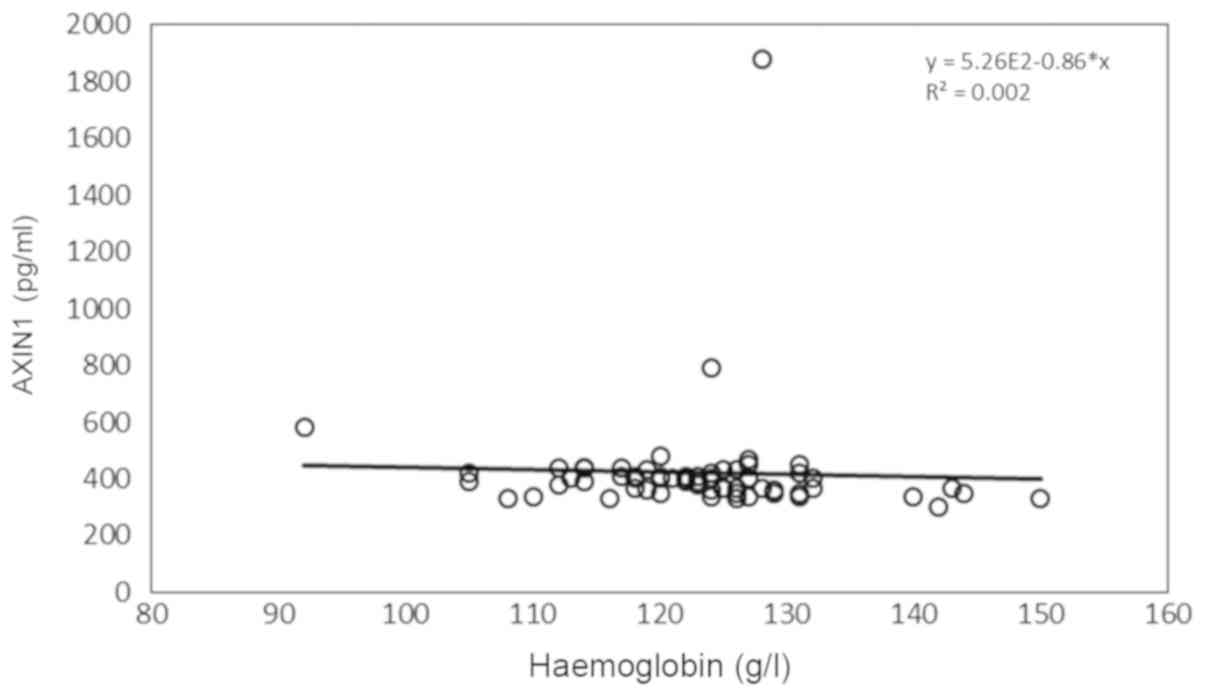
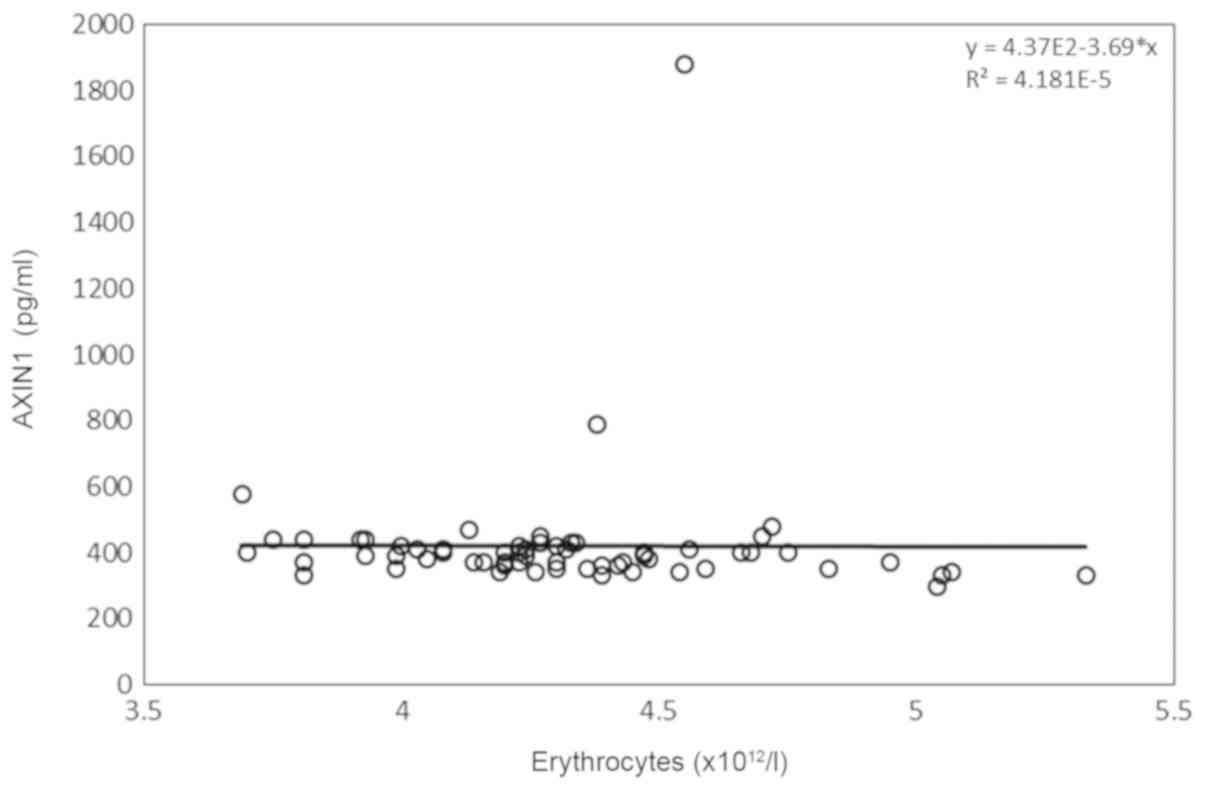
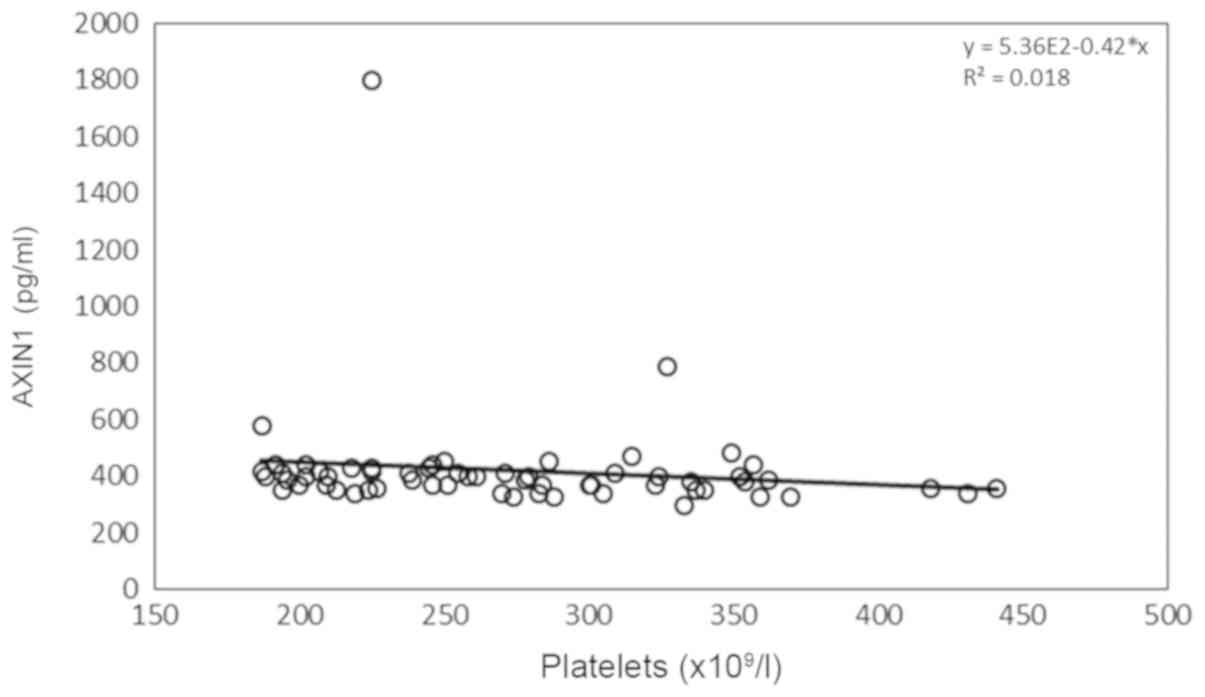
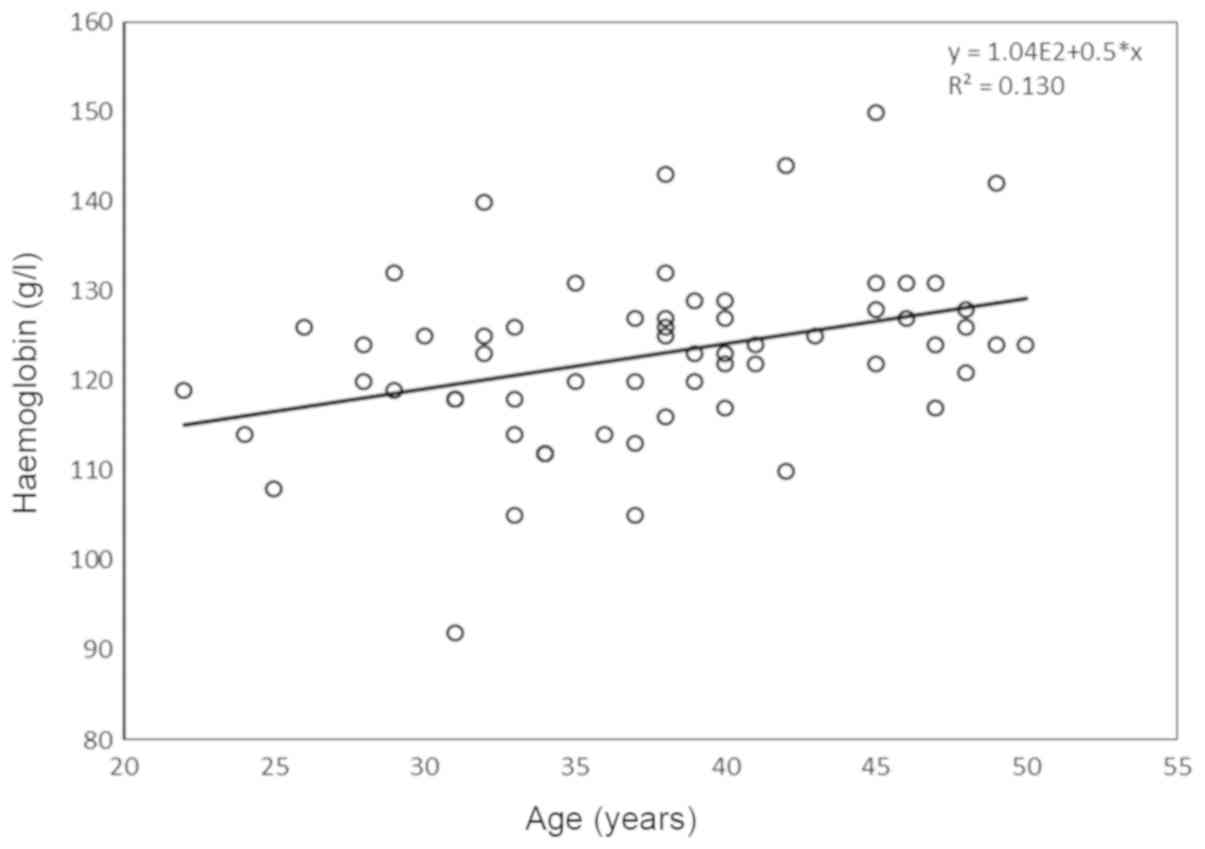
|
1
|
Eskenazi B and Warner ML: Epidemiology of
endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 24:235–258.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Creed J, Maggrah A, Reguly B and Harbottle
A: Mitochondrial DNA deletions accurately detect endometriosis in
symptomatic females of child-bearing age. Biomark Med. 13:291–306.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bulun SE, Yilmaz BD, Sison C, Miyazaki K,
Bernardi L, Liu S, Kohlmeier A, Yin P, Milad M and Wei J:
Endometriosis. Endocr Soc. 40:1048–1079. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Viganò D, Zara F and Usai P: Irritable
bowel syndrome and endometriosis: New insights for old diseases.
