Introduction
HaCaT cells are an immortalized, non-tumorigenic
cell line derived from keratinocytes of normal adult skin (1). Pathologically excessive proliferation
of these cells reportedly leads to various skin diseases, such as
psoriatic lesions and various skin cancers (2). Thus, HaCaT cells are extensively
employed as an extrinsic cell instrument in anti-neoplastic
medicine experiments (3).
Metformin, a biguanide insulin sensitizer widely prescribed to type
2 diabetes (4), has gained
increasing focus due to its newly discovered anti-neoplastic
capacity in a broad spectrum of malignant tumors, including
prostate, pancreatic, ovarian and gastric cancers (5–8).
However, the anti-growth ability of metformin seems to have tumor
type dependence (9) and the
mechanism whereby metformin affects various cancers is still not
completely understood (10).
MicroRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) are a class of small
modulatory non-coding RNA molecules that can either bring about
instability or translational efficiency repression through
base-pairing to target mRNAs (11), effectively resulting in the
repression of molecules that take part in cell cycle processes
including cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis
(12). miR-21 is reportedly
overexpressed in the vast majority of solid neoplasms (13). Among the target molecules of
miR-21, phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and AKT
serine/threonine kinase 1 (Akt) are of particular interest
(14). PTEN protein has been
identified as a potent neoplasm inhibitor, while Akt is found
positioned at the intersection of multiple signaling pathways, and
is a verified sensing node that is upregulated in most tumors and
can be suppressed by reversing the phosphorylation of the
phosphoinositide 3-kinase (15).
Therefore, the present study aimed to explore the
in vitro proliferation inhibition effect of metformin on
HaCaT cells and to investigate the mechanism which might be
involved in the miR-21/PTEN/Akt signaling pathway.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and metformin
treatment
HaCaT cells were purchased from American Type
Culture Collection (cat. no. PCS-200-011; American Type Culture
Collection, Manassas, VA, USA). Cells were cultivated in Dulbecco's
modified Eagle's medium (DMEM, cat. no. 12491–015; Gibco; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) containing 10%
heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; cat. no. 26170043; Gibco;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml
streptomycin at 37°C in a humidified incubator with 5%
CO2. The medium was changed every 2 days. Metformin
hydrochloride with 98.8% purity was obtained from Shouguang Fukang
Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (cat. no. 1115-70-4; Shouguang, China) and
was diluted in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) to a concentration
of 1 M. It was used at increasing concentrations (0–100 mM) and
different action durations (up to 72 h) in serum-free media.
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) cell
viability assay
HaCaT cells were seeded into 96-well plates at
density of 1,500 cells per well in 100 µl common media overnight.
The next day, cells were washed and incubated with 20, 40, 60, 80
and 100 mM metformin in serum-free DMEM for 24, 48 and 72 h.
Following addition of 10 µl colorimetric water-soluble CCK-8
tetrazolium salt solution to each well (cat. no. CK04; Dojindo
Molecular Technologies, Inc., Kumamoto, Japan), cells were cultured
at 37°C for 1 h. A quantitative automatic microplate reader (model
no. 2010; Anthos Labtec Instruments GmbH, Salzburg, Austria) was
used to measure the absorbance of reactions at 450 nm
(A450). Growth inhibition rates of HaCaT cells at
various treatment times and metformin concentrations were
calculated using the formula: Cell growth inhibition rate
(%)=(A450 control-A450
metformin)/A450 control ×100%.
Reverse transcription-quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR)
TRIzol® reagent (cat. no. 15596-018;
Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) was used for total RNA
isolation. The amount and purity of RNA was assessed
spectrophotometrically. Extracted RNA was reverse-transcribed into
cDNA using a miRNA cDNA synthesis kit (cat. no. 203301; Universal
cDNA Synthesis kit II; Takara Bio, Inc., Otsu, Japan) in accordance
with the manufacturer's specification. qPCR was performed with the
primers listed in Table I and
ExiLENT SYBR® Green master mix (cat. no. 203403; Takara
Bio, Inc.), as outlined in Table
II. An ABI 7500 Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) was used. The amplification
conditions of the PCR were as follows: 95°C for 10 min, followed by
40 cycles at 95°C for 10 sec and 60°C for 1 min, the ramp-rate was
1.6°C/sec. A total of three experimental repeats were performed.
