Article
Open Access
Optimal dose of silymarin for the management of drug‑induced liver injury in oncology
- Authors:
- Filip Kohutek
- Branislav Bystricky
-
View Affiliations / Copyright
Affiliations:
Faculty Hospital Trencin, Department of Oncology and Faculty of Health Sciences, Trencin University, Trencin 91171, Slovakia
-
Article Number:
35
|
Published online on:
March 8, 2023
https://doi.org/10.3892/mco.2023.2631
- Expand metrics +
Metrics:
Total
Views: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
Metrics:
Total PDF Downloads: 0
(Spandidos Publications: | PMC Statistics:
)
This article is mentioned in:
Abstract
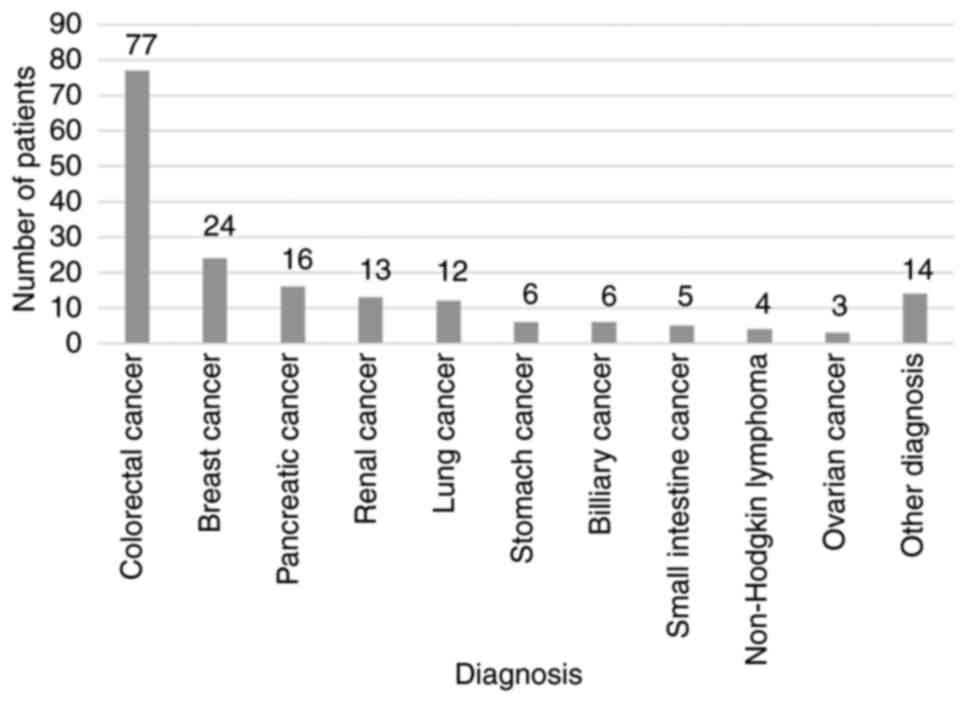
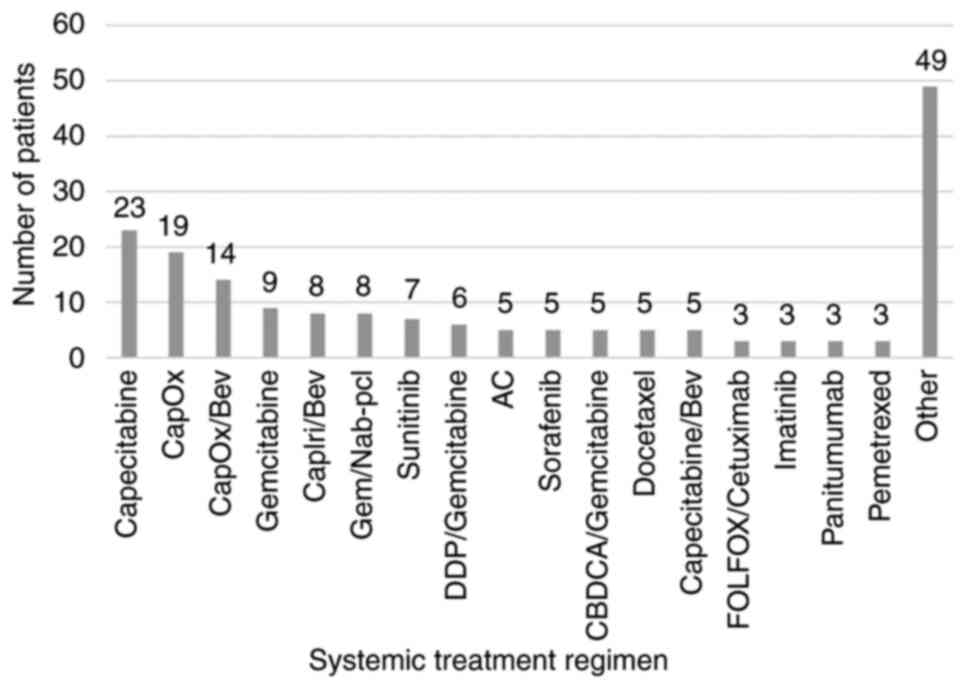
Systemic oncological treatment may cause drug‑induced liver injury (DILI). Therefore, there is a pressing need for an active drug able to accelerate liver regeneration. Silymarin mitigates oxidative stress, and inhibits pro‑inflammatory and pro‑apoptotic cytokines and the fibrotic transformation of liver tissue. Currently, there are a lack of data regarding the optimal dosage of silymarin and its efficacy. Thus, the present retrospective study aimed to determine the optimal dose of silymarin for use in oncological DILI treatment. For this purpose, 180 patients with solid malignancies treated with systemic oncological therapy and silymarin between January, 2015 and November, 2021 were enrolled in the study. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and total bilirubin (Bil) levels, as well as the dose of silymarin were assessed at the initiation of silymarin treatment, after 3‑6 weeks and after 6‑12 weeks. Pearson's correlation analysis was performed to evaluate the correlation between the initial dose of silymarin (IDoS), and the ALT, AST and Bil levels. The effects of four independent variables, namely IDoS, the initial dose reduction of systemic treatment, the systemic treatment dose reduction at first assessment (DR1M) and the elevation of the silymarin dose at first control on the ALT, AST and Bil levels were evaluated using regression analysis. The median IDoS was 450 mg. A decrease in or the stabilization of the ALT, AST and Bil levels after 6‑12 weeks were observed in 68.63, 65.85 and 53.25% of patients, respectively. There was a weak correlation between IDoS and the decrease in ALT and AST levels after 6‑12 weeks (correlation coefficient, R=0.361 and 0.277 respectively, P<0.001). No significant correlation between the IDoS and a decrease in Bil levels was observed. DR1M was a negative predictor for a decrease in Bil levels in patients with liver tumors. On the whole, the present study demonstrates that silymarin appears to be efficient in alleviating DILI at a dose of 300‑450 mg. A further increase in the dose of silymarin may not lead to an adequate increase in its efficacy.
View References
|
1
|
Ramadori G and Cameron S: Effects of