Dig Liver Dis. 50:213–219. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Giudice LC and Kao LC: Endometriosis.
Lancet. 364:1789–1799. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Fassbender A, Burney RO, O DF, D'Hooghe T
and Giudice L: Update on biomarkers for the detection of
endometriosis. Biomed Res Int. 2015(130854)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ek M, Roth B, Engström G and Ohlsson B:
AXIN1 in plasma or serum is a potential new biomarker for
endometriosis. Int J Mol Sci. 20(189)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kikuchi A: Roles of axin in the Wnt
signalling pathway. Cell Signal. 11:777–788. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
MacDonald BT, Tamai K and He X:
Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Components, mechanisms, and diseases.
Dev Cell. 17:9–26. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shi J, Chi S, Xue J, Yang J, Li F and Liu
X: Emerging role and therapeutic implication of Wnt signaling
pathways in autoimmune diseases. J Immunol Res.
2016(9392132)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hod K, Dickman R, Sperber A, Melamed S,
Dekel R, Ron Y, Halpern Z, Berliner S and Maharshak N: Assessment
of high-sensitivity CRP as a marker of micro-inflammation in
irritable bowel syndrome. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 23:1105–1110.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pletikosic S, Plavsic I, Hauser G and
Tkalcic M: Fecal calprotectin and serum chromogranin A as potential
biomarkers of irritable bowel syndrome symptom severity. Med
Hypotheses. 85:339–342. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Thubert T, Santulli P, Marcellin L, Menard
S, M'Baye M, Streuli I, Borghese B, de Ziegler D and Chapron C:
Measurement of hs-CRP is irrelevant to diagnose and stage
endometriosis: Prospective study of 834 patients. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 210:533.e1–533.e10. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ni Bhriain H, Trovik J, Wik E, Stefansson
IM, Akslen LA, Salvesen HB and Staff AC: Plasma calprotectin
concentrations in women with endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol.
114:491–495. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kostakis ID, Cholidou KG, Kallianidis K,
Perrea D and Antsaklis A: The role of calprotectin in obstetrics
and gynecology. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 151:3–9.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yang Z, Clark N and Park KT: Effectiveness
and cost-effectiveness of measuring fecal calprotectin in diagnosis
of inflammatory bowel disease in adults and children. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:253–262, e2. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Mumolo MG, Bertani L, Ceccarelli L, Laino
G, Di Fluri G, Albano E, Tapete G and Costa F: From bench to
bedside: Fecal calprotectin in inflammatory bowel diseases clinical
setting. World J Gastroenterol. 24:3681–3694. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
World Medical Association: World medical
association declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA 310: 2191-2194, 2013.
|
|
19
|
Ek M, Roth B, Nilsson PM and Ohlsson B:
Characteristics of endometriosis: A case-cohort study showing
elevated IgG titers against the TSH receptor (TRAb) and mental
comorbidity. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 231:8–14.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bengtsson M, Ohlsson B and Ulander K:
Development and psychometric testing of the visual analogue scale
for irritable bowel syndrome (VAS-IBS). BMC Gastroenterol.
