|
1
|
Katto J and Mahlknecht U: Epigenetic
regulation of cellular adhesion in cancer. Carcinogenesis.
32:1414–1418. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Liu J, Lin PC and Zhou BP: Inflammation
fuels tumor progress and metastasis. Curr Pharm Des. 21:3032–3040.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang L, Song X, Mohri Y and Qiao L: Role
of inflammation and tumor microenvironment in the development of
gastrointestinal cancers: What induced pluripotent stem cells can
do? Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 10:245–250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li Y, Wang L, Pappan L, Galliher-Beckley A
and Shi J: IL-1β promotes stemness and invasiveness of colon cancer
cells through Zeb1 activation. Mol Cancer. 11:872012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
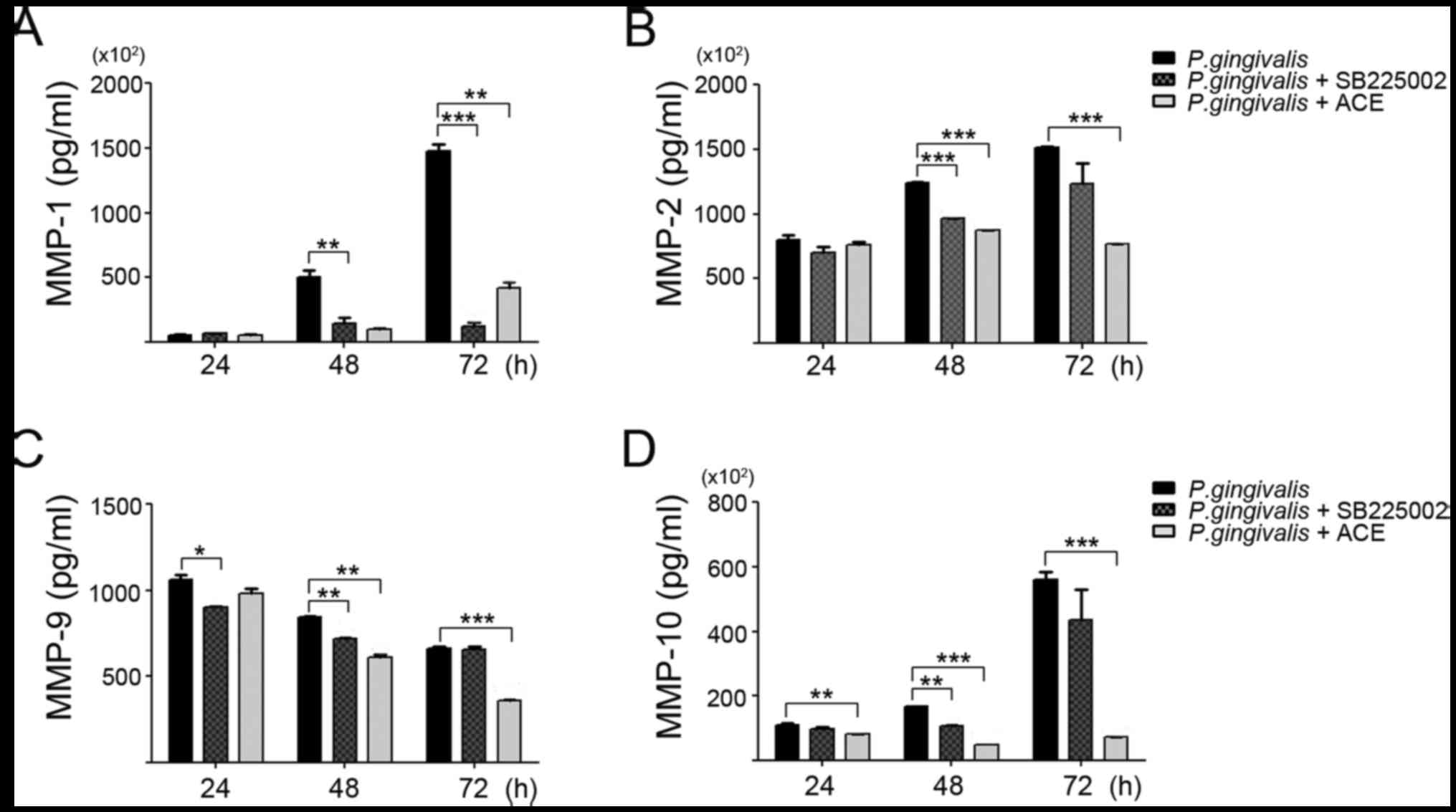
|
Diakos CI, Charles KA, McMillan DC and
Clarke SJ: Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness.
