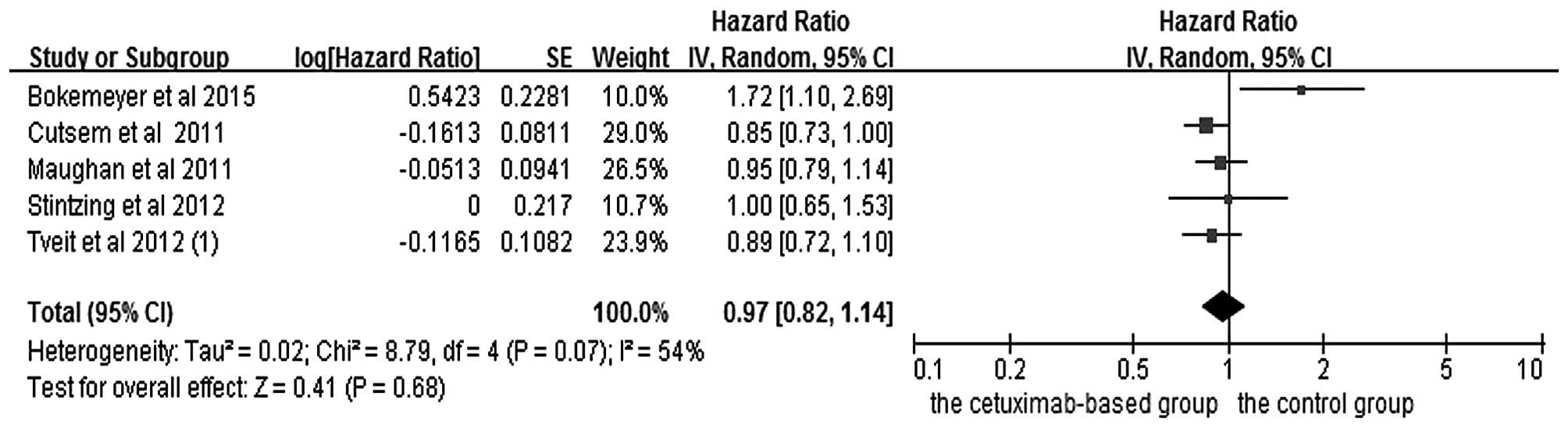
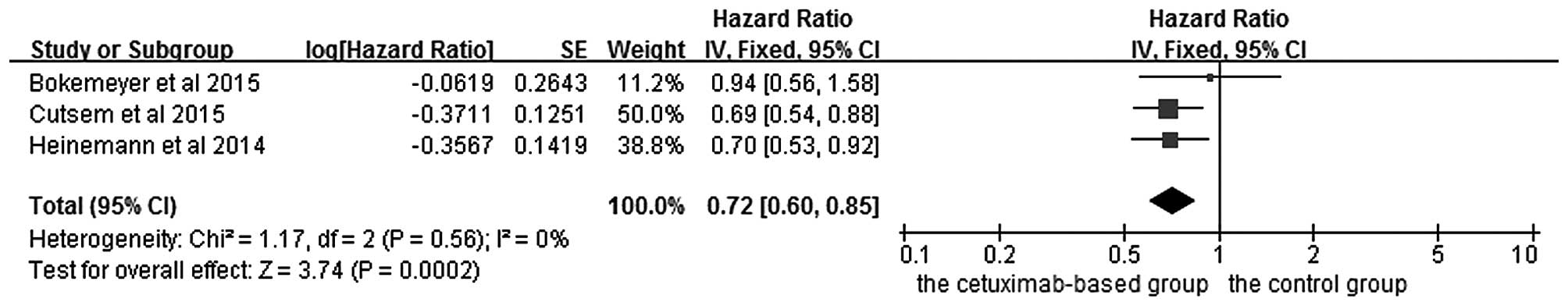
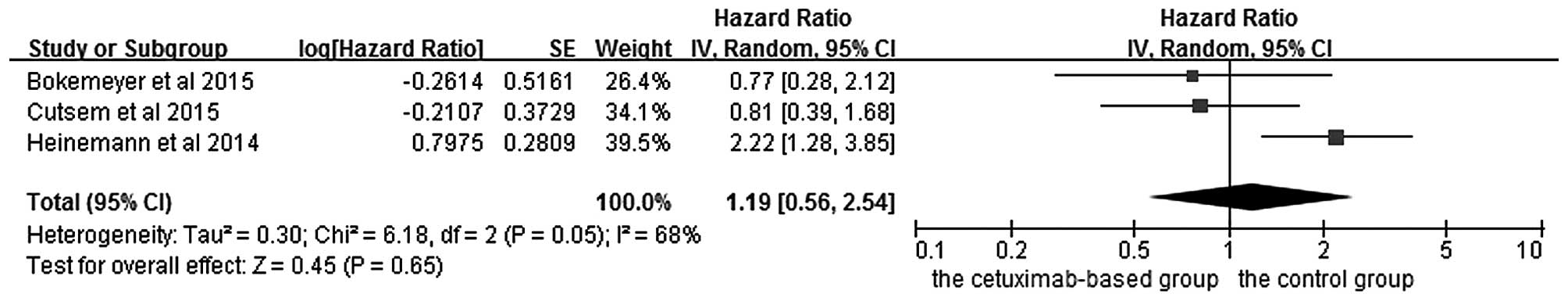
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Láng I, Folprecht
G, Nowacki MP, Cascinu S, Shchepotin I, Maurel J, Cunningham D,
Tejpar S, et al: Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil and
leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal
cancer: Updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor
KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol. 29:2011–2019. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Hartmann JT, de
Braud F, Schuch G, Zubel A, Celik I, Schlichting M and Koralewski
P: Efficacy according to biomarker status of cetuximab plus
FOLFOX-4 as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer:
The OPUS study. Ann Oncol. 22:1535–1546. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maughan TS, Adams RA, Smith CG, Meade AM,
Seymour MT, Wilson RH, Idziaszczyk S, Harris R, Fisher D, Kenny SL,
et al: Addition of cetuximab to oxaliplatin-based first-line
combination chemotherapy for treatment of advanced colorectal
cancer: Results of the randomised phase 3 MRC COIN trial. Lancet.
377:2103–2114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tveit KM, Guren T, Glimelius B, Pfeiffer
P, Sorbye H, Pyrhonen S, Sigurdsson F, Kure E, Ikdahl T, Skovlund
E, et al: Phase III trial of cetuximab with continuous or
intermittent fluorouracil, leucovorin and oxaliplatin (Nordic FLOX)
versus FLOX alone in first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal
cancer: The NORDIC-VII study. J Clin Oncol. 30:1755–1762. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bokemeyer C, Bondarenko I, Makhson A,
Hartmann JT, Aparicio J, de Braud F, Donea S, Ludwig H, Schuch G,
Stroh C, et al: Fluorouracil, leucovorin and oxaliplatin with and
without cetuximab in the first-line treatment of metastatic
colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:663–671. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Douillard JY, Siena S, Cassidy J,
Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, Humblet Y, Bodoky G, Cunningham
D, Jassem J, et al: Final results from PRIME: Randomized phase III
study of panitumumab with FOLFOX4 for first-line treatment of
metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol. 25:1346–1355. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Price TJ, Peeters M, Kim TW, Li J, Cascinu
S, Ruff P, Suresh AS, Thomas A, Tjulandin S, Zhang K, et al:
Panitumumab versus cetuximab in patients with
chemotherapy-refractory wild-type KRAS exon 2 metastatic colorectal
cancer (ASPECCT): A randomised, multicentre, open-label,
non-inferiority phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 15:569–579. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network: Comprehensive
molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer.
Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De
Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G, Kalogeras KT, Kotoula V,
Papamichael D, Laurent-Puig P, et al: Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS
and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy
in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: A
retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol. 11:753–762. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Douillard JY, Oliner KS, Siena S,
Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, Humblet Y, Bodoky G, Cunningham
D, Jassem J, et al: Panitumumab-FOLFOX4 treatment and RAS mutations
in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 369:1023–1034. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bokemeyer C, Van Cutsem E, Rougier P,
Ciardiello F, Heeger S, Schlichting M, Celik I and Köhne CH:
Addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment for
KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: Pooled analysis of the
CRYSTAL and OPUS randomised clinical trials. Eur J Cancer.
