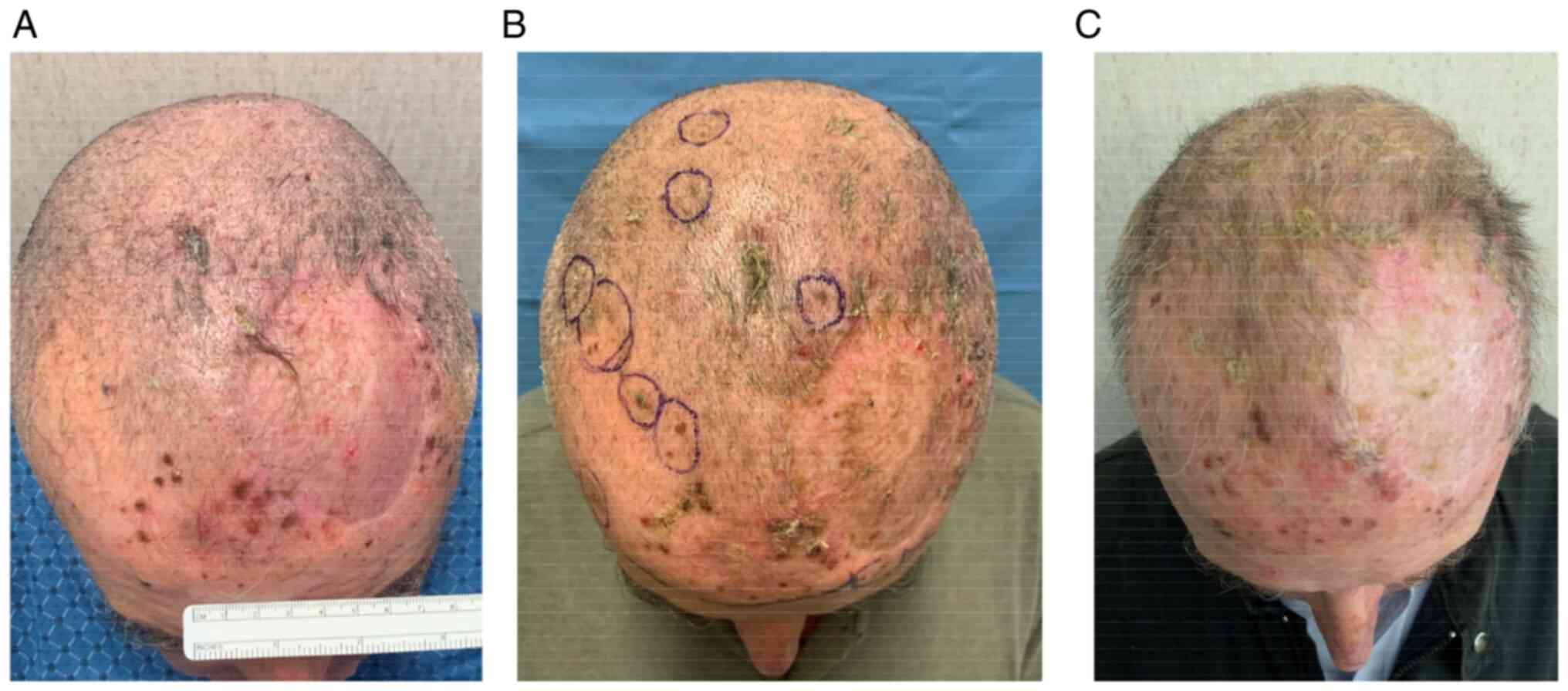
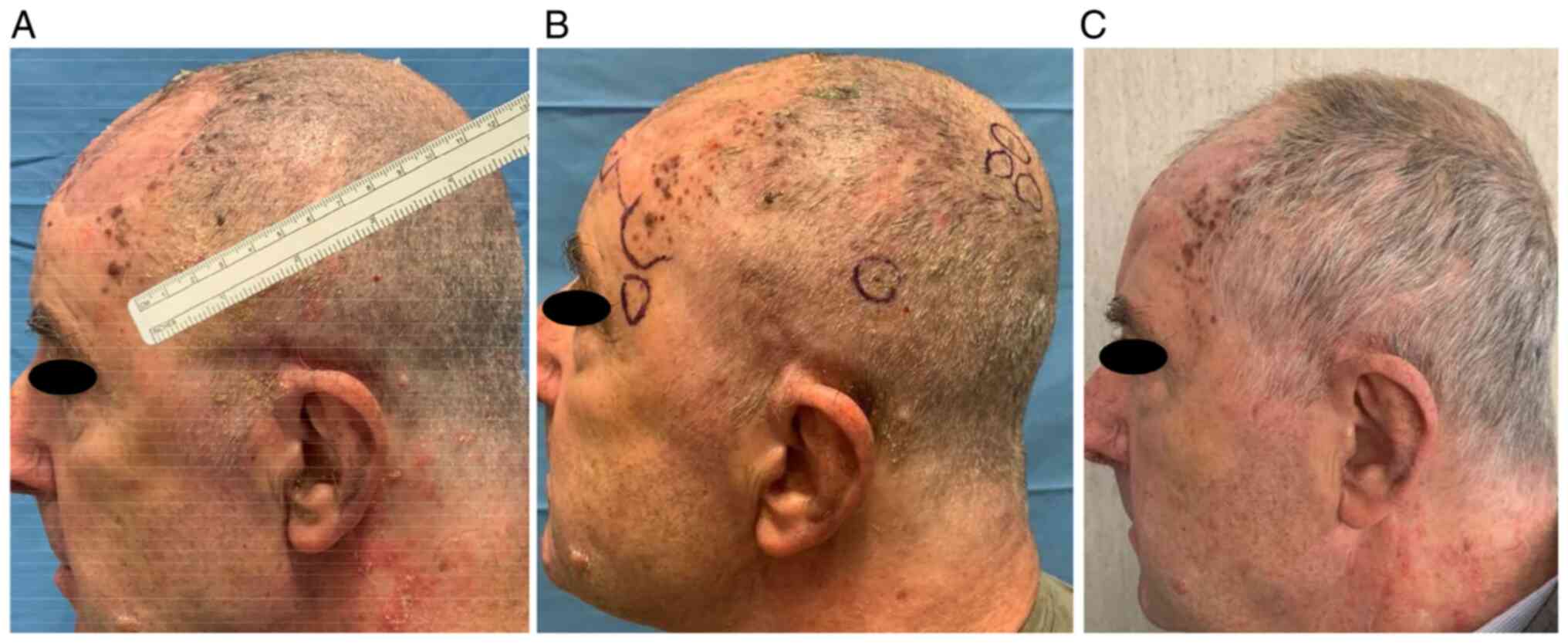
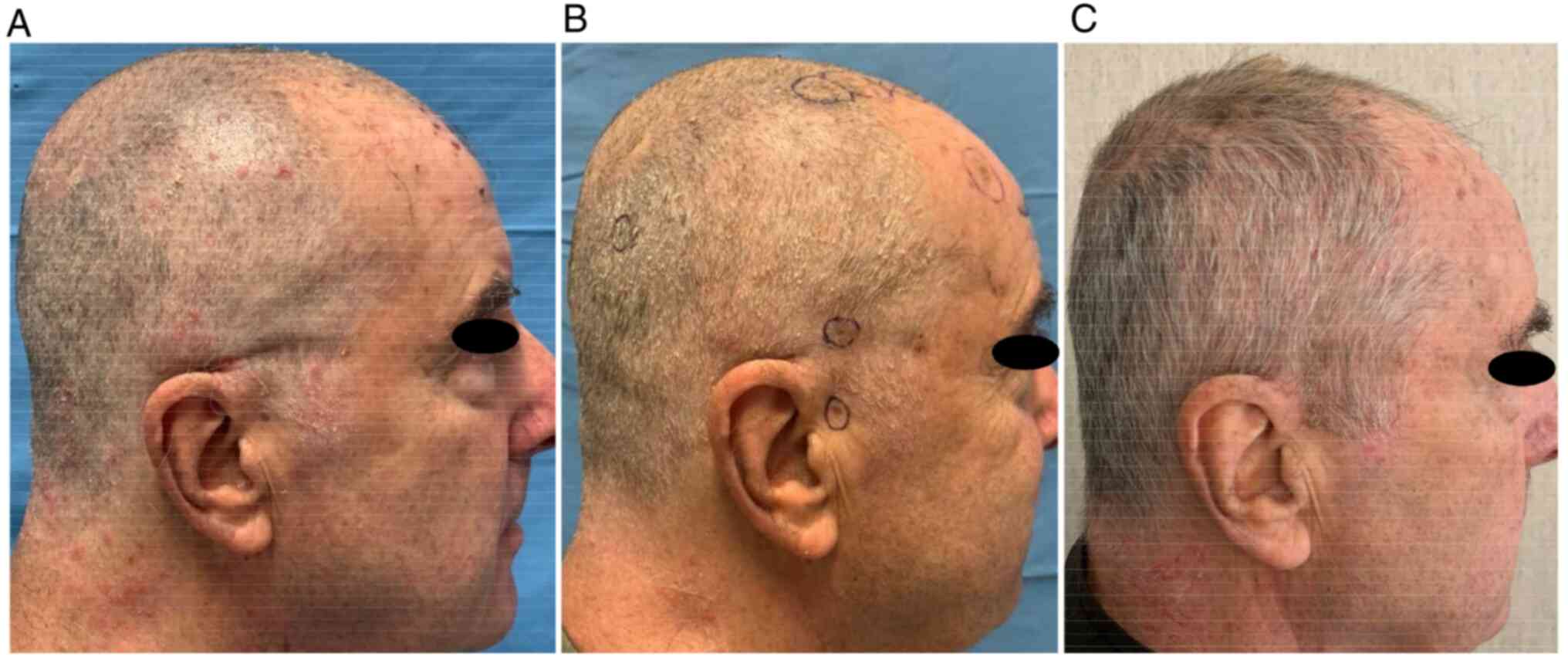
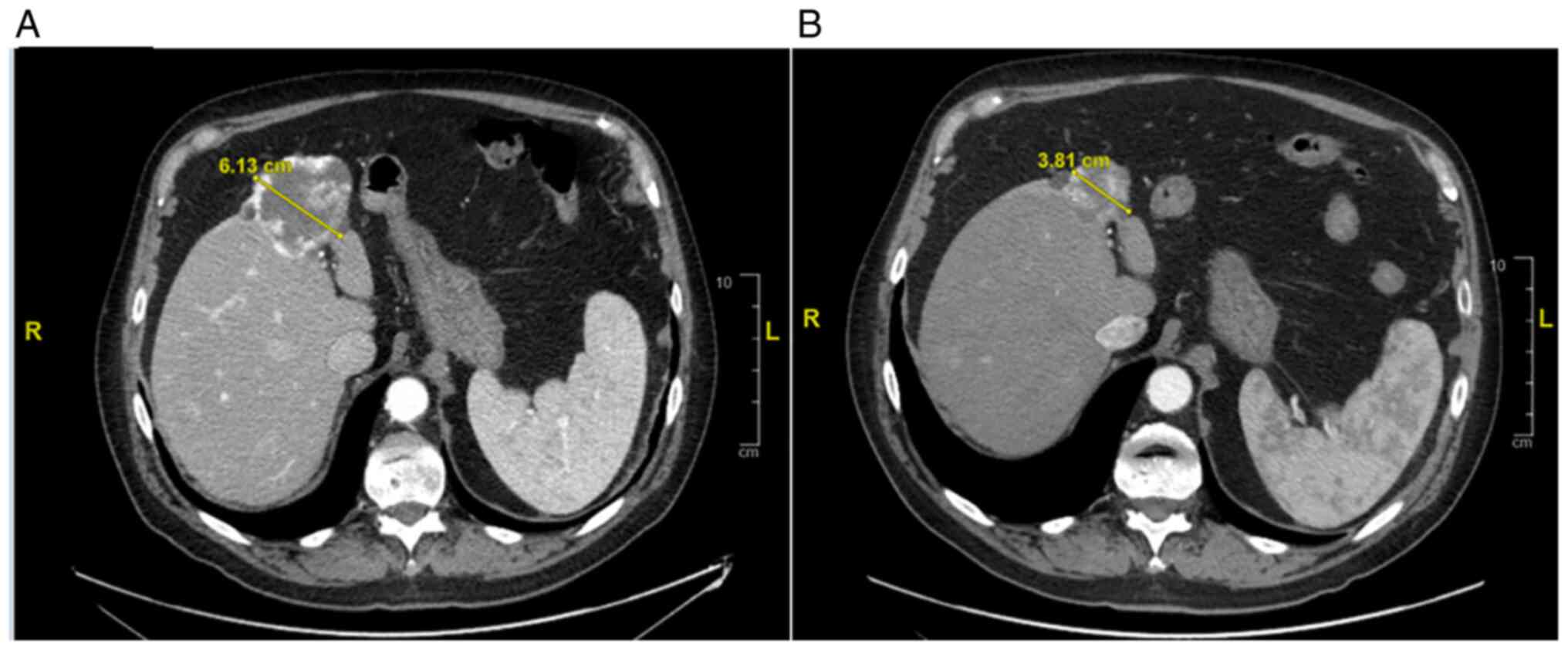
|
1
|
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW,
Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel
JC, et al: Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with
metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 363:711–723. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R,
Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Lao CD, Cowey CL, Schadendorf D, Wagstaff J,
Dummer R, et al: Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and
ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 381:1535–1546.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Weber J, Mandala M, Del Vecchio M, Gogas
HJ, Arance AM, Cowey CL, Dalle S, Schenker M, Chiarion-Sileni V,
Marquez-Rodas I, et al: Adjuvant nivolumab versus ipilimumab in
resected stage III or IV melanoma. N Engl J Med. 377:1824–1835.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Eggermont AMM, Blank CU, Mandalà M, Long
