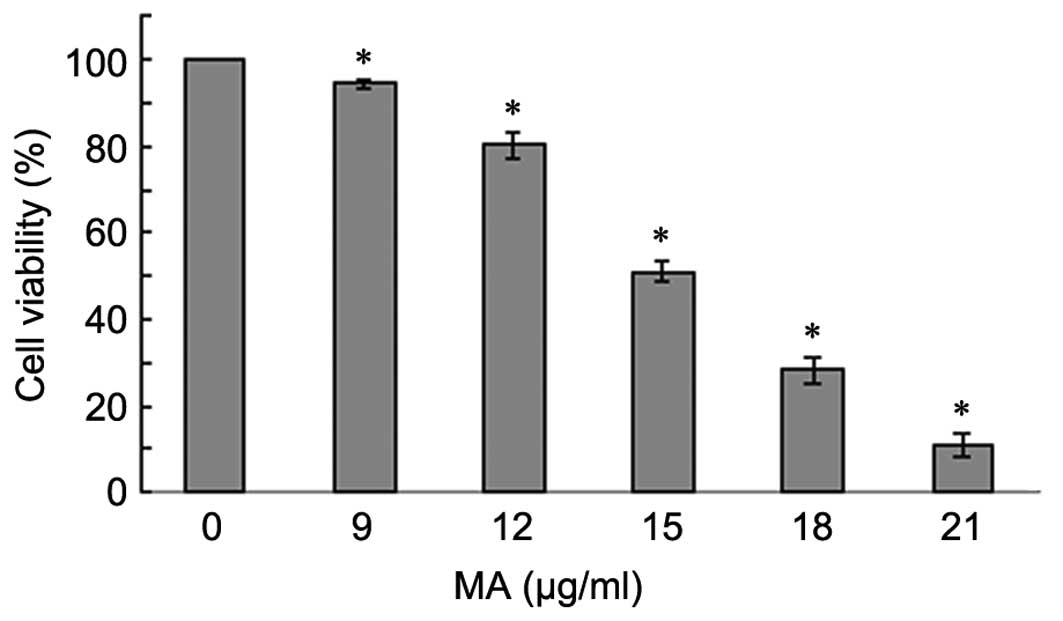
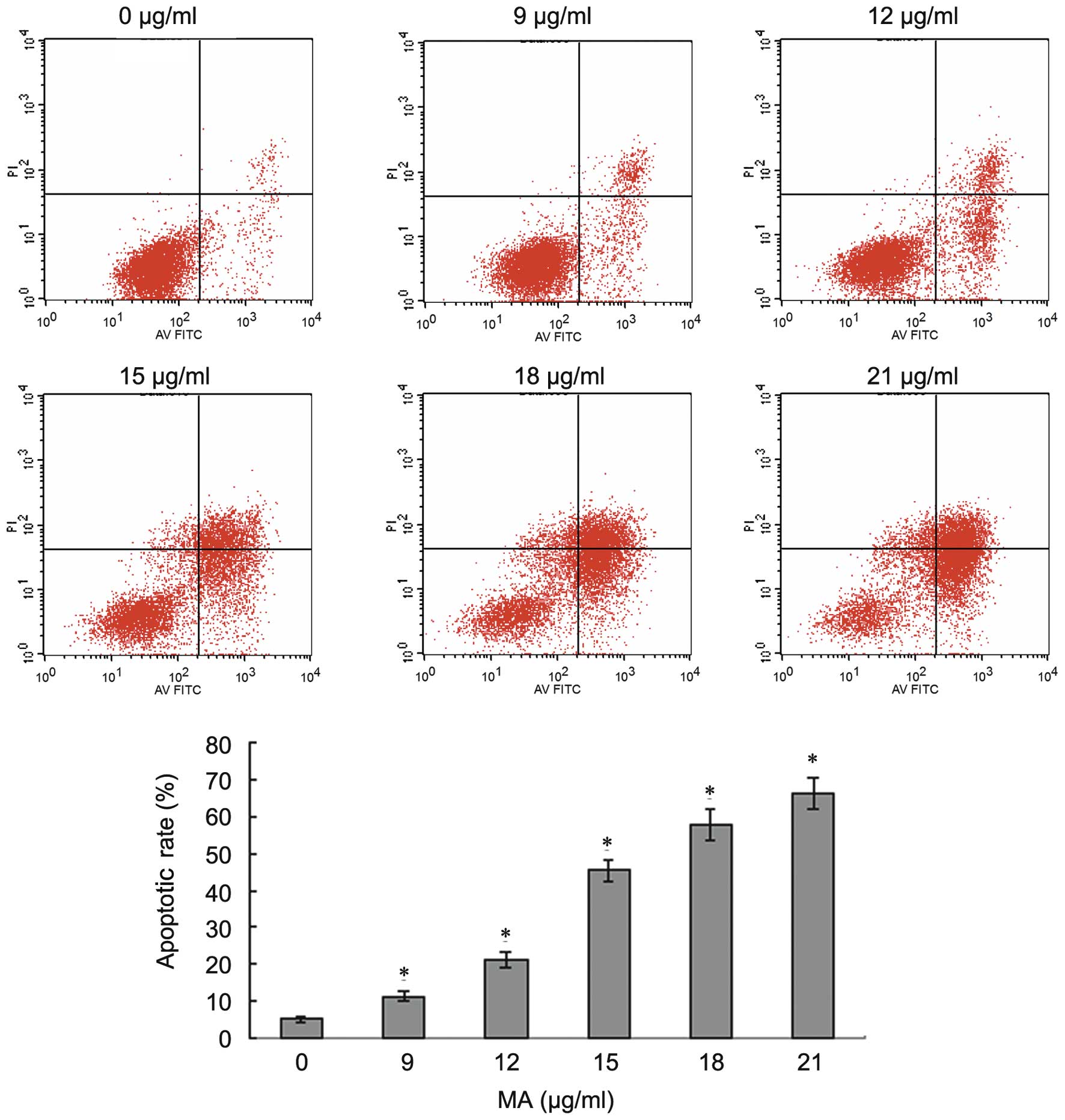
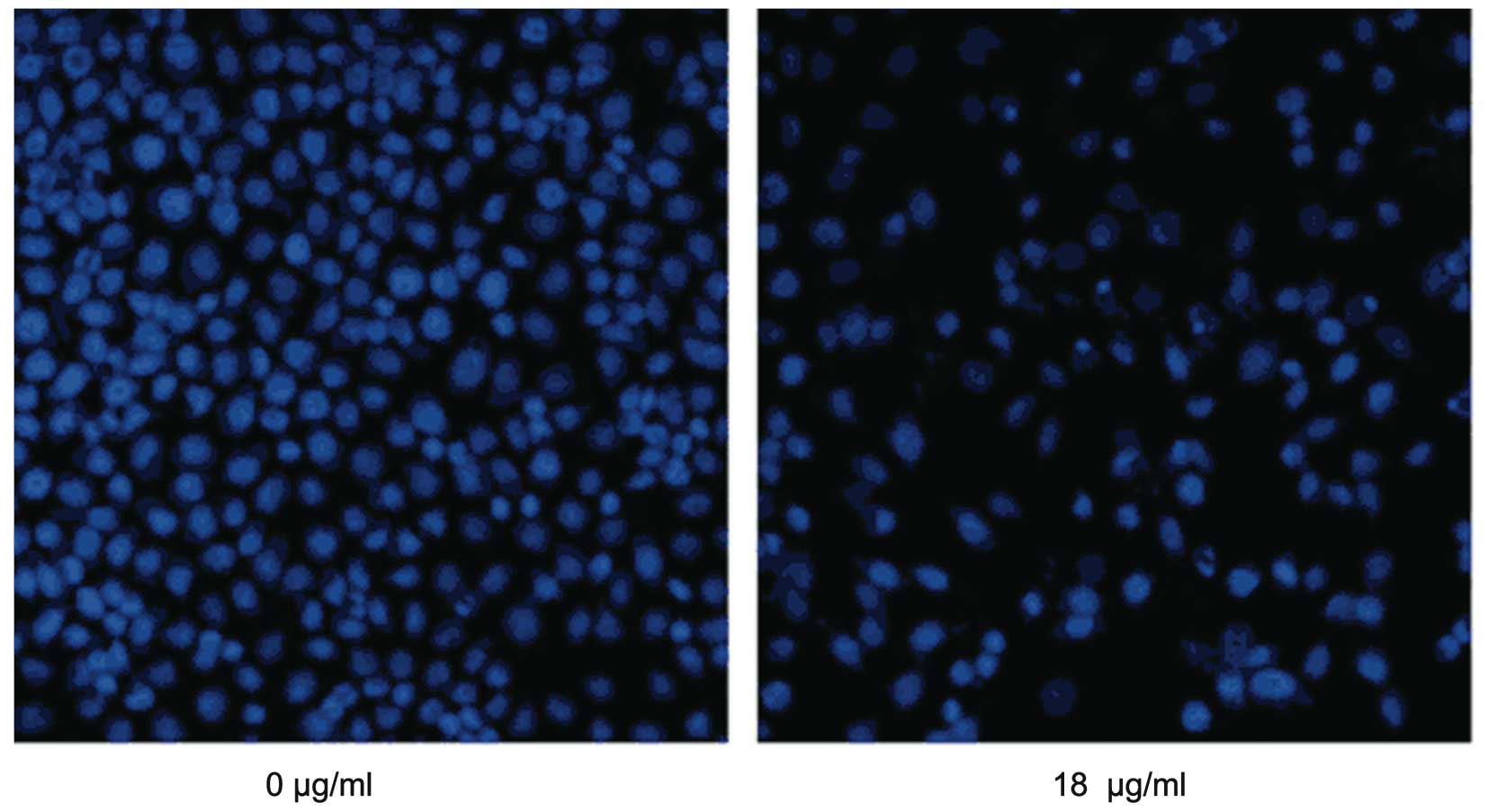
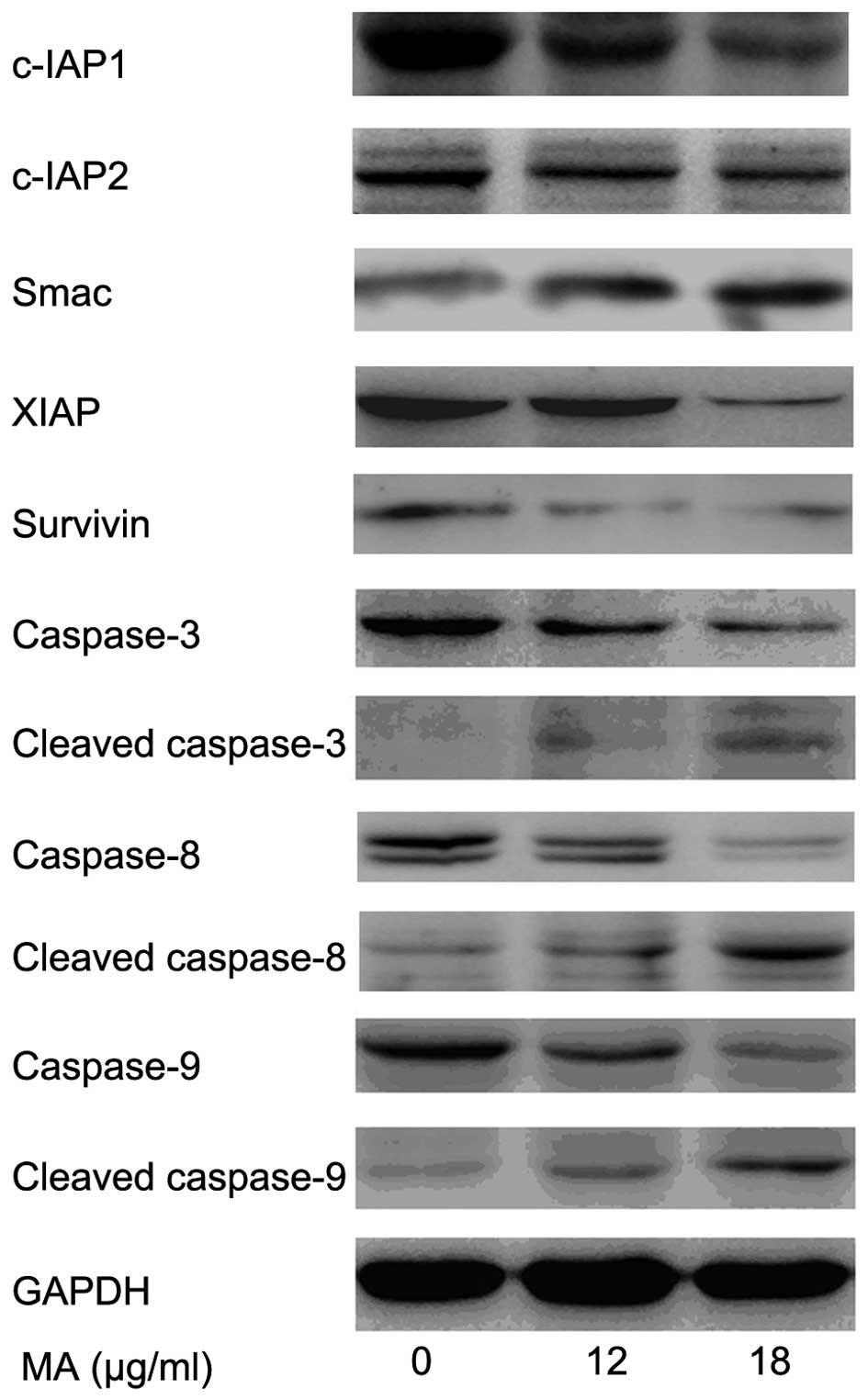
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raponi M, Zhang Y, Yu J, Chen G, Lee G,
Taylor JM, Macdonald J, Thomas D, Moskaluk C, Wang Y and Beer DG:
Gene expression signatures for predicting prognosis of squamous
cell and adenocarcinomas of the lung. Cancer Res. 66:7466–7472.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP,
Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, Zhu J and Johnson DH; Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group: Comparison of four chemotherapy
regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med.
346:92–98. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mountain CF: The international system for
