Introduction
In recent years, the prevalence of food allergies
(FA) in children has been increasing. Food allergy prevalence
increased from 3.5% in 1999 to 7.7% in 2009 among Chinese infants
(1). A more than threefold increase
in the prevalence of peanut and tree nut allergy between 1997 and
2008 has been documented (2). The
most reliable diagnostic method for FA is oral food challenge
(OFC). Predictors of symptoms that may appear by OFC include
history of anaphylaxis, type of food allergy, high levels of
specific (s)IgE antibody titer and asthma (3,4). As
sIgE is a numerical value, it is easy to observe changes over time.
sIgE is associated with food tolerance up to 3 years of age, making
it useful in evaluating the course of FA in clinical practice
(5-7).
Furthermore, probability curve may be used as a reference to
predict the results of OFC. However, it is difficult to conclude
whether probability curves have external validity if the patient
population and dose differ from those in clinical practice. In
addition, each probability curve has its own 95% confidence
interval and it is challenging to predict the outcome of OFC based
on the probability curve alone, even if it is well-adapted to the
patient population from which the curve was generated and the
clinical situation. In patients with sIgE >100 UA/ml (≥100
group), the positive rate of OFC is ~100%; however, reports
indicate that the positive predictive value does not reach 90% in
≥100 group (5,8-10).
There are conflicting reports regarding whether sIgE
levels are associated with anaphylaxis and severity of FA (11-13).
Patients may continue unnecessary food elimination based solely on
sIgE levels, leading to overestimation of high-risk cases. Delays
in OFC lead to prolonged and unnecessary elimination of food and
contribute to adverse effects such as decreased bone density, as in
the case of eliminating milk (14).
The more the food type is removed, the more it affects growth
(15). Furthermore, unbalanced diet
may be a risk factor for obesity (16).
sIgE assayed by Immuno CAP® (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) is classified into seven levels ranging from
class 0 to 6 (≥100 group) (17).
The association between sIgE levels and clinical characteristics of
children with FAs is unclear. Therefore, the present study aimed to
clarify the characteristics of children with FAs and sIgE ≥100
compared with patients with sIgE <100 UA/ml, with a focus on
clinical characteristics and OFC results.
Materials and methods
Study design
The present retrospective study was performed at
Gifu Prefectural General Medical Center, Gifu, Japan from July 2017
to March 2023. The study was approved (approval no. 773-2) by the
Ethics Committee. The study was based on chart review of OFC
results eliciting objective reactions to wheat, egg and milk
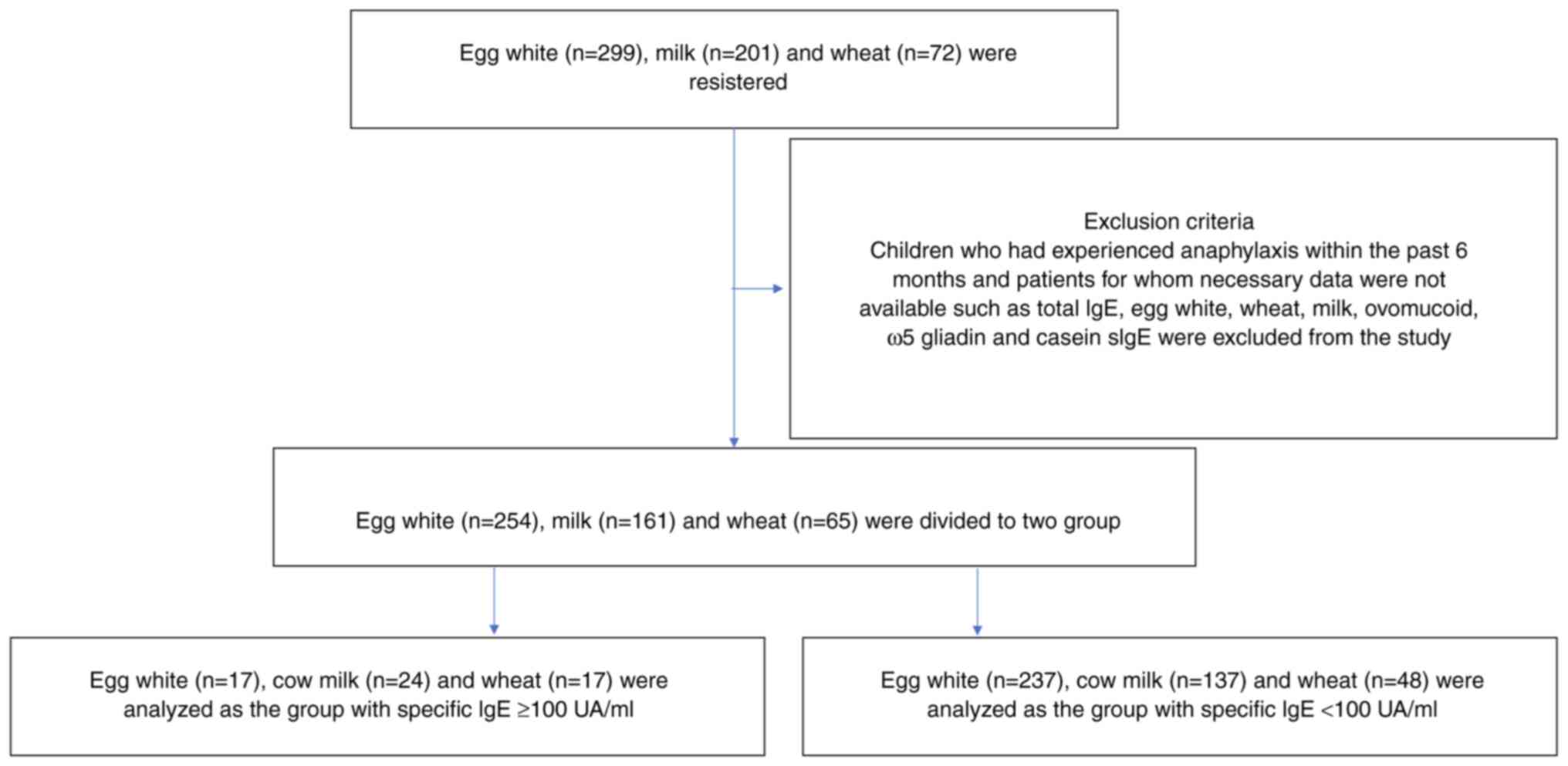
