Ischaemic heart disease, particularly myocardial
infarction (MI), is the leading cause of mortality worldwide
(1,2). The risk of 1-year mortality is
increased by 7.5% for each 30-min delay in primary angioplasty for
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (1). Free calcium ion (Ca2+)
concentration in mitochondria may serve a key role in the
regulation of myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury,
especially in regulation of Ca2+ balance (3–6).
Mitochondria, as Ca2+ storage organelles, regulate
Ca2+ homeostasis (7,8).
This is important in cellular homeostasis (9–11).
Mitochondrial Ca2+ maintains dynamic balance of
cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration, which is a key
regulatory factor of mitochondrial respiration (12,13).
Mitochondrial calcium uniporter (MCU) is a key component of the
mitochondrial Ca2+ channel (14–17).
MCU regulator 1 (MCUR1) is a regulatory protein of MCU. MCUR1 is a
key component of the mitochondrial unidirectional transporter
complex required for mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and
maintenance of normal cell bioenergy. Normal Ca2+
expression and function are key for mitochondrial Ca2+
homeostasis (18–23). MCUR1-mediated remodelling of the
mitochondrial Ca2+ environment promotes proliferation
and resistance to apoptosis, facilitating malignant progression of
hepatoma cells (24,25). Thus, MCUR1 is key in the
development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Under pathological
conditions, mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake mediated by MCU
activates the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, resulting
in cell death during myocardial I/R (26–33).
However, the role of MCUR1 in myocardial I/R is unclear.
microRNAs (miRNAs or miRs) are small non-coding RNAs
that mediate post-transcriptional gene modulation. miRNAs are key
in aging and development of cancer and cardiovascular diseases.
Increasing evidence indicates that miRNAs regulate cardiac balance
and response to injury (34–37).
miR-124 is the most abundant miRNA, with a range of biological
functions in the central nervous system (38). Previous studies have showed that
miR-124 was elevated in acute myocardial infarction and was
correlated with myocardial pathophysiology and cardiac function
(39–41). The expression of miR-124 is
upregulated in smokers and is associated with increased risk of
subclinical arteriosclerosis due to altered single-cell phenotypes
(42). Randomised clinical trials
have indicated that serum miR-124 levels may be a useful prognostic
indicator of outcomes after cardiac arrest (43,44).
Circulating miR-124 is upregulated in patients with acute coronary
syndrome, with requirement for urgent coronary occlusion
differentiating this syndrome from membranous inflammation
(45). Although clinical and
preclinical data indicate a key role of miR-124 in the
cardiovascular system (46–48),
data that substantiate this role are limited. Whether miR-124
affects cardiomyocyte apoptosis and MI requires further
investigation.
To investigate the role of miR-124 in cardiomyocyte
apoptosis and MI, cardiomyocyte apoptosis was induced using
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to simulate
oxidative stress induced by I/R injury. We investigated the
mechanism of miR-124 regulated during
H2O2-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
The H9C2 cell line is a subclone of the original
clonal cell line derived from embryonic BD1X rat heart tissue
(49). H9C2 cells exhibit a number
of skeletal muscle properties. Up to 95% of cells fused to form
myotubes are characteristic of skeletal muscle (50). The length, diameter, and
arrangement of sarcomeres and fine myofilaments in their myotubes
are similar to those of developing skeletal and cardiac
myofilaments in vitro. Cells were obtained from the Whole
Gold Cell Bank (Beijing, China) and cultured in Dulbecco's Modified
Eagle's Medium (Merck KGaA) containing 10% FBS (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) in an atmosphere of 95% oxygen and 5% carbon
dioxide at 37°C. After starvation in serum-free DMEM (37°C) for 12
h, oxidative stress was induced by treatment at 37°C with 200 µM
H2O2 for 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 h. Cells were
collected at each time point for subsequent analysis.
