Introduction
Isolated fourth ventricle (IFV) is a rare
complication following shunt replacement during treatment for
post-hemorrhagic, post-infective, post-inflammatory, and congenital
hydrocephalus (1). IFV is most
commonly seen in infancy with a history of prematurity following
ventriculoperitoneal shunt for post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus. IFV
occurs in post-hemorrhagic or post-infective hydrocephalus, causing
ependymal inflammation (2,3). Obstruction of the aqueduct and fourth
ventricle outlet results in progressive dilation of the fourth
ventricle followed by compression of the brainstem and the
cerebellar parenchyma (1).
Dilation of the fourth ventricle elevates infratentorial pressure
and compression of the brain stem, and this can result in eye
movement disorder, ataxia, and impaired consciousness. As it is an
unusual and complicated disease, it may be missed on initial
diagnosis. T2-weighted sagittal MRI to assess dilation of the
fourth ventricle and obstruction of the aqueduct or fourth
ventricular outlet is accurate for diagnosis of IFV (3). The development of clinical and
radiographic features of IFV is slowly progressive, often remaining
asymptomatic for months or years. When clinical symptoms develop
and radiographic deterioration is detected, urgent operative
intervention is necessitated. Several treatment options have been
reported, including suboccipital craniectomy and outlet
fenestration, fourth ventricular shunting procedures, and
endoscopic procedures (3,4). Here, we report a rare case of a
hemangioblastoma of the medulla oblongata that caused IFV due to
intraventricular deposition of fibrin after stereotactic
radiosurgery.
Case report
A 34-year-old man was referred to our outpatient
department with intermittent headache from a month previously.
Physical examination on admission revealed no neurological deficit.