(18). Participants (n=572) with
egg white (n=299), milk allergy (n=201) and wheat allergy (n=72)
were recruited. A total of 69% of participants were male.
Participants were patients aged 0-16 years who were clinically
reactive to eggs, milk and wheat with sIgE >0.35 UA/ml. OFC was
performed for diagnosis of food allergies, confirmation of
tolerance and increase of intake of allergic food at home. The age
and the clinical history of each patient were analyzed. Children
who had experienced anaphylaxis within the past 6 months and those
for whom data such as total (t)IgE levels and egg white, wheat,
milk, ovomucoid, ω5 gliadin and casein sIgE allergy were not
available were excluded from the study. Probability curves for
predicting OFC outcomes were taken from reference (10).
IgE test
tIgE and sIgE serum levels in response to egg white,
cow milk, wheat, ovomucoid, casein and ω5 gliadin were assessed
using sandwich assays (ImmunoCAP®, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.),
according to the manufacturer's instructions (Cat. nos. UF1, UF2,
UF4, UF233, UF78 and UF416 for egg white, cow milk, wheat,
ovomucoid, casein and ω5 gliadin respectively. Within 1 year of the
OFC, serum samples were taken by venipuncture. In the ≥100 group,
samples were diluted 10-fold or 100-fold and then assayed by
ImmunoCap®.
OFC
Written consent was obtained from parents or
guardians of participants prior to OFC. Following IgE tests, OFC
was performed within 1 year. The open OFC test was performed in
accordance with the Japanese Guideline for Food Allergy
2020(19). Anaphylaxis was defined
in accordance with National Institute of Allergy and Infectious
Disease (20). The total challenge
dose depended on the dose of egg white, cow milk and wheat ingested
daily before the OFC test. OFC was performed under medical
supervision with access to emergency support. Patients underwent
physical examination by a doctor prior to feeding initiation to
ensure that patients are healthy enough to undergo OFC. Vital signs
and observations for lung and skin were recorded on clinical
charts. Any signs or symptoms during the OFC were recorded. Eggs
were boiled at 100˚C for 20 min and separated into egg white and
yolk immediately after cooking, of which only egg whites were used
for the test. Udon noodles were used as the wheat source. The
number of load was one to five times.
The interval between each load was 15 to 60 min.
After 2 h from the last load, the patient was allowed to go home if
no symptoms were induced. Eliciting dose was defined as the lowest
dose of egg white, cow milk or wheat eliciting an objective
allergic reaction as described in the allergy guidelines (19). The eliciting dose was converted to
protein mass as follows: 45 g boiled egg = 4.5 g egg white protein;
10 g cow milk = 0.33 g protein and 10 g udon = 0.26 g wheat
protein.
