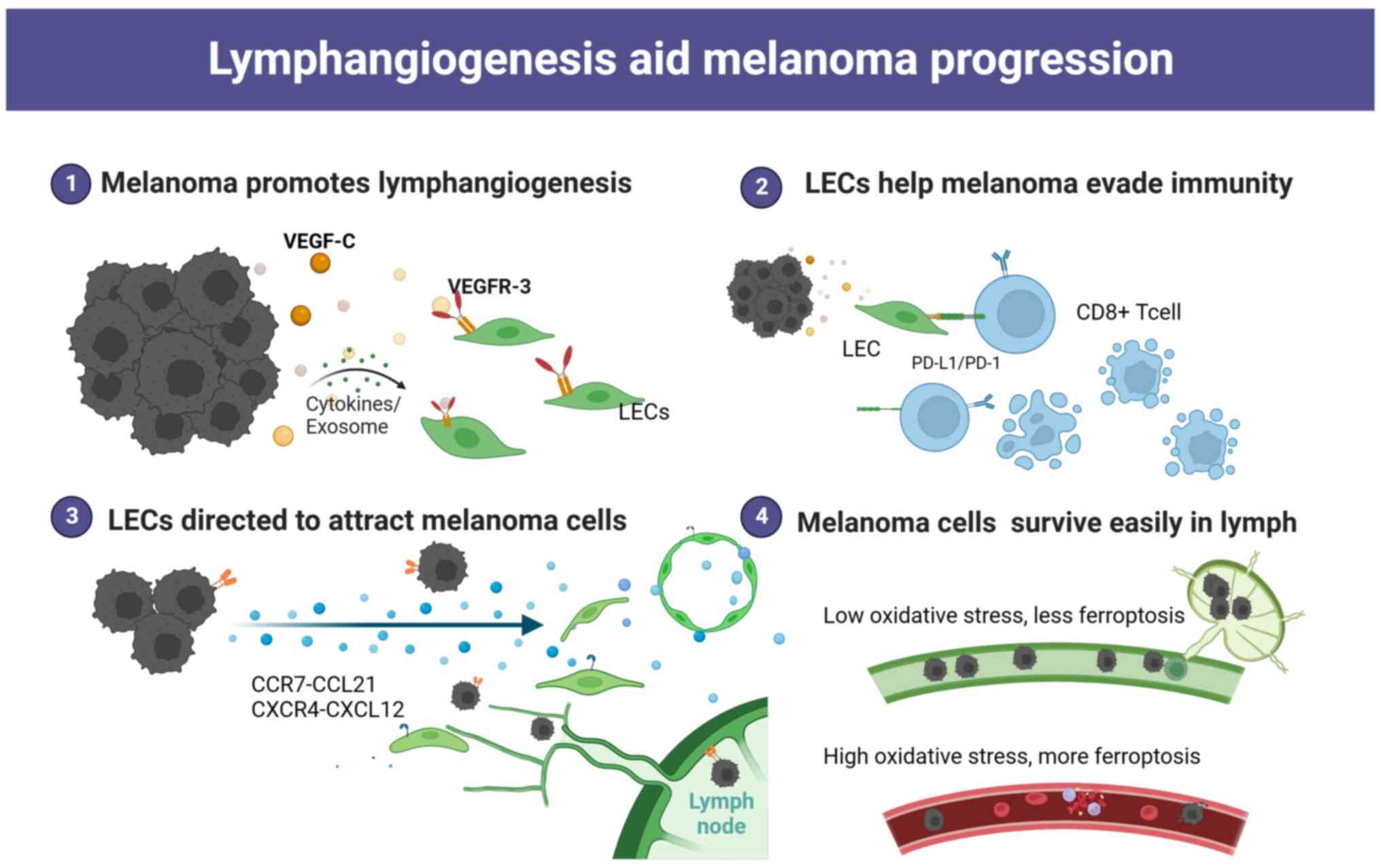
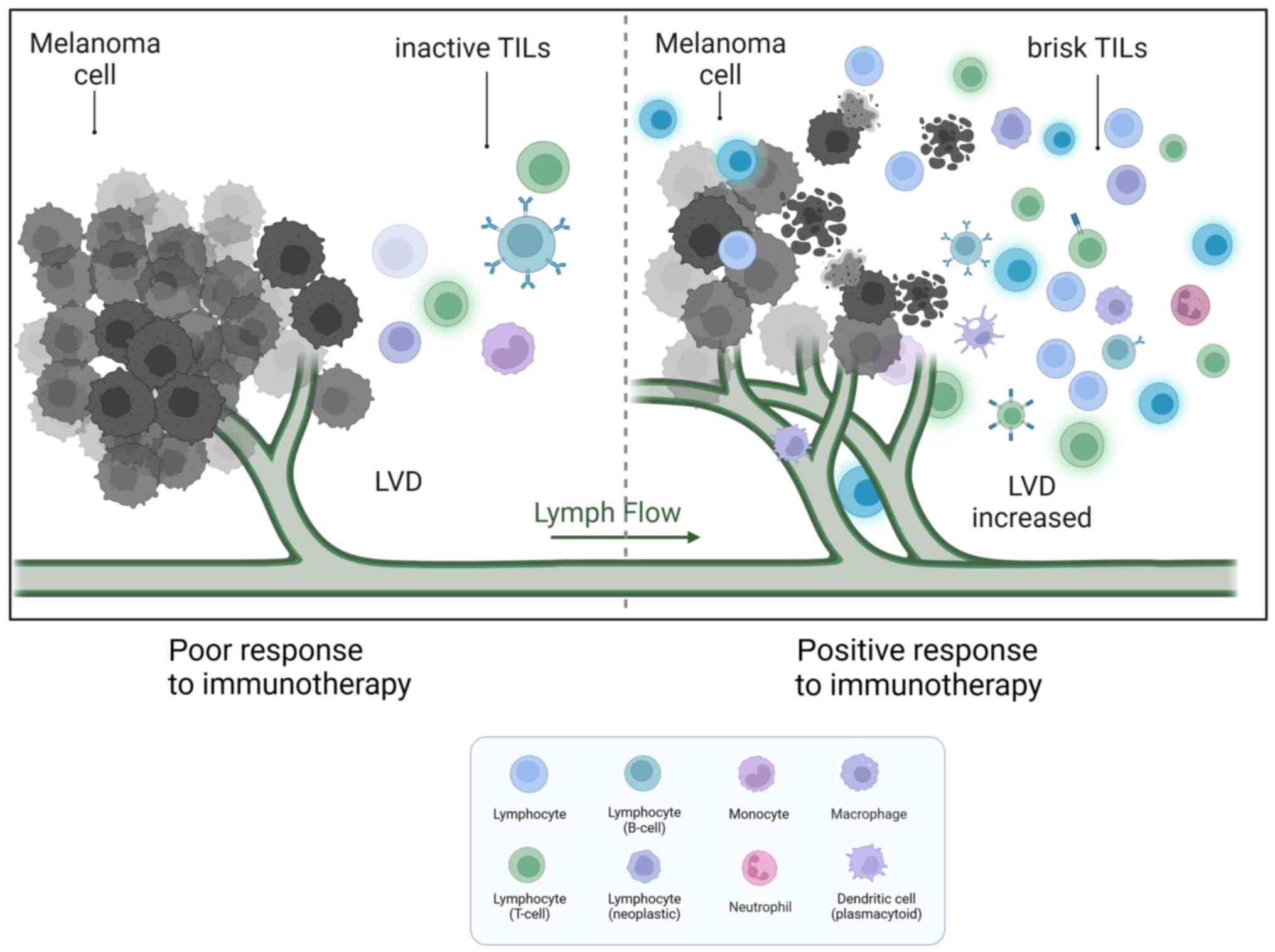
|
1
|
Hussein Al-Janabi M, Mohammad JG, Mohsen
AY, Saad A and Issa R: Metastatic melanoma to the gallbladder
presented as a polyp with acute cholecystitis: A case report from
Syria. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 76:1035142022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Eddy K and Chen S: Overcoming immune
evasion in melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 21:89842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schadendorf D, van Akkooi ACJ, Berking C,
Griewank KG, Gutzmer R, Hauschild A, Stang A, Roesch A and Ugurel
S: Melanoma. Lancet. 392:971–984. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Falk Delgado A, Zommorodi S and Falk
Delgado A: Sentinel lymph node biopsy and complete lymph node
dissection for melanoma. Curr Oncol Rep. 21:542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hartman RI and Lin JY: Cutaneous
melanoma-a review in detection, staging, and management. Hematol
Oncol Clin North Am. 33:25–38. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ribas A, Hamid O, Daud A, Hodi FS, Wolchok
JD, Kefford R, Joshua AM, Patnaik A, Hwu WJ, Weber JS, et al:
Association of pembrolizumab with tumor response and survival among
patients with advanced melanoma. JAMA. 315:1600–1609. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Knackstedt T, Knackstedt RW, Couto R and
Gastman B: Malignant melanoma: Diagnostic and management update.
