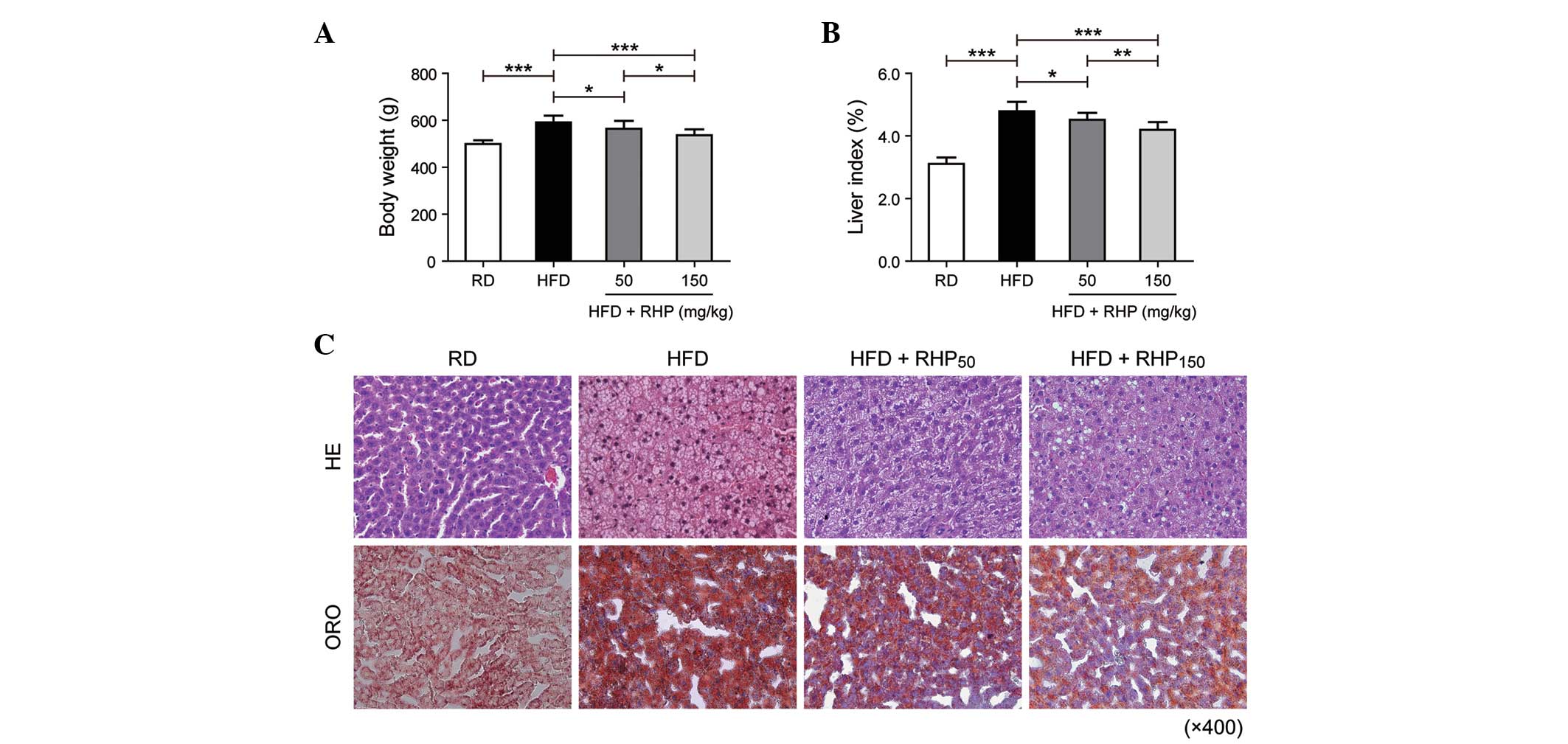
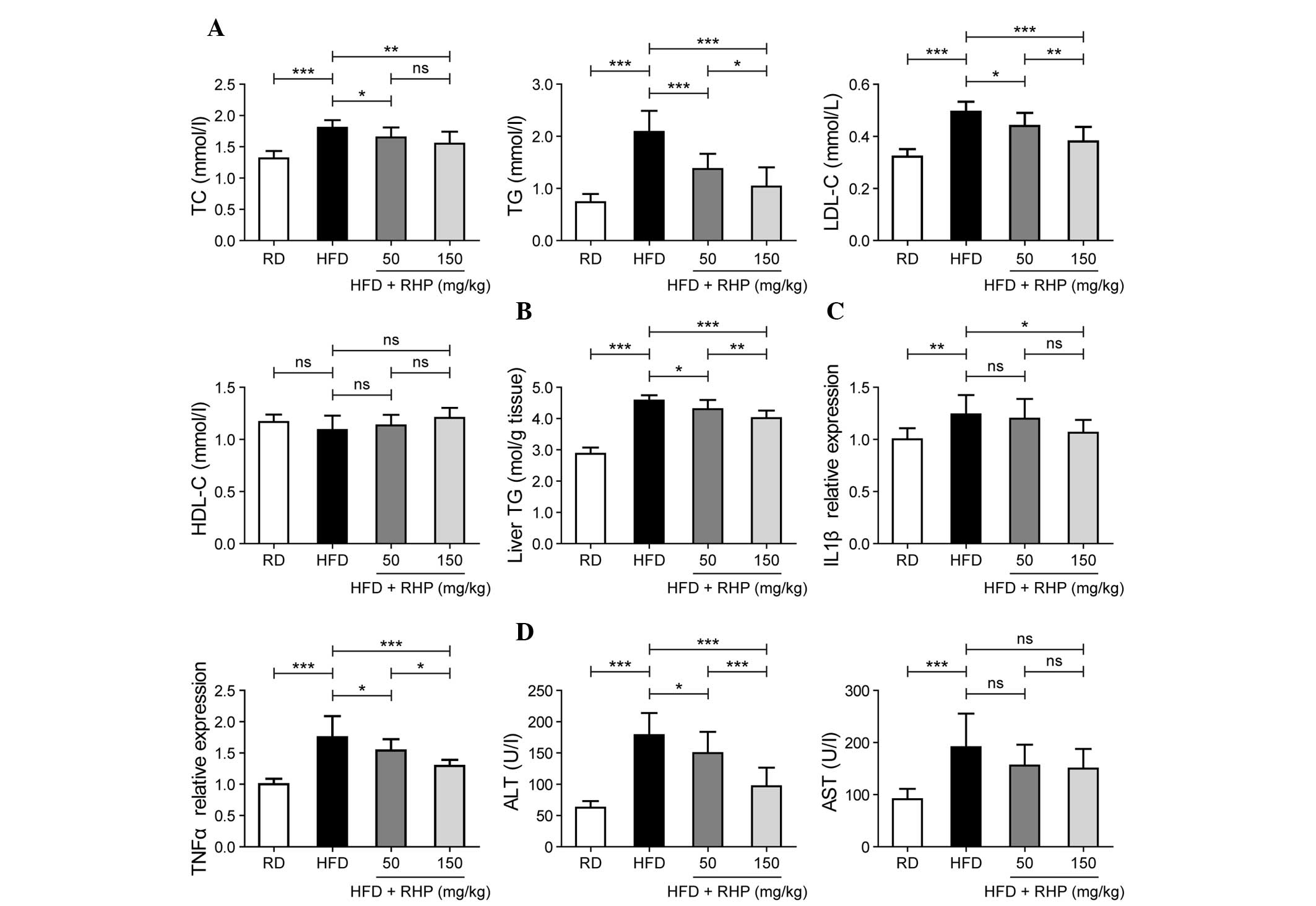
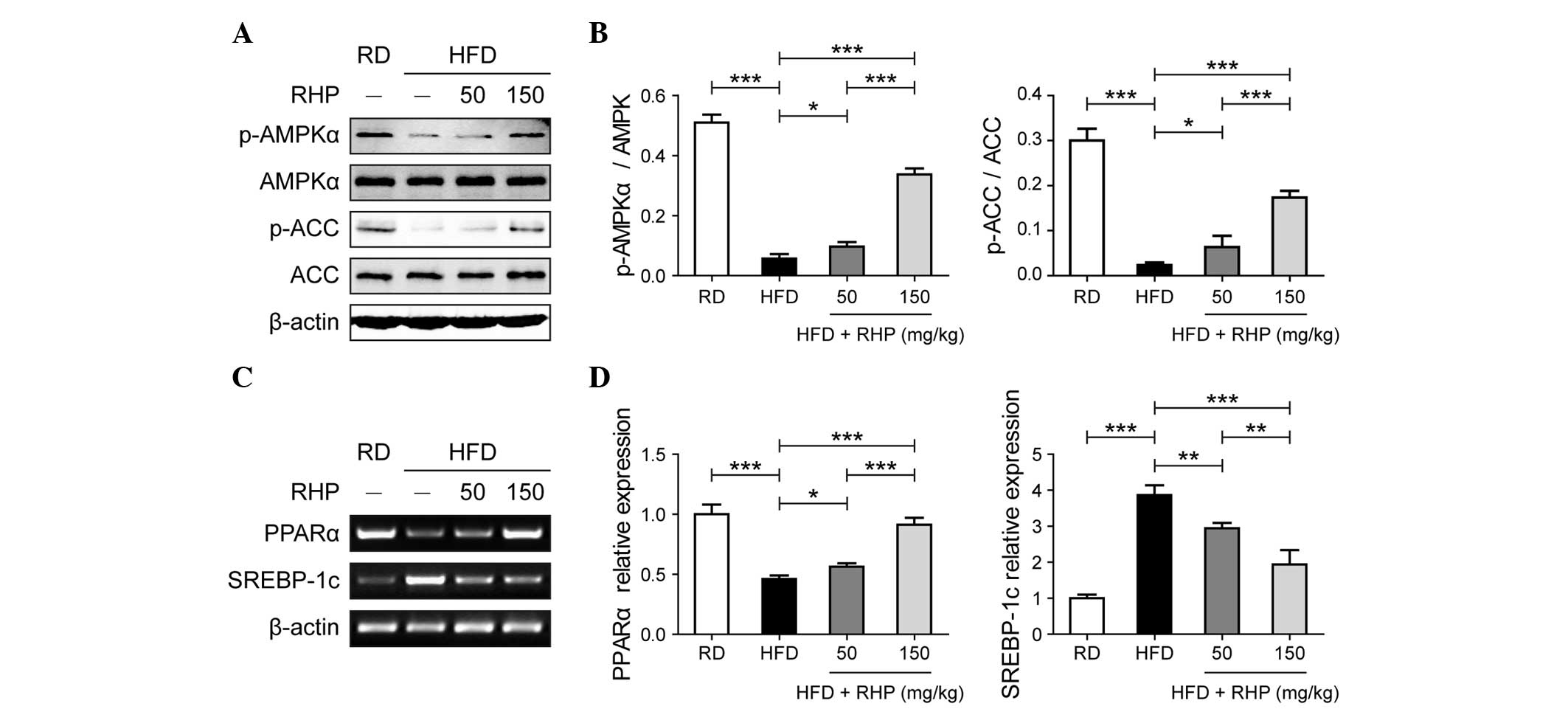
|
1
|
Farrell GC and Larter CZ: Nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology.
43:S99–S112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Targher G: Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease, the metabolic syndrome and the risk of cardiovascular
disease: the plot thickens. Diabetic Med. 24:1–6. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Koot BG, van der Baan-Slootweg OH,
Tamminga-Smeulders CL, et al: Lifestyle intervention for
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: prospective cohort study of its
efficacy and factors related to improvement. Arch dis Child.
96:669–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Park HJ, DiNatale DA, Chung MY, et al:
Green tea extract attenuates hepatic steatosis by decreasing
adipose lipogenesis and enhancing hepatic antioxidant defenses in
ob/ob mice. J Nutr Biochem. 22:393–400. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Quan HY, Kim do Y, Kim SJ, Jo HK, Kim GW
and Chung SH: Betulinic acid alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver
by inhibiting SREBP1 activity via the AMPK-mTOR-SREBP signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:1330–1340. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wei D, Cheng W, Wei Y and Zhang L:
Phosphorylated modification and in vitro antioxidant activity of
Radix Hedysari polysaccharide. Glycoconj J. 29:167–172. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hui HP, Feng SL, Hu FD, Cui F and Wu YQ:
Study on antioxidative activity of polysaccharide from radix
hedysari in vitro. J Anhui Agri Sci. 38:4056–4057. 2010.
