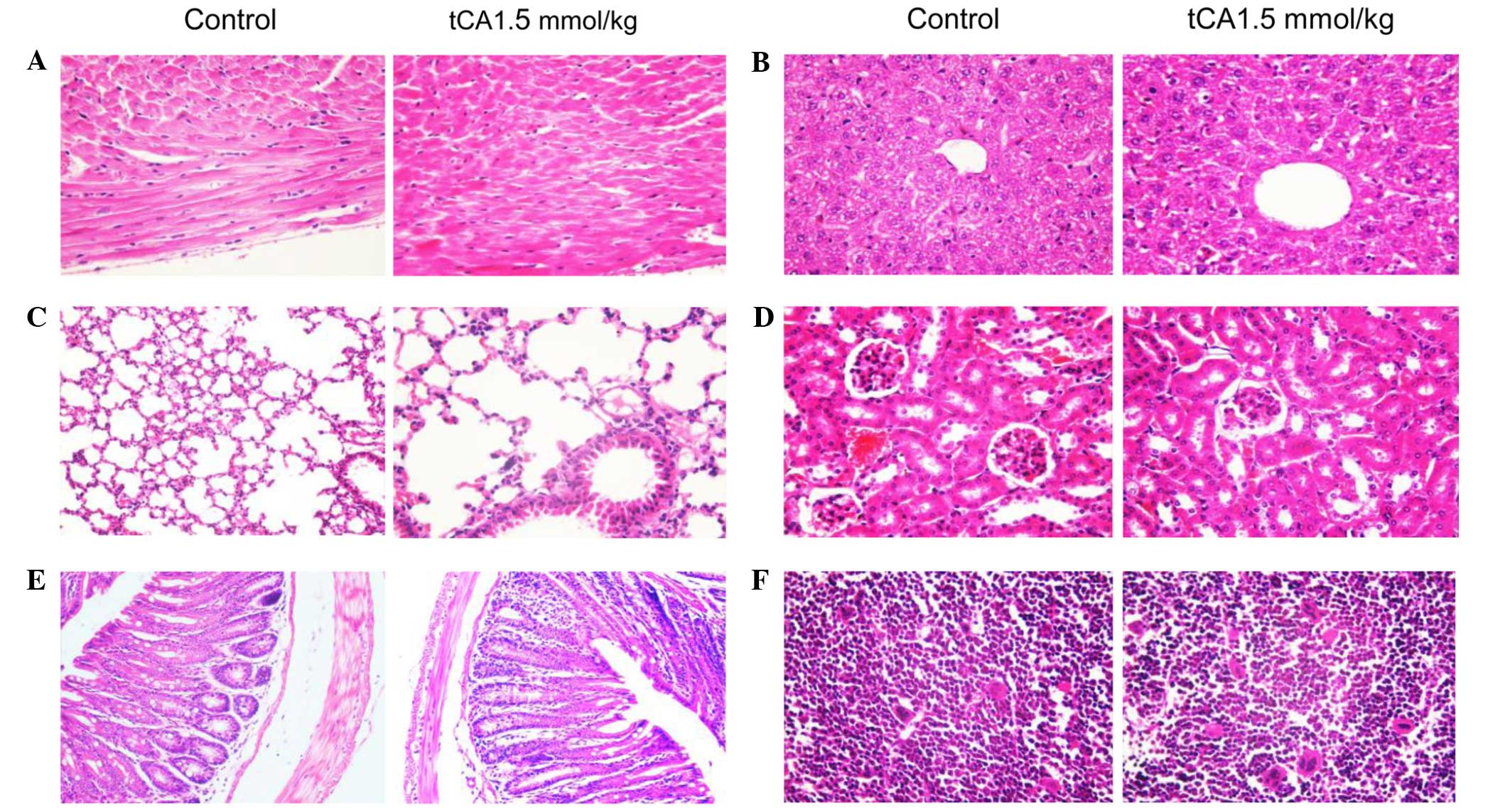
|
1
|
Jaenisch R and Bird A: Epigenetic
regulation of gene expression: How the genome integrates intrinsic
and environmental signals. Nat Genet. (33 Suppl): 245–254. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yoo CB and Jones PA: Epigenetic therapy of
cancer: Past, present and future. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:37–50.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Knower KC, To SQ, Leung YK, Ho SM and
Clyne CD: Endocrine disruption of the epigenome: a breast cancer
link. Endocr Relat Cancer. 21:T33–T55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sterner DE and Berger SL: Acetylation of
histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev.
64:435–459. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Glozak MA and Seto E: Histone deacetylases
and cancer. Oncogene. 26:5420–5432. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu WS, Parmigiani RB and Marks PA: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors: Molecular mechanisms of action. Oncogene.
