael Z and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu F, Gu LN, Shan BE, Geng CZ and Sang
MX: Biomarkers for EMT and MET in breast cancer: An update. Oncol
Lett. 12:4869–4876. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
David S, Socorro María RP, Hardisson D,
Cano A, Moreno-Bueno G and Palacios J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype.
Cancer Res. 68:989–997. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yi P, Jing L, Zhang Y, Wang N, Liang H,
Liu Y, Zhang CY, Zen K and Gu H: SLUG-upregulated miR-221 promotes
breast cancer progression through suppressing E-cadherin
expression. Sci Rep. 6:257982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hajra KM, Chen DY and Fearon ER: The SLUG
zinc-finger protein represses E-cadherin in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 62:1613–1618. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vuoriluoto K, Haugen H, Kiviluoto S,
Mpindi JP, Nevo J, Gjerdrum C, Tiron C, Lorens JB and Ivaska J:
Vimentin regulates EMT induction by SLUG and oncogenic H-Ras and
migration by governing Axl expression in breast cancer. Oncogene.
30:1436–1448. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu S, Ren J, Chen HB, Wang Y, Liu Q, Zhang
R, Jiang SW and Li J: Cytostatic and apoptotic effects of DNMT and
HDAC inhibitors in endometrial cancer cells. Curr Pharm Des.
20:1881–1887. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dowdy SC, Jiang S, Zhou XC, Hou X, Jin F,
Podratz KC and Jiang SW: Histone deacetylase inhibitors and
paclitaxel cause synergistic effects on apoptosis and microtubule
stabilization in papillary serous endometrial cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:2767–2776. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshikawa M, Hishikawa KT and Fujita T:
Inhibition of histone deacetylase activity suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition induced by TGF-beta1 in human
renal epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 18:58–65. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiao W, Chen X, Liu X, Luo L, Ye S and Liu
Y: Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses
proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in retinal
pigment epithelium cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:646–655. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aki K, Potter JJ, Michael C, Zhen D,
Esteban M and Koteish AA: Histone deacetylase inhibition suppresses
the transforming growth factor beta1-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in hepatocytes. Hepatology.
52:1033–1045. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Xu J, Wang H, Wu L, Yuan W, Du J
and Cai S: Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor,
reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer
SW480 and prostate cancer PC3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
456:320–326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hao W, Wang HS, Zhou BH, Li CL, Zhang F,
Wang XF, Zhang G, Bu XZ, Cai SH and Du J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition (EMT) induced by TNF-α requires AKT/GSK-3β-mediated
stabilization of snail in colorectal cancer. PLoS One.
8:e566642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gilles C, Newgreen DF, Sato H and Thompson
EW: Matrix metalloproteases and epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Faghihloo E, Akbari A, Adjaminezhad-Fard F
and Mokhtari-Azad T: Transcriptional regulation of E-cadherin and
oncoprotein E7 by valproic acid in HPV positive cell lines. Iran J
Basic Med Sci. 19:601–607. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Grzegrzolka J, Biala M, Wojtyra P,
Kobierzycki C, Olbromski M, Gomulkiewicz A, Piotrowska A, Rys J,
Podhorska-Okolow M and Dziegiel P: Expression of EMT Markers SLUG
and TWIST in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 35:3961–3968.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shih JY and Yang PC: The EMT regulator
SLUG and lung carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:1299–1304. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jing Y, Cui D, Guo W, Jiang J, Jiang B, Lu
Y, Zhao W, Wang X, Jiang Q, Han B and Xia S: Activated androgen
receptor promotes bladder cancer metastasis via SLUG mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 348:135–145. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Y, Zhao Z, Xu C, Zhou Z, Zhu Z and You
T: HMGA2 induces transcription factor SLUG expression to promote
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and contributes to colon
cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 355:130–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu YN, Abou-Kheir W, Yin JJ, Fang L,
Hynes P, Casey O, Hu D, Wan Y, Seng V, Sheppard-Tillman H, et al:
Critical and reciprocal regulation of KLF4 and SLUG in transforming
growth factor β-initiated prostate cancer epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Mol Cell Biol. 32:941–953. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang W, Li X, Zhang W, Li W, Yi M, Yang J,
Zeng Z, Colvin Wanshura LE, McCarthy JB, Fan S, et al:
Oxidored-nitro domain containing protein 1 (NOR1) expression
suppresses SLUG/vimentin but not snail in nasopharyngeal carcinoma:
Inhibition of EMT in vitro and in vivo in mice. Cancer Lett.
348:109–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lei W, Zhang K, Pan X, Hu Y, Wang D, Yuan
X, Shu G and Song J: Histone deacetylase 1 is required for
transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1489–1497. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Noh H, Oh EY, Seo JY, Yu MR, Kim YO, Ha H
and Lee HB: Histone deacetylase-2 is a key regulator of
diabetes-and transforming growth factor-β1-induced renal injury. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 297:F729–F739. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiao W, Chen X, Liu X, Luo L, Ye S and Liu
Y: Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses
proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in retinal
pigment epithelium cells. J Cell Mol Med. 18:646–655. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, Eaton EN, Ayyanan
A, Zhou AY, Brooks M, Reinhard F, Zhang CC, Shipitsin M, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Knutson KL, Lu H, Stone B, Reiman JM,
Behrens MD, Prosperi CM, Gad EA, Smorlesi A and Disis ML:
Immunoediting of cancers may lead to epithelial to mesenchymal
transition. J Immunol. 177:1526–1533. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kudo-Saito C, Shirako H, Takeuchi T and
Kawakami Y: Cancer metastasis is accelerated through
immunosuppression during Snail-induced EMT of cancer cells. Cancer
Cell. 15:195–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, Morel AP,
Bouchet BP, Thomas C, Fauvet F, Puisieux I, Doglioni C, Piccinin S,
et al: Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of
tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell.
14:79–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gal A, Sjoblom T, Fedorova L, Imreh S,
Beug H and Moustakas A: Sustained TGF beta exposure suppresses Smad
and non-Smad signalling in mammary epithelial cells, leading to EMT
and inhibition of growth arrest and apoptosis. Oncogene.
27:1218–1230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yongqing L, Shahenda EN, Darling DS,
Yujiro H and Dean DC: Zeb1 links epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and cellular senescence. Development. 135:579–588. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang AD, Fan F, Camp ER, van Buren G, Liu
W, Somcio R, Gray MJ, Cheng H, Hoff PM and Ellis LM: Chronic
oxaliplatin resistance induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
in colorectal cancer cell lines. Clin Cancer Res. 12:4147–4153.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li QQ, Xu JD, Wang WJ, Cao XX, Chen Q,
Tang F, Chen ZQ, Liu XP and Xu ZD: Twist1-mediated
adriamycin-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition relates to
multidrug resistance and invasive potential in breast cancer cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:2657–2665. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheng GZ, Joseph C, Qi W, Weizhou Z, Sun
CD and Wang LH: Twist transcriptionally up-regulates AKT2 in breast
cancer cells leading to increased migration, invasion and
resistance to paclitaxel. Cancer Res. 67:1979–1987. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kurrey NK, Jalgaonkar SP, Joglekar AV,
Ghanate AD, Chaskar PD, Doiphode RY and Bapat SA: Snail and Slug
mediate radioresistance and chemoresistance by antagonizing
p53-mediated apoptosis and acquiring a stem-like phenotype in
ovarian cancer cells. Stem Cells. 27:2059–2068. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yang H, Zhang G, Che X and Yu S: Slug
inhibition increases radiosensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cell line C666-1. Exp Ther Med. 15:3477–3482. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|