Introduction
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
is one of the most common genetic disorders worldwide, with a
frequency of 1 in 1,000 in the general population. The excessive
proliferation of renal tubular epithelial cells leads to cysts that
eventually replace most of the normal tissue. Consequently, ADPKD
results in severe enlargement of the kidneys, and renal failure
occurs by the age of 50 in the majority of cases (1–2).
Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) preferentially
binds to IGF-1 and insulin receptors. The two receptors are
structurally similar and a number of their downstream molecules are
the same, including insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1),
phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), protein kinase B (PKB/Akt),
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) and p70S6 kinase (p70S6K),
while their physiological functions are different. IGF-1 signaling
favors cell growth, proliferation and survival in relation to
nutrient availability (3). IGF-1
has a well-documented role in cancer development in several tissues
(4), and its expression has been
found to increase with the progression of cystic lesions in ADPKD
and murine polycystic kidney diseases (PKDs) (5); therefore, IGF-1 may contribute to the
progression of cystic lesions.
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) are anti-diabetic drugs
that improve insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes
since they are high-affinity ligands for peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)γ, a transcription factor
that is highly expressed in adipose tissues. Although TZDs are only
approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, they are also known
to have additional potentially beneficial effects (6). It has been shown that TZDs are
capable of inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in
a wide variety of tumor cell lines (7). Recent studies have suggested that
TZDs inhibit the progression of PKD (8–10).
However, the underlying mechanism of action of TZDs in PKD remains
unknown.
The IGF-1/p70S6K pathway is activated in PKD, and
rosiglitazone has been suggested to inhibit the expression of
IGF-1. Therefore, the present study used ADPKD cyst-lining
epithelial cells to investigate the effect of rosiglitazone on
IGF-1 mitogenic signaling, particularly on the IGF-1-induced
activation of p70S6K.
Materials and methods
Materials
Rosiglitazone was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St.
Louis, MO, USA). Stock solution was prepared in dimethyl sulfoxide
(DMSO) at 200 mM and stored in aliquots at −80°C. Antibodies
against p70S6K, p-p70S6K-Thr421/424, PPARγ and IGF-1
were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (Beverly, MA,
USA).
Cell culture and treatment
Immortalized epithelial cells from >30 individual
renal cysts obtained from 11 ADPKD patients (WT9–12) and normal
human renal cortical tubular epithelial cells (RCTEC) were kindly
provided by Dr Jing Zhou (Harvard Institutes of Medicine, Harvard
Medical School, Boston, MA, USA) (11). The cells were maintained in
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10%
fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 100 U/ml each of penicillin and
streptomycin. The cells were seeded at a density of 4,000
cells/well in a 96-well plate. After 24 h, 10% FBS growth medium
was replaced with serum-free medium. Cells were either treated with
rosiglitazone or IGF-1, or the combination of both. Cell growth
curves were determined 24, 48 and 72 h following treatment using a
tetrazolium salt
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT)
assay. Briefly, MTT (500 μg/ml) was added to cells for 4 h. The
cells were then collected using a DMSO solution. The rate of MTT
uptake and the formation of blue formazan crystals by live cells
were determined by absorption at a wavelength of 490 nm using an
enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) reader (ELX 800; BioTek
Intstruments, Winooski, VT, USA).
Western blot analysis
For western blot analysis, the cells treated with
various chemicals were washed with ice-cold phosphate-buffered
saline (PBS) and lysed in RIPA buffer (1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl
fluoride, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM NaF and 1 mM
Na3VO4) containing protease inhibitor
cocktail. Protein concentrations were determined using a BCA
protein assay kit (Pierce Biotechnology, Inc., Rockford, IL, USA).
Equal amounts of protein (100 μg) were loaded and separated on
SDS-polyacrylamide gels and then transferred to nitrocellulose
membranes. After blocking, membranes were probed with antibodies
against p70S6K, p-p70S6K-Thr421/424 and PPARγ followed
by the corresponding horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated
secondary antibody. Positive staining was revealed via a reaction
with an enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) reagent and development on
an X-ray film.
Transfection with small interfering RNAs
(siRNAs)
PPARγ and non-specific control siRNAs were purchased
from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. For the transfection, the
cells were grown until 30–40% confluence, and PPARγ or non-specific
control siRNAs were introduced into the cells using the
Lipofectamine™ 2000 reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, CA)
according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly,
Lipofectamine reagent and siRNA were diluted in a serum-free
medium. After 5 min, the two solutions were mixed and placed at
room temperature for an additional 20 min. The mixture was then
added to the cells. The final concentration of siRNA in each well
was 100 nM. A number of cells were treated with rosiglitazone (50
μM) 48 h after the transfection, and then cell lysates were
collected for western blot analysis 24 h after this treatment.