|
|
8
|
Liu J, Deng W, Fan L, et al: The role of
radix hedysari polysaccharide on the human umbilical vein
endothelial cells (HUVECs) induced by high glucose. Eur J Intern
Med. 23:287–292. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wei D, Wei Y, Cheng W and Zhang L:
Sulfated modification, characterization and antitumor activities of
Radix hedysari polysaccharide. Int J Biol Macromol. 51:471–476.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grasselli E, Voci A, Canesi L, et al:
Direct effects of iodothyronines on excess fat storage in rat
hepatocytes. J Hepatol. 54:1230–1236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Koopman R, Schaart G and Hesselink MK:
Optimisation of oil red O staining permits combination with
immunofluorescence and automated quantification of lipids.
Histochem Cell Biol. 116:63–68. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bligh EG and Dyer WJ: A rapid method of
total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol.
37:911–917. 1959. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang YP, Huang LY, Sun WM, et al: Insulin
receptor tyrosine kinase substrate activates EGFR/ERK signalling
pathway and promotes cell proliferation of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 337:96–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang LY, Wang YP, Wei BF, et al:
Deficiency of IRTKS as an adaptor of insulin receptor leads to
insulin resistance. Cell Res. 23:1310–1321. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saltiel AR and Kahn CR: Insulin signalling
and the regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism. Nature.
414:799–806. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Duvnjak M, Lerotic I, Barsic N, Tomasic V,
Virovic Jukic L and Velagic V: Pathogenesis and management issues
for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol.
13:4539–4550. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xiao J, Guo R, Fung ML, Liong EC and Tipoe
GL: Therapeutic approaches to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:
past achievements and future challenges. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int. 12:125–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sakata R, Nakamura T, Torimura T, Ueno T
and Sata M: Green tea with high-density catechins improves liver
function and fat infiltration in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
(NAFLD) patients: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int J
Mol Med. 32:989–994. 2013.
|
|
19
|
Vuppalanchi R and Chalasani N:
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:
Selected practical issues in their evaluation and management.
Hepatology. 49:306–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Musso G, Cassader M and Gambino R:
Cholesterol-lowering therapy for the treatment of nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: an update. Curr Opin Lipidol. 22:489–496.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Matthew Morris E, Fletcher JA, Thyfault JP
and Rector RS: The role of angiotensin II in nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 378:29–40. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kato J, Koda M, Kishina M, et al:
Therapeutic effects of angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker,
irbesartan, on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis using FLS-ob/ob male
mice. Int J Mol Med. 30:107–113. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leuschner UF, Lindenthal B, Herrmann G, et
al: High-dose ursodeoxycholic acid therapy for nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled
trial. Hepatology. 2:472–479. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Malaguarnera M, Gargante MP, Russo C, et
al: L-carnitine supplementation to diet: a new tool in treatment of
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis - a randomized and controlled clinical
trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 105:1338–1345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Long YC and Zierath JR: AMP-activated
protein kinase signaling in metabolic regulation. J Clin Inv.
116:1776–1783. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gray S and Kim JK: New insights into
insulin resistance in the diabetic heart. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
22:394–403. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kawaguchi T, Osatomi K, Yamashita H,
Kabashima T and Uyeda K: Mechanism for fatty acid ‘sparing’ effect
on glucose-induced transcription: regulation of
carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein by AMP-activated
protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 277:3829–3835. 2002.
|
|
28
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, et al: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J
Clin Invest. 108:1167–1174. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoshimura Y, Nishii S, Zaima N, Moriyama T
and Kawamura Y: Ellagic acid improves hepatic steatosis and serum
lipid composition through reduction of serum resistin levels and
transcriptional activation of hepatic ppara in obese, diabetic
KK-A(y) mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 434:486–491. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xu X, So JS, Park JG and Lee AH:
Transcriptional control of hepatic lipid metabolism by SREBP and
ChREBP. Semin Liver Dis. 33:301–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lee JH, Moon MH, Jeong JK, et al:
Sulforaphane induced adipolysis via hormone sensitive lipase
activation, regulated by AMPK signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 426:492–497. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|