7(16)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Labmedicin Skåne Analysportalen. Available
online: http://www.analysportalen-labmedicin.skane.se/.
|
|
22
|
Bengtsson M, Hammar O, Mandl T and Ohlsson
B: Evaluation of gastrointestinal symptoms In different patient
groups using the visual analogue scale for irritable bowel syndrome
(VAS-IBS). BMC Gastroenterol. 11(122)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
World Health Organization. Global databae
on body mass index. Available from: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/disease-prevention/nutrition/a-healthy-lifestyle/body-mass-index-bmi.
|
|
24
|
Moparthi L and Koch S: Wnt signaling in
intestinal inflammation. Differentiation. 108:24–32.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li VS, Ng SS, Boersema PJ, Low TY,
Karthaus WR, Gerlach JP, Mohammed S, Heck AJ, Maurice MM, Mahmoudi
T and Clevers H: Wnt signaling through inhibition of β-catenin
degradation in an intact Axin1 complex. Cell. 149:1245–1256.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Arend RC, Londoño-Joshi AI, Straughn JM Jr
and Buchsbaum DJ: The Wnt/β-catenin pathway in ovarian cancer: A
review. Gynecol Oncol. 131:772–779. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Silva-García O, Valdez-Alarcón JJ and
Baizabal-Aguirre VM: The Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway controls
the inflammatory response in infections caused by pathogenic
bacteria. Mediators Inflamm. 2014(310183)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Katoh M: Multi-layered prevention and
treatment of chronic inflammation, organ fibrosis and cancer
associated with canonical WNT/β-catenin signaling activation
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 42:713–725. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ikeda S, Kishida S, Yamamoto H, Murai H,
Koyama S and Kikuchi A: Axin, a negative regulator of the Wnt
signaling pathway, forms a complex with GSK-3beta and beta-catenin
and promotes GSK-3beta-dependent phosphorylation of beta-catenin.
EMBOJ. 17:1371–1384. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Song X, Wang S and Li L: New insights into
the regulation of Axin function in canonical Wnt signaling pathway.
Protein Cell. 5:186–193. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mukherjee A, Dhar N, Stathos M, Schaffer
DV and Kane RS: Understanding how Wnt influences destruction
complex activity and β-catenin dynamics. iScience. 6:13–21.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Matsuzaki S, Botchorishvili R, Pouly JL
and Canis M: Targeting the Wnt/beta-pathway in endometriosis: A
potentially effective approach for treatment and prevention. Mol
Cell Ther. 2(36)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang L, Xiong W, Xiong Y, Liu H and Liu
Y: 17 β-Estradiol promotes vascular endothelial growth factor
expression via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway during the pathogenesis of
endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod. 22:526–535. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Issa B, Onon TS, Agrawal A, Shekhar C,
Morrs J, Hamdy S and Whorwell PJ: Visceral hypersensitivity in
endometriosis: A new target for treatment? Gut. 61:3667–3672.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Nilholm C, Roth B and Ohlson B: A dietary
intervention with reduction of starch and sucrose leads to reduced
gastrointestinal and extra-intestinal symptoms in IBS patients.
Nutrients. 11: pii(E1662)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Daryabor G, Kabelitz D and Kalantar K: An
update on immune dysregulation in obesity-related insulin
resistance. Scand J Immunol. 89(e12747)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Røseth AG, Schmidt PN and Fagerhol MK:
Correlation between faecal excretion of indium-111-labelled
granulocytes and calprotectin, a granulocyte marker protein, in
patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol.
34:50–54. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Andréasson K, Scheja A, Saxne T, Ohlsson B
and Hesselstrand R: Faecal calprotectin: A biomarker of
gastrointestinal disease in systemic sclerosis. J Intern Med.
270:50–57. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ek M, Roth B, Valentin L, Nordengren J and
Ohlsson B: Autoantibodies common in patients with gastrointestinal
diseases are not found in patients with endometriosis: A
cross-sectional study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
240:370–374. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hirsch M, Begum MR, Paniz É, Barker C and
Davis CJ: Diagnosis and management of endometriosis: A systematic
review of international and national guidelines. BJOG. 125:556–564.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|