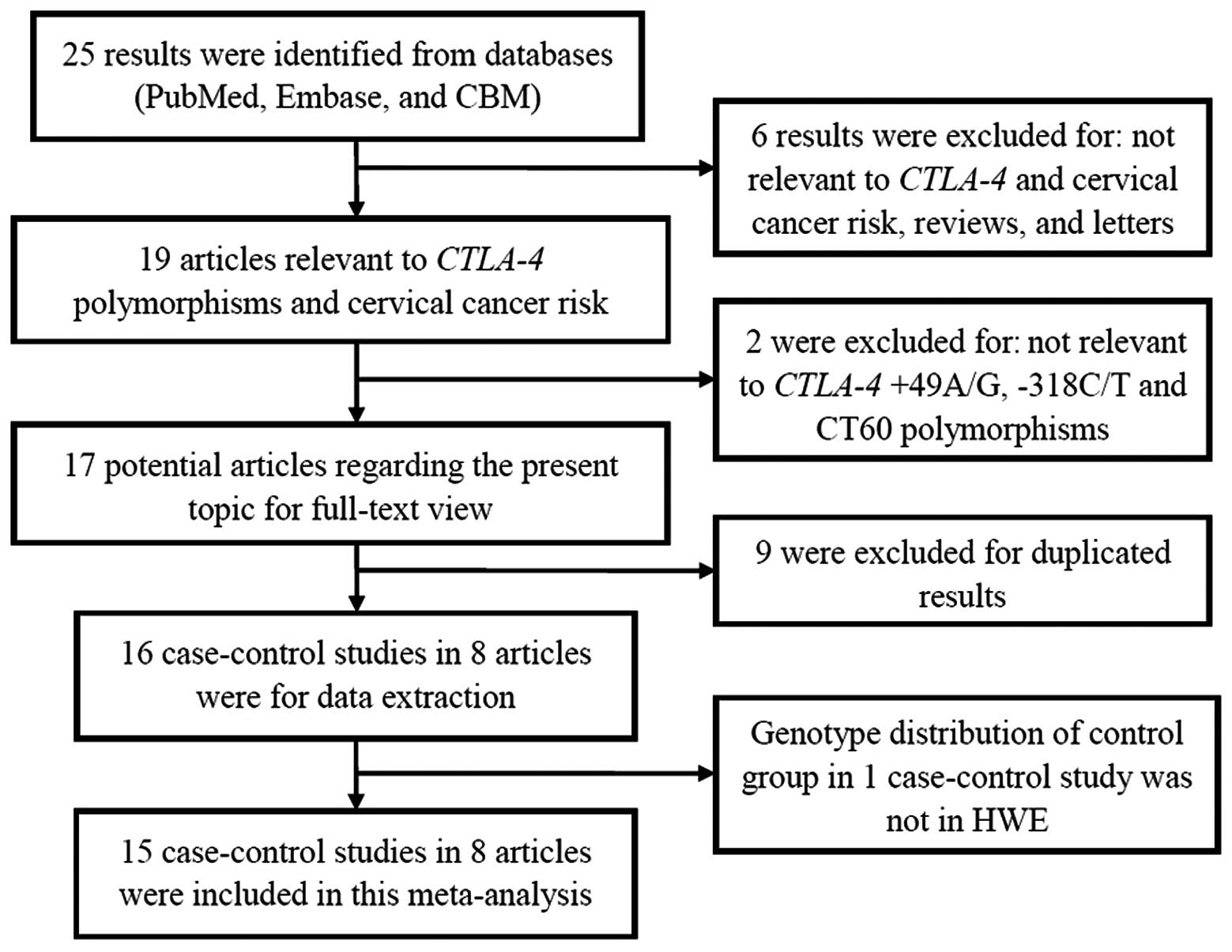
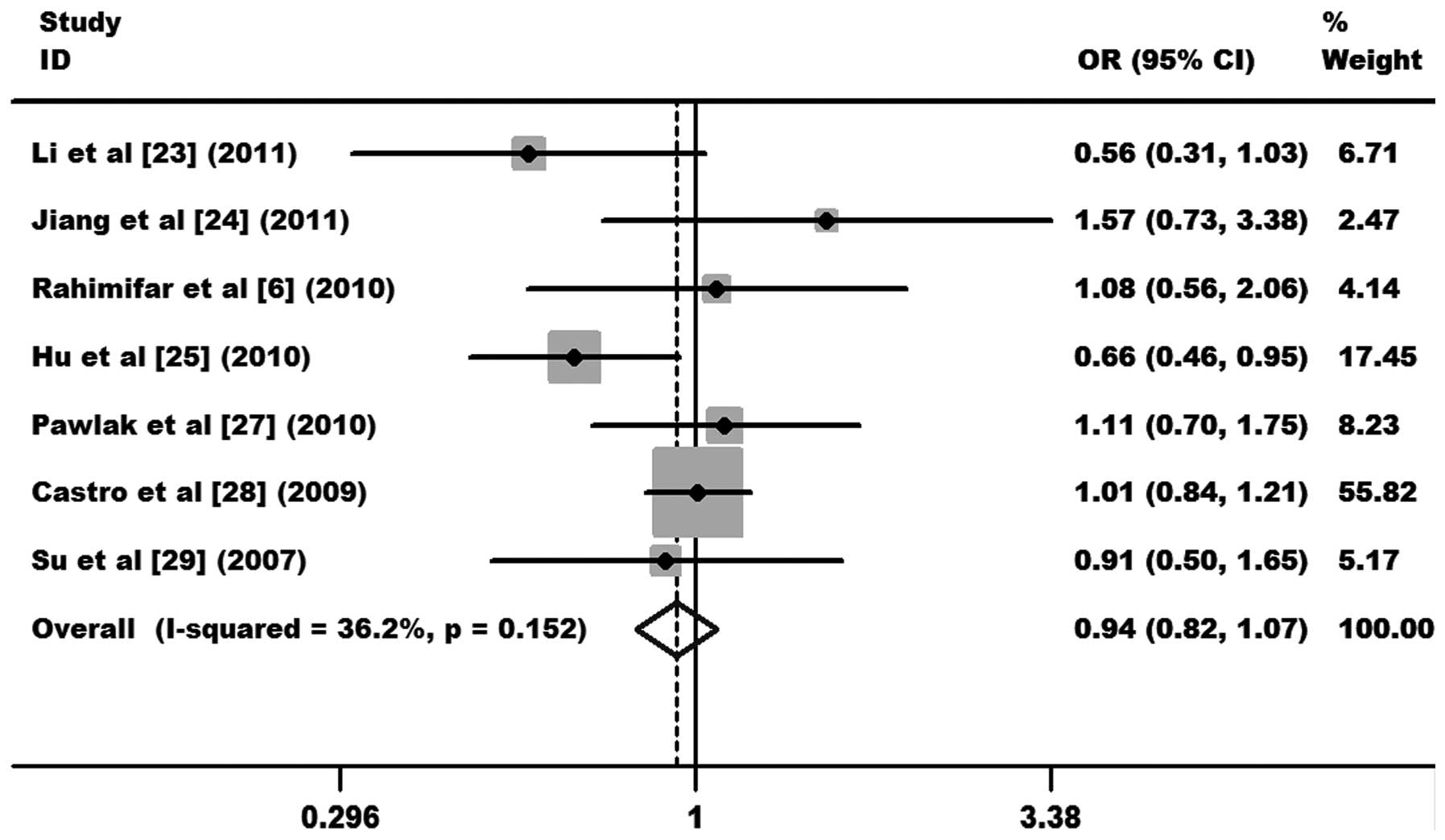
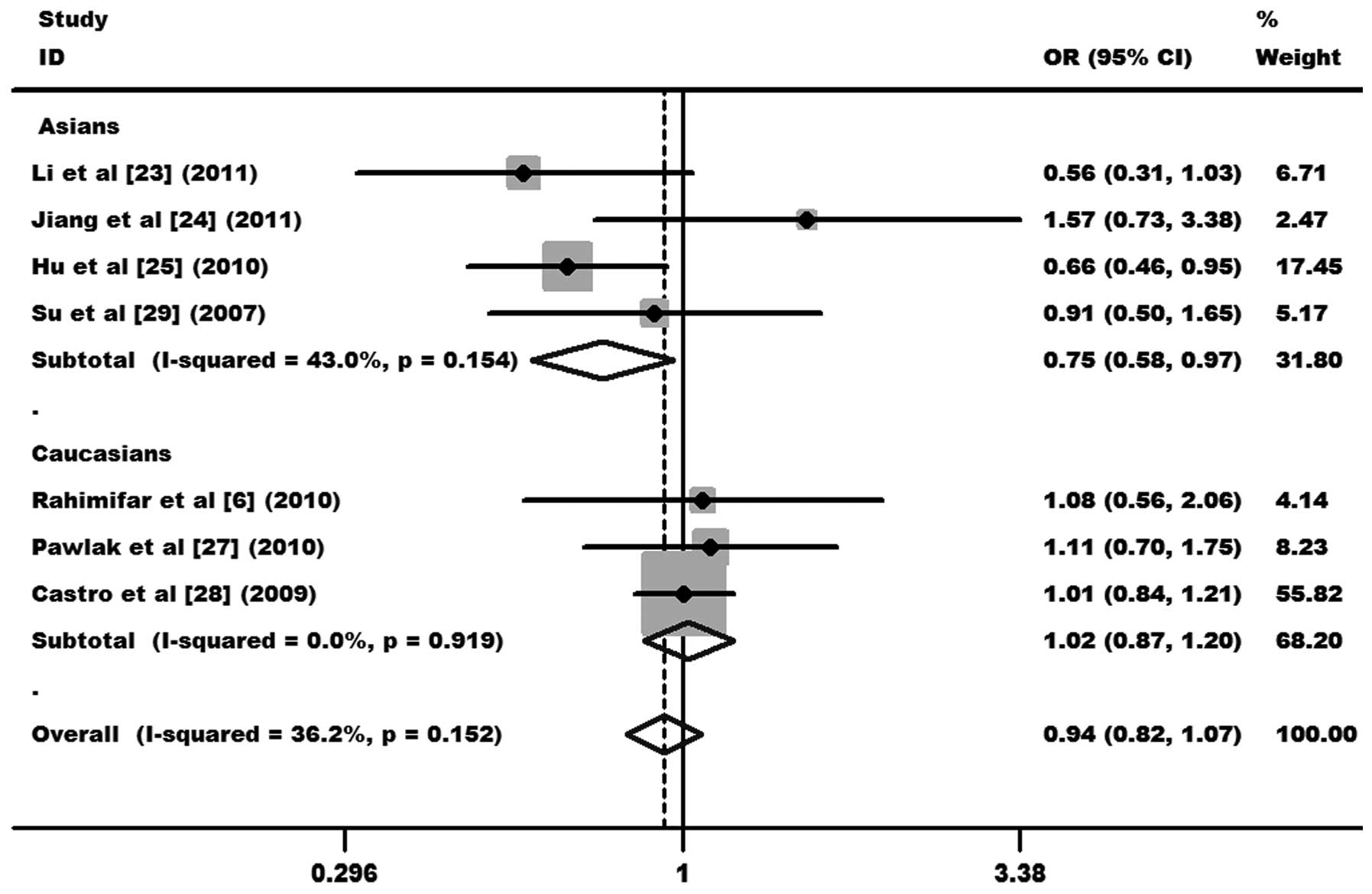
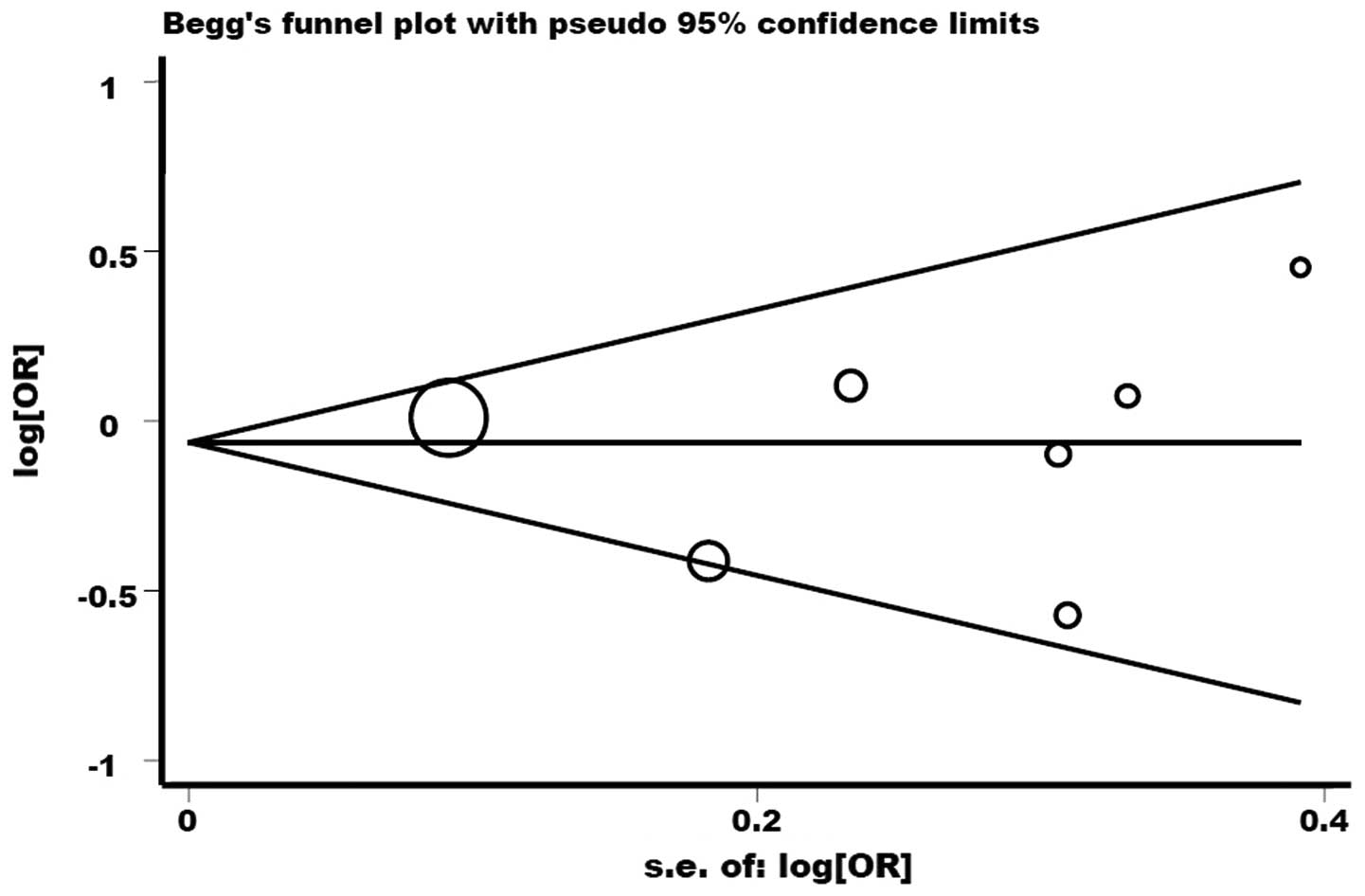
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Stanley M: HPV - immune response to
infection and vaccination. Infect Agent Cancer. 5:192010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moore EE, Wark JD, Hopper JL, Erbas B and