RNA constructs miR-124 mimics
(5′uaaggcacgcggugaaugcc3′), anti-miR-124 (5′ATCAAGGTCCGCTGTG3′) and
corresponding negative controls (NCs) were purchased from
GenePharma and transfected into H9C2 cells using FuGENE®
HD (Promega Corporation) at room temperature for 15 min, according
to the manufacturer's instructions. miRNA (10 µM) and 10 µl FuGENE
co-transfected in H9C2 cells. Following incubation at 37°C for 48
h, subsequent experiments were performed. In addition, miR-124
mimic, MCUR1 3′-untranslated region (UTR) plasmid, an MCUR1
overexpression plasmid vector [pEX-3(pGCMV/MCS/Neo)] (GenScript),
NC (mimic Ctrl and pcDNA3.1) and an MCUR1 small interfering RNA
(siRNA, 5′GCCAGAGACAGACAAUACUTT3′; GenePharma) were transfected
using FuGENE® HD (Promega Corporation).
Cells were harvested in the exponential growth phase
and suspended in complete medium. Medium containing cells (100 µl)
were added to the wells and incubated at 37°C for 24 h.
Subsequently, 200 µM (12.5 µl) H2O2 was
added. Each well was incubated with 10 µl CCK-8 (Beijing Solarbio;
cat. no. CA1210) for 1–4 h. The signal was measured by microplate
reader at an absorption wavelength of 450 nm and a reference
wavelength of 600–650 nm. Six samples was tested in triplicate.
MCUR1 3′-UTR was cloned into the gp-mirGLO vector
(GenScript) and mutant 3′-UTR was obtained by target mutation
(GenScript). The luciferase reporter plasmid (gp-miRGLO,
GenePharma) and miR-124 mimic (GenePharma;
5′-uaaggcacgcggugaaugcc3′)/miR-NC (5′UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT3′,
GenePharma) were co-transfected into H9C2 cells (2×104)
using FuGENE® HD (Promega Corporation) into H9C2 cells.
Following incubation at 37°C for 48 h, a Dual-Glo®
Luciferase Assay System (Promega Corporation, E2920) was used
according to the manufacturer's instructions and luciferase
activity was detected. Renilla luciferase activity was
compared with that of the control group.
Protein was extracted from H9C2 cells using the RIPA
extraction buffer (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co.,
Ltd.) containing phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride for 30 min and
prepared to measure protein concentration by BCA. The same amount
(15–40 µg) of protein was separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, transferred to
a pre-treated PVDF membrane, blocked with 5% milk at room
temperature for 1 h and incubated with primary antibody at 4°C
(MCUR1 1:500, BOSTER, cat. no. A08547-1; β-actin 1:5,000, Beyotime,
AF5003) over night. After washing with TBST (1% Tween-20) three
times, the washed membrane was incubated with HRP-conjugated, goat
anti-Rabbit IgG (Abbkin, cat. no. A21020, 1:10,000) at room
temperature for 2.5 h and visualised using a chemiluminescence kit
(Vazyme, E412-02). The results were visualized with a
chemiluminescence analyser. Protein quantification was analysed
using ImageJ software (ImageJ 1.51j8, National Institutes of
Health).
Cell samples were fixed in paraformaldehyde (4%) at
room temperature for 24 h and embedded in paraffin at 42°C, 4~8 h.
Paraffin sections (3–4 µm) were removed using xylene, dehydrated
and washed. FISH was performed according to a previously described
protocol (52). Briefly, the
slides were permeabilized by proteinase K (Solarbio, P1120) at 37°C
for 20 min. The slides were incubated with pre-hybridization buffer
5×SSC (saline sodium citrate) for 1 h at 37°C. The hybridization
buffer 5×SSC (Solarbio, S1030) was transferred to the sample, and a
single gene probe (working solution, 50 ng/µl, synthesis by
Shenggong Biotechnology Company) was added. Slides were incubated
at 37°C overnight to hybridise the probe with target DNA. The
slides were washed with 37°C preheated washing buffer (2×SSC) for
10 min, then washed with 37°C preheated washing buffer (1×SSC) for
10 min and 37°C preheated washing buffer (0.5×SSC) for 10 min. DAPI
was incubated in the dark for 8 min and sealed with
anti-fluorescence quenching sealing agent (Solarbio). The signal
from each probe was observed under a Leica TCS SP8 MP laser
scanning confocal microscope.
H9C2 cells were treated with 200 µM hydrogen
peroxide at 37°C for 6 h and transfected with miRNA. Treated fresh
cells were collected resuspended in 100 µl PBS. PI or
Annexin-V-FITC or PI plus Annexin-V were added for staining. After
15 min incubation at 4°C, C6 flow cytometry was performed using a
flow cytometer (BD accuri, C6 flow cytometry) equipped with FITC
signal filtered by a FL1 detector at 530/30 nm and PI signal
filtered by a FL2 detector at 585/42 nm. The flow cytometry data
are expressed as percentages of initial cell count. The data was
analyzed by FLOWJO v10 (Becton, Dickinson & Company)
software.