Statistical analysis
All the experiments were repeated at least three
times. Data were expressed as the mean ± SD. Statistical
significance was determined with Student’s t-test (two-tailed) for
comparisons between two groups. P<0.05 was considered to
indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
IGF-1 increases the proliferation of
cyst-lining epithelial cells
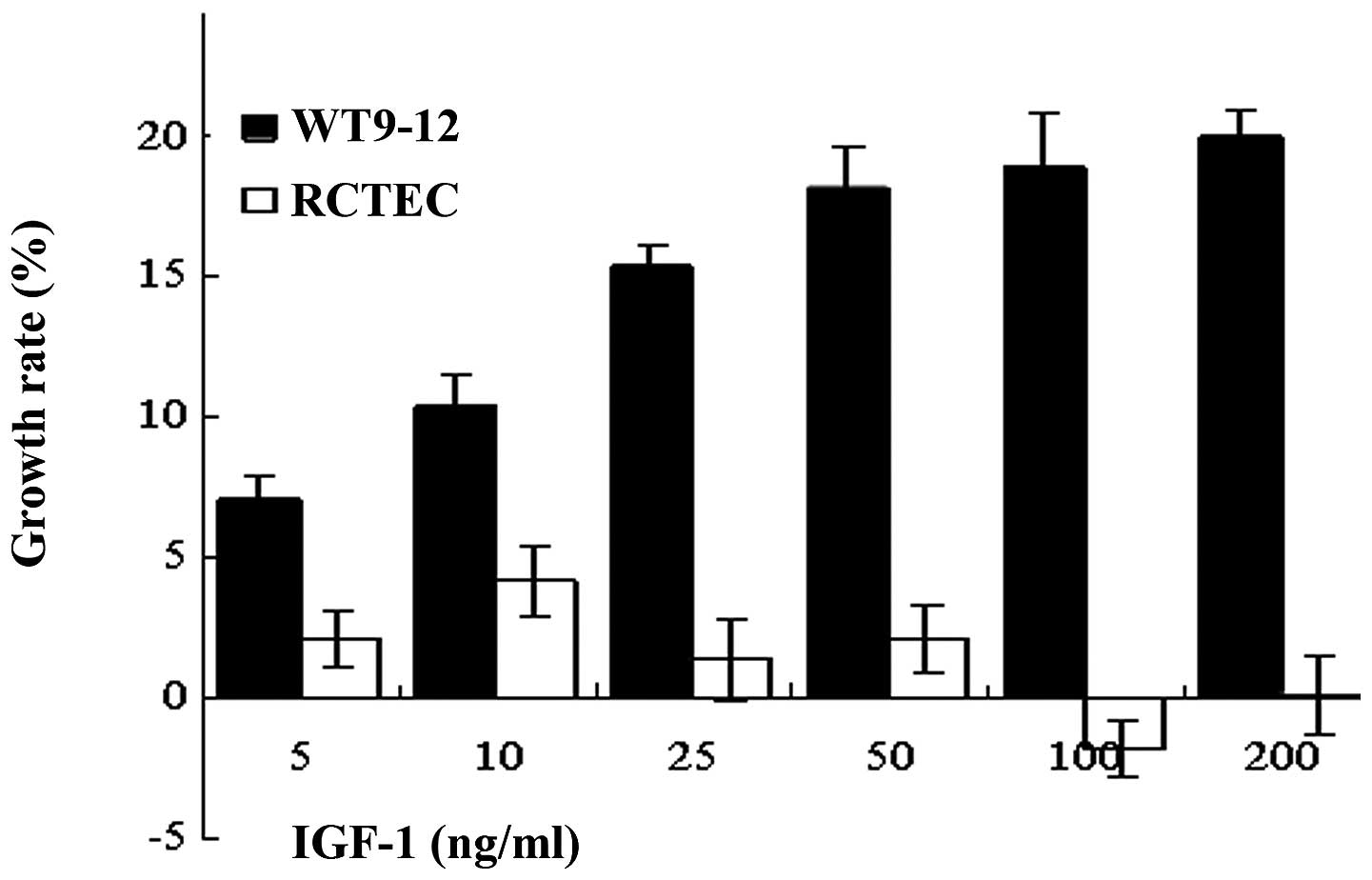
The growth of the cyst-lining epithelial cell line
WT9–12 was compared with that of a normal cell line (RCTEC) to
investigate the effect of IGF-1 on cell proliferation. The effect
of IGF-1 on cell growth was examined by treating the cells with
various concentrations of IGF-1 (5–200 ng/ml). The rate of cell
growth was determined 72 h following treatment using an MTT assay.