Plast Reconstr Surg. 142:202e–216e. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Faries MB, Thompson JF, Cochran AJ,
Andtbacka RH, Mozzillo N, Zager JS, Jahkola T, Bowles TL, Testori
A, Beitsch PD, et al: Completion dissection or observation for
sentinel-node metastasis in melanoma. N Engl J Med. 376:2211–2222.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pasquali S, van der Ploeg APT, Mocellin S,
Stretch JR, Thompson JF and Scolyer RA: Lymphatic biomarkers in
primary melanomas as predictors of regional lymph node metastasis
and patient outcomes. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 26:326–337. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma Q, Dieterich LC, Ikenberg K, Bachmann
SB, Mangana J, Proulx ST, Amann VC, Levesque MP, Dummer R, Baluk P,
et al: Unexpected contribution of lymphatic vessels to promotion of
distant metastatic tumor spread. Sci Adv. 4:eaat47582018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oliver G, Kipnis J, Randolph GJ and Harvey
NL: The lymphatic vasculature in the 21st century: Novel functional
roles in homeostasis and disease. Cell. 182:270–296. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Petrova TV and Koh GY: Organ-specific
lymphatic vasculature: From development to pathophysiology. J Exp
Med. 215:35–49. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Johnson LA: In sickness and in health: The
immunological roles of the lymphatic system. Int J Mol Sci.
22:44582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pereira ER, Kedrin D, Seano G, Gautier O,
Meijer EFJ, Jones D, Chin SM, Kitahara S, Bouta EM, Chang J, et al:
Lymph node metastases can invade local blood vessels, exit the
node, and colonize distant organs in mice. Science. 359:1403–1407.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takeda A, Hollmén M, Dermadi D, Pan J,
Brulois KF, Kaukonen R, Lönnberg T, Boström P, Koskivuo I, Irjala
H, et al: Single-cell survey of human lymphatics unveils marked
endothelial cell heterogeneity and mechanisms of homing for
neutrophils. Immunity. 51:561–572.e5. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rodda LB, Lu E, Bennett ML, Sokol CL, Wang
X, Luther SA, Barres BA, Luster AD, Ye CJ and Cyster JG:
Single-cell RNA sequencing of lymph node stromal cells reveals
niche-associated heterogeneity. Immunity. 48:1014–1028.e6. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fujimoto N, He Y, D'Addio M, Tacconi C,
Detmar M and Dieterich LC: Single-cell mapping reveals new markers
and functions of lymphatic endothelial cells in lymph nodes. PLoS
Biol. 18:e30007042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang L, Zhu L, Yao X, Lou X, Wan J, Duan
X, Pan L, Li A, Gu Z, Wang M, et al: Paclitaxel treatment enhances
lymphatic metastasis of B16F10 melanoma cells via CCL21/CCR7 axis.
Int J Biol Sci. 18:1476–1490. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cristiani CM, Turdo A, Ventura V, Apuzzo
T, Capone M, Madonna G, Mallardo D, Garofalo C, Giovannone ED,
Grimaldi AM, et al: Accumulation of circulating CCR7+
natural killer cells marks melanoma evolution and reveals a
CCL19-dependent metastatic pathway. Cancer Immunol Res. 7:841–852.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mendt M and Cardier JE: Activation of the
CXCR4 chemokine receptor enhances biological functions associated
with B16 melanoma liver metastasis. Melanoma Res. 27:300–308. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McConnell AT, Ellis R, Pathy B, Plummer R,
Lovat PE and O'Boyle G: The prognostic significance and impact of
the CXCR4-CXCR7-CXCL12 axis in primary cutaneous melanoma. Br J
Dermatol. 175:1210–1220. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Korbecki J, Grochans S, Gutowska I,
Barczak K and Baranowska-Bosiacka I: CC chemokines in a tumor: A
review of pro-cancer and anti-cancer properties of receptors CCR5,
CCR6, CCR7, CCR8, CCR9, and CCR10 ligands. Int J Mol Sci.