Cells were digested with trypsin, resuspended in PBS
and treated with rhodamine 123 (5 mg/l) at 37°C for 30 min, and
washed once with PBS followed by centrifugation at 300 g, 10 min)
at room temperature. Flow cytometric analysis (BD Accuri C6 Flow
Cytometer, BD Company) was used to detect cells at an excitation
wavelength of 488 nm. The data was analyzed by FLOWJO v10 (Becton,
Dickinson & Company) software.
TargetScan was used to predict miRNA-binding sites
in mammals (targetscan.org/vert_80/). MiRanda
(bioinformatics.com.cn/local_miranda_miRNA_target_prediction_120)
and miRDB (mirdb.org/) online databases analysis was performed
according to previously described protocol (53,54).
The experimental data were analysed using the
GraphPad Prism 6.02 software (Dotmatics). All experiments were
repeated three times (n=3). The data are presented as the mean ±
SD. Independent-sample t test was used for comparisons between two
groups. One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc test was used
for comparisons between >2 groups. Pearson's correlation
coefficient was used for correlation analysis. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Cardiomyocytes undergo apoptosis and necrosis
induced by hypoxia and oxidative stress during coronary artery
occlusion and subsequent MI (55,56).
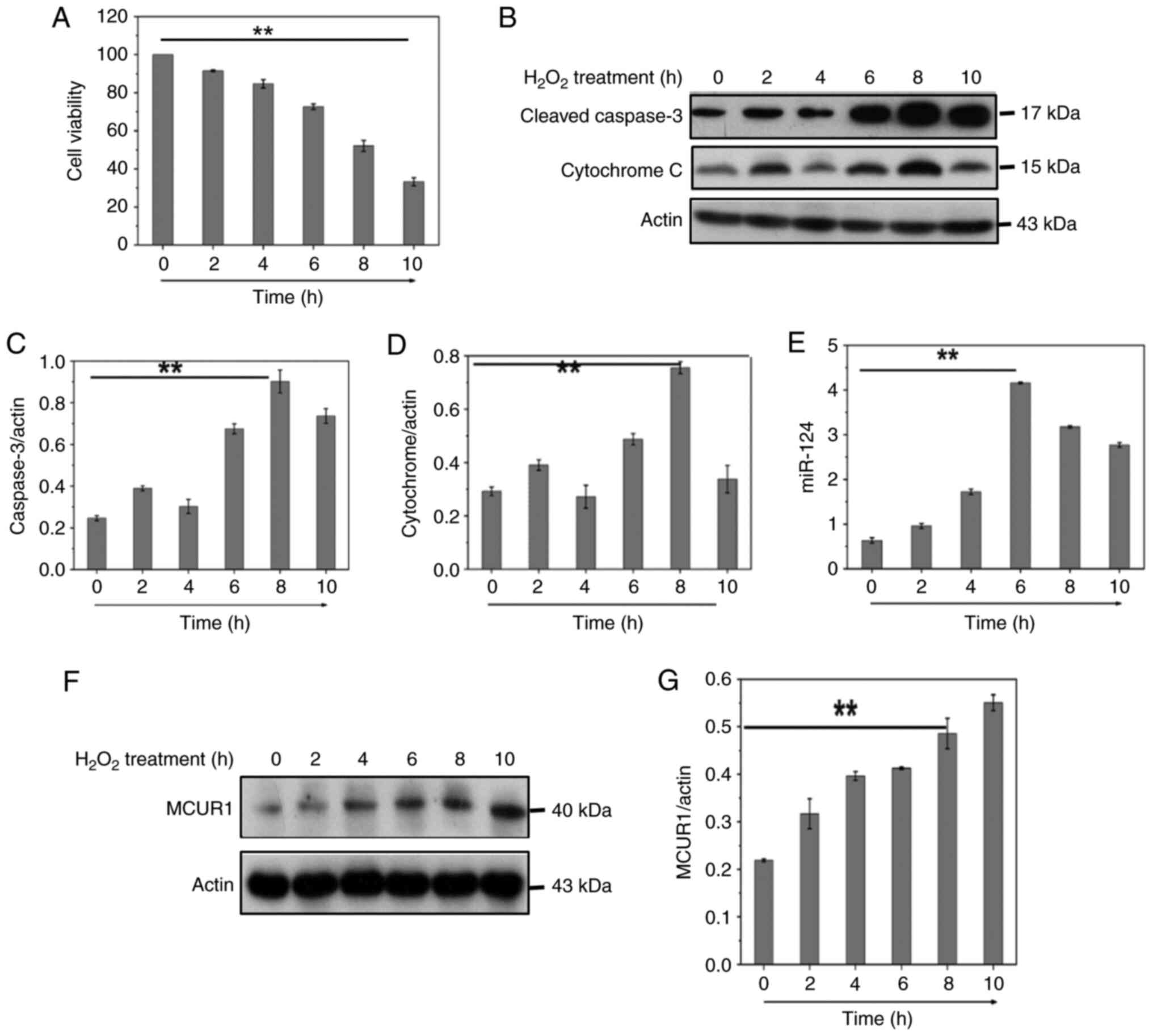
CCK-8 viability assay was used to test cell activity following
H2O2 treatment (Fig. 1A). To determine the involvement of
caspase-3 in H2O2-induced apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes, cleaved caspase-3 was measured by western blotting
(Fig. 1B). The release of
cytochrome c into the cytoplasm is a key step in the apoptotic
process and plays an important role in the apoptotic mechanism. We
therefore measured the release of cytochrome c by western blot
(Fig. 1B). Flow cytometry
(Fig. 2G) showed
H2O2 induced both apoptosis and necrosis in
cardiomyocytes, and H2O2 was used to generate
oxidative stress to mimic I/R injury. The results indicated that
H2O2 decreased cardiomyocyte viability,
induced apoptosis and decreased mitochondrial membrane potential
(Figs. 1A-D and 2G-I). H2O2
treatment significantly increased mRNA expression of miR-124 in
H9C2 cells (Fig. 1E). These data
suggested that upregulation of miR-124 may be related to
H2O2-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. The
online databases TargetScan, miRanda and miRDB were used to predict
the potential targets of miR-124. Computational prediction