The 2−ΔΔCq method was employed for quantitation, with
miR-21 expression levels normalized to the U6 RNA control (16).
 | Table I.Primer sequences. Primers were
synthesized by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). |
Table I.
Primer sequences. Primers were
synthesized by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China).
| Target | Primer sequence |
|---|
| miR21 |
RT-5′-GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACTCAACA-3′ |
|
|
F-5′-GTGCAGGGTCCGAGGT-3′ |
|
|
R-5′-GCCGCTAGCTTATCAGACTGATGT-3′ |
| U6 |
RT-5′-CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT-3′ |
|
|
F-5′-GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT-3′ |
|
|
R-5′-CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGTGTCAT-3′ |
 | Table II.Quantitative PCR reaction setup, as
instructed by the manufacturer. |
Table II.
Quantitative PCR reaction setup, as
instructed by the manufacturer.
| Reaction
compound | Volume (µl) | Final
concentration |
|---|
| SYBR premix Ex Tap™
II | 10.0 | 1X |
| Template | 2.0 | ------ |
| F primer | 0.8 | 0.4 µM |
| R primer | 0.8 | 0.4 µM |
| ROX | 0.4 | ------ |
| RNase free
H2O | 6.0 | ------ |
| Total | 20 µl |
|
Western blotting analysis
Following 48 h of treatment with 30 mM metformin,
total protein was isolated from cells by incubation in
radioimmunoprecipitation assay buffer (cat. no. P0013C; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology, Haimen, China) containing 1 mM
phenylmethane sulfonyl on ice for 30 min, followed by
centrifugation at 13,690 × g, 4°C for 30 min. Protein concentration
was evaluated by bicinchoninic acid assay (cat. no. P0010; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology). Proteins (50 µg per lane) were
separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, then transferred to polyvinylidene
difluoride membranes. Non-specific binding was blocked by
incubation in 5% skimmed milk in Tris-buffered saline with 0.05%
Tween-20 (TBST) buffer for 2 h at room temperature. Membranes were
subsequently incubated at 4°C overnight in the following primary
antibodies: rabbit monoclonal anti-PTEN (1:1,000; cat. no. 9188;
Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Danvers, MA, USA), rabbit
monoclonal anti-Akt1/2/3 (1:1,000; cat. no. 4685; Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc.) or rabbit monoclonal anti-GAPDH (1:1,000; cat.
no. 5174; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.) as an internal
reference. Membranes were then incubated with a horseradish
peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:10,000; cat. no. 7074;
Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.) at room temperature for 2 h. The
membrane was developed using enhanced chemiluminescence (cat. no.
05-1327; EMD Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and scanned with an
electrophoresis gel imaging analysis system (Tanon-5000R; Tanon
Science & Technology Co., Ltd, Shanghai, China). Gray value of
each band was quantified using ImageJ 1.46b (National Institutes of
Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) relative to the GAPDH control.
Transfection with miR-21-inhibiting
oligonucleotides
HaCaT cells were divided into three groups: IN
group, transfected miR-21-inhibitor (5′-TCAACATCAGTCTGATAAGCTA-3′;
Ambion; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.); NC group, transfected with
miR-21 inhibitor negative control (5′-CATTAATGTCGGACAACTCAAT-3′;
Ambion; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.); and MOCK group,
mock-transfected with PBS. Transfections were performed by
incubating 1 µl Lipofectamine® 2000 (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.), 100 µl serum-free RPMI-1640 (cat. no. 11875085;
Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), and 20 pM miR-21 inhibitor
or miR-21 inhibitor negative control at room temperature for 20
min, then adding to HaCaT cells and culturing at 37°C for 6 h.