systemic chemotherapy on the liver. Ann Hepatol. 9:133–143.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grigorian A and O'Brien CB: Hepatotoxicity
secondary to chemotherapy. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2:95–102.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Veitch Z, Khan OF, Tilley D, Tang PA,
Ribnikar D, Stewart DA, Kostaras X, King K and Lupichuk S: Impact
of cumulative chemotherapy dose on survival with adjuvant FEC-D
chemotherapy for breast cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 17:957–967.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nielson CM, Bylsma LC, Fryzek JP, Saad HA
and Crawford J: Relative dose intensity of chemotherapy and
survival in patients with advanced stage solid tumor cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncologist. 26:e1609–e1618.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gillessen A and Schmidt HHJ: Silymarin as
supportive treatment in liver diseases: A narrative review. Adv
Ther. 37:1279–1301. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Federico A, Dallio M and Loguercio C:
Silymarin/silybin and chronic liver disease: A marriage of many
years. Molecules. 22(191)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Luangchosiri C, Thakkinstian A, Chitphuk
S, Stitchantrakul W, Petraksa S and Sobhonslidsuk A: A
double-blinded randomized controlled trial of silymarin for the
prevention of antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 15(334)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Marjani M, Fahim F, Sadr M, Kazempour
Dizaji M, Moniri A, Khabiri S, Tabarsi P and Velayati AA:
Evaluation of Silymarin for management of anti-tuberculosis drug
induced liver injury: A randomized clinical trial. Gastroenterol
Hepatol Bed Bench. 12:138–142. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moezian GSA, Javadinia SA, Sales SS,
Fanipakdel A, Elyasi S and Karimi G: Oral silymarin formulation
efficacy in management of AC-T protocol induced hepatotoxicity in
breast cancer patients: A randomized, triple blind,
placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Oncol Pharm Pract. 28:827–835.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mohaghegh F, Solhi H and Kazemifar AM:
Silymarin (Milk Thistle) can revoke liver enzyme changes during
chemotherapy of breast cancer with Taxanes. Eur J Integr Med.
7:650–652. 2015.
|
|
11
|
Fathalah WF, Abdel Aziz MA, Abou El Soud
NH and El Raziky MES: High dose of silymarin in patients with
decompensated liver disease: A randomized controlled trial. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 37:480–487. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sohail I, Malkani N, Tahir N, Khalil A,
Attar R and Mumtaz S: Silymarin protects the liver from
α-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestasis by modulating the
expression of genes involved in bile acid homeostasis. Cell Mol
Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 68:208–212. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|