Introduction
In recent years, novel drugs for metastatic and
recurrent breast cancer have been approved, and treatment options
are increasing. However, as there is no clear consensus on which
drug to use and in what order, there has been much debate regarding
the choice of treatment. Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK)4/6
inhibitors selectively inhibit CDK4 and CDK6, arrest cell cycle
progression and suppress tumor growth (1). To date, 3 types of CDK4/6 inhibitors
have been developed, and in Japan, 2 drugs, palbociclib and
abemaciclib, have been approved. Palbociclib is a newly launched
molecular-targeted therapeutic agent for use in inoperable or
recurrent breast cancer and was the first selective CDK4/6
inhibitor to be introduced worldwide (2-5).
In the PALOMA 3 trial, the median progression-free survival (PFS)
times were shown to be 9.2 months in the palbociclib combination
group and 3.8 months in the placebo group, with significantly
better results in the palbociclib combination group [hazard ratio
(HR), 0.42; 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.32-0.56) (6). Its efficacy and safety have been
confirmed in Japan, and the drug was approved in December, 2017 in
combination with endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive
human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer
(7,8).
The efficacy and safety of abemaciclib were subsequently validated,
and abemaciclib was then approved in Japan in 2018 (9-11). In
the MONARCH 2 trial, the median PFS times were 16.4 months for the
abemaciclib combination group and 9.3 months for the placebo group,
with significantly better results in the abemaciclib combination
group (HR, 0.553; 95% CI, 0.449-0.681) (10). The side-effects associated with the
use of CDK4/6 inhibitors are primarily blood toxicity and digestive
complications, such as nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. However, the
side-effect profiles are somewhat different; palbociclib has been
reported to induce a high frequency of hematologic toxicity, and
abemaciclib has been reported to induce a high frequency of
diarrhea (2-6,9-11).
Thus, the appropriate applications for the use of these 2 CDK4/6
inhibitors have not yet been determined.
In this study, we analyzed the efficacy and
side-effects associated with the use of palbociclib in patients at
our hospital and examined the suitability of palbociclib or
abemaciclib based on adverse events.
Patients and methods
Patients
This study included 35 patients who were able to
continuously receive 2 or more courses of palbociclib from
December, 2017 to December, 2018 at Kitasato University Hospital.
The patient information is presented in Table I. All patients had recurrent or
metastatic hormone-positive breast cancer (stage IV). The ages of
the patients ranged from 39 to 83 years (median, 55 years). None of
the patients discontinued treatment due to adverse events.
 | Table IPatient background. |
Table I
Patient background.
| Parameter | Number |
|---|
| Age (years) | |
|
39-83
(median, 55) | |
| Combination
drugs | |
|
Fulvestrant | 20 |
|
Fulvestrant
+ LH-RH | 7 |
|
Letrozole | 8 |
| Initial dose | |
|
125 mg | 29 |
|
100 mg | 6 |
| Prior treatment
regimens | |
|
Chemotherapy
only | 6 |
|
Hormone
therapy only | 13 |
|
Both
chemotherapy and hormone therapy | 8 |
|
No prior
treatment history | 8 |
| Number of prior
treatment regimens | |
|
0 | 8 |
|
1 | 3 |
|
2 | 7 |
|
3 | 10 |
|
More than 4
regimens | 7 |
| Metastatic site | |
|
Lymph
node | 20 |
|
Bone | 20 |
|
Lung | 16 |
|
Liver | 13 |
|
Brain | 2 |
|
Pleural
dissemination | 4 |
Analysis methods
The effects of palbociclib were evaluated using the
response evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST) RECIST.
Adverse events were evaluated using CTCAE ver4.1. Factors related
to neutropenia of grade 3 or higher were also analyzed.
Statistical analysis
We calculated the average of the disease-free period
and PFS. PFS was estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method and
P-values were generated using the Wilcoxon test. For categorical
variables, P-values were calculated using the Chi-square test. A
value of P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference. All statistical analyzes were performed
using JMP Pro version 11 software (SAS Institute).
Results
Patient demographics and clinical
data
The patient information is presented in Table I. All patients had stage IV, invasive
ductal carcinoma. The ages of the patients ranged from 39 to 83
years (median, 55 years). The patients receiving treatment with a
combination of drugs included 20 patients (57%) with fulvestrant, 8
patients (20%) with letrozole, and 7 patients (23%) with
fulvestrant + LH-RH (leuprorelin). Fourteen patients (40%) had a
history of chemotherapy, and 21 (60%) had no history of
chemotherapy. The number of prior treatment regimens (including
chemotherapy and hormone therapy) was 0-11 (mean, 2.9). The initial
dose of palbociclib was 125 mg for 29 patients (83%) and 100 mg for
6 patients (17%). Patients who were reduced to 100 mg were patients
74 years of age or older, or patients with brain metastases and a
performance status (PS) of ≤2.