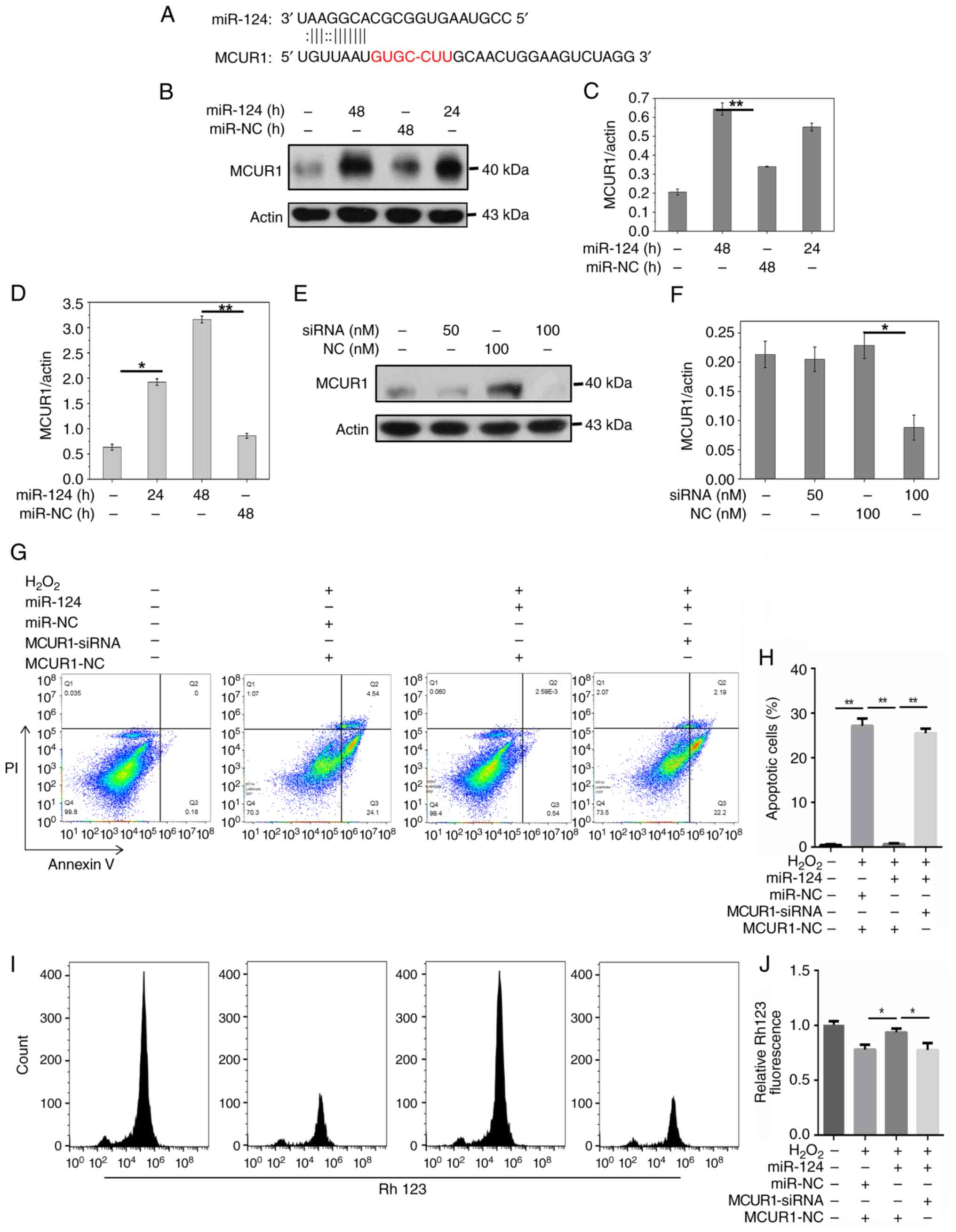
(Fig. 2A) showed miR-124 binding
sites exist in the 3′ UTR of MCUR1. MCUR1 was identified as a
potential target gene of miR-124 in cardiomyocyte apoptosis. A
prior study demonstrated that MCUR1-mediated mitochondrial
Ca2+ environment remodelling markedly promotes
proliferation and apoptosis resistance of hepatoma cell lines
(25). Therefore, expression of
MCUR1 was investigated during cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by
H2O2. MCUR1 protein expression increased in a
time-dependent manner following H2O2
treatment (Fig. 1F and G). These
results indicated that the MCUR1 protein expression was increased
during cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
Compared with miR-NC, miR-124 overexpression
increased the protein expression of MCUR1 compared with miR-NC
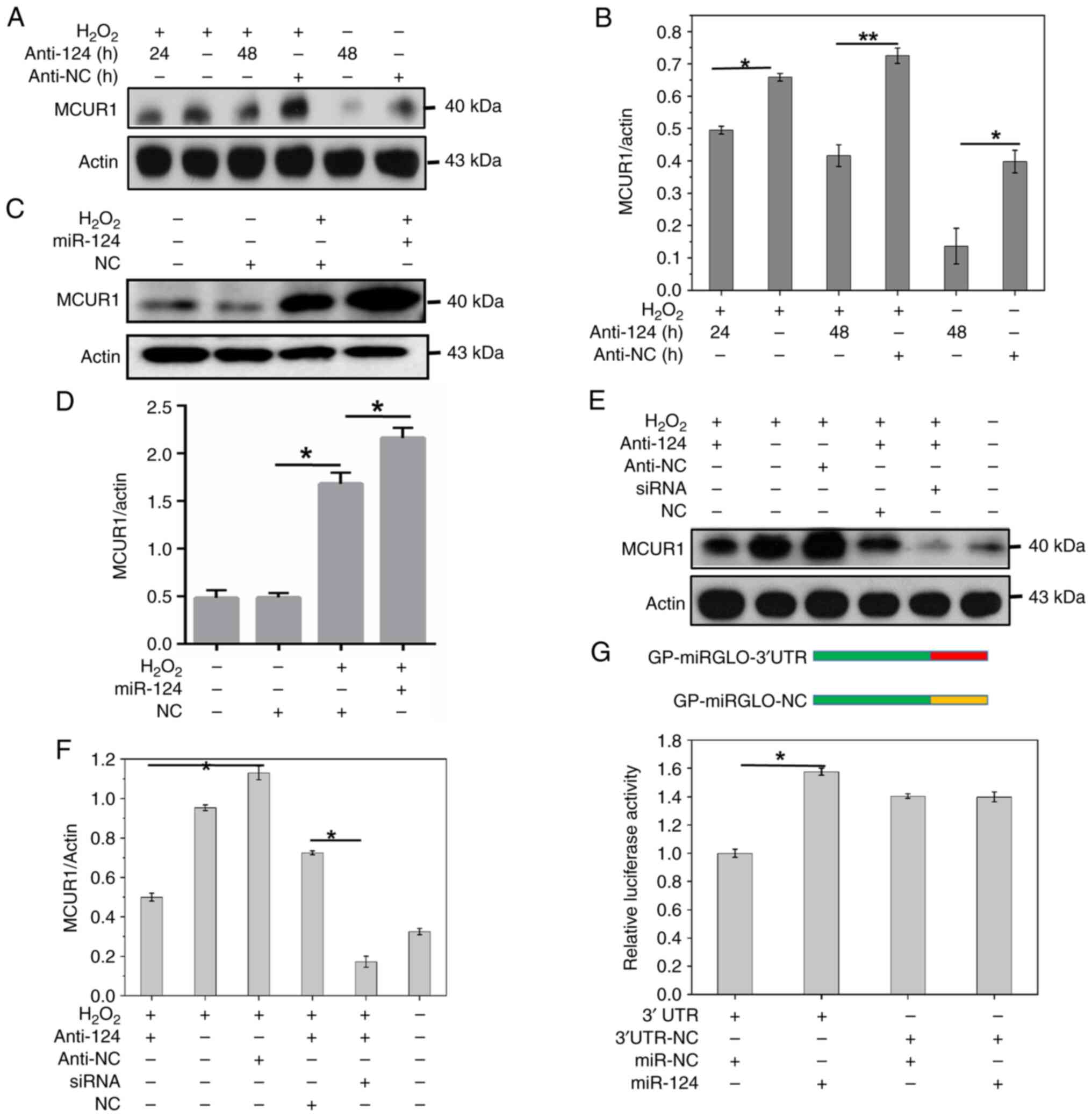
(Fig. 2B-D). Treatment with
H2O2 increased the protein expression of
MCUR1 and miR-124 further increased this following treatment with
H2O2 (Fig. 3C
and D). Simultaneously, the addition of the anti-124 in
presence of H2O2 significantly decreased
expression of MCUR1 (Fig. 3A and
B). MCUR1 siRNA treatment (100 nM) decreased the expression of
MCUR1 (Fig. 2E and F). In the
