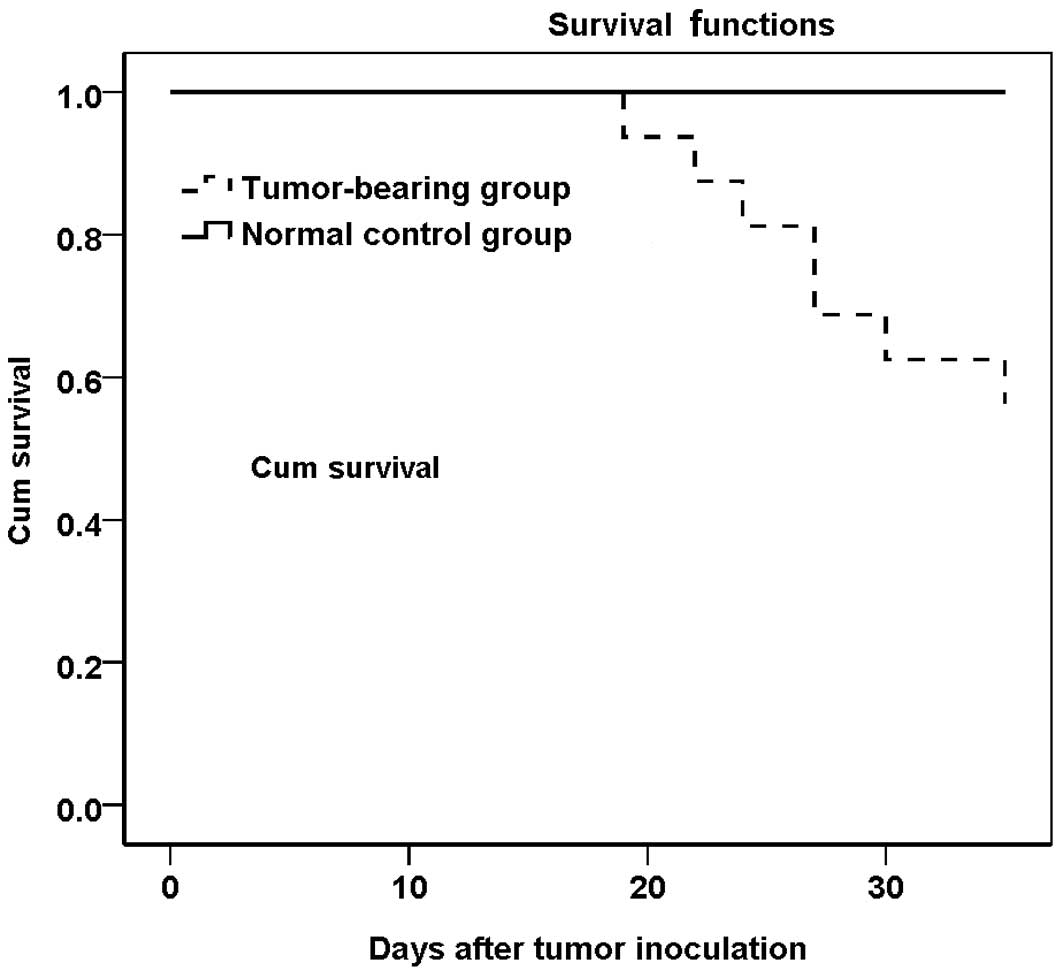
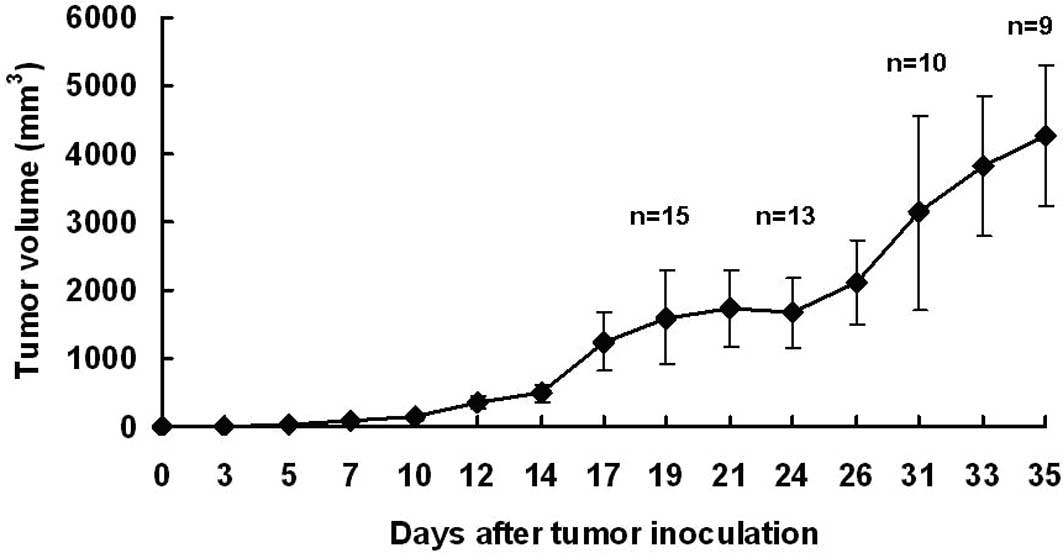
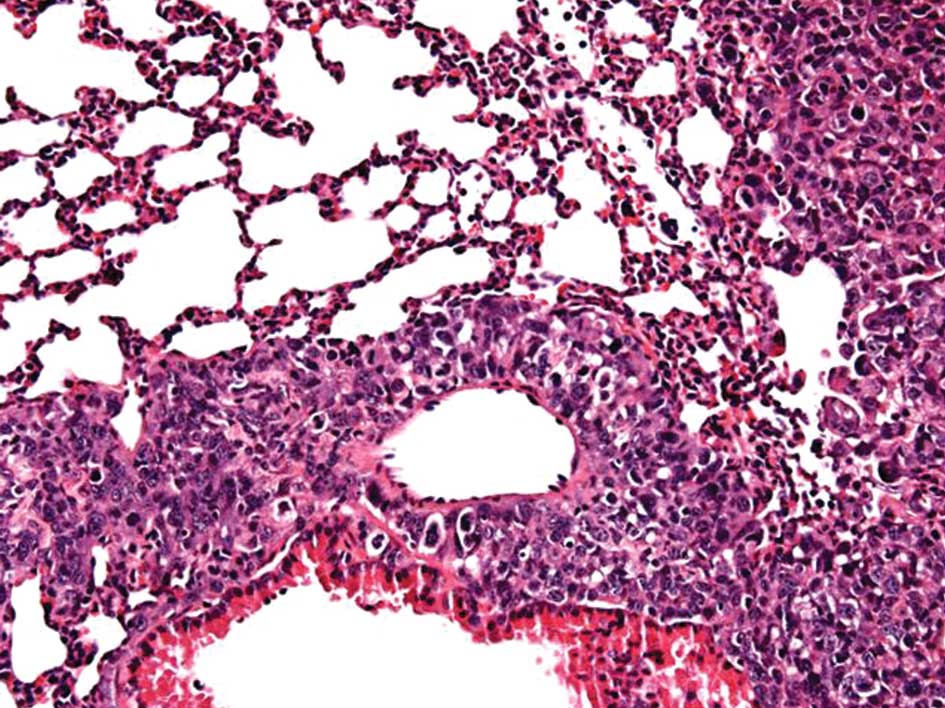
|
1
|
Parkin M, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global Cancer Statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Department of Health EY R.O.C. (Taiwan).
Statistics of causes of death. Department of Health, Executive
Yuan, R.O.C. (Taiwan); 2008
|
|
3
|
Tisdale MJ: Mechanisms of cancer cachexia.
Physiol Rev. 89:381–410. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O’Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, et al:
Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the
suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell.
79:315–328. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Maniwa Y, Okada M, Ishii N and Kiyooka K:
Vascular endothelial growth factor increased by pulmonary surgery
accelerates the growth of micrometastases in metastatic lung
cancer. Chest. 114:1668–1675. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Savai R, Wolf JC, Greschus S, et al:
Analysis of tumor vessel supply in Lewis lung carcinoma in mice by
fluorescent microsphere distribution and imaging with micro-and
flat-panel computed tomography. Am J Pathol. 167:937–946. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen HC: Studies on the inhibitory
mechanism of angiogenesis inhibitor, endostatin. Department of
Biological Sciences, National Sun Yat-Sen University; pp.
1082000
|
|
8
|
Rashidi B, Yang M, Jiang P, et al: A
highly metastatic Lewis lung carcinoma orthotopic green fluorescent
protein model. Clin Exp Metastasis. 18:57–60. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Wu Z, Zuo S, Zhou Y, Chen Y and
Wang X: Establishment of orthotopic Lewis lung cancer model in
mouse. Chin J Lung Cancer. 13:42–47. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Argilés JM, Figueras M, Ametller E, et al:
Effects of CRF2R agonist on tumor growth and cachexia in mice
implanted with Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Muscle Nerve.