GV, Atkinson VG, Dalle S, Haydon AM, Meshcheryakov A, Khattak A,
Carlino MS, et al: Adjuvant pembrolizumab versus placebo in
resected stage III melanoma (EORTC 1325-MG/KEYNOTE-054): Distant
metastasis-free survival results from a double-blind, randomised,
controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 22:643–654.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Robert C, Ribas A, Schachter J, Arance A,
Grob JJ, Mortier L, Daud A, Carlino MS, McNeil CM, Lotem M, et al:
Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma (KEYNOTE-006):
Post-hoc 5-year results from an open-label, multicentre,
randomised, controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 20:1239–1251.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kretschmer L, Beckmann I, Thoms KM,
Mitteldorf C, Bertsch HP and Neumann C: Factors predicting the risk
of in-transit recurrence after sentinel lymphonodectomy in patients
with cutaneous malignant melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:1105–1112.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pawlik TM, Ross MI, Thompson JF, Eggermont
AM and Gershenwald JE: The risk of in-transit melanoma metastasis
depends on tumor biology and not the surgical approach to regional
lymph nodes. J Clin Oncol. 23:4588–4590. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Campana LG, Testori A, Mozzillo N and
Rossi CR: Treatment of metastatic melanoma with
electrochemotherapy. J Surg Oncol. 109:301–307. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Quaresmini D, Di Lauro A, Fucci L,
Strippoli S, De Risi I, Sciacovelli AM, Albano A, Achille G,
Montepara M, Russo S, et al: Electrochemotherapy as a trigger to
overcome primary resistance to Anti-PD-1 treatment: A case report
of melanoma of the scalp. Front Oncol. 11(742666)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Brizio M, Fava P, Astrua C, Cavaliere G
and Savoia P: Complete regression of melanoma skin metastases after
electrochemotherapy plus ipilimumab treatment: An unusual clinical
presentation. Eur J Dermatol. 25:271–272. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mozzillo N, Simeone E, Benedetto L,
Curvietto M, Giannarelli D, Gentilcore G, Camerlingo R, Capone M,
Madonna G, Festino L, et al: Assessing a novel
immuno-oncology-based combination therapy: Ipilimumab plus
electrochemotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 4(e1008842)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Heppt MV, Eigentler TK, Kähler KC, Herbst
RA, Göppner D, Gambichler T, Ulrich J, Dippel E, Loquai C, Schell
B, et al: Immune checkpoint blockade with concurrent
electrochemotherapy in advanced melanoma: A retrospective
multicenter analysis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 65:951–959.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Karaca B, Yayla G, Erdem M and Gürler T:
Electrochemotherapy with anti-PD-1 treatment induced durable
complete response in heavily pretreated metastatic melanoma
patient. Anticancer Drugs. 29:190–196. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Slominski RM, Sarna T, Płonka PM, Raman C,
Brożyna AA and Slominski AT: Melanoma, melanin, and melanogenesis:
The Yin and Yang relationship. Front Oncol.
12(842496)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sersa G, Miklavcic D, Cemazar M, Rudolf Z,
Pucihar G and Snoj M: Electrochemotherapy in treatment of tumours.