Serum-free culture media was then substituted with complete
RPMI-1640, and cells were harvested 48 h later.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation
unless otherwise stated. Statistical Program for Social Science
software v.19.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) was used for
statistical analysis. Two independent samples t-tests were applied
to compare the difference between experimental and control groups,
while Mantel Haenszel χ2 tests were used to analyze the
results of CCK-8 assays. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
Effect of metformin on HaCaT cell
viability
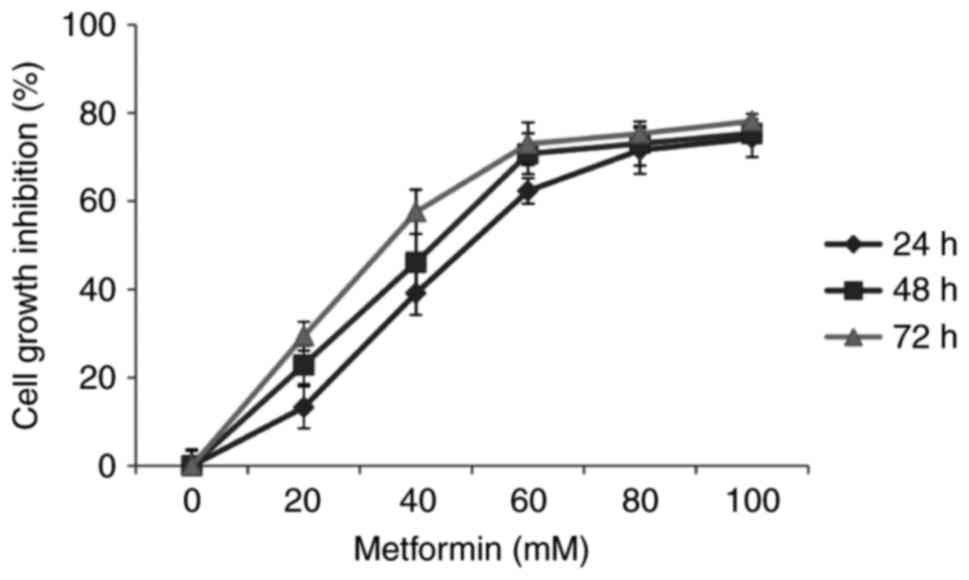
CCK-8 assays demonstrated that increasing
concentrations and durations of metformin treatment resulted in
attenuation of HaCaT cell viability (χ2=3.974;
P<0.05; Fig. 1). This result
indicated a time- and dosage-dependent inhibitory action of
metformin on the viability of HaCaT cells.
Expression of miR-21 in HaCaT cells
following metformin treatment
Assessment of the effect of metformin treatment on
the expression of miR-21 was a primary consideration. As
demonstrated in Table III,
miR-21 levels in the experimental and control groups were 1.14±0.18
and 2.67±0.23, respectively (P<0.05). Therefore, the levels of
miR-21 expression were significantly reduced by metformin
treatment.
 | Table III.Expression of miR-21 following
treatment with 30 mM metformin. Levels of miR-21 expression were
evaluated by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Data are
presented as the mean ± standard deviation. |
Table III.
Expression of miR-21 following
treatment with 30 mM metformin. Levels of miR-21 expression were
evaluated by quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Data are
presented as the mean ± standard deviation.
|
| Experimental group
expression | Control group
expression | t value |
|---|
| miR-21 | 1.14±0.18 | 2.67±0.23 | −8.903a |
Transfection results
To acquire a better understanding of the function of
miR-21, a miR-21 inhibitor was transfected into HaCaT cells.
RT-qPCR was then used to confirm the efficacy of miR-21 inhibition.