37:190–195. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lippman MM, Laster WR, Abbott BJ, Venditti
J and Baratta M: Antitumor activity of macromomycin B (NSC 170105)
against murine leukemias, melanoma, and lung carcinoma. Cancer Res.
35:939–945. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li LM, Shin DM and Fidler IJ:
Intrabronchial implantation of the Lewis lung tumor cell does not
favor tumorigenicity and metastasis. Invasion Metastasis.
10:129–141. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Savai R, Langheinrich AC, Schermuly RT, et
al: Evaluation of angiogenesis using micro-computed tomography in a
xenograft mouse model of lung cancer. Neoplasia. 11:48–56.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Z, Hatori T and Nonaka H: An
experimental model of brain metastasis of lung carcinoma.
Neuropathology. 28:24–28. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Argiles JM, Figueras M, Ametller E, et al:
Effects of CRF2R agonist on tumor growth and cachexia in mice
implanted with Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Muscle Nerve.
37:190–195. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Harlos JP and Weiss L: Differences in the
peripheries of Lewis lung tumor cells growing in different sites in
the mouse. Int J Cancer. 32:745–750. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Papetti M and Herman IM: Mechanisms of
normal and tumor-derived angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
282:C947–970. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhan P, Wang J, Lv XL, et al: Prognostic
value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients
with lung cancer: A systematic review with meta-analysis. J Thorac
Oncol. 4:1094–1103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shimanuki Y, Takahashi K, Cui R, et al:
Role of serum vascular endothelial growth factor in the prediction
of angiogenesis and prognosis for non-small cell lung cancer. Lung.
183:29–42. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li J, Dong X, Xu Z, et al: Endostatin gene
therapy enhances the efficacy of paclitaxel to suppress breast
cancers and metastases in mice. J Biomed Sci. 15:99–109. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maillard CM, Bouquet C, Petitjean MM, et
al: Reduction of brain metastases in plasminogen activator
inhibitor-1-deficient mice with transgenic ocular tumors.
Carcinogenesis. 29:2236–2242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hotz HG, Hines OJ, Masood R, et al: VEGF
antisense therapy inhibits tumor growth and improves survival in
experimental pancreatic cancer. Surgery. 137:192–199. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Langley RR and Fidler IJ: The seed and
soil hypothesis revisited–the role of tumor-stroma interactions in
metastasis to different organs. Int J Cancer. 128:2527–2535.
2011.
|
|
24
|
Chung DC, Zetter BR and Brodt P: Lewis
lung carcinoma variants with differing metastatic specificities
adhere preferentially to different defined extracellular matrix
molecules. Invasion Metastasis. 8:103–117. 1988.
|
|
25
|
Llovera M, Garcia-Martinez C,
Lopez-Soriano J, et al: Protein turnover in skeletal muscle of
tumour-bearing transgenic mice overexpressing the soluble TNF
receptor-1. Cancer Lett. 130:19–27. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Van Royen M, Carbo N, Busquets S, et al:
DNA fragmentation occurs in skeletal muscle during tumor growth: A
link with cancer cachexia? Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 270:533–537.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Al-Majid S and McCarthy DO: Resistance
exercise training attenuates wasting of the extensor digitorum
longus muscle in mice bearing the colon-26 adenocarcinoma. Biol Res
Nurs. 2:155–166. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gupta MK and Qin RY: Mechanism and its
regulation of tumor-induced angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol.
9:1144–1155. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wicki A and Christofori G: The angiogenic
switch in tumorigenesis. Tumor angiogenesis. Marme D and Fusenig N:
Springer Berlin; Heidelberg, New York: pp. 67–88. 2008, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Austin K, Sookhai S, Wang J, Pedmond K,
Kirwan W and Pedmond H: Anti-angiogenic therapy attenuates
micrometastatic tumour growth in a Lewis lung carcinoma model. Ir J
Med Sci. 170:112001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Erdem F, Gündogdu M and Kiziltunç A: Serum
vascular endothelial growth factor level in Patients with
hematological malignancies. Eur J Gen Med. 3:116–120. 2006.
|
|
32
|
Vicioso L, Gonzalez FJ, Alvarez M, et al:
Elevated serum levels of vascular endothelial growth factor are
associated with tumor-associated macrophages in primary breast
cancer. Am J Clin Pathol. 125:111–118. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Poon RT, Lau CP, Cheung ST and Yu WC:
Quantitative correlation of serum levels and tumor expression of
vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 63:6121–6126. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kivela R, Silvennoinen M, Lehti M, Jalava
S, Vihko V and Kainulainen H: Exercise-induced expression of
angiogenic growth factors in skeletal muscle and in capillaries of
healthy and diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 7:132008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|