Garland SM; CeCaGeEn Study Group. The roles of genetic and
environmental factors on risk of cervical cancer: a review of
classical twin studies. Twin Res Hum Genet. 15:79–86. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
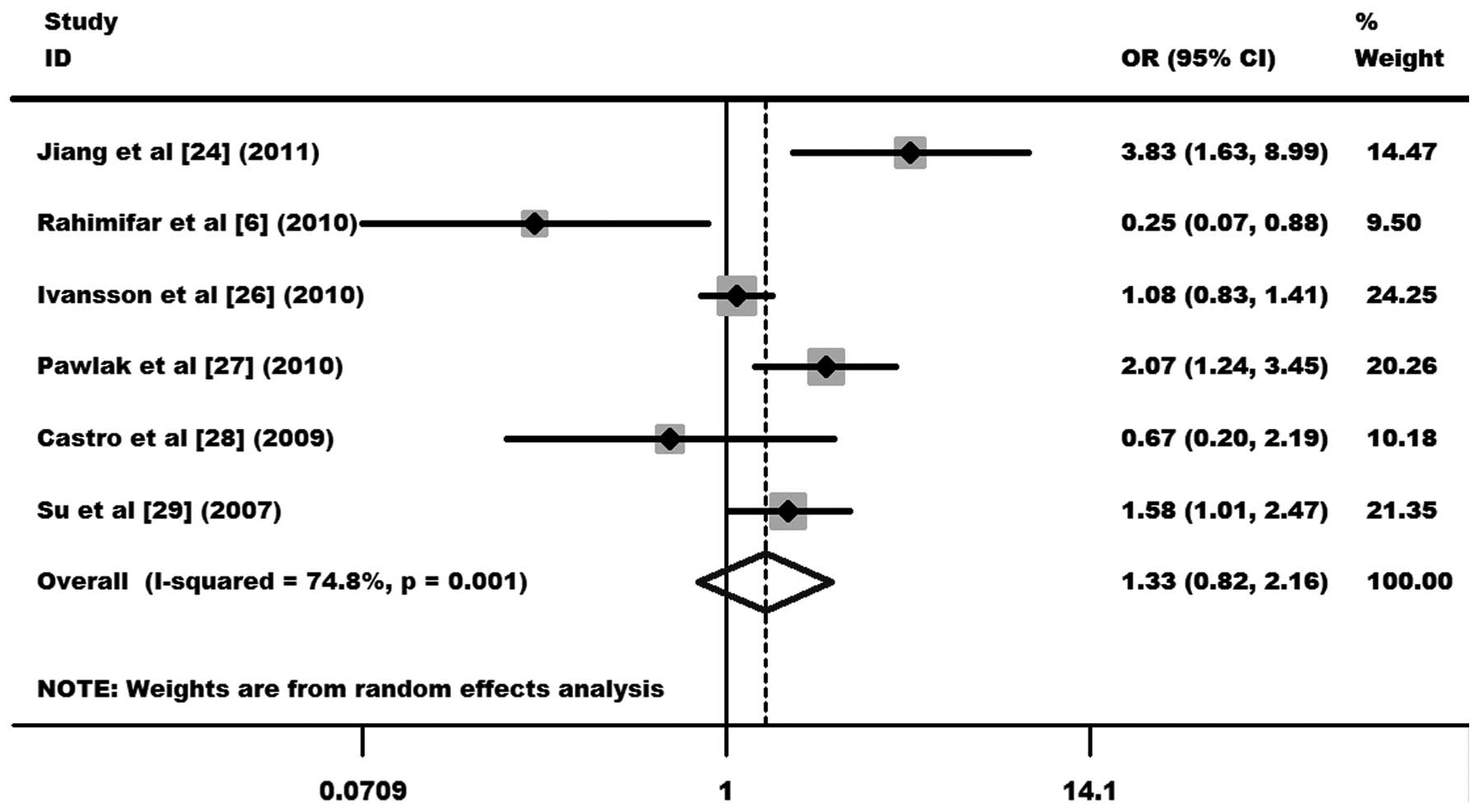
|
4
|
Zoodsma M, Sijmons RH, de Vries EG and Zee
AG: Familial cervical cancer: case reports, review and clinical
implications. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2:99–105. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wank R and Thomssen C: High risk of
squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix for women with HLA-DQw3.
Nature. 352:723–725. 1991. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rahimifar S, Erfani N, Sarraf Z and
Ghaderi A: ctla-4 gene variations may influence cervical cancer
susceptibility. Gynecol Oncol. 119:136–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Matsumoto K, Oki A, Satoh T, et al:
Interleukin-10 -1082 gene polymorphism and susceptibility to
cervical cancer among Japanese women. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
40:1113–1116. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Satinder K, Chander SR, Pushpinder K, Indu
G and Veena J: Cyclin D1 (G870A) polymorphism and risk of cervix
cancer: a case control study in north Indian population. Mol Cell
Biochem. 315:151–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Teft WA, Kirchhof MG and Madrenas J: A
molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Annu Rev Immunol.