Analysis of efficacy
The efficacy of the treatment is presented in
Table II. There were 6 cases (17%)
of partial response (PR), 19 cases (54%) of stable disease (SD) and
10 cases (29%) of progressive disease (PD). The disease-free period
averaged 5.5 months (1.17-10.73 months)
 | Table IIEfficacy of palbociclib treatment
(n=35). |
Table II
Efficacy of palbociclib treatment
(n=35).
| Response | Number | % |
|---|
| Partial
responsea | 6 | 17 |
| Stable
diseaseb | 19 | 54 |
| Progressive
diseasec | 10 | 29 |
Analysis of side-effects
The side-effects of treatment are presented in
Table III. There were 24 cases with
leukocytopenia (7 cases with grade 3 or higher), 26 cases with
neutropenia (16 cases with grade 3 or higher), 13 cases with anemia
(1 case with grade 3 or higher) and 15 cases with thrombocytopenia
(grade 3 or higher). There were 3 cases of fatigue, 1 case of itchy
skin and 1 case of febrile neutropenia (FN).
 | Table IIISide-effects associated with
palbociclib treatment. |
Table III
Side-effects associated with
palbociclib treatment.
| | All grades | Higher than grade
3 |
|---|
| Side-effect | Number | % | Number | % |
|---|
| Leukocytopenia | 24 | 69 | 7 | 20 |
| Neutropenia | 26 | 74 | 16 | 46 |
| Anemia | 13 | 37 | 1 | 3 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 15 | 43 | 0 | 0 |
| Fatigue | 3 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| Itchy skin | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| Febrile
neutropeniaa | 1 | 3 | 1 | 3 |
Risk factors for severe
neutropenia
Subsequently, we examined the expression of
neutropenia of grade 3 or higher (Table
IV). There were no significant differences in the presence or
absence of prior chemotherapy treatment, the number of regimens, or
age. Although the presence or absence of bone metastasis did not
differ significantly, bone metastasis cases tended to exhibit
neutropenia of grade 3 or higher (P=0.09). In patients with
<3,000 neutrophils prior to palbociclib induction, neutropenia
of grade 3 or higher was observed in all 12 patients
(P<0.0001).
 | Table IVRisk factors for severe
neutropenia. |
Table IV
Risk factors for severe
neutropenia.
| | Number of patients
with neutropenia of grade 3 or higher (%) | |
|---|
| Risk factor | - | + | P-value |
|---|
| Chemotherapy
history |
|
+ | 8(57) | 6(43) | P=0.09 |
|
- | 6(29) | 15(71) | |
| The number of
regimens |
|
<4 | 12(43) | 16(57) | P=0.48 |
|
≥4 | 2(29) | 5(71) | |
| Age (years) |
|
<50 | 3(33) | 6(67) | P=0.63 |
|
≥50 | 11(42) | 15(58) | |
| Bone metastasis |
|
- | 8(57) | 6(43) | P=0.09 |
|
+ | 6(29) | 15(71) | |
| Number of neutrophils
prior to palbociclib induction |
|
<3,000 | 0 (0) | 12(100) | P<0.0001 |
|
≥3,000 | 14(61) | 9(39) | |
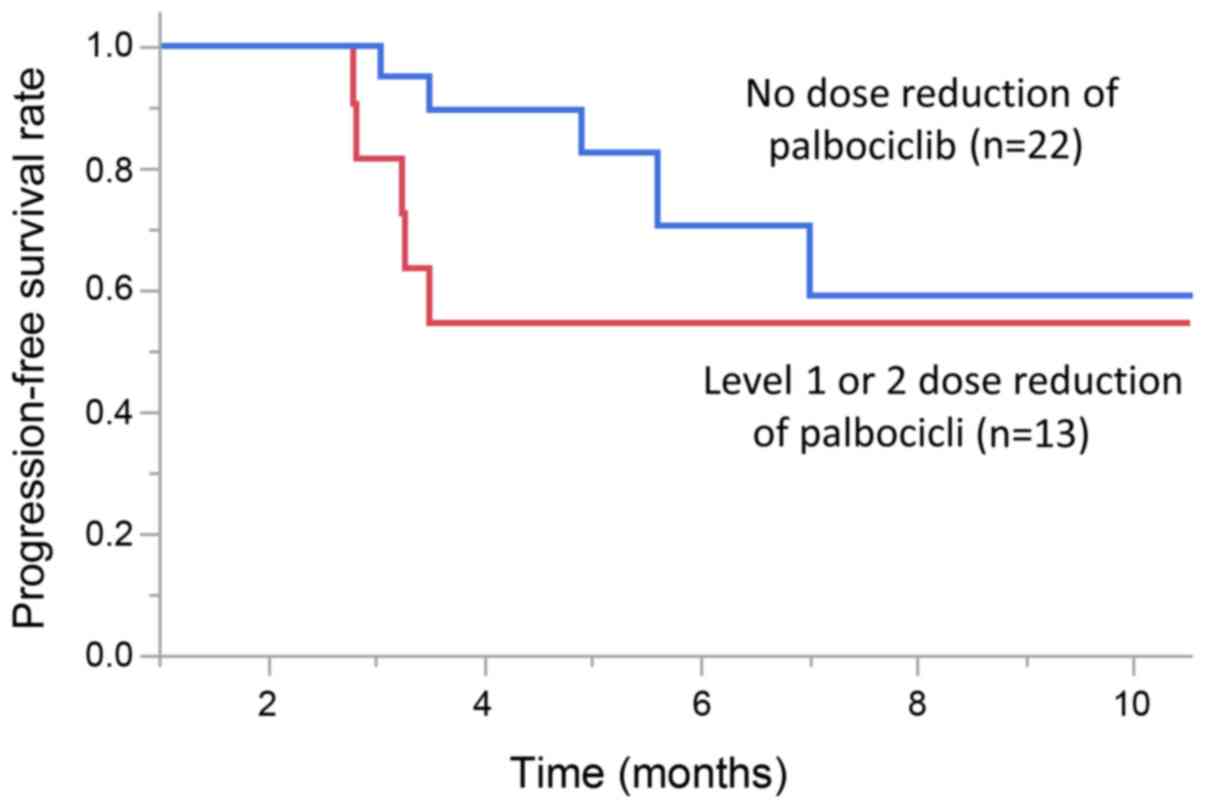
Dose reduction
The dose of pabociclib was reduced in 13 patients