Lancet Oncol. 15:e493–e503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
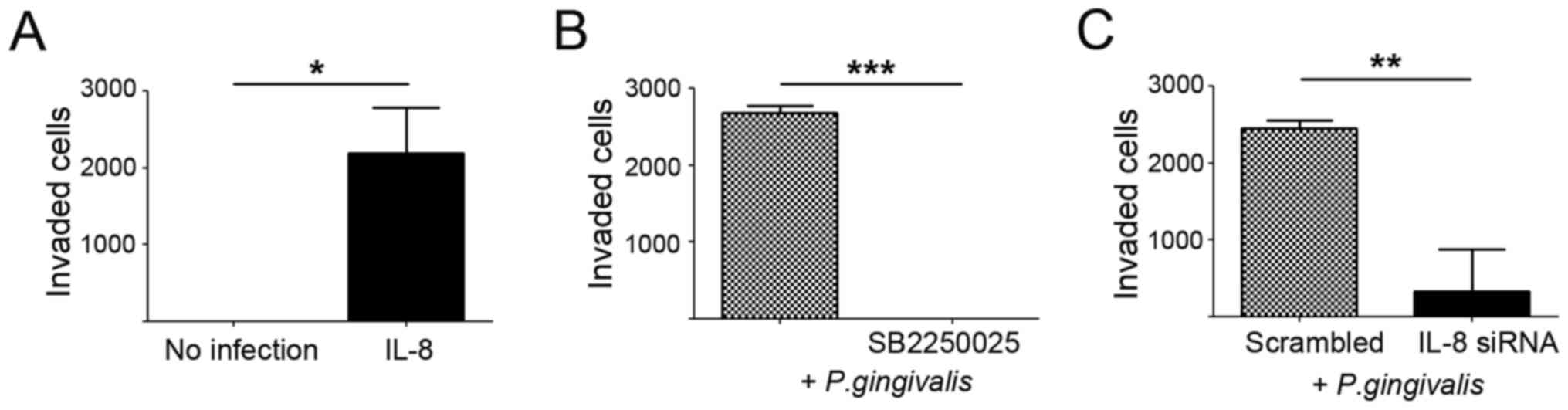
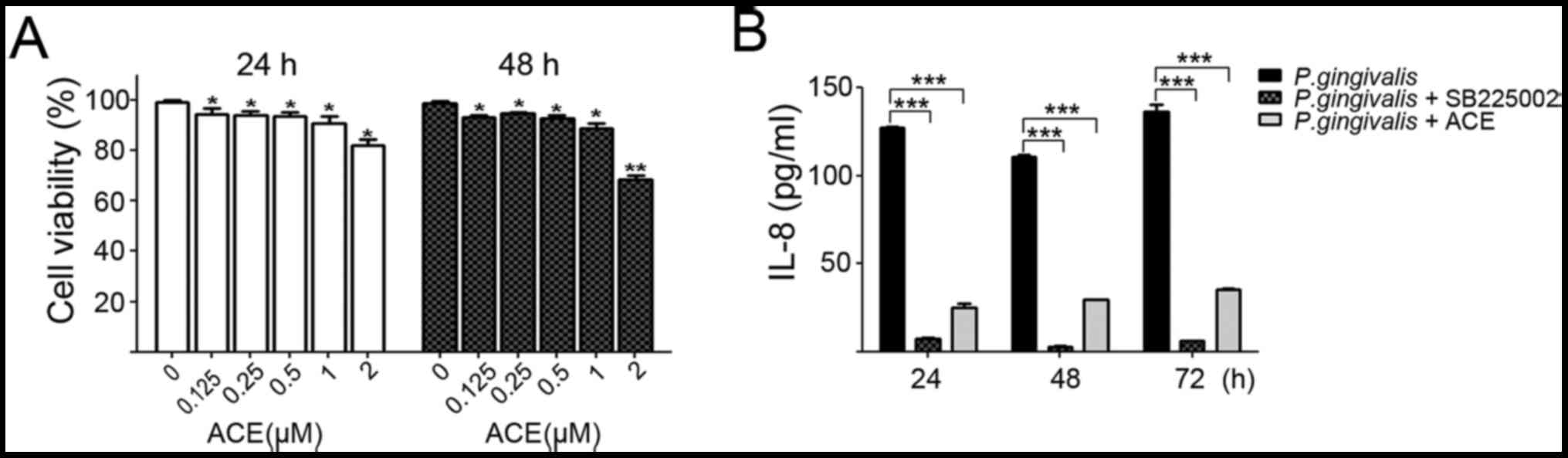
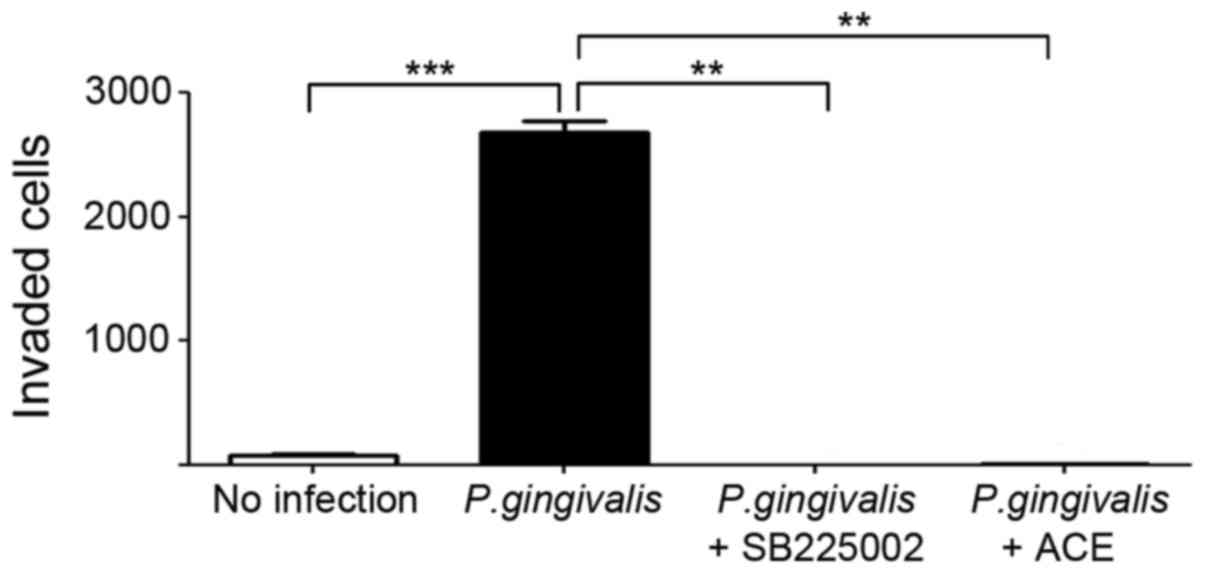
|
Bharti R, Dey G and Mandal M: Cancer
development, chemoresistance, epithelial to mesenchymal transition
and stem cells: A snapshot of IL-6 mediated involvement. Cancer
Lett. 375:51–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang D, Fu L, Sun H, Guo L and DuBois RN:
Prostaglandin E2 promotes colorectal cancer stem cell expansion and
metastasis in mice. Gastroenterology. 149:1884–1895. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
St John MA: Inflammatory mediators drive
metastasis and drug resistance in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Laryngoscope. 125 Suppl 3:S1–S11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yadav A, Kumar B, Datta J, Teknos TN and
Kumar P: IL-6 promotes head and neck tumor metastasis by inducing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via the JAK-STAT3-SNAIL signaling
pathway. Mol Cancer Res. 9:1658–1667. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Eke PI, Dye BA, Wei L, Thornton-Evans GO
and Genco RJ: CDC periodontal disease surveillance workgroup: James
beck (university of north carolina, chapel hill, usa), gordon
douglass (past president, american academy of periodontology), roy
page (university of washin: Prevalence of periodontitis in adults
in the united states: 2009 and 2010. J Dent Res. 91:914–920. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Natarajan E and Eisenberg E: Contemporary