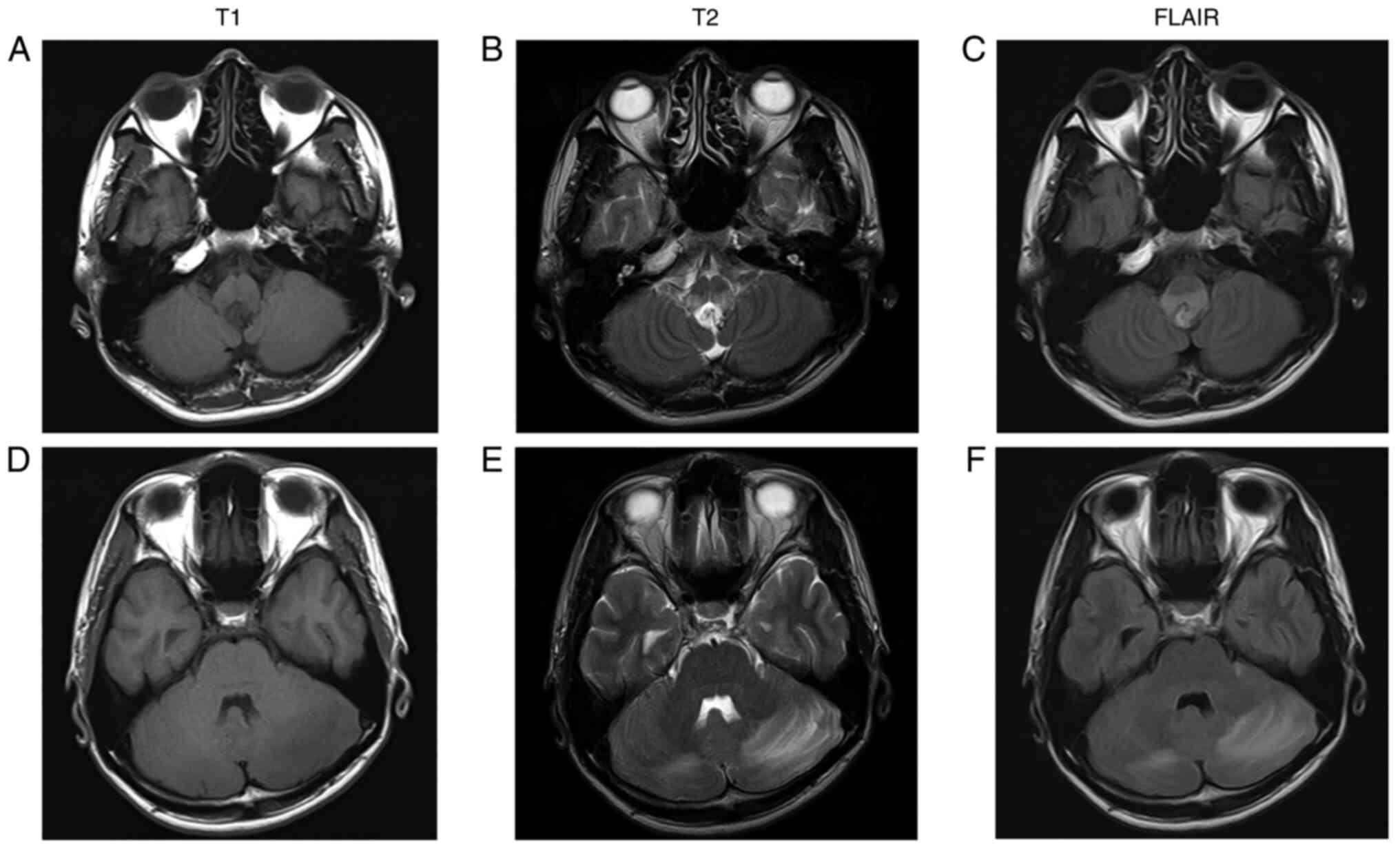
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) indicated a mass in the dorsal
medulla oblongata and bilateral cerebellar edema (Fig. 1A-F). Post-contrast T1-imaging
showed a 15 mm mass in the dorsal medulla oblongata and multiple
masses <10 mm in bilateral cerebellar hemispheres that were
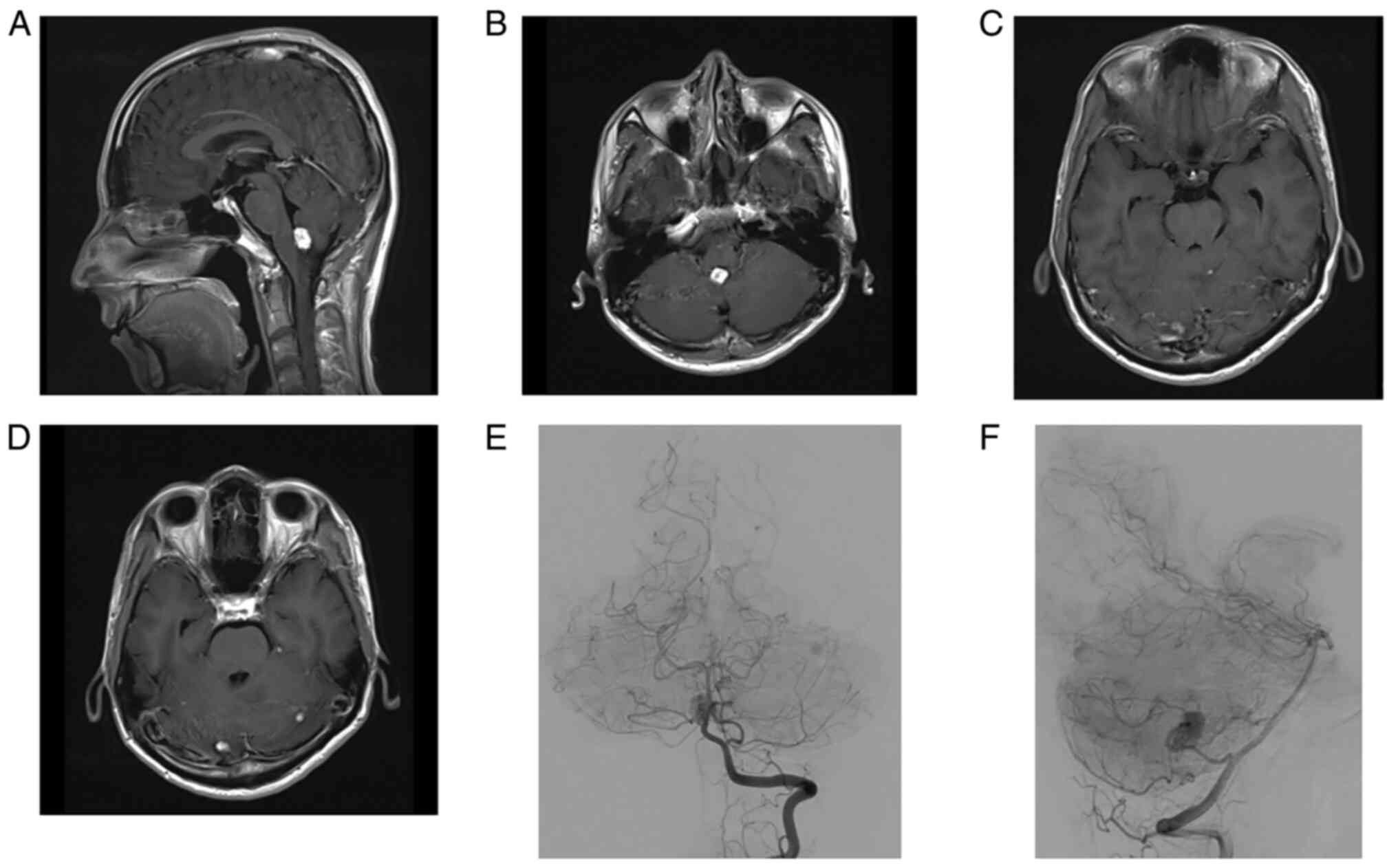
strongly enhanced with gadolinium (Fig. 2A-D). Cerebral angiography showed
that the mass in the dorsal medulla oblongata received a blood
supply from the left posterior inferior cerebellar artery (Fig. 2E and F). Systemic computed tomography (CT)
showed a right renal tumor, multiple pancreatic cysts, and
cystadenoma of the epididymis. The patient's family history was
negative for von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome, and therefore he was
diagnosed with solitary VHL syndrome clinically. With consideration
of the operative risk, he elected to undergo stereotactic