(37%). Of these, 7 cases had 1 dose reduction, and 6 cases had a
2-stage dose reduction. PFS was improved in patients who did not
have a dose reduction (P=0.04, Wilcoxon test). The median PFS (95%
CI) was 6.3 months (5.6-NE) in patients who did not have a dose
reduction, and the median PFS (95% CI) was 3.3 months (2.8-NE) in
patients who had a level 1 or 2 dose reduction (Fig. 1).
Discussion
Currently, there are no clear guidelines regarding
the use of palbociclib and abemaciclib. In this study, in cases in
which the number of neutrophils prior to the introduction of a
CDK4/6 inhibitor was <3,000 or less, neutropenia of grade 3 or
higher was observed in all cases owing to palbociclib. We believe
that abemaciclib may be selected in cases in which the number of
neutrophils prior to introduction of the CDK4/6 inhibitor is
<3,000.
CDK4/6 inhibitors are agents that block the cell
cycle and lead to similar side-effects as cytotoxic preparations
(1). The use of palbociclib
frequently leads to side-effects associated with the blood system.
In the PALOMA-3 trial, neutropenia, anemia and thrombocytopenia
were detected in 79, 26 and 19% of cases when palbociclib was used
in combination with fulvestrant (6);
in particular, neutropenia of grade 3 or higher was as high as 62%,
and the incidence of adverse events of febrile neutopenia was 0.9%.
Although not frequent, we experienced 1 case of febrile
neutropenia, in which hospitalization was required; thus, the
occurrence of febrile neutopenia should be avoided. Moreover, in
the PALOMA-3 trial, the proportion of patients experiencing
withdrawal of palbociclib for neutropenia was 59.7%, and the
proportion of patients experiencing dose reduction was 27%. By
contrast, in the MONARCH 2 test, when administered a combination of
fulvestrant and abemaciclib, the incidences of neutropenia, anemia,
thrombocytopenia and neutropenia of grade 3 or higher were 46, 29,
15 and 26%, respectively (10).
The side-effect of cytopenia was lower for
abemaciclib compared with that of palbociclib. Palbociclib has not
been reported to result in differences in PFS between those who had
dose reductions of 1 or more levels (n=100) and those who did not
have dose reductions (n=245) (12).
However, no analysis has been conducted for patients who had dose
reductions in 1 or 2 stages. In the current study, the initial dose
of palbociclib was 125 mg for 29 patients (83%) and 100 mg for 6
patients (17%). Patients who were reduced to 100 mg were patients
74 years of age or older, or patients with brain metastases and PS2
or greater. PFS was significantly improved in patients who did not
have a dose reduction. In addition, there were 6 cases in which a
2-stage dose reduction was required, indicating a relatively high
frequency. The current study differs from previous clinical trials.