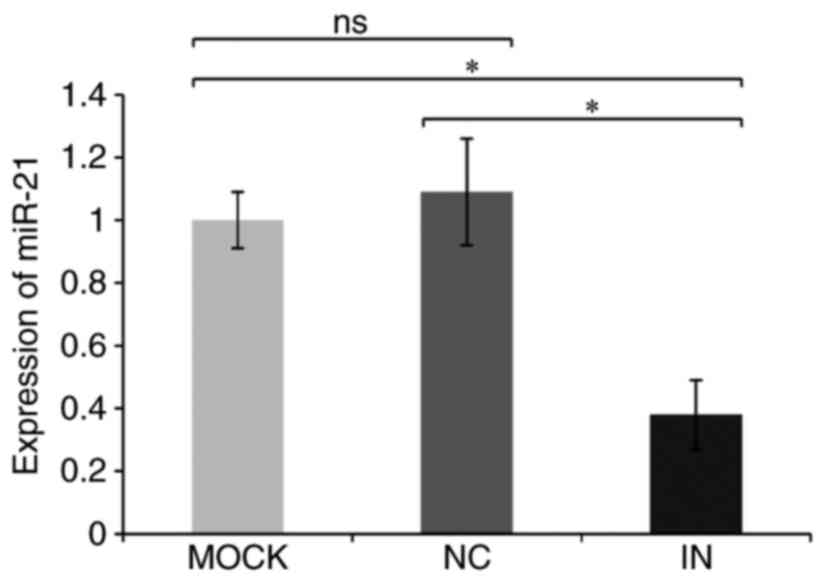
Relative miR-21 quantitation data in the IN, NC and MOCK groups
were 0.38±0.11, 1.09±0.17, and 1.03±0.09, respectively (Table IV and Fig. 2). miR-21 expression was, therefore,
significantly reduced in the IN group compared with the NC and MOCK
groups (both P<0.05), indicating that the miR-21 inhibitor was
effective at reducing miR-21 expression.
 | Table IV.Expression levels of miR-21 and PTEN
and Akt proteins were detected by reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western
blotting, respectively. |
Table IV.
Expression levels of miR-21 and PTEN
and Akt proteins were detected by reverse
transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western
blotting, respectively.
|
| MOCK | NC | IN |
|---|
| miR-21 | 1.03±0.09 | 1.09±0.17 | 0.38±0.11 |
| PTEN protein | 1.05±0.07 | 1.11±0.07 | 2.29±0.08 |