Response to symptom induction
Depending on the severity of symptoms, oral
antihistamines, inhaled β-stimulants and intramuscular adrenaline
injection were administered according to the Japanese Guideline for
Food Allergy 2020(19).
Statistical analysis
The data are presented as median and inter quartile
range. Mann-Whitney U test was used for continuous variables.
Fisher's exact test was used to analyze categorical variables.
Spearman's rank correlation coefficient was used to determine
correlation of eliciting dose and sIgE that did not follow a normal
distribution. All tests were two-sided. All analyses were performed
using EZR ver 1.61 (jichi.ac.jp/saitama-sct/SaitamaHP.files/statmed.html).
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
Characteristic of participants
A total of 299 patients with egg, 201 with cow milk
and 72 with wheat allergy were recruited; patients with incomplete
data were excluded from the study. A total of 17 patients with egg,
24 with cow milk and 17 with wheat allergy were included in the
≥100 group (Fig. 1). A total 237
patients with egg, 137 with cow milk and 48 with wheat allergy were
included in the <100 group.
The median age in the ≥100 group was older than that
in the <100 group. In patients with egg white allergy, ≥100
group had significantly more previous anaphylaxis than the <100
group. In the ≥100 group, positive rates were 100, 64 and 67% for
egg white, milk and wheat allergies, respectively In the <100
group, positive rates were 17, 40 and 28% for egg white, milk and
wheat allergies, respectively (Table
I). Other allergic complications such as asthma, allergic
rhinitis and atopic dermatitis tended to be more common in the ≥100
group. tIgE in ≥100 was higher than in the <100 group. Median
sIgE levels in the ≥100 group were 170, 248, 197, 144 and 285 UA/ml
for egg white, cow milk, wheat, ovomucoid and casein, respectively
(Table II). Median sIgE levels in
the <100 group were 6.1, 6.4, 11.6, 2.8, 5.5 and 1.0 for egg
white, cow milk, wheat, ovomucoid, casein and ω-5 gliadin
allergies, respectively.
 | Table IPatient characteristics. |
Table I
Patient characteristics.
| Characteristic | Egg white ≥100 | Egg white
<100 | Milk ≥100 | Milk <100 | Wheat ≥100 | Wheat <100 |
|---|
| Male (%) | 11(65) | 155(63) | 15(63) | 106(71) | 9(53) | 37(65) |
| Age, years (IQR) | 7 (5-8)a | 4 (2-7) | 7 (6-8)a | 6 (3-8) | 9 (8-11)a | 6 (3-8) |
| History of
anaphylaxis (%) | 6(35)a | 34(14) | 9(36) | 29(19) | 3(18) | 11(19) |
| Asthma (%) | 5(29) | 45(18) | 7(29) | 25(17) | 9(53) | 16(28) |
| Allergic rhinitis
(%) | 0 (0) | 36(15) | 2(8) | 12(8) | 1(7) | 11(19) |
| Atopic dermatitis
(%) | 5(29) | 84(34) | 8(3) | 43(29) | 4(24) | 28(49) |
| sIgE, UA/ml
(IQR) | 170 (151-212) | 6.07 (3-17) | 248 (161-332) | 6 (3-25) | 197 (133-354) | 13.4 (4-42) |
| tIgE, UA/ml
(IQR) | 1154
(1,028-2,297)a | 361.5
(96-1,055) | 2,542
(1,560-5,008)a | 463
(151-1,304) | 627
(423-1,128) | 824
(272-1,883) |
| Number of OFC tests
(%) | 7(41) | 247(100) | 11(46) | 150(100) | 9(53) | 57(100) |
| Positive OFC rate,
% | 100a | 17 | 64 | 40 | 67 | 28 |
 | Table IIMedian specific IgE levels. |
Table II
Median specific IgE levels.
| Group | Egg white | Cow milk | Wheat | Ovomucoid | Casein | ω5 gliadin |
|---|
| ≥100 UA/ml | 170 | 248 | 197 | 144 | 285 | Not detected |
| <100 UA/ml | 6 | 6 | 12 | 3 | 6 | 1 |
OFC and eliciting dose
The ≥100 group had significantly lower total loading
dose than the <100 group. (Table
III). In the ≥100 group of patients with milk and wheat
allergy, there was no significant difference in the loading dose
regardless of whether the test result was positive or negative. In
the <100 group, the egg loadings were significantly lower for
positive compared with negative OFC; however, no significant
differences were found for milk and wheat. The minimum amount of
loading protein that did not induce symptoms was 0.0033 and 0.0026
g for milk and wheat, respectively.