26:5541–5552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades NS, McMullan CJ,
Poulaki V, Shringarpure R, Hideshima T, Akiyama M, Chauhan D,
Munshi N, Gu X, et al: Transcriptional signature of histone
deacetylase inhibition in multiple myeloma: Biological and clinical
implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:540–545. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Zhang Z, Yamashita H, Toyama T, Sugiura H,
Omoto Y, Ando Y, Mita K, Hamaguchi M, Hayashi S and Iwase H: HDAC6
expression is correlated with better survival in breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 10:6962–6968. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vannini A, Volpari C, Filocamo G, Casavola
EC, Brunetti M, Renzoni D, Chakravarty P, Paolini C, De Francesco
R, Gallinari P, et al: Crystal structure of a eukaryotic
zinc-dependent histone deacetylase, human HDAC8, complexed with a
hydroxamic acid inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:15064–15069.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Falkenberg KJ and Johnstone RW: Histone
deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases
and immune disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 13:673–691. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Donia MS, Cimermancic P, Schulze CJ,
Wieland Brown LC, Martin J, Mitreva M, Clardy J, Linington RG and
Fischbach MA: A systematic analysis of biosynthetic gene clusters
in the human microbiome reveals a common family of antibiotics.
Cell. 158:1402–1414. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marks PA, Richon VM, Miller T and Kelly
WK: Histone deacetylase inhibitors. Adv Cancer Res. 91:137–168.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jenner AM, Rafter J and Halliwell B: Human
fecal water content of phenolics: The extent of colonic exposure to
aromatic compounds. Free Radic Biol Med. 38:763–772. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Waldecker M, Kautenburger T, Daumann H,
Busch C and Schrenk D: Inhibition of histone-deacetylase activity
by short-chain fatty acids and some polyphenol metabolites formed
in the colon. J Nutr Biochem. 19:587–593. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang LP and Ji ZZ: Synthesis,
antiinflammatory and anticancer activity of cinnamic acids, their
derivatives and analogues. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 27:817–823.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Akao Y, Maruyama H, Matsumoto K, Ohguchi
K, Nishizawa K, Sakamoto T, Araki Y, Mishima S and Nozawa Y: Cell
growth inhibitory effect of cinnamic acid derivatives from propolis
on human tumor cell lines. Biol Pharm Bull. 26:1057–1059. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Foti MC, Daquino C and Geraci C:
Electron-transfer reaction of cinnamic acids and their methyl
esters with the DPPH(*) radical in alcoholic solutions.
J Org Chem. 69:2309–2314. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song F, Li H, Sun J and Wang S: Protective
effects of cinnamic acid and cinnamic aldehyde on
isoproterenol-induced acute myocardial ischemia in rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 150:125–130. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
El-Sayed el SM, Abd El-Raouf OM, Fawzy HM
and Manie MF: Comparative study of the possible protective effects
of cinnamic acid and cinnamaldehyde on cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 27:508–514. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Conti BJ, Búfalo MC, Golim Mde A, Bankova
V and Sforcin JM: Cinnamic Acid is partially involved in propolis
immunomodu-latory action on human monocytes. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:1098642013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Adisakwattana S, Sompong W, Meeprom A,
Ngamukote S and Yibchok-Anun S: Cinnamic acid and its derivatives
inhibit fructose-mediated protein glycation. Int J Mol Sci.
13:1778–1789. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kasetti RB, Nabi SA, Swapna S and Apparao
C: Cinnamic acid as one of the antidiabetic active principle(s)
from the seeds of Syzygium alternifolium. Food Chem Toxicol.
50:1425–1431. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen YL, Huang ST, Sun FM, Chiang YL,
Chiang CJ, Tsai CM and Weng CJ: Transformation of cinnamic acid
from trans- to cis-form raises a notable bactericidal and
synergistic activity against multiple-drug resistant Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Eur J Pharm Sci. 43:188–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Barros MP, Lemos M, Maistro EL, Leite MF,
Sousa JP, Bastos JK and Andrade SF: Evaluation of antiulcer
activity of the main phenolic acids found in Brazilian Green
Propolis. J Ethnopharmacol. 120:372–377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong YH, Jo YO, Cho CW, Son D, Park S, Rho
J and Choi SY: Inhibitory effects of cinnamic acid on melanin
biosynthesis in skin. Biol Pharm Bull. 31:946–948. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Niero EL and Machado-Santelli GM: Cinnamic
acid induces apoptotic cell death and cytoskeleton disruption in
human melanoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 32:312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsai CM, Sun FM, Chen YL, Hsu CL, Yen GC
and Weng CJ: Molecular mechanism depressing PMA-induced invasive
behaviors in human lung adenocarcinoma cells by cis- and
trans-cinnamic acid. Eur J Pharm Sci. 48:494–501. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wheatley NC, Andrews KT, Tran TL, Lucke
AJ, Reid RC and Fairlie DP: Antimalarial histone deacetylase
inhibitors containing cinnamate or NSAID components. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 20:7080–7084. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Halley F, Reinshagen J, Ellinger B, Wolf
M, Niles AL, Evans NJ, Kirkland TA, Wagner JM, Jung M, Gribbon P
and Gul S: A bioluminogenic HDAC activity assay: validation and
screening. J Biomol Screen. 16:1227–1235. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang LT, Liou JP, Li YH, Liu YM, Pan SL
and Teng CM: A novel class I HDAC inhibitor, MPT0G030, induces cell
apoptosis and differentiation in human colorectal cancer cells via
HDAC1/PKCδ and E-cadherin. Oncotarget. 5:5651–5662. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|