IGF-1 treatment was found to increase WT9–12 cell growth by 15–20%
in a dose-dependent manner, while it had no effect on RCTEC cell
proliferation (Fig. 1).
Rosiglitazone inhibits IGF-1-induced PKD
cell growth
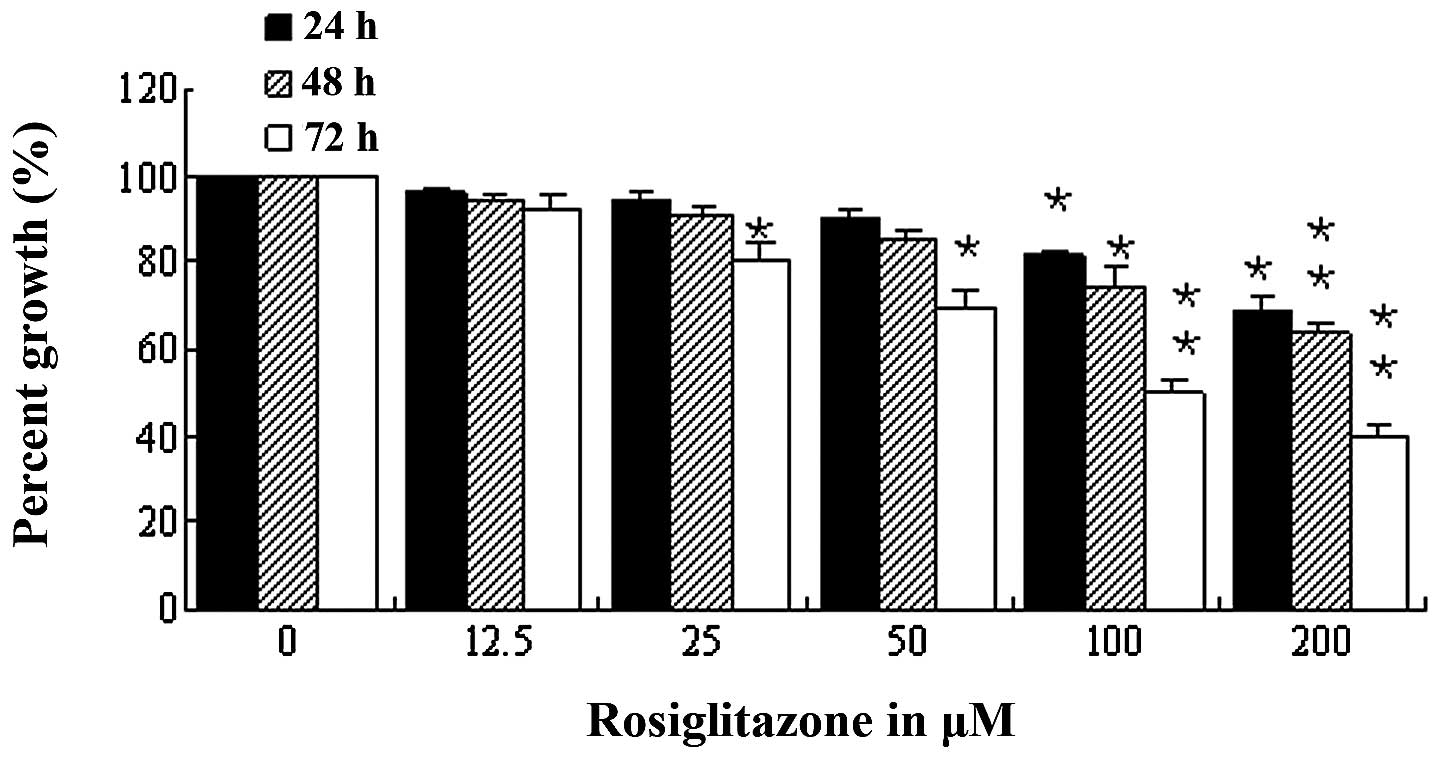
The effect of rosiglitazone or rosiglitazone
combined with IGF-1 on cell growth was examined in order to