 | Table IIIMedian total protein load. |
Table III
Median total protein load.
| Group | Egg white ≥100, g
(IQR) | Egg white <100,
g (IQR) | Milk ≥100, g
(IQR) | Milk <100, g
(IQR) | Wheat ≥100, g
(IQR) | Wheat <100, g
(IQR) |
|---|
| Overall | 2
(1-4)a | 29 (7-40) | 1.0
(0.3-2.2)a | 14.0
(3.0-68.0) | 1.00
(1.00-3.00)a | 50.0
(10.0-200.0) |
| Positive | 2
(1-4)a | 3 (1-4) | 0.03
(0.01-0.08)a | 0.5 (0.1-2.2) | 0.04
(0.03-0.07)a | 1.3 (0.3-5.2) |
| Negative | Not detected | 3 (1-3) | 0.09
(0.01-0.29)a | 1.7 (0.3-2.2) | 0.003
(0.003-0.070)a | 1.3 (0.3-5.2) |
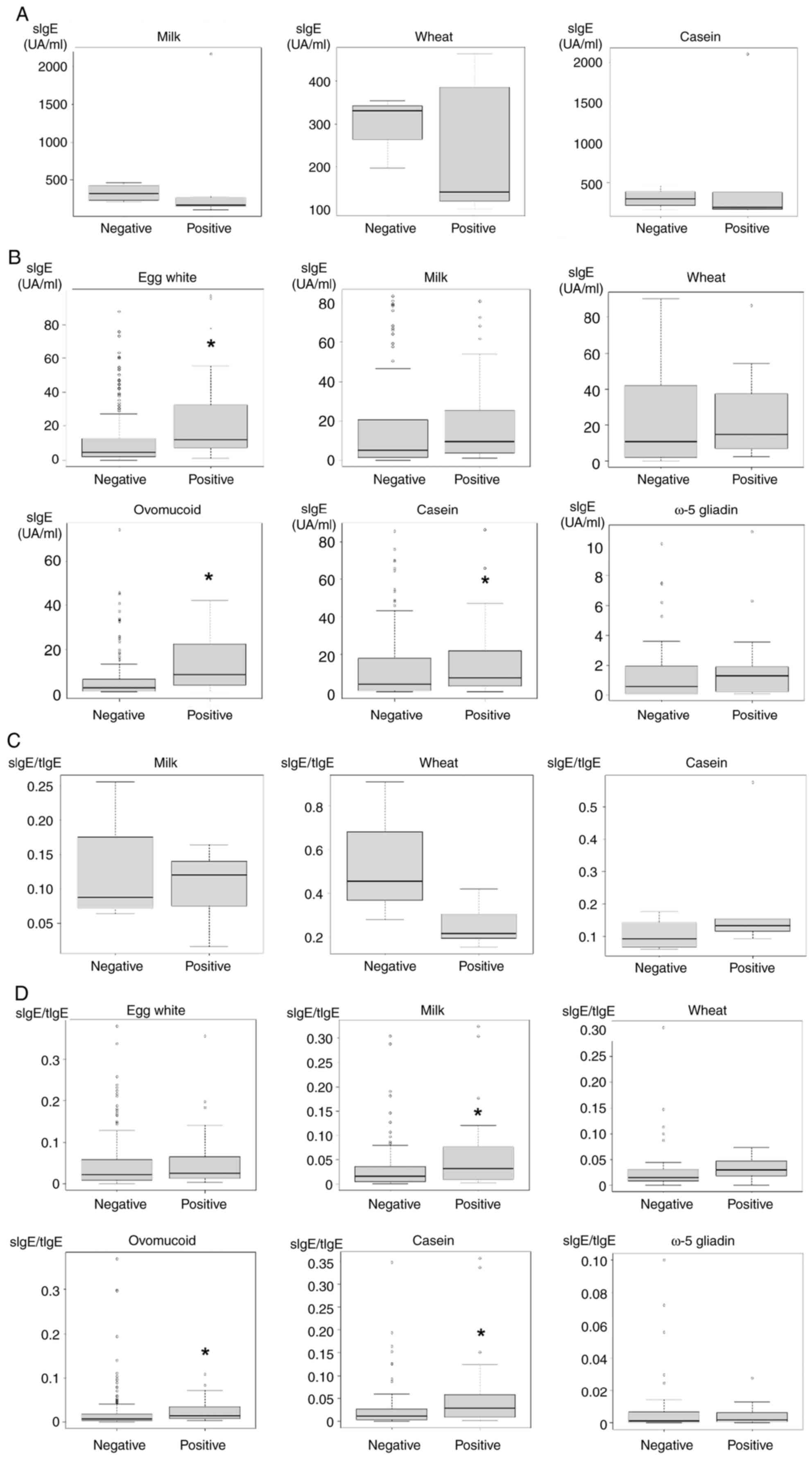
sIgE predicts the probability of positive outcomes
in OFC (3,5). Therefore, correlation between positive
OFC and sIgE were analyzed. In the ≥100 group, a significant
difference in sIgE between positive and negative OFC was not
observed (Fig. 2A). In the <100
group, positive OFC showed higher sIgE for egg white, ovomucoid and
casein allergies compared with those shown by the negative OFC
(Fig. 2B).