| Akt protein | 1.03±0.09 | 1.10±0.07 | 0.47±0.05 |
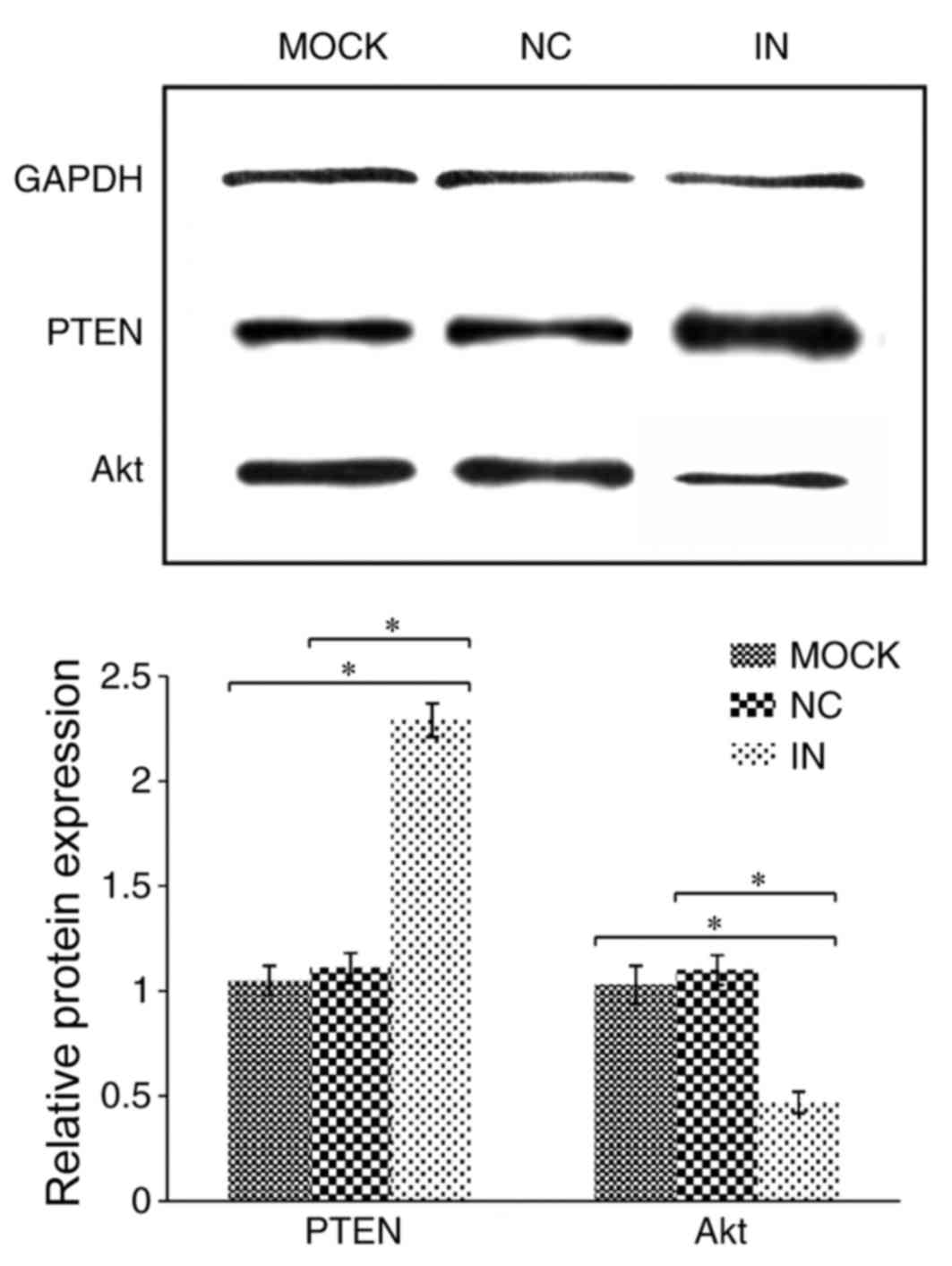
Inhibition of miR-21 enhances PTEN
protein expression but reduces Akt protein expression
PTEN protein expression was demonstrated to be
significantly upregulated in cells in the IN group compared with
the NC and MOCK groups (both P<0.05; Table IV and Fig. 3). By contrast, Akt protein
expression was demonstrated to be significantly downregulated in
cells in the IN group compared with the NC and MOCK groups (both
P<0.05; Table IV and Fig. 3).
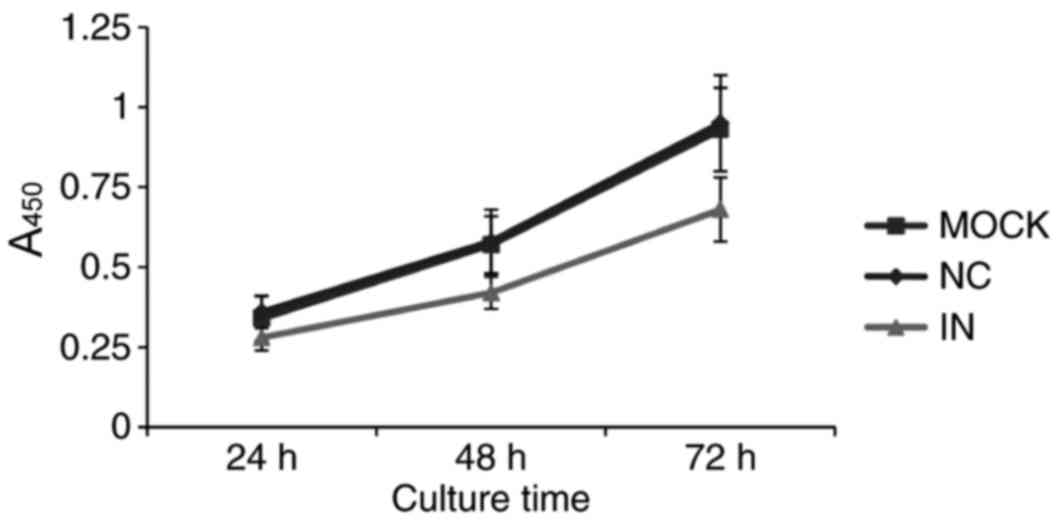
Inhibition of miR-21 inhibits HaCaT
cell viability
Since miR-21 is overexpressed in most solid tumors
(17), miR-21 is hypothesized to
promote tumor proliferation. Therefore, cell viability was examined
by CCK-8 assay in cells with artificially lowered miR-21 levels.