However, blood levels [maximum blood concentration, Cmax and the
area under the blood concentration-time curve (AUC)] are
proportional to the dose (13). When
the relative dose intensity (RDI) decreases, the clinical effect
may not be sufficient. However, since the sample size was small in
this study, verification with a larger sample size is also
necessary. Thus, in order to maintain the RDI, it is better to
avoid drug withdrawal and dose reduction as much as possible in
most cases. In order to avoid the appearance of neutropenia of
grade 3 or higher and to maintain RDI, it is suggested that
abemaciclib should be considered for cases with neutrophils of
<3,000 prior to the introduction of a CDK4/6 inhibitor.
In conclusion, the results revealed that palbociclib
administration was extremely likely to cause neutropenia of grade 3
or higher in cases in which the number of neutrophils was <3,000
prior to induction. Therefore, such cases should be treated with
neutropenia in mind.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are
included in this published article or are available from the
corresponding author on reasonable request.
Authors' contributions
YT, MY, HN, HK and NS designed the study, and wrote
the initial draft of the manuscript. YK contributed to the analysis
and interpretation of the data, and assisted in the preparation of
the manuscript. All authors (MK, YT, MY, HN, HK, NS and YK) have
contributed to data collection and interpretation, and have
critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and
approved the final version of the manuscript, and agree to be
accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions
related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are
appropriately investigated and resolved.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
This study is a retrospective study. This study was
approved by the Kitasato University Hospital Ethics Committee
(B18-294). Our survey began on May 17, 2019.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL,
Meade M, Trachet E, Albassam M, Zheng X, Leopold WR, Pryer NK, et
al: Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by PD
0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor
xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:1427–1438. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
European Medicines Agency: IBRANCE Product
Information. http://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/ibrance.
|
|
3
|
Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices
Agency: New drugs approved in September (2017) (In Chinese).
https://www.pmda.go.jp/index.html.
|
|
4
|
Ibrance (palbociclib): Full prescribing
information. Pfizer Inc., New York, 2018. http://labeling.pfizer.com/ShowLabeling.aspx?id=2191.
|
|
5
|
Finn RS, Martin M, Rugo HS, Jones S, Im
SA, Gelmon K, Harbeck N, Lipatov ON, Walshe JM, Moulder S, et al:
Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
375:1925–1936. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Turner NC, Ro J, André F, Loi S, Verma S,
Iwata H, Harbeck N, Loibl S, Huang Bartlett C, Zhang K, et al:
PALOMA3 Study Group: Palbociclib in hormone receptor positive
advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:209–219. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tamura K, Mukai H, Naito Y, Yonemori K,
Kodaira M, Tanabe Y, Yamamoto N, Osera S, Sasaki M, Mori Y, et al:
Phase I study of palbociclib, a cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6
inhibitor, in Japanese patients. Cancer Sci. 107:755–763.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Masuda N, Nishimura R, Takahashi M, Inoue
K, Ohno S, Iwata H, Mori Y, Hashigaki S, Muramatsu Y, Nagasawa T,
et al: Palbociclib in combination with letrozole as first-line
treatment for advanced breast cancer: A Japanese phase II study.
Cancer Sci. 109:803–813. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Dickler MN, Tolaney SM, Rugo HS, Cortés J,
Diéras V, Patt D, Wildiers H, Hudis CA, O'Shaughnessy J, Zamora E,
et al: MONARCH 1, a phase II study of abemaciclib, a CDK4 and CDK6
inhibitor, as a single agent, in patients with refractory
HR+/HER2- metastatic breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 23:5218–5224. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sledge GW Jr, Toi M, Neven P, Sohn J,
Inoue K, Pivot X, Burdaeva O, Okera M, Masuda N, Kaufman PA, et al:
MONARCH 2: Abemaciclib in combination with fulvestrant in women
with HR+/HER2- advanced breast cancer who had
progressed while receiving endocrine therapy. J Clin Oncol.
35:2875–2884. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Goetz MP, Toi M, Campone M, Sohn J,
Paluch-Shimon S, Huober J, Park IH, Trédan O, Chen SC, Manso L, et
al: MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 35:3638–3646. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Loibl S, Turner NC, Ro J, Cristofanilli M,
Iwata H, Im SA, Masuda N, Loi S, André F, Harbeck N, et al:
Palbociclib combined with fulvestrant in premenopausal women with
advanced breast cancer and prior progression on endocrine therapy:
PALOMA-3 results. Oncologist. 22:1028–1038. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pfizer Internal Materials:
Pharmacokinetics in Japanese healthy adults (single administration)
[L20170116042]. https://www.pfizer.com/science/find-a-trial/search/Ibrance.
|