Total IgE in the ≥100 group was higher than in the
<100 group. Therefore, correlation between positive OFC and
sIgE/tIgE was analyzed. In the ≥100 group, a significant difference
in sIgE/tIgE between positive and negative OFC was not observed
(Fig. 2C). In the <100 group,
positive OFC showed higher sIgE/tIgE for ovomucoid, cow milk and
casein allergies compared with those shown by the negative OFC
(Fig. 2D).
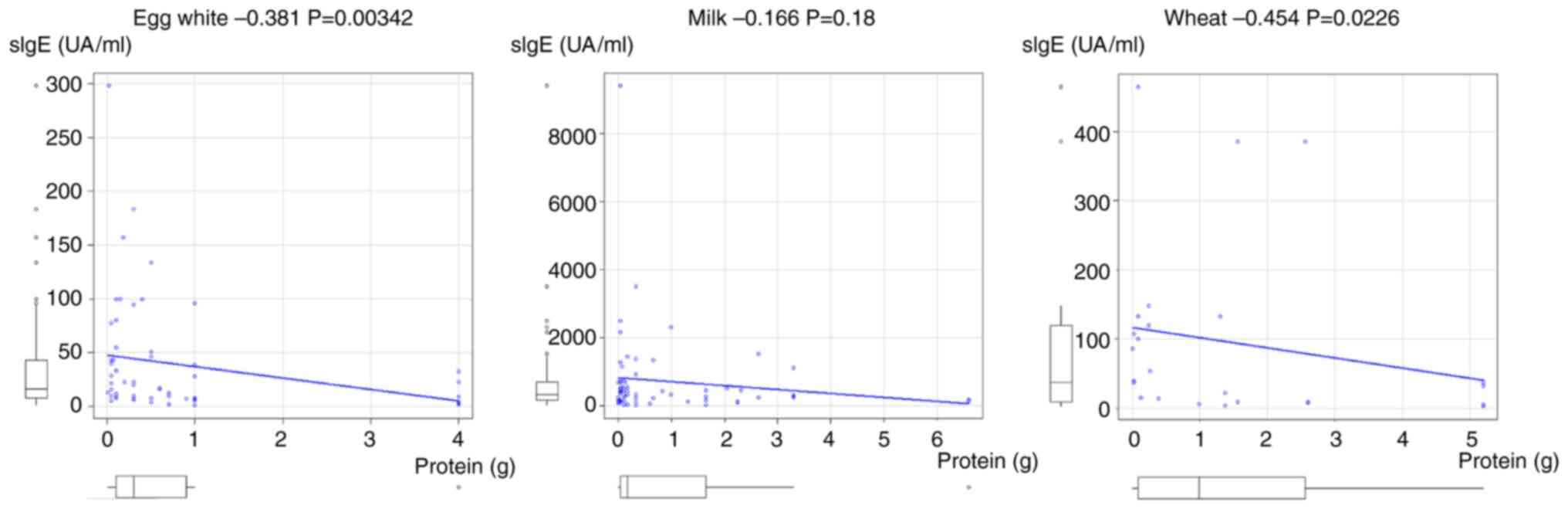
Finally, eliciting dose in OFC was analyzed
(Fig. 3). The eliciting dose of egg
white and udon noodles was correlated with sIgE for egg white and
wheat allergy, respectively; however, there was no correlation
between eliciting dose and sIgE for cow milk allergy.