21:76192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alimohammadi M, Rahimi A, Faramarzi F,
Alizadeh-Navaei R and Rafiei A: Overexpression of chemokine
receptor CXCR4 predicts lymph node metastatic risk in patients with
melanoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine.
148:1556912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Doron H, Amer M, Ershaid N, Blazquez R,
Shani O, Lahav TG, Cohen N, Adler O, Hakim Z, Pozzi S, et al:
Inflammatory activation of astrocytes facilitates melanoma brain
tropism via the CXCL10-CXCR3 signaling axis. Cell Rep.
28:1785–1798.e6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Soler-Cardona A, Forsthuber A, Lipp K,
Ebersberger S, Heinz M, Schossleitner K, Buchberger E, Gröger M,
Petzelbauer P, Hoeller C, et al: CXCL5 facilitates melanoma
cell-neutrophil interaction and lymph node metastasis. J Invest
Dermatol. 138:1627–1635. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Broggi MAS, Maillat L, Clement CC, Bordry
N, Corthésy P, Auger A, Matter M, Hamelin R, Potin L, Demurtas D,
et al: Tumor-associated factors are enriched in lymphatic exudate
compared to plasma in metastatic melanoma patients. J Exp Med.
216:1091–1107. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ubellacker JM, Tasdogan A, Ramesh V, Shen
B, Mitchell EC, Martin-Sandoval MS, Gu Z, McCormick ML, Durham AB,
Spitz DR, et al: Lymph protects metastasizing melanoma cells from
ferroptosis. Nature. 585:113–118. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Piskounova E, Agathocleous M, Murphy MM,
Hu Z, Huddlestun SE, Zhao Z, Leitch AM, Johnson TM, DeBerardinis RJ
and Morrison SJ: Oxidative stress inhibits distant metastasis by
human melanoma cells. Nature. 527:186–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Habenicht LM, Kirschbaum SB, Furuya M,
Harrell MI and Ruddell A: Tumor regulation of lymph node lymphatic
sinus growth and lymph flow in mice and in humans. Yale J Biol Med.
90:403–415. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peppicelli S, Bianchini F and Calorini L:
Inflammatory cytokines induce vascular endothelial growth factor-C
expression in melanoma-associated macrophages and stimulate
melanoma lymph node metastasis. Oncol Lett. 8:1133–1138. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leary N, Walser S, He Y, Cousin N, Pereira
P, Gallo A, Collado-Diaz V, Halin C, Garcia-Silva S, Peinado H and
Dieterich LC: Melanoma-derived extracellular vesicles mediate
lymphatic remodelling and impair tumour immunity in draining lymph
nodes. J Extracell Vesicles. 11:e121972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dadras SS, Paul T, Bertoncini J, Brown LF,
Muzikansky A, Jackson DG, Ellwanger U, Garbe C, Mihm MC and Detmar
M: Tumor lymphangiogenesis: A novel prognostic indicator for
cutaneous melanoma metastasis and survival. Am J Pathol.
162:1951–1960. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pastushenko I, Van den Eynden GG,
Vicente-Arregui S, Prieto-Torres L, Alvarez-Alegret R, Querol I,
Dirix LY, Carapeto FJ, Vermeulen PB and Van Laere SJ: Increased
angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in metastatic sentinel lymph
nodes is associated with nonsentinel lymph node involvement and
distant metastasis in patients with melanoma. Am J Dermatopathol.
38:338–346. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ayubi E and Safiri S: Lymphatic vessel
density and VEGF-C expression as independent predictors of melanoma
metastases: Methodological issues. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.
71:604–605. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pastushenko I, Vermeulen PB, Carapeto FJ,
Van den Eynden G, Rutten A, Ara M, Dirix LY and Van Laere S: Blood
microvessel density, lymphatic microvessel density and lymphatic
invasion in predicting melanoma metastases: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Br J Dermatol. 170:66–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Špirić Z, Eri Ž and Erić M: Lymphatic
vessel density and VEGF-C expression as independent predictors of
melanoma metastases. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 70:1653–1659.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Skobe M, Hamberg LM, Hawighorst T,
Schirner M, Wolf GL, Alitalo K and Detmar M: Concurrent induction
of lymphangiogenesis, angiogenesis, and macrophage recruitment by
vascular endothelial growth factor-C in melanoma. Am J Pathol.