Eur J Surg Oncol. 34:232–240. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kranjc S, Kranjc M, Scancar J, Jelenc J,
Sersa G and Miklavcic D: Electrochemotherapy by pulsed
electromagnetic field treatment (PEMF) in mouse melanoma B16F10 in
vivo. Radiol Oncol. 50:39–48. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Roux S, Bernat C, Al-Sakere B,
Ghiringhelli F, Opolon P, Carpentier AF, Zitvogel L, Mir LM and
Robert C: Tumor destruction using electrochemotherapy followed by
CpG oligodeoxynucleotide injection induces distant tumor responses.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 57:1291–1300. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Di Gennaro P, Gerlini G, Urso C, Sestini
S, Brandani P, Pimpinelli N and Borgognoni L:
CD4+FOXP3+ T regulatory cells decrease and
CD3+CD8+ T cells recruitment in TILs from
melanoma metastases after electrochemotherapy. Clin Exp Metastasis.
33:787–798. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gerlini G, Sestini S, Di Gennaro P, Urso
C, Pimpinelli N and Borgognoni L: Dendritic cells recruitment in
melanoma metastasis treated by electrochemotherapy. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 30:37–45. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu CC, Yang H, Zhang R, Zhao JJ and Hao
DJ: Tumour-associated antigens and their anti-cancer applications.
Eur J Cancer Care. 26(e12446)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sersa G, Stabuc B, Cemazar M, Miklavcic D
and Rudolf Z: Electrochemotherapy with cisplatin: The systemic
antitumour effectiveness of cisplatin can be potentiated locally by
the application of electric pulses in the treatment of malignant
melanoma skin metastases. Melanoma Res. 10:381–385. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kaehler KC, Egberts F and Hauschild A:
Electrochemotherapy in symptomatic melanoma skin metastases:
Intraindividual comparison with conventional surgery. Dermatol
Surg. 36:1200–1202. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mozzillo N, Caracò C, Mori S, Di Monta G,
Botti G, Ascierto PA, Caracò C and Aloj L: Use of neoadjuvant
electrochemotherapy to treat a large metastatic lesion of the cheek
in a patient with melanoma. J Transl Med. 10(131)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Möller MG, Salwa S, Soden DM and
O'Sullivan GC: Electrochemotherapy as an adjunct or alternative to
other treatments for unresectable or in-transit melanoma. Expert
Rev Anticancer Ther. 9:1611–1630. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kis E, Oláh J, Ócsai H, Baltas E, Gyulai
R, Kemény L and Horvath AR: Electrochemotherapy of cutaneous
metastases of melanoma-a case series study and systematic review of
the evidence. Dermatol Surg. 37:816–824. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Colombo GL, Di Matteo S and Mir LM:
Cost-effectiveness analysis of electrochemotherapy with the
Cliniporator™ vs other methods for the control and
treatments of cutaneous and subcutaneous tumors. Therap Clin Risk
Manag. 4:541–548. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Campana LG, Mocellin S, Basso M, Puccetti
O, De Salvo GL, Chiarion-Sileni V, Vecchiato A, Corti L, Rossi CR
and Nitti D: Bleomycin-based electrochemotherapy: Clinical outcome
from a single institution's experience with 52 patients. Ann Surg
Oncol. 16:191–199. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Snoj M, Paulin-Kosir Z, Cemazar S and
Sersa G: Long lasting complete response in melanoma treated by
electrochemotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 4 (Suppl)(S2)2006.
|
|
29
|
Queirolo P, Marincola F and Spagnolo F:
Electrochemotherapy for the management of melanoma skin metastasis:
A review of the literature and possible combinations with
immunotherapy. Arch Dermatol Res. 306:521–526. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Goggins CA and Khachemoune A: The use of
electrochemotherapy in combination with immunotherapy in the
treatment of metastatic melanoma: A focused review. Int J Dermatol.
58:865–870. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Longo F, Perri F, Caponigro F, Della
Vittoria Scarpati G, Guida A, Pavone E, Aversa C, Muto P, Giuliano
M, Ionna F and Solla R: Boosting the immune response with the
combination of electrochemotherapy and immunotherapy: A new weapon
for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck? Cancers (Basel).
12(2781)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Maglietti F, Tellado M, De Robertis M,
Michinski S, Fernández J, Signori E and Marshall G: Electroporation
as the immunotherapy strategy for cancer in veterinary medicine:
State of the art in Latin America. Vaccines (Basel).
8(537)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hompland T, Fjeldbo CS and Lyng H: Tumor
hypoxia as a barrier in cancer therapy: Why levels matter. Cancers
(Basel). 13(499)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Saenger YM and Wolchok JD: The
heterogeneity of the kinetics of response to ipilimumab in
metastatic melanoma: Patient cases. Cancer Immun.
8(1)2008.PubMed/NCBI
|