Discussion
The present assessed clinical characteristics and
OFC results in the ≥100 group. To the best of our knowledge, no
previous studies investigated sIgE ≥100. Previous studies on
peanuts showed that the higher the sIgE value, the lower the
eliciting dose in OFC (21,22). For other foods, the higher the sIgE
value, the lower the eliciting dose. The results of the present
study may be useful in determining the loading levels for OFC. For
egg white, the prevalence of anaphylaxis was significantly higher
in the ≥100 compared with that in the <100 group. In the ≥100
group, positive rates were 100, 64 and 67% for egg white, milk and
wheat allergies, respectively, which differed from those expected
by the probability curve except for egg white allergy (10). In addition, there was a significant
difference in the positive rate of egg white allergy in the ≥100
compared with <100 group, whereas there was no significant
difference in positive rates of milk and wheat allergies in the
≥100 group compared with those in the <100 group. Because the
positive rate of OFC was 100%, avoiding OFC for egg white allergy
with 0.02 g loading protein in the ≥100 group may be recommended;
however, OFC may be safely performed for milk and wheat allergies
in the ≥100 group by setting the amount of intake appropriately. In
the present study, the minimum amount of loading protein that did
not induce symptoms upon wheat intake was 0.0026 g, hence this
amount could be used as a guide for loading tests. In milk intake,
a loading protein level <0.0033 g may not induce symptoms. For
egg white intake, all OFCs of the ≥100 group were positive, and it
was not known what loading level might safely be used in OFC;
however, it was considered necessary to at least decrease the
loading level to <0.02 g protein, which was the minimum loading
level in the present study. With regard to the interval between
loading, 60 min interval is associated with significantly lower
symptom severity than 30 and 40 min intervals (23). Although single doses were mostly
used in the present study due to the minute amounts, it may be
possible to perform loading tests more safely by using smaller
doses at 60-min intervals.
The ≥100 group for egg white allergy exhibited
significantly more anaphylaxis than the <100 group; however,
prediction of the onset of anaphylaxis is challenging based on sIgE
(24). To the best of our
knowledge, no study which have analyzed ≥100 group; however, the
results should be verified in the future with a larger number of
patients
sIgE/tIgE ratio is useful in predicting outcome of
OFC to distinguish it from false-positive sIgE in patients with
atopic dermatitis (24). However,
significant correlations have been observed only for peanut allergy
and no correlations have been shown for egg white, milk and wheat
allergy. In the <100 group, the correlation among egg white,
wheat, ovomucoid and casein allergies for both sIgE and sIgE/total
IgE ratio between positive and negative groups, was consistent with
that of a previously reported study (25). By contrast, in the ≥100 group, there
was no significant difference for sIgE and sIgE/tIgE ratio between
the positive and negative groups. The values of sIgE above 100 and
sIgE/tIgE levels may be not useful for predicting OFC result in the
≥100 group.
Further investigation is needed to determine whether
sIgE and sIgE/tIgE correlate with the results of the OFC,
especially in the ≥100 group.
Previous studies have suggested a significant
negative correlation between sIgE and the threshold of OFC loading
(22,26). In the present study, the ≥100 group
had a significantly lower threshold than the <100 group,
indicating a negative association between sIgE and threshold. This
does not mean that OFC cannot be performed in patients with high
sIgE; however, it is necessary to decrease the loading amount to
the maximum extent for safety. Eliciting dose in OFC gradually
increases as the patient continues to eat small amounts of food
(27); hence, exploring the dose
which does not induce the allergic symptoms by performing OFC with
very small quantities of food is meaningful. Continuing to eat that
amount may raise the eliciting dose.
Moreover, if the threshold can be raised, induction
of allergic symptoms by accidental ingestion of small amounts of
food may be decreased.
The present study has certain limitations. First, it
was a single-center, retrospective study with a small number of
patients and lack of age-matching. These effects may have caused
selection bias. To resolve this, the sample size should be
increased and the population should be age-matched. Second, the
amounts of food loaded were not matched. The loading dose was
determined at the discretion of the physician in charge of the
loading test. Since the amount of food loaded has a notable impact
on the results of the loading test (19), it is necessary to conduct the test
with the same amount of food loaded in the future.
In peanut allergy, patient characteristics
associated with symptom thresholds are sex and atopic dermatitis
(28,29). For the present study, significant
difference was not found in either of these in the ≥100 group;
however, if the number of patients was increased, a change may be
observed. The ages of patients in the ≥100 group were significantly
higher than in the <100 group. There are reports that older age
is associated with symptom severity and adrenaline administration
in OFC (30,31). Therefore, in the present study, age
may have influenced the results. This suggests that acquiring
tolerance takes a long period for the ≥100 group. However,
increasing the amount of food that can be eaten can decrease the
burden on patients and their families. Additionally, decreasing the
opportunity to perform OFC based solely on sIgE may be
disadvantageous to patients and their families. Food allergies not
only affect individuals with allergic reactions but also cause
psychological stress for both patients and their families due to
the limitations that come with avoiding certain foods (32,33).