159:893–903. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang M, Xu Y, Wen GZ, Wang Q and Yuan SM:
Rapamycin suppresses angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in melanoma
by downregulating VEGF-A/VEGFR-2 and VEGF-C/VEGFR-3 expression.
Onco Targets Ther. 12:4643–4654. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee JY, Hong SH, Shin M, Heo HR and Jang
IH: Blockade of FLT4 suppresses metastasis of melanoma cells by
impaired lymphatic vessels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
478:733–738. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Korhonen EA, Murtomäki A, Jha SK, Anisimov
A, Pink A, Zhang Y, Stritt S, Liaqat I, Stanczuk L, Alderfer L, et
al: Lymphangiogenesis requires Ang2/Tie/PI3K signaling for VEGFR3
cell-surface expression. J Clin Invest. 132:e1554782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rezzola S, Sigmund EC, Halin C and Ronca
R: The lymphatic vasculature: An active and dynamic player in
cancer progression. Med Res Rev. 42:576–614. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wouters J, Kalender-Atak Z, Minnoye L,
Spanier KI, De Waegeneer M, Bravo González-Blas C, Mauduit D, Davie
K, Hulselmans G, Najem A, et al: Robust gene expression programs
underlie recurrent cell states and phenotype switching in melanoma.
Nat Cell Biol. 22:986–998. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Arozarena I and Wellbrock C: Phenotype
plasticity as enabler of melanoma progression and therapy
resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:377–391. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Reticker-Flynn NE, Zhang W, Belk JA, Basto
PA, Escalante NK, Pilarowski GOW, Bejnood A, Martins MM, Kenkel JA,
Linde IL, et al: Lymph node colonization induces tumor-immune
tolerance to promote distant metastasis. Cell. 185:1924–1942.e23.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
García-Silva S, Benito-Martín A, Nogués L,
Hernández-Barranco A, Mazariegos MS, Santos V, Hergueta-Redondo M,
Ximénez-Embún P, Kataru RP, Lopez AA, et al: Melanoma-derived small
extracellular vesicles induce lymphangiogenesis and metastasis
through an NGFR-dependent mechanism. Nat Cancer. 2:1387–1405. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gowda R, Robertson BM, Iyer S, Barry J,
Dinavahi SS and Robertson GP: The role of exosomes in metastasis
and progression of melanoma. Cancer Treat Rev. 85:1019752020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wakisaka N, Hasegawa Y, Yoshimoto S, Miura
K, Shiotani A, Yokoyama J, Sugasawa M, Moriyama-Kita M, Endo K and
Yoshizaki T: Primary tumor-secreted lymphangiogenic factors induce
pre-metastatic lymphvascular niche formation at sentinel lymph
nodes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01440562015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li L, Wu J, Abdi R, Jewell CM and Bromberg
JS: Lymph node fibroblastic reticular cells steer immune responses.
Trends Immunol. 42:723–734. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rovera C, Berestjuk I, Lecacheur M,
Tavernier C, Diazzi S, Pisano S, Irondelle M, Mallavialle A,
Albrengues J, Gaggioli C, et al: Secretion of IL1 by
dedifferentiated melanoma cells inhibits JAK1-STAT3-driven
actomyosin contractility of lymph node fibroblastic reticular
cells. Cancer Res. 82:1774–1788. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Clasper S, Royston D, Baban D, Cao Y,
Ewers S, Butz S, Vestweber D and Jackson DG: A novel gene
expression profile in lymphatics associated with tumor growth and
nodal metastasis. Cancer Res. 68:7293–7303. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Van de Velde M, Ebroin M, Durré T, Joiret
M, Gillot L, Blacher S, Geris L, Kridelka F and Noel A: Tumor
exposed-lymphatic endothelial cells promote primary tumor growth
via IL6. Cancer Lett. 497:154–164. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dieterich LC, Ikenberg K, Cetintas T,
Kapaklikaya K, Hutmacher C and Detmar M: Tumor-associated lymphatic
vessels upregulate PDL1 to inhibit T-cell activation. Front
Immunol. 8:662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lane RS, Femel J, Breazeale AP, Loo CP,
Thibault G, Kaempf A, Mori M, Tsujikawa T, Chang YH and Lund AW:
IFNγ-activated dermal lymphatic vessels inhibit cytotoxic T cells
in melanoma and inflamed skin. J Exp Med. 215:3057–3074. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nörder M, Gutierrez MG, Zicari S, Cervi E,
Caruso A and Guzmán CA: Lymph node-derived lymphatic endothelial
cells express functional costimulatory molecules and impair
dendritic cell-induced allogenic T-cell proliferation. FASEB J.