48:1466–1475. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Hitre E, Zaluski
J, Chang Chien CR, Makhson A, D'Haens G, Pintér T, Lim R, Bodoky G,
et al: Cetuximab and chemotherapy as initial treatment for
metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 360:1408–1417. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Van Cutsem E, Lenz HJ, Köhne CH, Heinemann
V, Tejpar S, Melezínek I, Beier F, Stroh C, Rougier P, van Krieken
JH and Ciardiello F: Fluorouracil, leucovorin and irinotecan plus
cetuximab treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 33:692–700. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stintzing S, von Fischer Weikersthal L,
Decker T, Vehling-Kaiser U, Jäger E, Heintges T, Stoll C, Giessen
C, Modest DP, Neumann J, et al: FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus
FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer-subgroup analysis of patients with
KRAS: Mutated tumours in the randomised German AIO study KRK-0306.
Ann Oncol. 23:1693–1699. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Heinemann V, von Weikersthal LF, Decker T,
Kiani A, Vehling-Kaiser U, Al-Batran SE, Heintges T, Lerchenmüller
C, Kahl C, Seipelt G, et al: FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI
plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment for patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer (FIRE-3): A randomised, open-label,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15:1065–1075. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ye LC, Liu TS, Ren L, Wei Y, Zhu DX, Zai
SY, Ye QH, Yu Y, Xu B, Qin XY and Xu J: Randomized controlled trial
of cetuximab plus chemotherapy for patients with KRAS wild-type
unresectable colorectal liver-limited metastases. J Clin Oncol.
31:1931–1938. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bokemeyer C, Köhne CH, Ciardiello F, Lenz
HJ, Heinemann V, Klinkhardt U, Beier F, Duecker K, van Krieken JH
and Tejpar S: FOLFOX4 plus cetuximab treatment and RAS mutations in
colorectal cancer. Eur J Cancer. 51:1243–1252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Venook AP, Niedzwiecki D, Lenz HJ,
Innocenti F, Mahoney MR, O'Neil BH, Shaw JE, Polite BN, Hochster
HS, Atkins AN, et al: CALGB/SWOG 80405: Phase III trial of
irinotecan/5-FU/leucovorin (FOLFIRI) or oxaliplatin/5-FU/leucovorin
(mFOLFOX6) with bevacizumab (BV) or cetuximab (CET) for patients
(pts) with KRAS wild-type (wt) untreated metastatic adenocarcinoma
of the colon or rectum (MCRC). ASCO Meeting Abstracts.
32:LBA32014.
|
|
22
|
Tveit K, Guren T, Glimelius B, Pfeiffer P,
Sorbye H, Pyrhonen S, Kure E, Ikdahl T, Skovlund T and
Christoffersen T: Randomized phase III study of
5-fluorouracil/folinate/oxaliplatin given continuously or
intermittently with or without cetuximab, as first-line treatment
of metastatic colorectal cancer: The NORDIC VII study
(NCT00145314), by the Nordic colorectal cancer biomodulation group.
ASCO Meeting Abstracts. 29:3652011.
|
|
23
|
Pietrantonio F, Petrelli F, Coinu A, Di
Bartolomeo M, Borgonovo K, Maggi C, Cabiddu M, Iacovelli R, Bossi
I, Lonati V, et al: Predictive role of BRAF mutations in patients
with advanced colorectal cancer receiving cetuximab and
panitumumab: A meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 51:587–594. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cui D, Cao D, Yang Y, Qiu M, Huang Y and
Yi C: Effect of BRAF V600E mutation on tumor response of anti-EGFR
monoclonal antibodies for first-line metastatic colorectal cancer
treatment: A meta-analysis of randomized studies. Mol Biol Rep.
41:1291–1298. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|