Basophil activation test is associated with symptom severity and
threshold in OFC in peanut allergy (34). Basophil activation test, which were
not investigated in this study, may predicts OFC positivity in the
patients with food allergy.
For milk and wheat allergy, there was no significant
difference in positive OFC in the ≥100 compared with that in the
<100 group, Therefore OFC may be safely performed by adjusting
the amount of intake for the ≥100 group. When performing OFC for
the ≥100 group for egg white allergy, the timing and the amount of
intake must be considered.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
SY and KH wrote the manuscript and analyzed data. ME
and IA contributed to the conception and design of the study and
revised the manuscript. SY and KH confirm the authenticity of all
the raw data. MK and HK analyzed and interpreted and revised the
manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final
manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The requirement for informed consent was waived due
to the retrospective nature of the study. The study was approved by
the Ethical Review Committee of Gifu Prefectural General Medical
Center, Gifu, Japan (approval no. 773-2).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Hu Y, Chen J and Li H: Comparison of food
allergy prevalence among Chinese infants in Chongqing, 2009 versus
1999. Pediatr Int. 52:820–824. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Peters RL, Krawiec M, Koplin JJ and Santos
AF: Update on food allergy. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 32:647–657.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kawahara T, Tezuka J, Ninomiya T, Honjo S,
Masumoto N, Nanishi M, Nakayama H and Ohga S: Risk prediction of
severe reaction to oral challenge test of cow's milk. Eur J
Pediatr. 178:181–188. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yanagida N, Sato S, Takahashi K, Nagakura
KI, Asaumi T, Ogura K and Ebisawa M: Increasing specific
immunoglobulin E levels correlate with the risk of anaphylaxis
during an oral food challenge. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 29:417–424.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Celik-Bilgili S, Mehl A, Verstege A,
Staden U, Nocon M, Beyer K and Niggemann B: The predictive value of
specific immunoglobulin E levels in serum for the outcome of oral
food challenges. Clin Exp Allergy. 35:268–273. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Palosuo K, Kukkonen AK, Pelkonen AS and
Mäkelä MJ: Gal d 1-specific IgE predicts allergy to heated egg in
Finnish children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 29:637–643.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kim H, Jeong K, Park M, Roh YY, Jung JH,
Kim SY, Kim JD, Kim MJ, Kim YH, Sohn MH, et al: Predicting the
outcome of pediatric oral food challenges for determining tolerance
development. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 16:179–190.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Komata T, Söderström L, Borres MP,
Tachimoto H and Ebisawa M: The predictive relationship of
food-specific serum IgE concentrations to challenge outcomes for
egg and milk varies by patient age. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
119:1272–1274. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Komata T, Söderström L, Borres MP,
Tachimoto H and Ebisawa M: Usefulness of wheat and soybean specific
IgE antibody titers for the diagnosis of food allergy. Allergol
Int. 58:599–603. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sato S, Ogura K, Takahashi K, Sato Y,
Yanagida N and Ebisawa M: Usefulness of antigen-specific IgE
probability curves derived from the 3gAllergy assay in diagnosing
egg, cow's milk, and wheat allergies. Allergol Int. 66:296–301.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Buyuktiryaki B and Santos AF: Food allergy
severity predictions based on cellular in vitro tests. Expert Rev
Mol Diagn. 20:679–692. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Malucelli M, Farias Junior R, Mello RG and
Prando C: Biomarkers associated with persistence and severity of
IgE-mediated food allergies: A systematic review. J Pediatr (Rio
J). 99:315–321. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Qi W, Chen J, Zheng H, Zhu W, Guan K and
Sha L: Serum levels of specific IgE to cow's milk and its
components as predictors of anaphylaxis in Chinese children with
cow's milk allergy. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol: January 6, 2024
(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
14
|
Mailhot G, Perrone V, Alos N, Dubois J,
Delvin E, Paradis L and Des Roches A: Cow's milk allergy and bone
mineral density in prepubertal children. Pediatrics.
137(e20151742)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hobbs CB, Skinner AC, Burks AW and Vickery
BP: Food allergies affect growth in children. J Allergy Clin
Immunol Pract. 3:133–134.e1. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Meyer R, Wright K, Vieira MC, Chong KW,
Chatchatee P, Vlieg-Boerstra BJ, Groetch M, Dominguez-Ortega G,
Heath S, Lang A, et al: International survey on growth indices and
impacting factors in children with food allergies. J Hum Nutr Diet.