investigate the effect of rosiglitazone on IGF-1-induced PKD cell
growth. Rosiglitazone at doses of 50–200 μM was found to inhibit
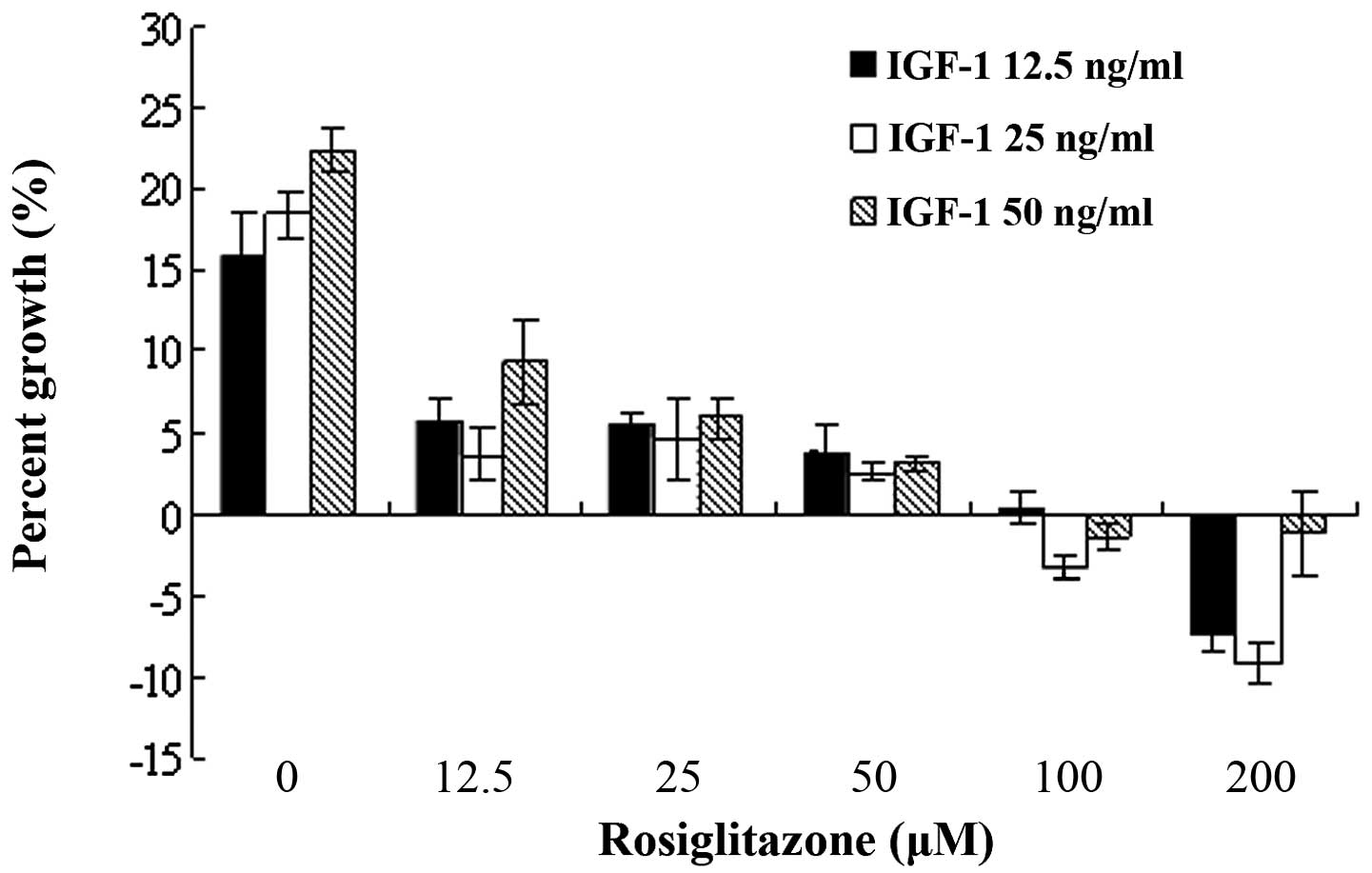
WT9–12 cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 2). However, IGF-1-induced WT9–12
cell proliferation was inhibited with a 12.5-μM dose of
rosiglitazone (Fig. 3).