24:65–97. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Buonavista N, Balzano C, Pontarotti P, Le
Paslier D and Golstein P: Molecular linkage of the human CTLA4 and
CD28 Ig-superfamily genes in yeast artificial chromosomes.
Genomics. 13:856–861. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ligers A, Teleshova N, Masterman T, Huang
WX and Hillert J: CTLA-4 gene expression is influenced by promoter
and exon 1 polymorphisms. Genes Immun. 2:145–152. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Egen JG, Kuhns MS and Allison JP: CTLA-4:
new insights into its biological function and use in tumor
immunotherapy. Nat Immunol. 3:611–618. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Leach DR, Krummel MF and Allison JP:
Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science.
271:1734–1736. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hurwitz AA, Foster BA, Kwon ED, et al:
Combination immunotherapy of primary prostate cancer in a
transgenic mouse model using CTLA-4 blockade. Cancer Res.
60:2444–2448. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Curran MA and Allison JP: Tumor vaccines
expressing flt3 ligand synergize with ctla-4 blockade to reject
preimplanted tumors. Cancer Res. 69:7747–7755. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hou R, Cao B, Chen Z, Li Y, et al:
Association of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 gene
haplotype with the susceptibility to gastric cancer. Mol Biol Rep.
37:515–520. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sun T, Zhou Y, Yang M, et al: Functional
genetic variations in cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4 and
susceptibility to multiple types of cancer. Cancer Res.
68:7025–7034. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lang C, Chen L and Li S: Cytotoxic
T-lymphocyte antigen-4 +49G/A polymorphism and susceptibility to
pancreatic cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 31:683–687. 2012.
|
|
19