staging lung cancer. Semin Surg Oncol. 18:106–115. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu B, Wang SS and Du Q: Traditional
Chinese medicine for prevention and treatment of hepatocarcinoma:
From bench to bedside. World J Hepatol. 7:1209–1232. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang CF, Lin SS, Liao PH, Young SC and
Yang CC: The immunopharmaceutical effects and mechanisms of herb
medicine. Cell Mol Immunol. 5:23–31. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu HB, Zheng LP, Li L, Xu LZ and Fu J:
Elemene, one ingredient of a Chinese herb, against malignant
tumors: A literature-based meta-analysis. Cancer Invest.
31:156–166. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mokhtari K, Rufino-Palomares EE,
Pérez-Jiménez A, Reyes-Zurita FJ, Figuera C, García-Salguero L,
Medina PP, Peragón J and Lupiáñez JA: Maslinic acid, a triterpene
from olive, affects the antioxidant and mitochondrial status of
B16F10 melanoma cells grown under stressful conditions. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2015:2724572012.
|
|
9
|
Yan SL, Yang HT, Lee HL and Yin MC:
Protective effects of maslinic acid against alcohol-induced acute
liver injury in mice. Food Chem Toxicol. 74:149–155. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin X, Qui C and Zhao L: Maslinic acid
protects vascular smooth muscle cells from oxidative stress through
Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 390:61–67. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Reyes-Zurita FJ, Pachón-Peña G, Lizárraga
D, Rufino-Palomares EE, Cascante M and Lupiáñez JA: The natural
triterpene maslinic acid induces apoptosis in HT29 colon cancer
cells by a JNK-p53-dependent mechanism. BMC cancer. 11:1542011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park SY, Nho CW, Kwon DY, Kang YH, Lee KW
and Park JH: Maslinic acid inhibits the metastatic capacity of
DU145 human prostate cancer cells: Possible mediation via
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α signalling. Br J Nutr. 109:210–222.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Parra A, Rivas F, Martin-Fonseca S,
Garcia-Granados A and Martinez A: Maslinic acid derivatives induce
significant apoptosis in b16f10 murine melanoma cells. Eur J Med
Chem. 46:5991–6001. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peragón J, Rufino-Palomares EE,
Muñoz-Espada I, Reyes-Zurita FJ and Lupiáñez JA: A new HPLC-MS
method for measuring maslinic acid and oleanolic acid in HT29 and
HepG2 human cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 16:21681–21694. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuribayashi K, Mayes PA and El-Deiry WS:
What are caspases 3 and 7 doing upstream of the mitochondria?