radiosurgery for multiple hemangioblastomas. Stereotactic
radiosurgery (SRS) was performed with a dose of 18 Gy for the tumor
of the dorsal medulla oblongata and 20 Gy for the other tumors. He
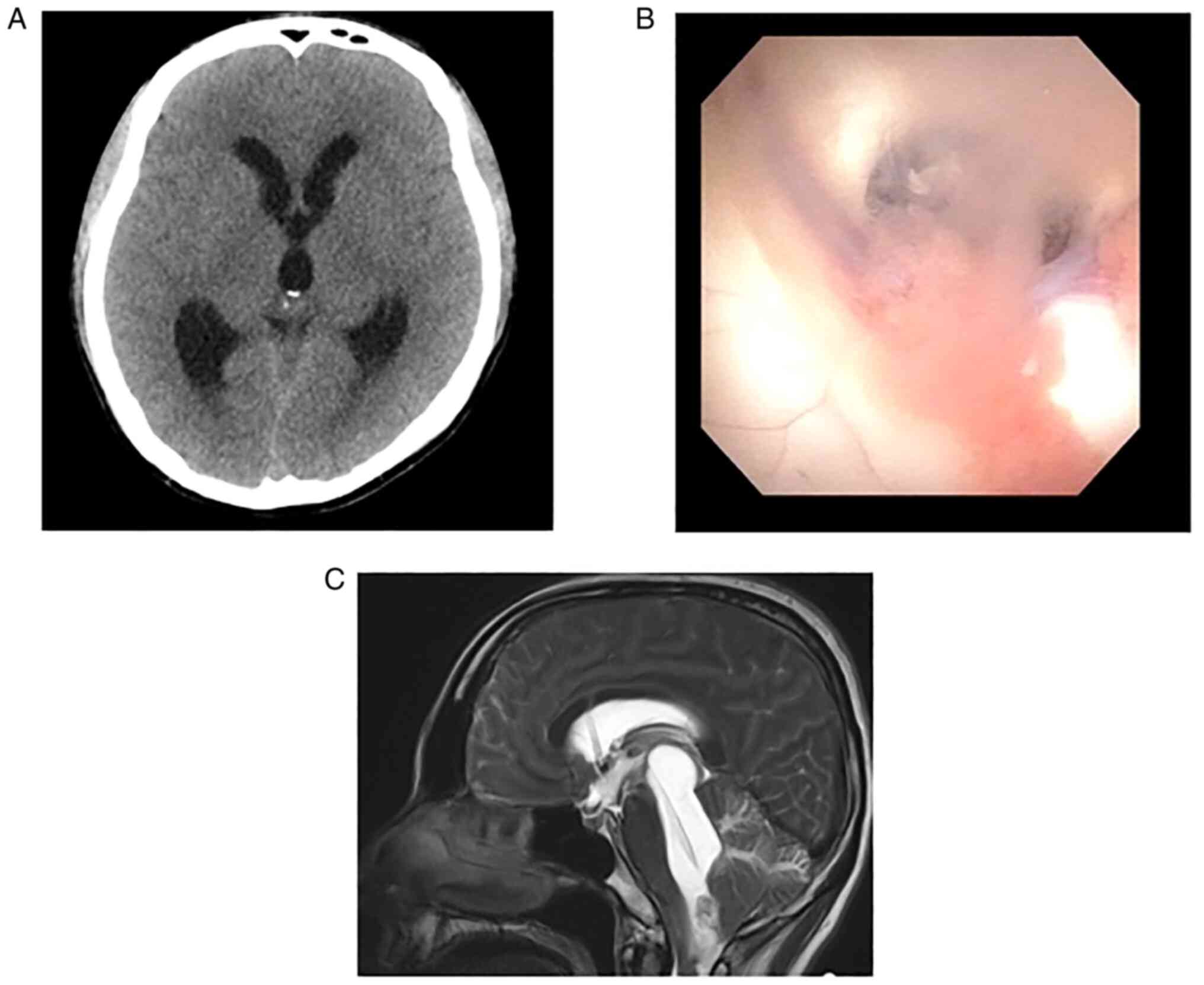
began to develop progressive headache and nausea three days after
SRS, and CT showed obstructive hydrocephalus (Fig. 3A). We performed endoscopic third
ventriculostomy (ETV), the endoscopic view of which showed turbid
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and that the walls of the lateral and
third ventricle were covered with white membrane-like substance
(Fig. 3B). The protein level of
CSF was 760 mg/dl. Subsequently, a ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt
was placed a week after ETV because there was no improvement of
hydrocephalus after ETV. However, the patient's consciousness
deteriorated gradually and the sagittal view of T2 weighted image