concepts in the diagnosis of oral cancer and precancer. Dent Clin
North Am. 55:63–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dehai C, Bo P, Qiang T, Lihua S, Fang L,
Shi J, Jingyan C, Yan Y, Guangbin W and Zhenjun Y: Enhanced
invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells after co-culture with
THP-1-derived macrophages via the induction of EMT by IL-6. Immunol
Lett. 160:1–10. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim S, Lee J, Jeon M, Lee JE and Nam SJ:
MEK-dependent IL-8 induction regulates the invasiveness of
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. 37:4991–4999.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Li L, Guo X, Jin X, Sun W, Zhang X
and Xu RC: Interleukin-6 signaling regulates anchorage-independent
growth, proliferation, adhesion and invasion in human ovarian
cancer cells. Cytokine. 59:228–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abiko Y, Sato T, Mayanagi G and Takahashi
N: Profiling of subgingival plaque biofilm microflora from
periodontally healthy subjects and from subjects with periodontitis
using quantitative real-time PCR. J Periodontal Res. 45:389–395.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wolff L, Dahlen G and Aeppli D: Bacteria
as risk markers for periodontitis. J Periodontol. 65:498–510. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Yang L, Oppenheim JJ and Howard
MZ: Cellular pharmacology studies of shikonin derivatives.