Cancer Biol Ther. 5:763–765. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter GA
Jr, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ, Inayat I and Flavell RA: Caspases 3 and 7:
Key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science.
311:847–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fuentes-Prior P and Salvesen GS: The
protein structures that shape caspase activity, specificity,
activation and inhibition. Biochem J. 384:201–232. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
LaCasse EC, Baird S, Korneluk RG and
MacKenzie AE: The inhibitors of apoptosis (IAPs) and their emerging
role in cancer. Oncogene. 17:3247–3259. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Deveraux QL and Reed JC: IAP family
proteins-suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev. 13:239–252. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Deveraux QL, Leo E, Stennicke HR, Welsh K,
Salvesen GS and Reed JC: Cleavage of human inhibitor of apoptosis
protein XIAP results in fragments with distinct specificities for
caspases. EMBO J. 18:5242–5251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Riedl SJ, Renatus M, Schwarzenbacher R,
Zhou Q, Sun C, Fesik SW, Liddington RC and Salvesen GS: Structural
basis for the inhibition of caspase-3 by XIAP. Cell. 104:791–800.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rothe M, Pan MG, Henzel WJ, Ayres TM and
Goeddel DV: The TNFR2-TRAF signaling complex contains two novel
proteins related to baculoviral inhibitor of apoptosis proteins.
Cell. 83:1243–1252. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV
and Baldwin AS Jr: NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and
TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation.
Science. 281:1680–1683. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li F: Survivin study: What is the next
wave? J Cell Physiol. 197:8–29. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ambrosini G, Adida C and Altieri DC: A
novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and
lymphoma. Nat Med. 3:917–921. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shiozaki EN and Shi Y: Caspases, IAPs and
Smac/DIABLO: Mechanisms from structural biology. Trends Biochem
Sci. 29:486–494. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Srinivasula SM, Hegde R, Saleh A, Datta P,
Shiozaki E, Chai J, Lee RA, Robbins PD, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Shi Y
and Alnemri ES: A conserved XIAP-interaction motif in caspase-9 and
Smac/DIABLO regulates caspase activity and apoptosis. Nature.
410:112–116. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song Z, Yao X and Wu M: Direct interaction
between survivin and Smac/DIABLO is essential for the
anti-apoptotic activity of survivin during taxol-induced apoptosis.
J Biol Chem. 278:23130–23140. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang X, Feng Y, Wang N, Cheung F, Tan HY,
Zhong S, Li C and Kobayashi S: Chinese medicines induce cell death:
The molecular and cellular mechanisms for cancer therapy. Biomed
Res Int. 2014:5303422014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leake I: Colorectal cancer:
Chemopreventive action of synthetic triterpenoids in CRC. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 11:3952014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yap WH and Lim YH: Mechanistic
perspectives of maslinic acid in targeting inflammation. Biochem
Res Int. 2015:2793562015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lin CC, Huang CY, Mong MC, Chan CY and Yin
MC: Antiangiogenic potential of three triterpenic acids in human
liver cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem. 59:755–762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Rufino-Palomares EE, Reyes-Zurita FJ,
García-Salguero L, Mokhtari K, Medina PP, Lupiáñez JA and Peragón
J: Maslinic acid, a triterpenic anti-tumoural agent, interferes
with cytoskeleton protein expression in HT29 human colon-cancer
cells. J Proteomics. 83:15–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Reyes-Zurita FJ, Rufino-Palomares EE,
Lupiáñez JA and Cascante M: Maslinic acid, a natural triterpene
from Olea europaea L., induces apoptosis in HT29 human colon-cancer
cells via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Cancer Lett.
273:44–54. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|