showed isolated fourth ventricle and upward herniation 2 weeks
after the VP shunt (Fig. 3C). The
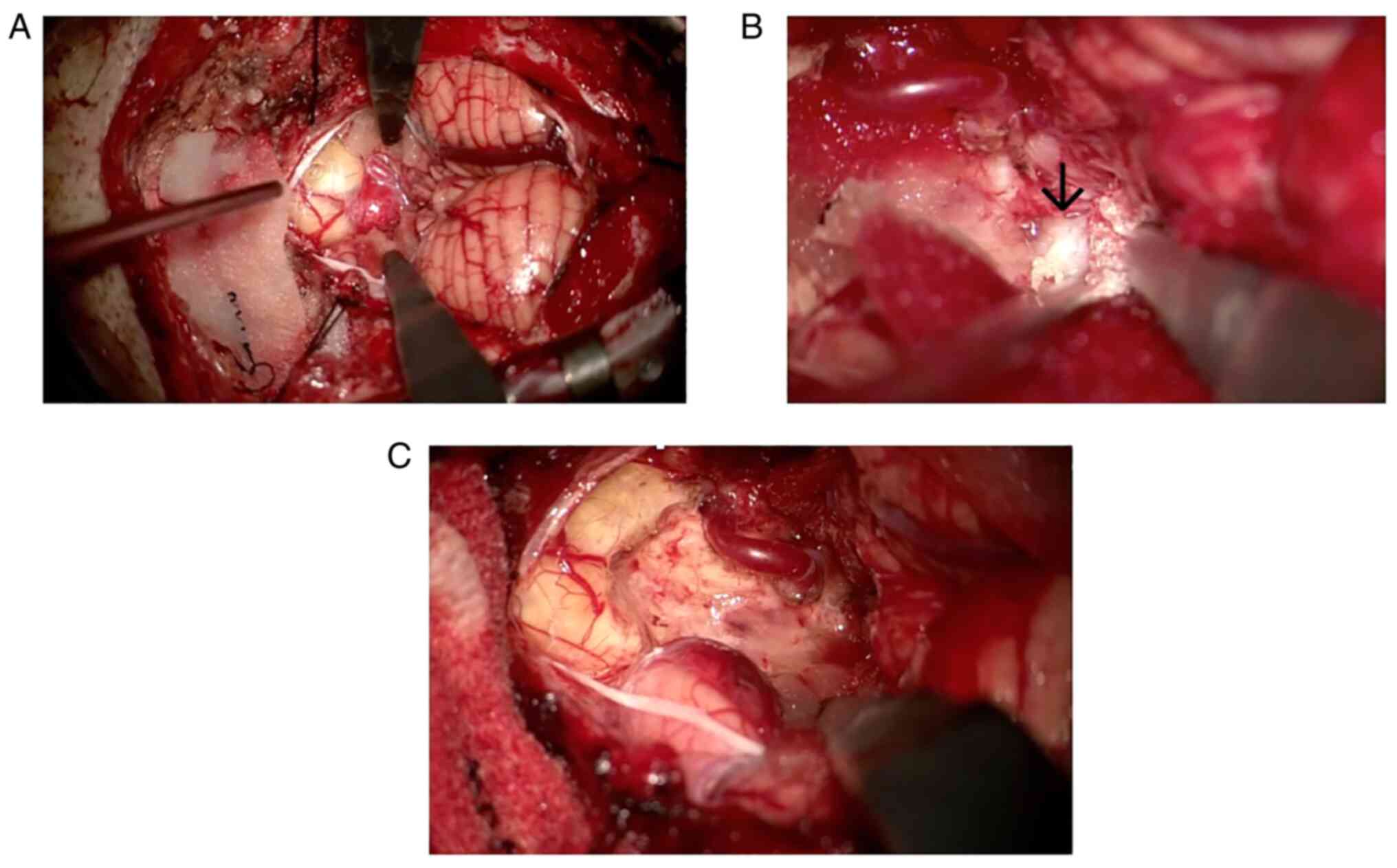
tumor in the medulla oblongata was emergently removed via posterior
fossa craniotomy and telovelar approach. The fourth ventricle was
filled with a white membrane-like substance, which was all
surgically removed (Fig. 4A-C). We
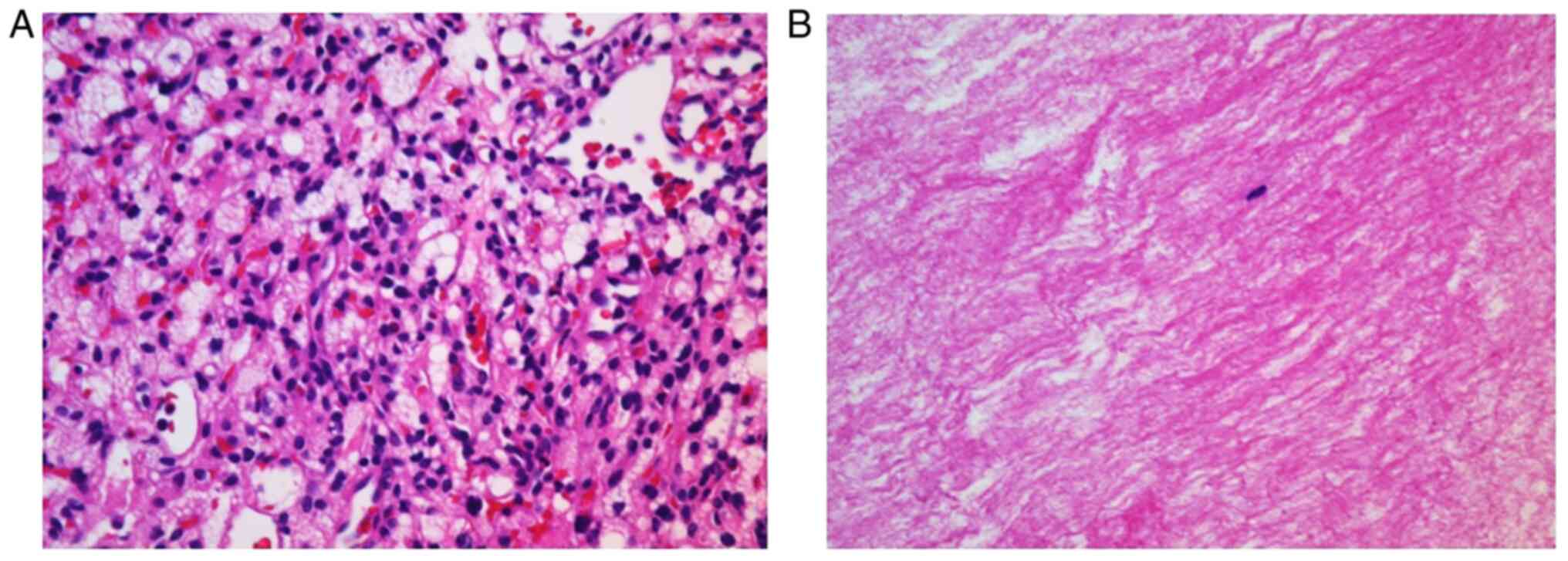
performed hematoxylin and eosin staining of the surgical specimen,
following a protocol that included deparaffinization, rehydration,
hematoxylin staining, eosin staining, and dehydration. Hematoxylin
and eosin staining showed stromal cells with abundant vacuolated or
lightly eosinophilic cytoplasm and histopathological diagnosis was
hemangioblastoma (Fig. 5A).
Pathologically, the white membrane-like substance was shown to
consist of fibrin (Fig. 5B). The
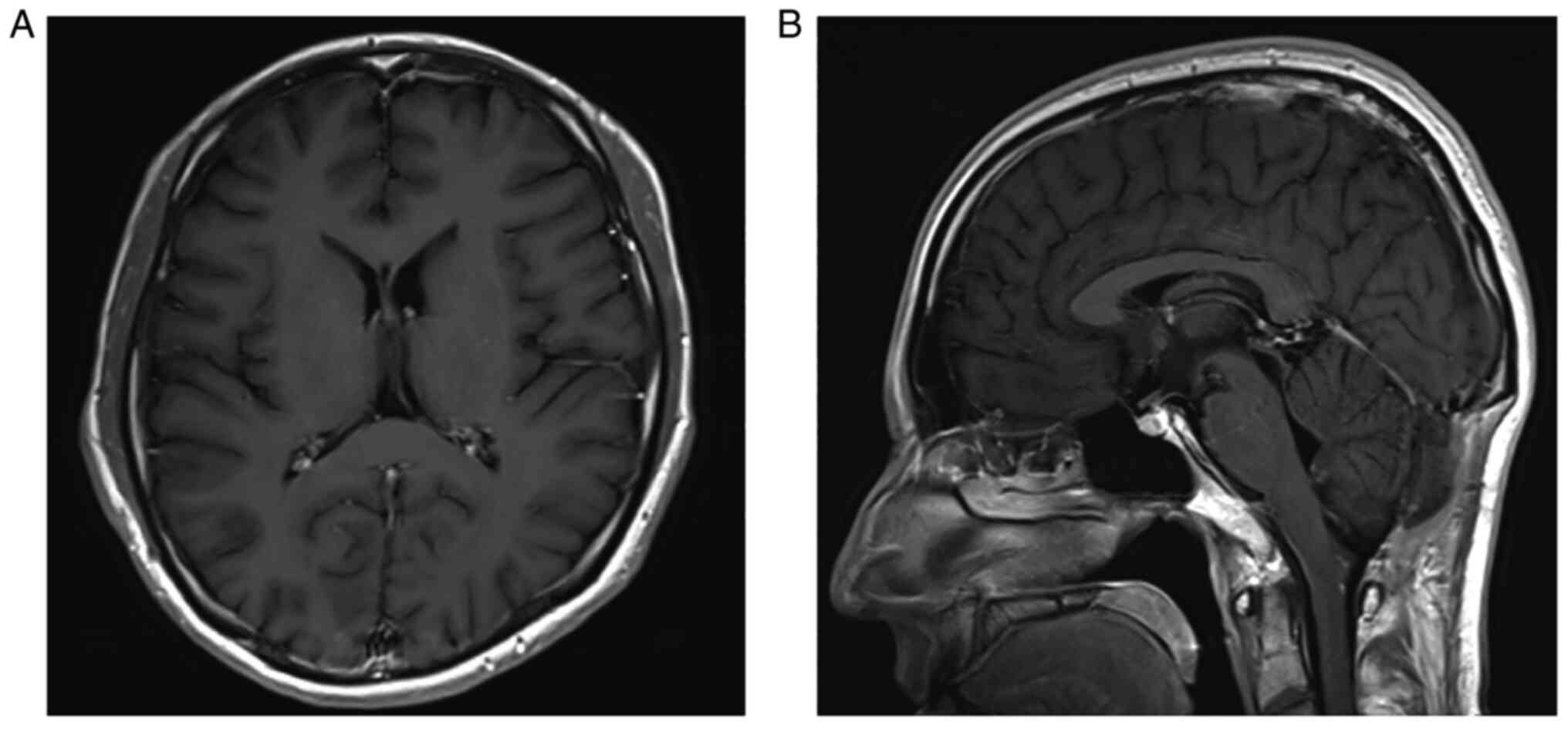
patient's consciousness and obstructive hydrocephalus improved