Phytother Res. 16:199–209. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim DJ, Lee JH, Park HR and Choi YW:
Acetylshikonin inhibits growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma by
inducing apoptosis. Arch Oral Biol. 70:149–157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee HJ, Lee HJ, Magesh V, Nam D, Lee EO,
Ahn KS, Jung MH, Ahn KS, Kim DK, Kim JY and Kim SH: Shikonin,
acetylshikonin and isobutyroylshikonin inhibit VEGF-induced
angiogenesis and suppress tumor growth in lewis lung
carcinoma-bearing mice. Yakugaku Zasshi. 128:1681–1688. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moon J, Koh SS, Malilas W, Cho IR,
Kaewpiboon C, Kaowinn S, Lee K, Jhun BH, Choi YW and Chung YH:
Acetylshikonin induces apoptosis of hepatitis B virus X
protein-expressing human hepatocellular carcinoma cells via
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Eur J Pharmacol. 735:132–140. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
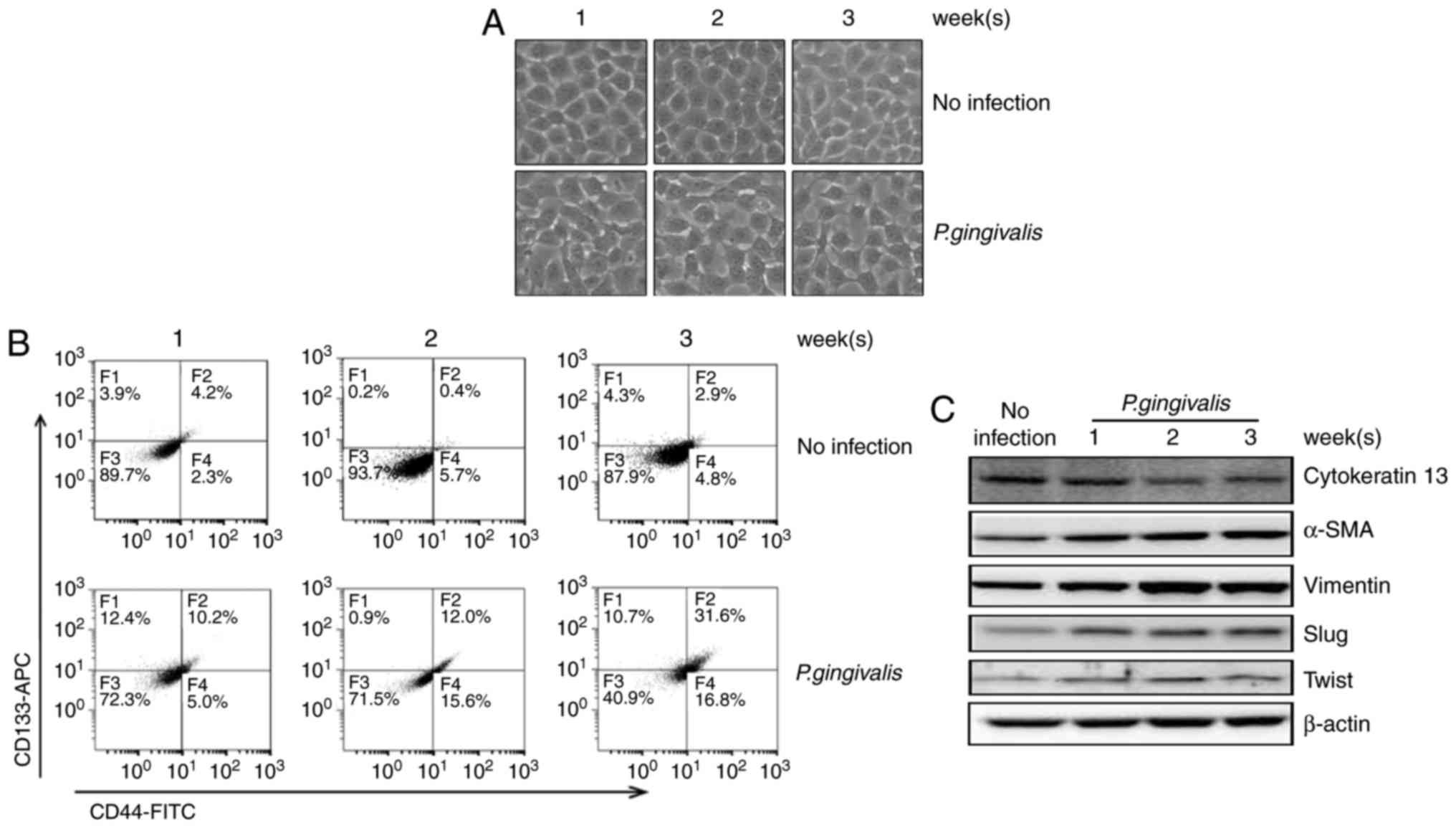
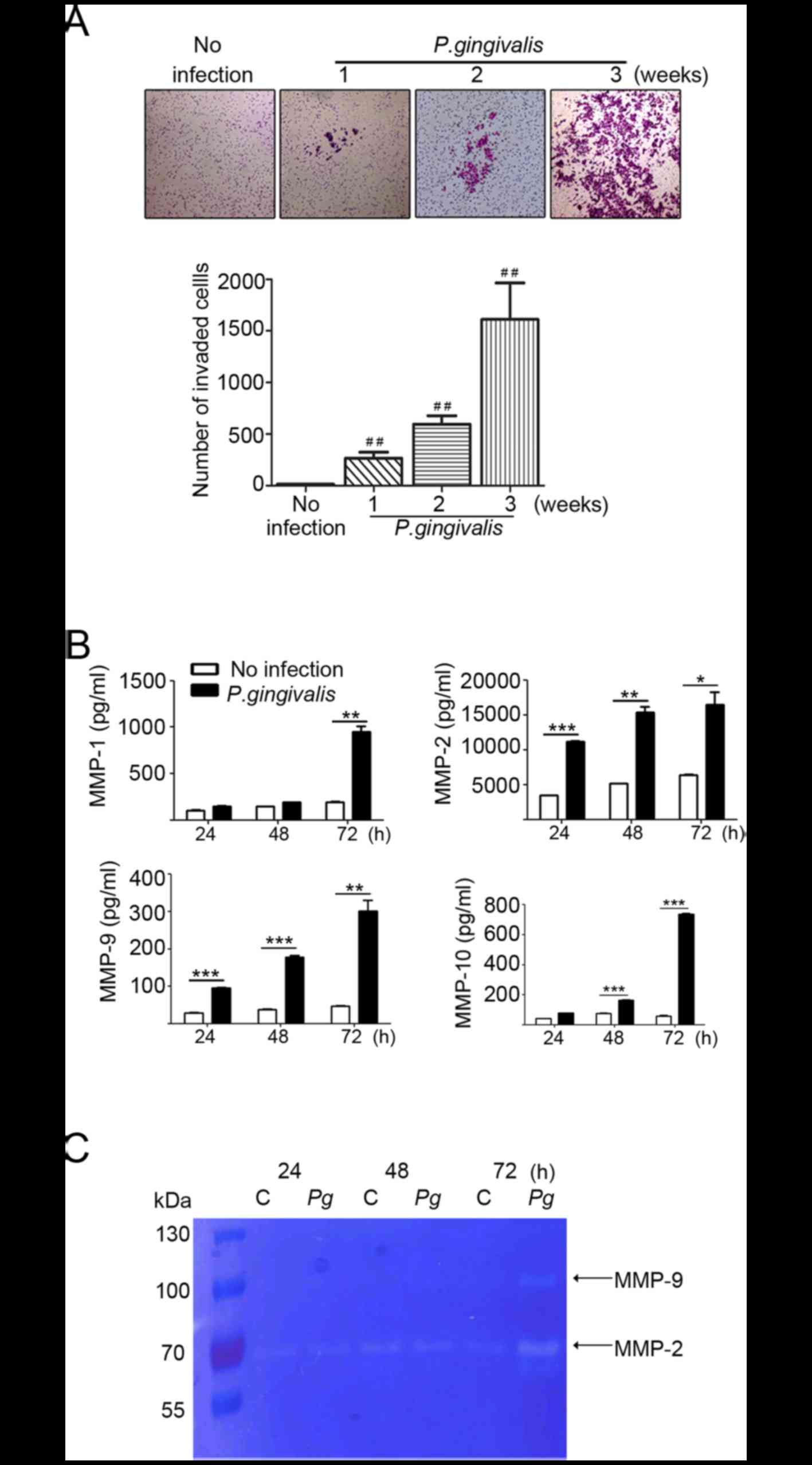
Ha NH, Woo BH, Kim DJ, Ha ES, Choi JI, Kim
SJ, Park BS, Lee JH and Park HR: Prolonged and repetitive exposure
to porphyromonas gingivalis increases aggressiveness of oral cancer
cells by promoting acquisition of cancer stem cell properties.
Tumour Biol. 36:9947–9960. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Okamoto A, Chikamatsu K, Sakakura K,