Cell growth was demonstrated to be downregulated in cells in the IN
group compared with the NC and MOCK groups (Fig. 4). This result indicates that
reduced miR-21 expression inhibits HaCaT cell viability.
Discussion
To the best of the authors' knowledge, the present
study is the first to demonstrate a duration- and dosage-dependent
inhibitory effect of the anti-diabetic drug metformin on HaCaT cell
viability. Furthermore, the miR-21 expression levels were observed
to be significantly reduced following metformin treatment.
Therefore, the present study conjectured that miR-21 serves a
pivotal role in adjusting the proliferative activity of HaCaT
cells. To investigate the suspected vital function of miR-21 in the
anti-viability effect of metformin, miR-21 inhibitor transfection
was used to artificially reduce miR-21 expression in HaCaT cells,
which resulted in reduced growth compared with control cells.
Therefore, a tentative conclusion was drawn that
miR-21 might be at the core of the basic mechanism by which
metformin inhibits HaCaT cell growth. In order to further examine
the function of miR-21, the effect of reduced miR-21 expression on
2 functional downstream targets of miR-21, PTEN and Akt, was
examined (18,19). Significantly increased PTEN
expression and decreased Akt expression was observed in cells
transfected with the miR-21 inhibitor compared with cells
transfected with the scrambled-sequence oligonucleotide or PBS
(20). Combined with the
previously reported critical role of PTEN and Akt in regulating
cellular biological procedures (21,22),
an intricate modulatory network including miR-21 and PTEN/Akt was
hypothesized to be involved in metformin's anti-proliferation
effect. Yang et al (23)
observed a high level of homology between the sequence of miR-21
and the 3′untranslated region (UTR) of PTEN mRNA, suggesting that
miR-21 would bind to the 3′UTR of PTEN mRNA. This structural
similarity between miR-21 and PTEN is a powerful mechanism
explanation of miR-21's downregulatory effect on PTEN protein
expression. A negative association has previously been demonstrated
between PTEN and Akt activation (24). However, some limitations and
unsolved problems remain in the present study, such as the detailed
mechanism of metformin's inhibitory effect on miR-21 and whether
other signaling pathways are also involved in this effect. Further
studies will examine these questions in the future.
Therefore, the present study concluded that
metformin inhibits HaCaT cell viability via the miR-21/PTEN/Akt
signaling pathway. The miR-21/PTEN/Akt signaling pathway may
therefore be considered as a potential target to further
investigate the molecular mechanism of metformin's action. This
conclusion may consolidate certain theoretical foundations for
associated research (25) and
promote the application of metformin in skin cancer remedy
(26).
References
|
1
|
Wilson VG: Growth and differentiation of
HaCaT Ketatinocytes. Methods Mol Biol. 1195:33–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coperchini F, Leporati P, Rotondi M and
Chiovato L: Expanding the therapeutic spectrum of metformin: From
diabetes to cancer. J Endocrinol Invest. 38:1047–1055. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Radhakrishnan P, Dabelsteen S, Madsen FB,
Francavilla C, Kopp KL, Steentoft C, Vakhrushev SY, Olsen JV,
Hansen L, Bennett EP, et al: Immature truncated O-glycophenotype of
cancer directly induces oncogenic features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:pp. E4066–E4075. 2014; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Viollet B, Guigas B, Sanz Garcia N,
Leclerc J, Foretz M and Andreelli F: Cellular and molecular
mechanisms of metformin: an overview. Clin Sci (Lond). 122:253–270.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Malaguarnera R, Sacco A, Morcavallo A,
Squatrito S, Migliaccio A, Morrione A, Maggiolini M and Belfiore A:
Metformin inhibits androgen-induced IGF-IR upregulation in prostate
cancer cells by disrupting membrane-initiated androgen signaling.