after surgery (Fig. 6). Vocal cord
paralysis occurred after surgery and he required tracheotomy, but
the paralysis improved within a few weeks. Postoperative CSF
protein level decreased to within normal range. The patient was
discharged to his home three weeks after surgery with vertical
diplopia as the only remaining symptom. Next generation sequence
using peripheral was outsourced to SRL, Inc., Tokyo, Japan. The
direct sequencing revealed his VHL variant mutation (NM_000551.3:
c.464-2A>G). This variant is registered in ClinVar as pathogenic
(Accession:VCV000223222.13). At the two-year follow-up, he was
working in the same occupation as before the onset, and there had
been no recurrence of the tumor.
Discussion
IFV is an unusual type of obstructive hydrocephalus,
which is characterized by the disproportionately enlarged fourth
ventricle with caudal and rostral obstruction. IFV has often been
observed after shunt treatment in patients with a history of
ependymal inflammation from infection, or after hemorrhage in
children (1-3).
Dilation of the fourth ventricle elevates infratentorial pressure
and compression of the brain stem, and this can result in eye
movement disorder, ataxia, and impaired consciousness. IFV can be
diagnosed by T2-weighted sagittal MRI to assess obstruction of the
aqueduct or fourth ventricular outlet (4). Conventionally, patients with IFV have
been managed by fourth ventricle shunt placement or fenestration of
the occluded outlet foramen via posterior fossa craniotomy
(3). With the development of
neuroendoscopic surgery, patients with IFV have also been treated
with endoscopic procedures, including aqueductoplasty and
aqueductal stenting (4,5).
In our patient, hydrocephalus with
hyperproteinorachia presented after SRS for hemangioblastoma of the
medulla oblongata, and VP shunt was performed, but IFV developed.