Hatsushika K, Takahashi G and Masuyama K: Expansion and
characterization of cancer stem-like cells in squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. Oral Oncol. 45:633–639. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cao L, Zhou Y, Zhai B, Liao J, Xu W, Zhang
R, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen L, Qian H, et al: Sphere-forming cell
subpopulations with cancer stem cell properties in human hepatoma
cell lines. BMC Gastroenterol. 11:712011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Murray GI, Duncan ME, O'Neil P, Melvin WT
and Fothergill JE: Matrix metalloproteinase-1 is associated with
poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Nat Med. 2:461–462. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gu ZD, Li JY, Li M, Gu J, Shi XT, Ke Y and
Chen KN: Matrix metalloproteinases expression correlates with
survival in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J
Gastroenterol. 100:1835–1843. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gong L, Wu D, Zou J, Chen J, Chen L, Chen
Y, Ni C and Yuan H: Prognostic impact of serum and tissue MMP-9 in
non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Oncotarget. 7:18458–18468. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bodet C, Chandad F and Grenier D:
Modulation of cytokine production by porphyromonas gingivalis in a
macrophage and epithelial cell co-culture model. Microbes Infect.
7:448–456. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sandros J, Karlsson C, Lappin DF, Madianos
PN, Kinane DF and Papapanou PN: Cytokine responses of oral
epithelial cells to porphyromonas gingivalis infection. J Dent Res.
79:1808–1814. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao JJ, Feng XP, Zhang XL and Le KY:
Effect of porphyromonas gingivalis and lactobacillus acidophilus on
secretion of IL1B, IL6 and IL8 by gingival epithelial cells.
Inflammation. 35:1330–1337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Beklen A, Ainola M, Hukkanen M, Gürgan C,
Sorsa T and Konttinen YT: MMPs, IL-1 and TNF are regulated by IL-17
in periodontitis. J Dent Res. 86:347–351. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Franco C, Patricia HR, Timo S, Claudia B
and Marcela H: Matrix metalloproteinases as regulators of
periodontal inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E4402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mauviel A: Cytokine regulation of
metalloproteinase gene expression. J Cell Biochem. 53:288–295.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Teng J, Wang X, Xu Z and Tang N:
HBx-dependent activation of twist mediates STAT3 control of
epithelium-mesenchymal transition of liver cells. J Cell Biochem.