Endocrinology. 155:1207–1221. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fasih A, Elbaz HA, Hüttemann M, Konski AA
and Zielske SP: Radiosensitization of Pancreatic cancer cells by
metformin through the AMPK pathway. Radiat Res. 182:50–59. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tebbe C, Chhina J, Dar SA, Sarigiannis K,
Giri S, Munkarah AR and Rattan R: Metformin limits the adipocyte
tumor-promoting effect on ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 5:4746–4764.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han G, Gong H, Wang Y, Guo S and Liu K:
AMPK/mTOR-mediated inhibition of survivin partly contributes to
metformin-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancer cell. Cancer
Biol Ther. 16:77–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gandini S, Puntoni M, Heckman-Stoddard BM,
Dunn BK, Ford L, DeCensi A and Szabo E: Metformin and cancer risk
and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis taking into
account biases and confounders. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 7:867–885.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Viollet B, Guigas B, Sanz Garcia N,
Leclerc J, Foretz M and Andreelli F: Cellular and molecular
mechanisms of metformin: an overview. Clin Sci (Lond). 122:253–270.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Momtazi AA, Derosa G, Maffioli P, Banach M
and Sahebkar A: Role of microRNAs in the therapeutic effects of
curcumin in non-cancer diseases. Mol Diagn Ther. 20:335–345. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao DD, Li L and Chan WY: MicroRNAs: Key
regulators in the central nervous system and their implication in
neurological diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 17:E8422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao Y, Xu R, Xu X, Zhou Y, Cui L and He X:
Down-regulation of lncRNA CASC2 by microRNA-21 increases the
proliferation and migration of renal cell carcinoma cells. Mol Med
Rep. 14:1019–1025. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu YR, Qi HJ, Deng DF, Luo YY and Yang SL:
MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance
to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:12061–12070. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang W, Yang Y, Xia L, Yang Y, Wang F,
Song M, Chen X, Liu J, Song Y, Zhao Y and Yang C: MiR-221 promotes
capan-2 pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells proliferation by
targeting PTEN-Akt. Cell Physiol Biochem. 38:2366–2374. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang Y, Yang YB, Zhang XH, Yu XL, Wang ZB
and Cheng XC: MicroRNA-21 gene and cancer. Med Oncol. 30:3762013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jian H, Wang J, Wang T, Wei L, Li J and
Liu L: Identification of rapeseed MicroRNAs involved in early stage
seed germination under salt and drought stresses. Front Plant Sci.
7:6582016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guedes JR, Santana I, Cunha C, Duro D,
Almeida MR, Cardoso AM, de Lima MC and Cardoso AL: MicroRNA
deregulation and chemotaxis and phagocytosis impairment in
Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement (Amst). 12:7–17. 2015.
|
|
20
|
Sun H, Wang P, Zhang Q, He X, Zai G, Wang
X, Ma M and Sun X1: MicroRNA21 expression is associated with the
clinical features of patients with gastric carcinoma and affects
the proliferation, invasion and migration of gastric cancer cells
by regulating Noxa. Mol Med Rep. 13:2701–2707. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao J, Liu J, Xu R, Zhu X, Liu L and Zhao
X: MicroRNA-21 stimulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and
tumorigenesis in clear cell renal cells. Mol Med Rep. 13:75–82.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu RH, Ning B, Ma XE, Gong WM and Jia TH:
Regulatory roles of microRNA-21 in fibrosis through interaction
with diverse pathways (Review). Mol Med Rep. 13:2359–2366. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang F, Wang Y, Xue J, Ma Q, Zhang J, Chen
YF, Shang ZZ, Li QQ, Zhang SL and Zhao L: Effect of Corilagin on
the miR-21/smad7/ERK signaling pathway in a schistosomiasis-induced
hepatic fibrosis mouse model. Parasitol Int. 65:308–315. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mima K, Nishihara R, Yang J, Dou R, Masugi
Y, Shi Y, da Silva A, Cao Y, Song M, Nowak J, et al: MicroRNA MIR21
(miR-21) and PTGS2 Expression in Colorectal Cancer and Patient
Survival. Clin Cancer Res. 22:3841–3848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee JT, Shan J, Zhong J, Li M, Zhou B,
Zhou A, Parsons R and Gu W: RFP-mediated ubiquitination of PTEN
modulates its effect on AKT activation. Cell Res. 23:552–564. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Soares HP, Ni Y, Kisfalvi K, Sinnett-Smith
J and Rozengurt E: Different patterns of Akt and ERK feedback
activation in response to rapamycin, active-site mTOR inhibitors
and metformin in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e572892013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|