32:175–184. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lin IH, Tsai MC, Chen JP and Fu LS:
Allergic children with extremely high total IgE but no allergen
identified in the initial screening panel. J Microbiol Immunol
Infect. 54:474–481. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Otsuka Y, Morita H, Kimura Y, Mori R,
Miyazaki K, Shimokawa Y, Tatabayashi K, Funato M and Kaneko H:
Threshold dose of cow's milk in sensitization to casein higher than
those of casein and β-lactoglobulin in children with cow's milk
allergy. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol: April 18, 2021 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
19
|
Ebisawa M, Ito K and Fujisawa T: Committee
for Japanese Pediatric Guideline for Food Allergy, The Japanese
Society of Pediatric Allergy and Clinical Immunology; Japanese
Society of Allergology. Japanese guidelines for food allergy 2020.
Allergol Int. 69:370–386. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sampson HA, Muñoz-Furlong A, Campbell RL,
Adkinson NF Jr, Bock SA, Branum A, Brown SG, Camargo CA Jr, Cydulka
R, Galli SJ, et al: Second symposium on the definition and
management of anaphylaxis: Summary report-Second National Institute
of Allergy and Infectious Disease/Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis
Network symposium. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 117:391–397.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Elegbede CF, Papadopoulos A, Just J,
Moneret-Vautrin DA, Deschildre A and Crépet A: Gender, prick test
size and rAra h 2 sIgE level may predict the eliciting dose in
patients with peanut allergy: Evidence from the Mirabel survey.
Clin Exp Allergy. 49:677–689. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yanagida N, Sato S and Ebisawa M:
Relationship between eliciting doses and the severity of allergic
reactions to food. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 23:226–232.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kitamura K, Makino A, Matsui T, Takasato
Y, Sugiura S and Ito K: A 60-minute dosing interval is safer than a
30- or 40-minute interval in oral food challenge. Allergol Int.
71:230–235. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Turner PJ, Baumert JL, Beyer K, Boyle RJ,
Chan CH, Clark AT, Crevel RW, DunnGalvin A, Fernández-Rivas M,
Gowland MH, et al: Can we identify patients at risk of
life-threatening allergic reactions to food? Allergy. 71:1241–1255.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gupta RS, Lau CH, Hamilton RG, Donnell A
and Newhall KK: Predicting outcomes of oral food challenges by
using the allergen-specific IgE-total IgE ratio. J Allergy Clin
Immunol Pract. 2:300–305. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yanagida N, Sato S, Nagakura KI, Takahashi
K, Fusayasu N, Miura Y, Itonaga T, Ogura K and Ebisawa M:
Relationship between serum allergen-specific immunoglobulin E and
threshold dose in an oral food challenge. Pediatr Allergy Immunol.
34(e13926)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sugiura S, Kitamura K, Makino A, Matsui T,
Furuta T, Takasato Y, Kando N and Ito K: Slow low-dose oral
immunotherapy: Threshold and immunological change. Allergol Int.
69:601–609. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
van der Zee T, Dubois A, Kerkhof M, van
der Heide S and Vlieg-Boerstra B: The eliciting dose of peanut in
double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenges decreases with
increasing age and specific IgE level in children and young adults.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 128:1031–1036. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Just J, Elegbede CF, Deschildre A,
Bousquet J, Moneret-Vautrin DA and Crepet A: Mirabel study group.
Three peanut-allergic/sensitized phenotypes with gender difference.
Clin Exp Allergy. 46:1596–1604. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yanagida N, Sato S, Asaumi T, Ogura K and
Ebisawa M: Risk factors for severe reactions during double-blind
placebo-controlled food challenges. Int Arch Allergy Immunol.
172:173–182. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kennedy K, Alfaro MKC, Spergel ZC, Dorris
SL, Spergel JM and Capucilli P: Differences in oral food challenge
reaction severity based on increasing age in a pediatric
population. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 127:562–567.e1.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cummings AJ, Knibb RC, King RM and Lucas
JS: The psychosocial impact of food allergy and food
hypersensitivity in children, adolescents and their families: A
review. Allergy. 65:933–945. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Knibb RC, Ibrahim NF, Stiefel G, Petley R,
Cummings AJ, King RM, Keeton D, Brown L, Erlewyn-Lajeunesse M,
Roberts G and Lucas JS: The psychological impact of diagnostic food
challenges to confirm the resolution of peanut or tree nut allergy.
Clin Exp Allergy. 42:451–459. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Santos AF, Du Toit G, O'Rourke C, Becares
N, Couto-Francisco N, Radulovic S, Khaleva E, Basting M, Harris KM,
Larson D, et al: Biomarkers of severity and threshold of allergic
reactions during oral peanut challenges. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
146:344–355. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|