Exp Ther Med 17:[Related article:] 2451–2456, 2019; DOI:
10.3892/etm.2019.7253
Following the publication of the above article, and
also an erratum in 2019 (doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7994) in which an
error in the published acceptance date of the article was
corrected, the authors have contacted the Editorial Office to
explain that they have discovered a couple of further errors in
this paper that are in need of correction.
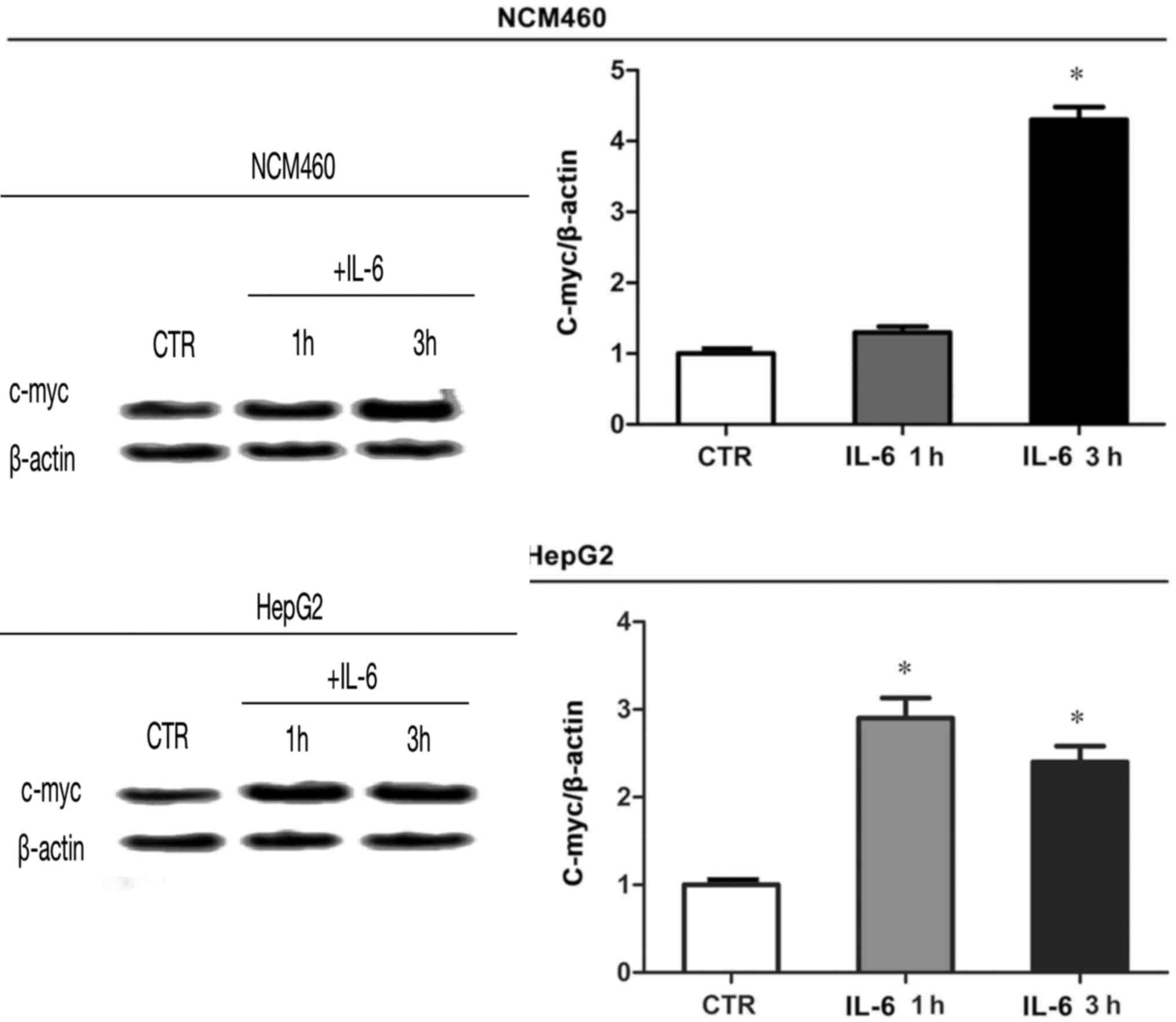
First, in the published version of Fig. 5C on p. 2454, the authors have
realized that the β-actin western blots selected for the NCM460 and
HepG2 cells were inadvertently the same.The authors have
re-examined their original data, and wish to present alternative
data for Fig. 5C, as shown in the
revised version of Fig. 5 on the
next page. Secondly, in the Results section on p. 2455, the
“Detection of p53 expression levels in UC patients and healthy
adults” subsection at the top of the page, the second sentence
[“The results revealed that the expression level of p53 in
peripheral blood of UC patients (312.16±36.34 ng/l) was obviously
decreased compared with that in healthy adults (152.66±44.42 ng/l)
(P<0.01) (Fig. 2)”] was written in error. The absolute levels of
p53 were incorrectly reported in this sentence based on the
detection methods of p53 here, and so the absolute values should
not have been stated as such. This sentence should be amended to
the following: “The results revealed that the expression level of
p53 in peripheral blood of UC patients was obviously decreased
compared with that in healthy adults (P<0.01) (Fig. 2)”.
Note that the errors made in the assembly of
Fig. 5 and the indicated changes
to this sentence in the Results section do not affect the overall
conclusions reported in the paper, and all the authors agree with
the publication of this corrigendum. The authors are grateful to
the Editor of Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine for
allowing them the opportunity to publish this, and they also
apologize to the readership for any inconvenience caused.