Rosiglitazone inhibits IGF-1-induced
phosphorylation of p70S6K in a PPARγ-independent manner
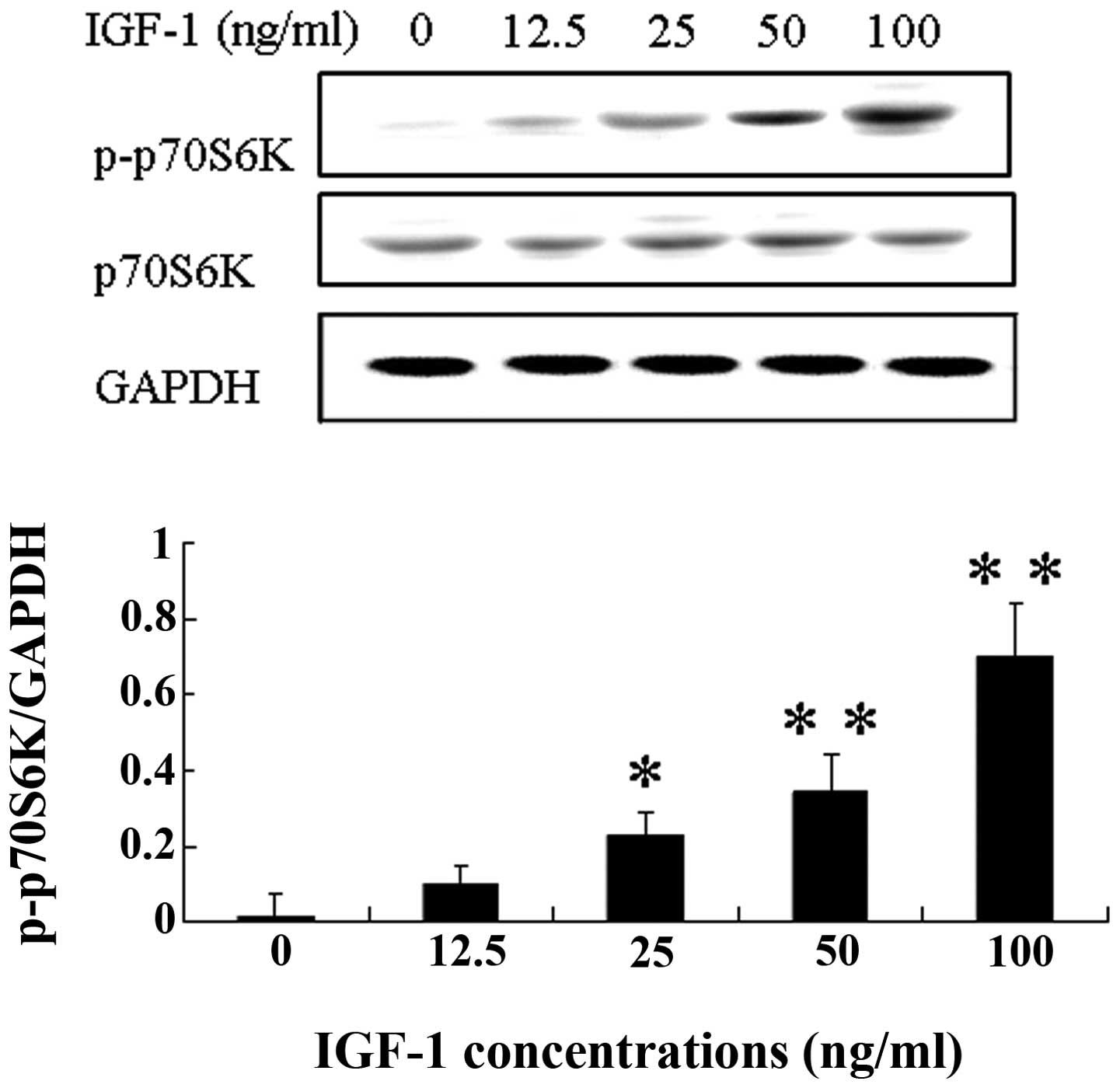
The p70S6K signaling molecule is involved in the
regulation of cell cycle progression and cell proliferation