26:2835–2846. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lund AW, Duraes FV, Hirosue S, Raghavan
VR, Nembrini C, Thomas SN, Issa A, Hugues S and Swartz MA: VEGF-C
promotes immune tolerance in B16 melanomas and cross-presentation
of tumor antigen by lymph node lymphatics. Cell Rep. 1:191–199.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
de Winde CM, Munday C and Acton SE:
Molecular mechanisms of dendritic cell migration in immunity and
cancer. Med Microbiol Immunol. 209:515–529. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Swartz MA and Lund AW: Lymphatic and
interstitial flow in the tumour microenvironment: Linking
mechanobiology with immunity. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:210–219. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dubrot J, Duraes FV, Harlé G, Schlaeppi A,
Brighouse D, Madelon N, Göpfert C, Stokar-Regenscheit N, Acha-Orbea
H, Reith W, et al: Absence of MHC-II expression by lymph node
stromal cells results in autoimmunity. Life Sci Alliance.
1:e2018001642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li CY, Park HJ, Shin J, Baik JE, Mehrara
BJ and Kataru RP: Tumor-associated lymphatics upregulate MHC-II to
suppress tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Int J Mol Sci.
23:134702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lukacs-Kornek V, Malhotra D, Fletcher AL,
Acton SE, Elpek KG, Tayalia P, Collier AR and Turley SJ: Regulated
release of nitric oxide by nonhematopoietic stroma controls
expansion of the activated T cell pool in lymph nodes. Nat Immunol.
12:1096–1104. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Antohe M, Nedelcu RI, Nichita L, Popp CG,
Cioplea M, Brinzea A, Hodorogea A, Calinescu A, Balaban M, Ion DA,
et al: Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes: The regulator of melanoma
evolution. Oncol Lett. 17:4155–4161. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mihm MC Jr and Mulé JJ: Reflections on the
histopathology of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in melanoma and
the host immune response. Cancer Immunol Res. 3:827–835. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Durante MA, Rodriguez DA, Kurtenbach S,
Kuznetsov JN, Sanchez MI, Decatur CL, Snyder H, Feun LG,
Livingstone AS and Harbour JW: Single-cell analysis reveals new
evolutionary complexity in uveal melanoma. Nat Commun. 11:4962020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Li H, van der Leun AM, Yofe I, Lubling Y,
Gelbard-Solodkin D, van Akkooi ACJ, van den Braber M, Rozeman EA,
Haanen JBAG, Blank CU, et al: Dysfunctional CD8 T cells form a
proliferative, dynamically regulated compartment within human
melanoma. Cell. 176:775–789.e18. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yang J, Lian JW, Chin YH, Wang L, Lian A,
Murphy GF and Zhou L: Assessing the prognostic significance of
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with melanoma using
pathologic features identified by natural language processing. JAMA
Netw Open. 4:e21263372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Khong HT, Wang QJ and Rosenberg SA:
Identification of multiple antigens recognized by
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from a single patient: Tumor escape
by antigen loss and loss of MHC expression. J Immunother.
27:184–190. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Maeurer MJ, Gollin SM, Martin D, Swaney W,
Bryant J, Castelli C, Robbins P, Parmiani G, Storkus WJ and Lotze
MT: Tumor escape from immune recognition: Lethal recurrent melanoma
in a patient associated with downregulation of the peptide
transporter protein TAP-1 and loss of expression of the
immunodominant MART-1/Melan-A antigen. J Clin Invest. 98:1633–1641.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Al-Batran SE, Rafiyan MR, Atmaca A,
Neumann A, Karbach J, Bender A, Weidmann E, Altmannsberger HM,
Knuth A and Jäger E: Intratumoral T-cell infiltrates and MHC class
I expression in patients with stage IV melanoma. Cancer Res.
