Estrogen receptor β inhibits
estradiol-induced proliferation and migration of MCF-7 cells
through regulation of mitofusin 2
LI MA, YUEPING LIU, CUIZHI GENG, XIAOWEI QI and JUN
JIANG
Int J Oncol 42: 1993–2000, 2013; DOI:
10.3892/ijo.2013.1903
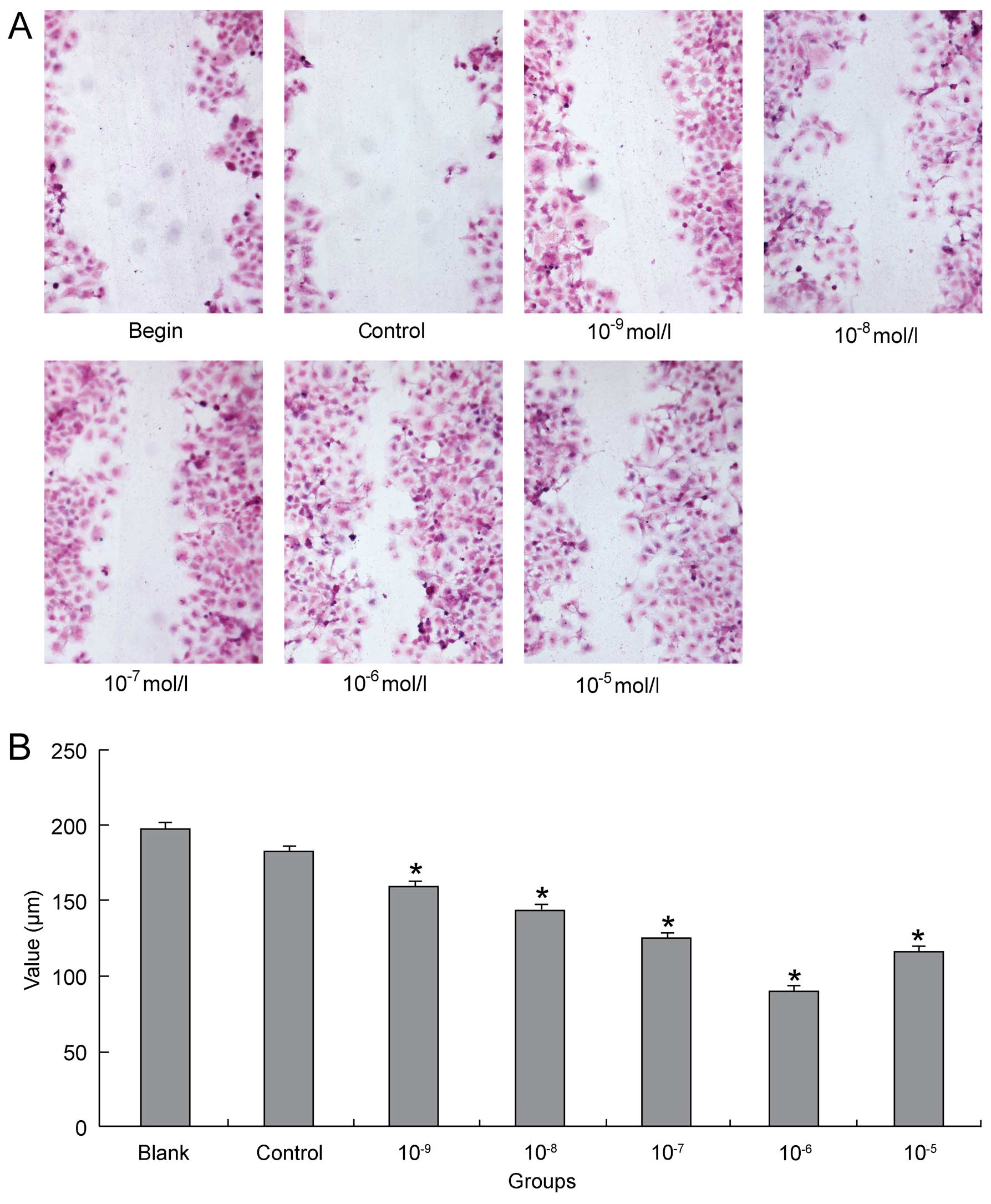
Following the publication of this article, an
interested reader drew to our attention an anomaly associated with
Fig. 2, which presented the
results of a wound-healing assay performed to determine whether
estradiol (E2) was able to exert an influence on MCF-7 cell
migration. Specifically, in comparing the ‘Control’ and the
‘10−8/mol/l’ panels, the data for the ‘Control’ panel
had erroneously been included as the ‘10−8/mol/l’ panel,
albeit the latter panel appeared in a slightly reorientated
position and was stretched longitudinally. After having re-examined
our original data, we realize that the inclusion of the identical
data for the ‘10−8/mol/l’ panel was incorrect.
Subsequently, we have recaptured the images, and a corrected
version of Fig. 2 is presented
here. The Figure now correctly demonstrates that E2 enhanced cell
motility in a dose-dependent manner in the concentration range of
E2 from 10−9 mol/l to 10−6 mol/l. This error
did not overall affect the conclusions reported in the study. We
sincerely apologize for this mistake, and thank the reader of our
article who drew this matter to our attention. Furthermore, we
regret any inconvenience this mistake has caused.