The tumor in the medulla oblongata was removed via posterior fossa
craniotomy and telovelar approach. The fourth ventricle was filled
with a white membrane-like substance, which was surgically removed.
Pathologically, the white membrane-like substance consisted of
eosinophilic fibrous matrix without atypical cells, which was shown
to be fibrin. This is the first known case report of
hemangioblastoma of the medulla oblongata causing IFV due to
intraventricular precipitation of fibrin. Tumor removal and opening
of the fourth ventricle resulted in improvement of the
hydrocephalus and the protein level of CSF decreased after surgical
treatment. We did not place a fourth ventricle shunt because the
fourth ventricle was filled with fibrin and the shunt was expected
to become occluded.
The mechanism behind hemangioblastoma cyst formation
remains unclear. Intra-tumoral cysts have recently been suggested
to result from vascular leakage and liquefaction of tumor cells
(6). In one study, proteomic
analysis indicated that the hemangioblastoma cyst fluid contained
serum proteins (6). In this case,
proteins secreted by the tumor flowed into the fourth ventricle and
the fibrin deposition likely occluded the outflow of CSF from the
fourth ventricle, leading to presentation of IFV. Our case suggests
that IFV may occur after VP shunt placement for the hydrocephalus
with hyperproteinorachia.
Resection of symptomatic hemangioblastomas may be
curative, but SRS can be applied for small, multiple,
high-surgical-risk hemangioblastomas. A retrospective international
study of SRS for hemangioblastoma indicated good local tumor
control and less adverse radiation effect, but a small number of
patients with hemangioblastomas treated with SRS required
additional surgical treatment (7).
In this case, SRS was performed in consideration of small multiple
lesions and the operative risk of lower cranial nerve palsy.
However, SRS aggravated the hydrocephalus and required tumor
removal. Careful treatment selection and follow-up after SRS are
therefore important.
In conclusion, we presented a rare case of a
hemangioblastoma of the medulla oblongata that caused IFV due to
intraventricular deposition of fibrin. IFV may occur after VP shunt
placement for hydrocephalus with hyperproteinorachia.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Benjamin Phillis
(Clinical Study Support Center, Wakayama Medical University,
Wakayama, Japan) for proofreading and editing.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
YH, TS, TY, JF, HN and NN contributed to the study
conception and design. YH and TS wrote the final manuscript and
acquired all data. YH and TS confirmed the authenticity of all the
raw data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
The featured patient provided written informed
consent for the publication of the data and images of his case.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Mohanty A: Endoscopic options in the
management of isolated fourth ventricles. Case report. J Neurosurg
Pediatr. 103:73–78. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ali K, Nannapaneni R and Hamandi K: The
isolated fourth ventricle. BMJ Case Rep.
2013(bcr2013008791)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dauda HA and Sale D: Trapped fourth
ventricle: A case report and review of literature. Int J Surg Case
Rep. 80(105638)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Panagopoulos D, Karydakis P and
Themistocleous M: The entity of the trapped fourth ventricle: A
review of its history, pathophysiology, and treatment options.
Brain Circ. 7:147–158. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Imperato A, Almaguer Ascencio LM, Ruggiero
C, Spennato P, Di Martino G, Aliberti F, Mirone G and Cinalli G:
Endoscopic aqueductoplasty and stenting in the treatment of
isolated fourth ventricle in children: 20-Year institutional
experience. Childs Nerv Syst. 37:1587–1596. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gläsker S, Vortmeyer AO, Lonser RR,
Lubensky IA, Okamoto H, Xia JB, Li J, Milne E, Kowalak JA, Oldfield
EH and Zhuang Z: Proteomic analysis of hemangioblastoma cyst fluid.
Cancer Biol Ther. 5:549–553. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kano H, Shuto T, Iwai Y, Sheehan J,
Yamamoto M, McBride HL, Sato M, Serizawa T, Yomo S, Moriki A, et
al: Stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial hemangioblastomas: A
retrospective international outcome study. J Neurosurg.
122:1469–1478. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|