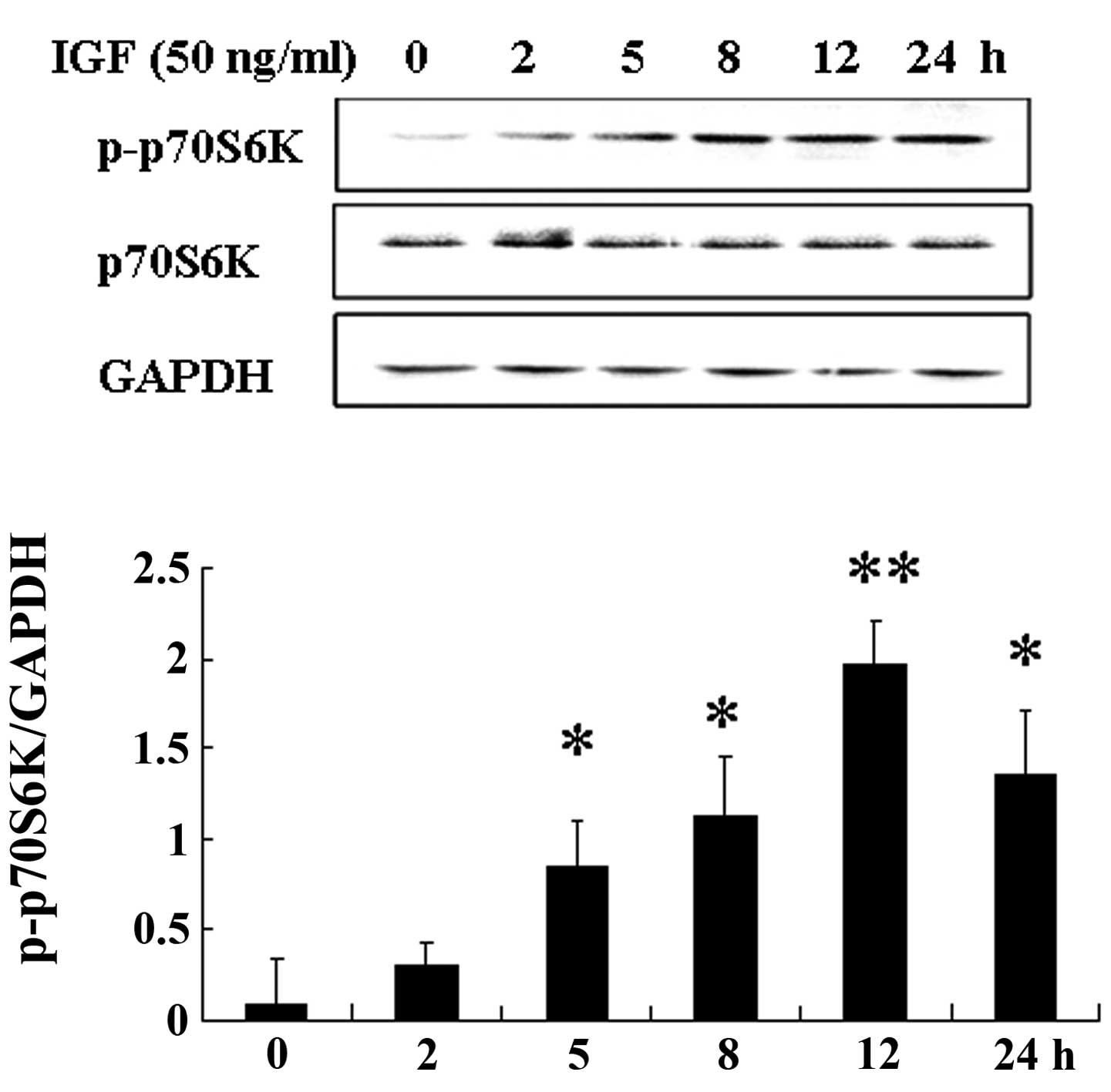
(12). We found that IGF-1
increased the phosphorylation of p70S6K in a dose- and
time-dependent manner in WT9–12 cells (Figs. 4 and 5). The expression of p-P70S6K was
increased after WT9–12 cells were treated with IGF-1 (20 ng/ml) for
2 h.