114:1097–1104. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Iqbal J, McRae S, Banaudha K, Mai T and
Waris G: Mechanism of hepatitis C virus (HCV)-induced osteopontin
and its role in epithelial to mesenchymal transition of
hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 288:36994–37009. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Horikawa T, Yoshizaki T, Kondo S, Furukawa
M, Kaizaki Y and Pagano JS: Epstein-barr virus latent membrane
protein 1 induces snail and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 104:1160–1167.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chandrakesan P, Roy B, Jakkula LU, Ahmed
I, Ramamoorthy P, Tawfik O, Papineni R, Houchen C, Anant S and Umar
S: Utility of a bacterial infection model to study
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, mesenchymal-epithelial
transition or tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 33:2639–2654. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sztukowska MN, Ojo A, Ahmed S, Carenbauer
AL, Wang Q, Shumway B, Jenkinson HF, Wang H, Darling DS and Lamont
RJ: Porphyromonas gingivalis initiates a mesenchymal-like
transition through ZEB1 in gingival epithelial cells. Cell
Microbiol. 18:844–858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
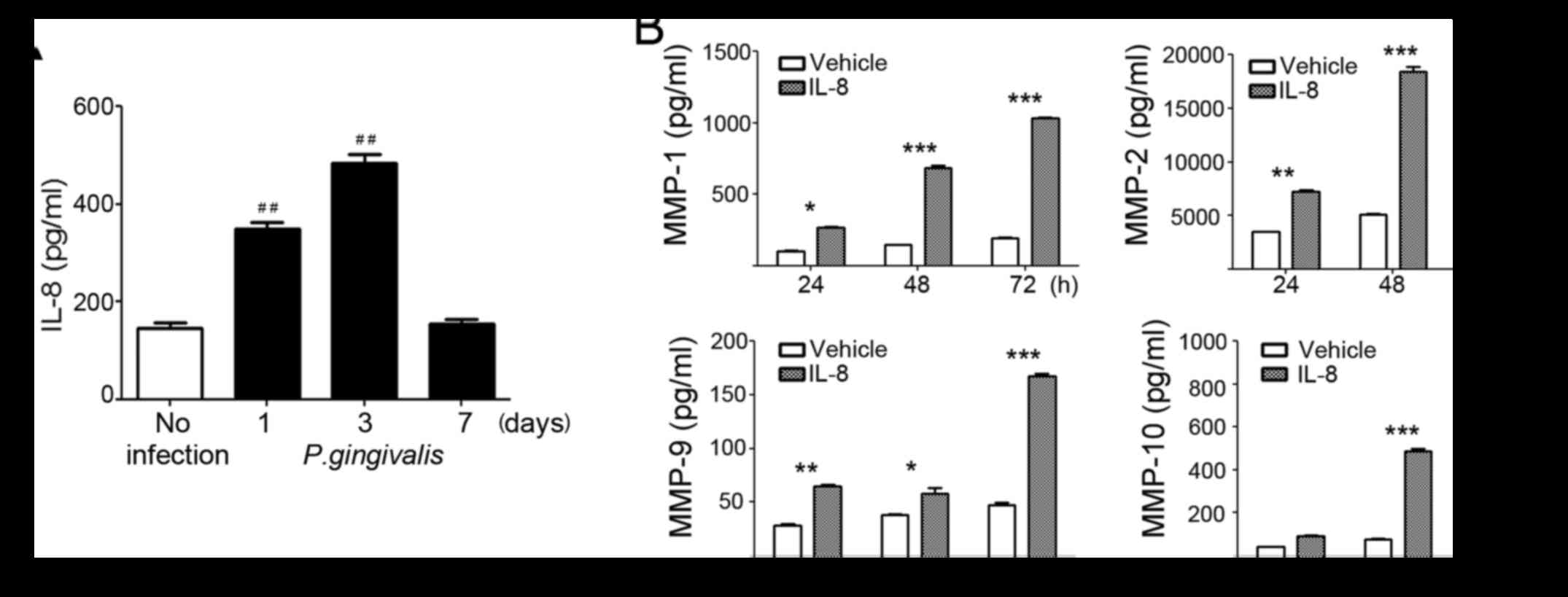
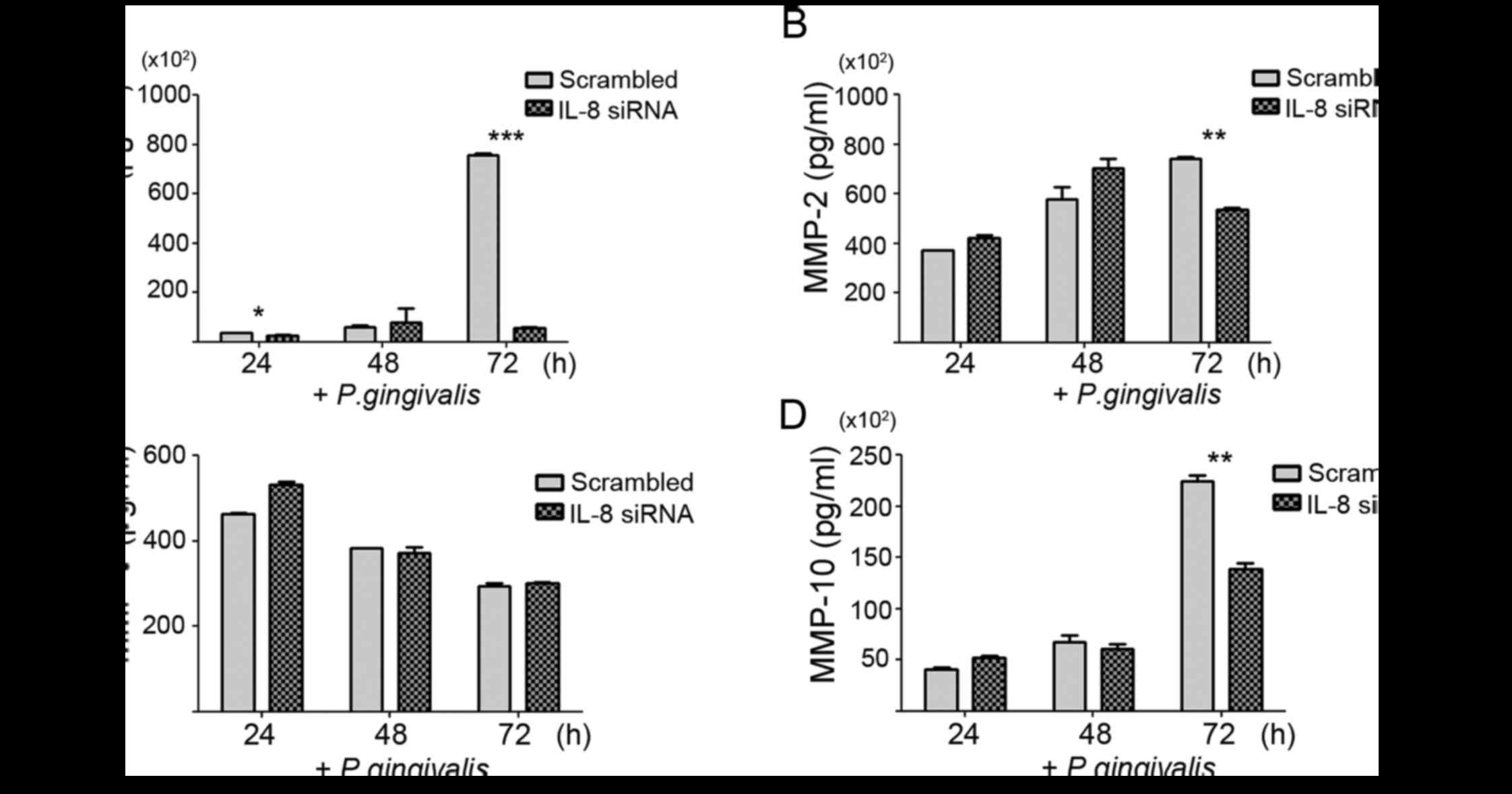
Ha NH, Park DG, Woo BH, Kim DJ, Choi JI,
Park BS, Kim YD, Lee JH and Park HR: Porphyromonas gingivalis
increases the invasiveness of oral cancer cells by upregulating
IL-8 and MMPs. Cytokine. 86:64–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Y, Xu RC, Zhang XL, Niu XL, Qu Y, Li
LZ and Meng XY: Interleukin-8 secretion by ovarian cancer cells
increases anchorage-independent growth, proliferation, angiogenic
potential, adhesion and invasion. Cytokine. 59:145–155. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ou Z, Wang Y, Liu L, Li L, Yeh S, Qi L and
Chang C: Tumor microenvironment B cells increase bladder cancer
metastasis via modulation of the IL-8/androgen receptor (AR)/MMPs
signals. Oncotarget. 6:26065–26078. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
George VC, Dellaire G and Rupasinghe HPV:
Plant flavonoids in cancer chemoprevention: Role in genome
stability. J Nutr Biochem. 45:1–14. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Niedzwiecki A, Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T and
Rath M: Anticancer efficacy of polyphenols and their combinations.
Nutrients. 8:E5522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|