presence of H2O2, miR-124 inhibitor
(anti-124), or MCUR1 siRNA inhibited MCUR1 protein expression.
Simultaneous treatment with miR-124 inhibitor and MCUR1 siRNA
further inhibited MCUR1 expression (Fig. 3E and F). Flow cytometry showed that
H2O2 enhanced apoptosis, while miR-124
significantly decreased apoptosis induced by
H2O2. However, when cells were co-treated
with MCUR1-siRNA and miR-124, H2O2-induced
apoptosis was restored (Fig. 2G and
H). These results indicated that miR-124 inhibited
cardiomyocyte apoptosis by activating MCUR1 following
H2O2 treatment. Overexpression of miR-124
restored mitochondrial membrane potential in
H2O2-treated cells (Fig. 2I). Moreover, when MCUR1-siRNA and
miR-124 were applied simultaneously in
H2O2-treated cells, mitochondrial membrane
potential was significantly decreased (Fig. 2I and J). The dual-luciferase
reporter assay confirmed binding of miR-124 to MCUR1 3′-UTR. The
relative luciferase activity was increased in H9C2 cells
co-transfected with MCUR1 3′UTR and miR-124 mimic compared to 3′UTR
and miR-NC co-transfected (Fig.
3G). These findings indicated that miR-124 may activate
expression of MCUR1 by binding to MCUR1 3′-UTR, decreasing
cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by H2O2.