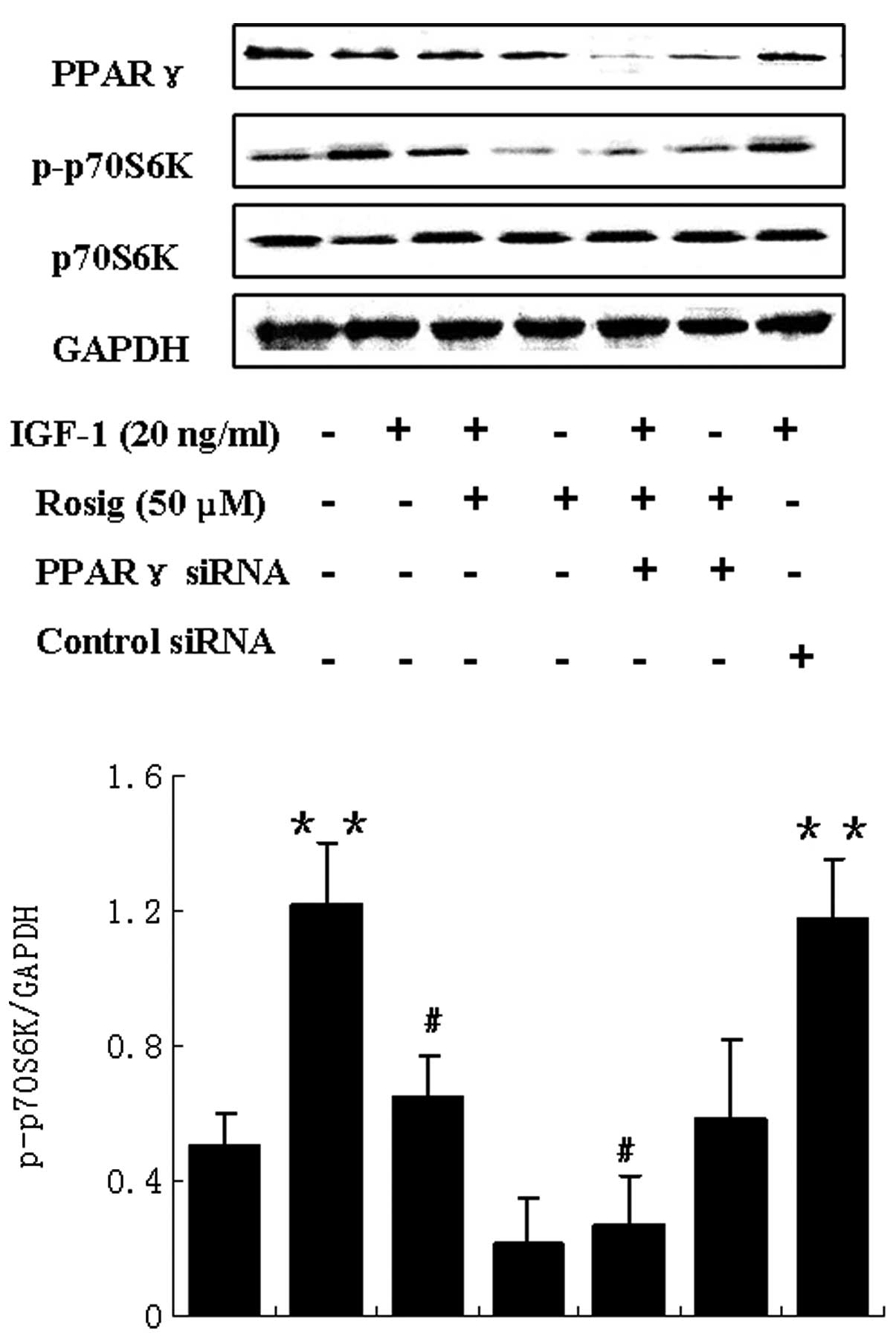
Rosiglitazone was found to inhibit IGF-1-induced
phosphorylation of p70S6K (Fig.
6). Rosiglitazone, a synthetic ligand for PPARγ, inhibits cell
growth through PPARγ-dependent and -independent signaling pathways
(19). Therefore, we investigated
whether the effect of rosiglitazone on IGF-1-induced
phosphorylation of p70S6K was mediated by the activation of PPARγ.
WT9–12 cells were transfected with PPARγ or control siRNA. The
cells were then treated with IGF-1 or rosiglitazone, or the
combination of both. As shown in Fig.
6, the effect of rosiglitazone on IGF-1-induced p70S6K
phosphorylation was unable to be blocked. This suggests that
rosiglitazone may inhibit IGF-1-induced phosphorylation of p70S6K
in a PPARγ-independent manner.
Discussion
One of the main changes in the PKD kidney is an
increase in the proliferative activity of cyst-lining epithelial
cells. Proliferating cells are frequently detected in normal
tubular segments and are relatively sparse in large cysts. These
findings suggest that the increase in proliferative activity is an
early event and may predispose these cells to the acquisition of a
cystic phenotype (13,14).
IGF-1 is a multifunctional hormone that has
pleiotropic effects on cellular proliferation, apoptosis,
hypertrophy, senescence and differentiation. Multiple lines of
evidence suggest that IGF-1 plays a role in mediating tubular cell
proliferation in the cystic kidney, particularly during the early
stages of PKD. The present and previous studies have found that
IGF-1 induces PKD cell proliferation, while no effect has been
observed in normal tubular cells (15). This indicates that PKD cells are
more sensitive to IGF-1 compared with normal cells.