|
Karabon L, Pawlak-Adamska E, Tomkiewicz A,
et al: Variations in suppressor molecule ctla-4 gene are related to
susceptibility to multiple myeloma in a polish population. Pathol
Oncol Res. 18:219–226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karabon L, Pawlak E, Tomkiewicz A, et al:
CTLA-4, CD28, and ICOS gene polymorphism associations with
non-small-cell lung cancer. Hum Immunol. 72:947–954. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kamesh L, Heward JM, Williams JM, et al:
CT60 and +49 polymorphisms of CTLA 4 are associated with
ANCA-positive small vessel vasculitis. Rheumatology (Oxford).
48:1502–1505. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Heidari A, Noori Daloii MR, Keramatipour
M, Rashikinezhad A, Sahmani AA and Amirzargar AA: CTLA-4 gene
polymorphisms (−318C/T, +49A/G, +6230A/G) in Iranian patients with
multiple sclerosis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 9:219–223.
2010.
|
|
23
|
Li H, Zhou YF, Guo HY, Sun T, Zhang WH and
Lin DX: Association between CTLA-4 gene polymorphism and
susceptibility to cervical cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
33:681–684. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
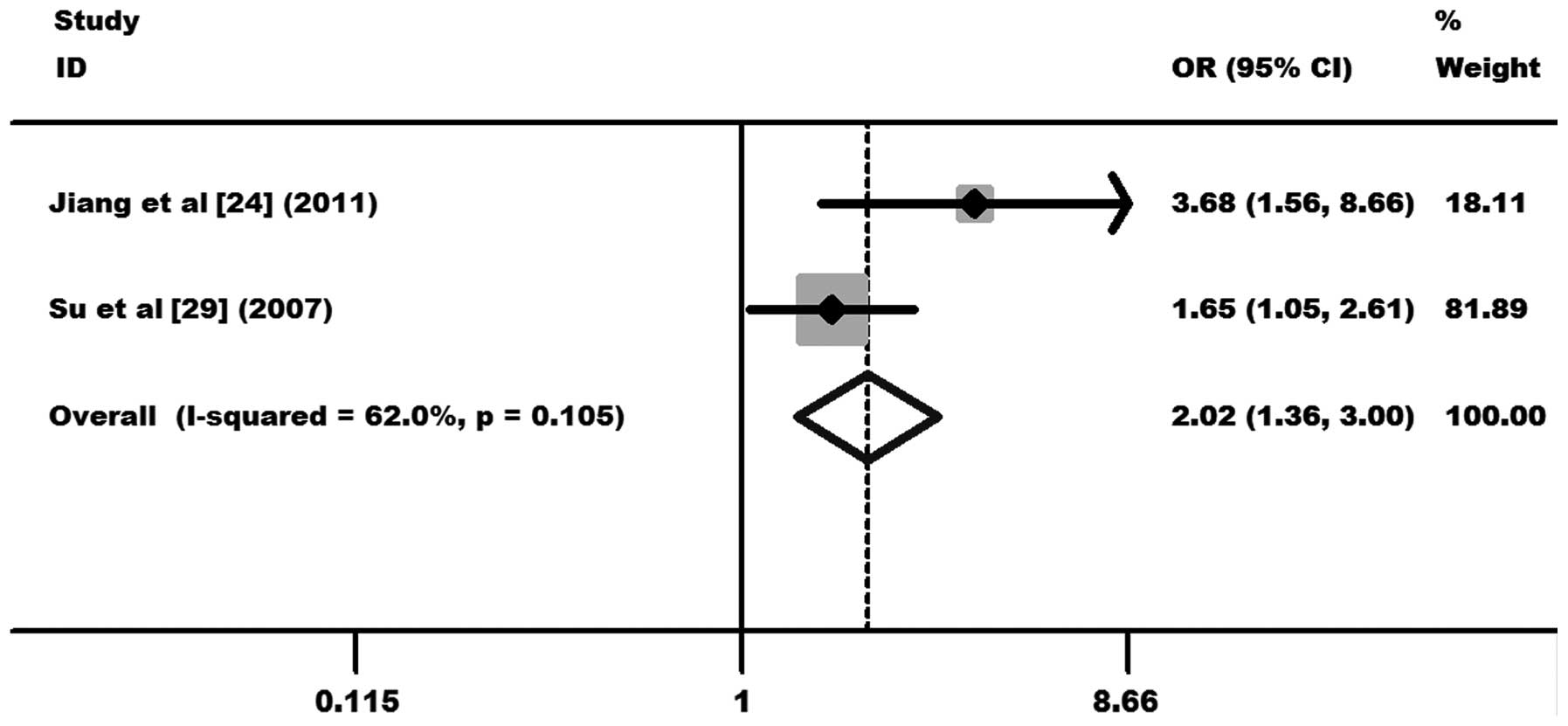
Jiang L, Luo RY, Zhang W, Wang LR, Wang F
and Cheng YX: Single nucleotide polymorphisms of CTLA4 gene and
their association with human cervical cancer. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi
Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 28:313–317. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
25
|
Hu L, Liu J, Chen X, et al: CTLA-4 gene
polymorphism +49 A/G contributes to genetic susceptibility to two
infection-related cancers - hepatocellular carcinoma and cervical
cancer. Hum Immunol. 71:888–891. 2010.
|
|
26
|
Ivansson EL, Juko-Pecirep I and Gyllensten
UB: Interaction of immunological genes on chromosome 2q33 and IFNG
in susceptibility to cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 116:544–548.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