65:3937–3941. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rodig SJ, Gusenleitner D, Jackson DG,
Gjini E, Giobbie-Hurder A, Jin C, Chang H, Lovitch SB, Horak C,
Weber JS, et al: MHC proteins confer differential sensitivity to
CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade in untreated metastatic melanoma. Sci
Transl Med. 10:eaar33422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Passarelli A, Mannavola F, Stucci LS,
Tucci M and Silvestris F: Immune system and melanoma biology: A
balance between immunosurveillance and immune escape. Oncotarget.
8:106132–106142. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Failli A, Legitimo A, Orsini G, Romanini A
and Consolini R: Numerical defect of circulating dendritic cell
subsets and defective dendritic cell generation from monocytes of
patients with advanced melanoma. Cancer Lett. 337:184–192. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS, Moreno BH, Saco J,
Escuin-Ordinas H, Rodriguez GA, Zaretsky JM, Sun L, Hugo W, Wang X,
et al: Interferon receptor signaling pathways regulating PD-L1 and
PD-L2 expression. Cell Rep. 19:1189–1201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jacobs JFM, Nierkens S, Figdor CG, de
Vries IJM and Adema GJ: Regulatory T cells in melanoma: The final
hurdle towards effective immunotherapy? Lancet Oncol. 13:e32–e42.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Petrova V, Arkhypov I, Weber R, Groth C,
Altevogt P, Utikal J and Umansky V: Modern aspects of immunotherapy
with checkpoint inhibitors in melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 21:23672020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Falleni M, Savi F, Tosi D, Agape E, Cerri
A, Moneghini L and Bulfamante GP: M1 and M2 macrophages'
clinicopathological significance in cutaneous melanoma. Melanoma
Res. 27:200–210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Chen G, Huang AC, Zhang W, Zhang G, Wu M,
Xu W, Yu Z, Yang J, Wang B, Sun H, et al: Exosomal PD-L1
contributes to immunosuppression and is associated with anti-PD-1
response. Nature. 560:382–386. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Fankhauser M, Broggi MAS, Potin L, Bordry
N, Jeanbart L, Lund AW, Da Costa E, Hauert S, Rincon-Restrepo M,
Tremblay C, et al: Tumor lymphangiogenesis promotes T cell
infiltration and potentiates immunotherapy in melanoma. Sci Transl
Med. 9:eaal47122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Moussion C and Turley SJ: Tumour lymph
vessels boost immunotherapy. Nature. 552:340–342. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Lund AW, Wagner M, Fankhauser M, Steinskog
ES, Broggi MA, Spranger S, Gajewski TF, Alitalo K, Eikesdal HP,
Wiig H and Swartz MA: Lymphatic vessels regulate immune
microenvironments in human and murine melanoma. J Clin Invest.
126:3389–3402. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bordry N, Broggi MAS, de Jonge K,
Schaeuble K, Gannon PO, Foukas PG, Danenberg E, Romano E,
Baumgaertner P, Fankhauser M, et al: Lymphatic vessel density is
associated with CD8+ T cell infiltration and
immunosuppressive factors in human melanoma. Oncoimmunology.
7:e14628782018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sautès-Fridman C, Petitprez F, Calderaro J
and Fridman WH: Tertiary lymphoid structures in the era of cancer
immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:307–325. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Helmink BA, Reddy SM, Gao J, Zhang S,
Basar R, Thakur R, Yizhak K, Sade-Feldman M, Blando J, Han G, et
al: B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy
response. Nature. 577:549–555. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Cipponi A, Mercier M, Seremet T, Baurain
JF, Théate I, van den Oord J, Stas M, Boon T, Coulie PG and van
Baren N: Neogenesis of lymphoid structures and antibody responses
occur in human melanoma metastases. Cancer Res. 72:3997–4007. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Ladányi A, Sebestyén T, Mohos A, Liszkay
G, Somlai B, Tóth E and Tímár J: Ectopic lymphoid structures in
primary cutaneous melanoma. Pathol Oncol Res. 20:981–985. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cabrita R, Lauss M, Sanna A, Donia M,
Skaarup Larsen M, Mitra S, Johansson I, Phung B, Harbst K,
Vallon-Christersson J, et al: Tertiary lymphoid structures improve
immunotherapy and survival in melanoma. Nature. 577:561–565. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Maibach F, Sadozai H, Seyed Jafari SM,
Hunger RE and Schenk M: Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and their
prognostic value in cutaneous melanoma. Front Immunol. 11:21052020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|