Rosiglitazone is effective in regulating cell
activation, differentiation, proliferation and/or apoptosis
(16). The efficacy of this
compound as an anticancer agent has been examined in a variety of
cancers, including colon, breast, prostate and non-small cell lung
carcinoma (6,17). In polycystic renal disease,
rosiglitazone has been suggested to inhibit the progression of PKD
(8–18). In the present study, we showed that
rosiglitazone inhibited the proliferation of PKD cells and that it
had a more predominant inhibiting effect on IGF-1-induced cell
proliferation. This finding indicates that rosiglitazone is
suitable for the treatment of early-stage PKD.
p70S6K is an important downstream signaling molecule
of IGF-1. The activity of p70S6K, which is determined by the
phosphorylation of p70S6K, is enhanced in the kidneys of ADPKD
patients and is important in the pathogenesis of ADPKD (19). In the present study, we found that
IGF-1 induced the phosphorylation of p70S6K in PKD cells, while
rosiglitazone inhibited the effect of IGF-1 on p70S6K
phosphorylation. TZDs are known to act in a PPARγ-dependent and
-independent manner (19). Our
study indicated that rosiglitazone inhibited IGF-1-induced
phosphorylation of p70S6K through a PPARγ-independent manner.
In summary, we found that rosiglitazone inhibited
the IGF-1-induced activation of p70S6K via a PPARγ-independent
mechanism. This appears to account for, at least in part, the
mechanism by which rosiglitazone inhibits IGF-1-induced PKD cell
proliferation. IGF-1 has an important effect on early-stage PKD;
therefore, rosiglitazone is suggested to be more effective in the
treatment of early-stage PKD.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National 973 Program
of China (2007CB507400).
References
|
1
|
Torres VE, Harris PC and Pirson Y:
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet.
369:1287–1301. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kazancioglu R, Ecder T, Altintepe L,
Altiparmak MR, Tuglular S, Uyanik A, et al: Demographic and
clinical characteristics of patients with autosomal dominant
polycystic kidney disease: a multicenter experience. Nephron Clin
Pract. 117:C270–C275. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nakae J, Kido Y and Accili D: Distinct and
overlapping functions of insulin and IGF-I receptors. Endocr Rev.
22:818–835. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES and Hankinson
SE: Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:505–518. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakamura T, Ebihara I, Nagaoka I, Tomino
Y, Nagao S, Takahashi H and Koide H: Growth factor gene expression
in kidney of murine polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol.
3:1378–1386. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Grommes C, Landreth GE and Heneka MT:
Antineoplastic effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma agonists. Lancet Oncol. 5:419–429. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yki-Järvinen H: Thiazolidinediones. N Engl
J Med. 351:1106–1118. 2004.
|
|
8
|
Muto S, Aiba A, Saito Y, et al:
Pioglitazone improves the phenotype and molecular defects of a
targeted Pkd1 mutant. Hum Mol Genet. 11:1731–1742. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dai B, Liu Y, Mei C, et al: Rosiglitazone
attenuates development of polycystic kidney disease and prolongs
survival in Han: SPRD rats. Clin Sci (Lond). 119:323–333. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Blazer-Yost BL, Haydon J, Eggleston-Gulyas
T, Chen JH, Wang X, Gattone V and Torres VE: Pioglitazone
attenuates cystic burden in the PCK rodent model of polycystic
kidney disease. PPAR Res. 2010:2743762010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Loghman-Adham M, Nauli SM, Soto CE,
Kariuki B and Zhou J: Immortalized epithelial cells from human
autosomal dominant polycystic kidney cysts. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 285:F397–F412. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou H and Huang S: The complexes of
mammalian target of rapamycin. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 11:409–424.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Torres VE and Harris PC: Autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease: the last 3 years. Kidney Int.
76:149–168. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Patel V, Chowdhury R and Igarashi P:
Advances in the pathogenesis and treatment of polycystic kidney
disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 18:99–106. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Parker E, Newby LJ, Sharpe CC, et al:
Hyperproliferation of PKD1 cystic cells is induced by insulin-like
growth factor-1 activation of the Ras/Raf signalling system. Kidney
Int. 72:157–165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zieleniak A, Wójcik M and WoŸniak LA:
Structure and physiological functions of the human peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Arch Immunol Ther Exp
(Warsz). 56:331–345. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Michalik L, Desvergne B and Wahli W:
Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors and cancers: complex
stories. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:61–70. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shillingford JM, Murcia NS, Larson CH, et
al: The mTOR pathway is regulated by polycystin-1, and its
inhibition reverses renal cystogenesis in polycystic kidney
disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:5466–5471. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Han SW and Roman J: Rosiglitazone
suppresses human lung carcinoma cell growth through
PPARgamma-dependent and PPARgamma-independent signal pathways. Mol
Cancer Ther. 5:430–437. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|