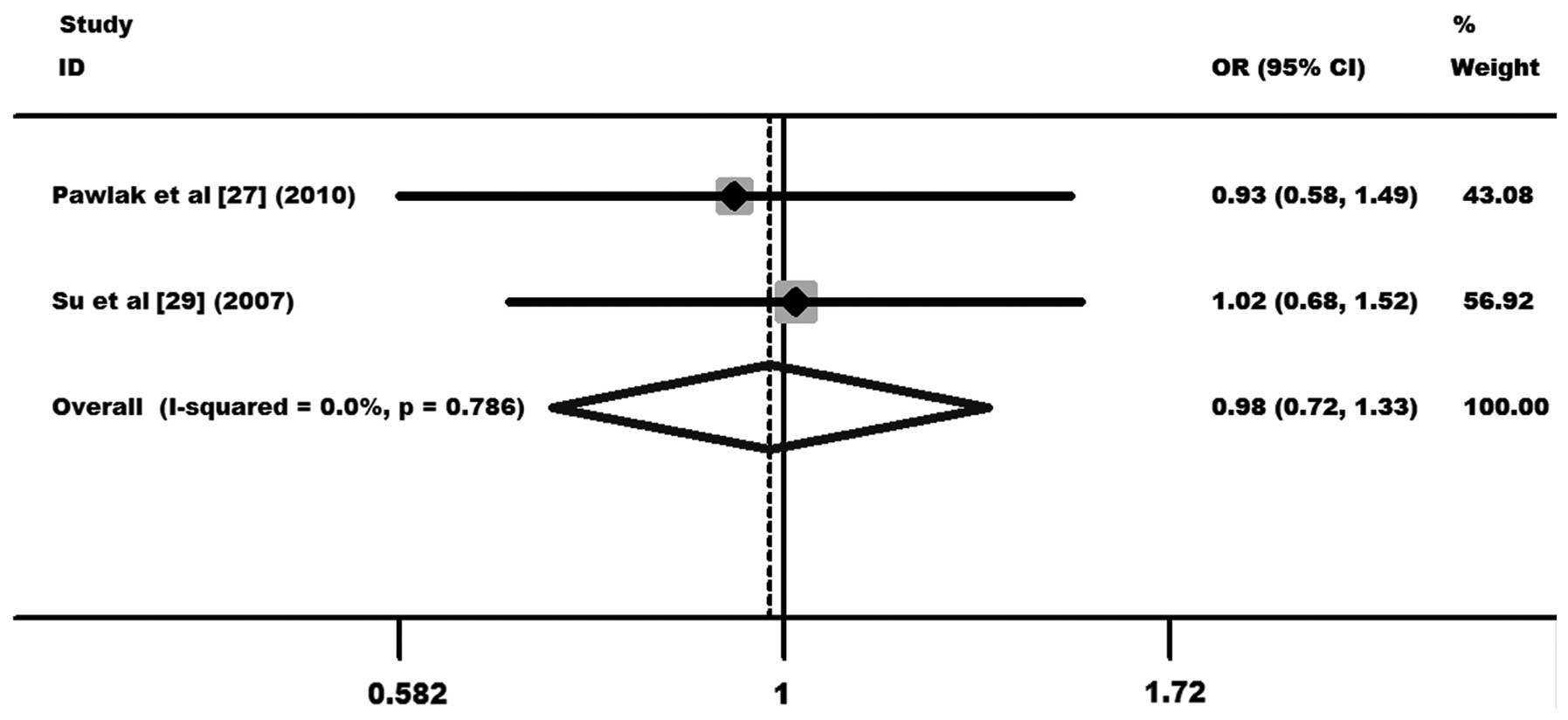
Pawlak E, Karabon L, Wlodarska-Polinska I,
et al: Influence of CTLA-4/CD28/ICOS gene polymorphisms on the
susceptibility to cervical squamous cell carcinoma and stage of
differentiation in the Polish population. Hum Immunol. 71:195–200.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Castro FA, Haimila K, Sareneva I, et al:
Association of HLA-DRB1, interleukin-6 and cyclin D1 polymorphisms
with cervical cancer in the Swedish population - a candidate gene
approach. Int J Cancer. 125:1851–1858. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Su TH, Chang TY, Lee YJ, et al: CTLA-4
gene and susceptibility to human papillomavirus-16-associated
cervical squamous cell carcinoma in Taiwanese women.
Carcinogenesis. 28:1237–1240. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vriens D, de Wilt JH, van der Wilt GJ,
Netea-Maier RT, Oyen WJ and de Geus-Oei LF: The role of
[18F]-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-d-glucose-positron emission
tomography in thyroid nodules with indeterminate fine-needle
aspiration biopsy: systematic review and meta-analysis of the
literature. Cancer. 117:4582–4594. 2011.
|
|
31
|
Pereira TV, Rudnicki M, Pereira AC,
Pombo-de-Oliveira MS and Franco RF: 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate
reductase polymorphisms and acute lymphoblastic leukemia risk: a
meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:1956–1963.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sousa H, Santos AM, Pinto D and Medeiros
R: Is the p53 codon 72 polymorphism a key biomarker for cervical
cancer development? A meta-analysis review within European
populations. Int J Mol Med. 20:731–741. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de Freitas AC, Gurgel AP, Chagas BS,
Coimbra EC and do Amaral CM: Susceptibility to cervical cancer: an
overview. Gynecol Oncol. 126:304–311. 2012.
|