Next, the association between miR-124 overexpression
and increased MCUR1 expression was investigated. By screening miRNA
database, the positions of numerous miRNAs including miR-24-1,
lin-4 in the genome were coincident with enhancer regions (57). Most miRNAs are localized in the
nucleus. These miRNAs bind to enhancers and activate gene
expression at the genome level (57–60).
miR-24-1 activated gene transcription by targeting enhancers
(45). It was reported that
overexpression of miR-26a-1 increased the transcription of
neighboring ITGA9 and VILL genes (57). TargetScan (61), miRanda (53) and miRDB online databases are
computational approaches have been used to predict mRNA-miRNA
interaction and microRNA targets (54). In this study, these online
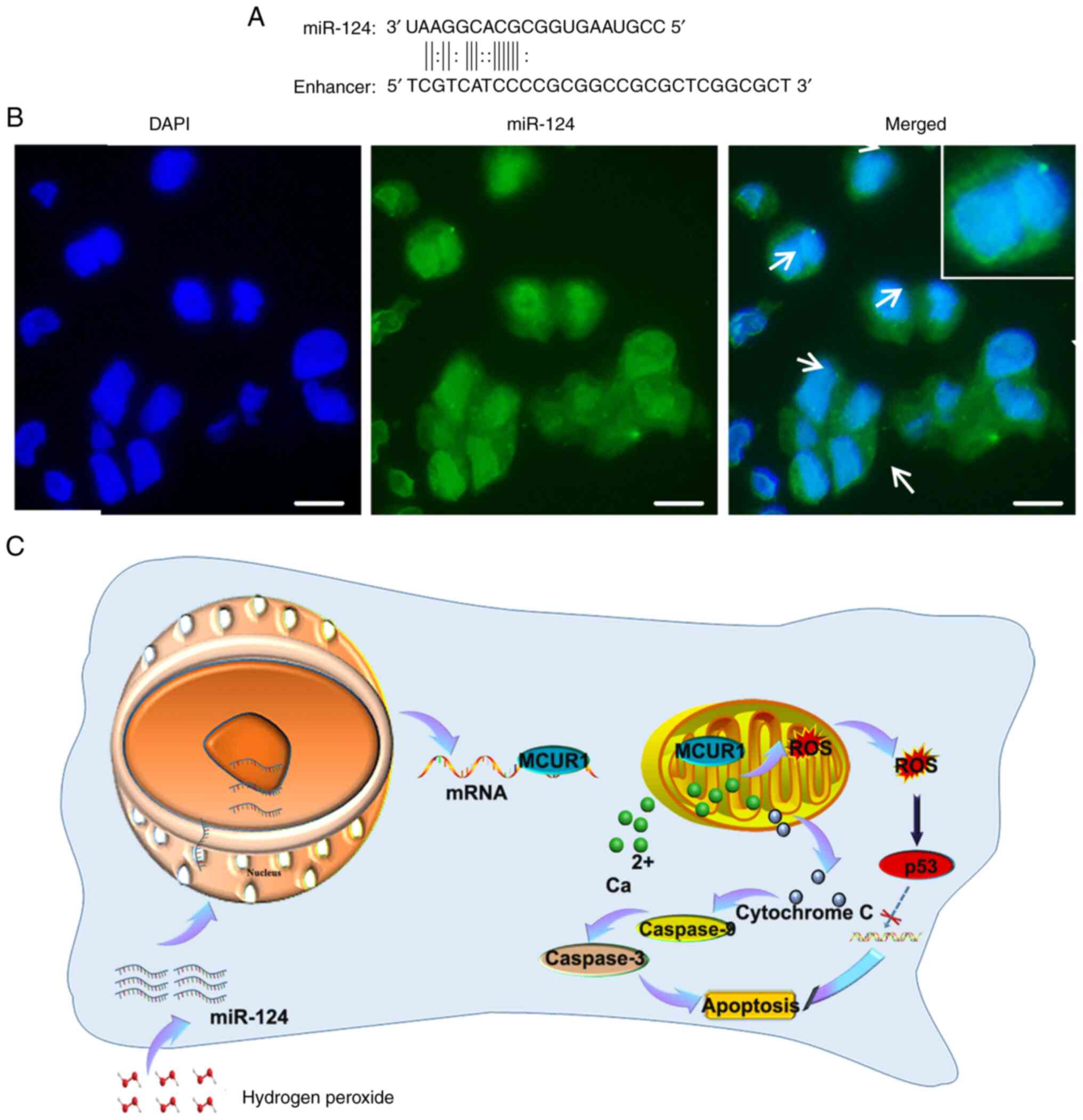
databases were used to predict MCUR1 enhancers. Comparison of the
miR-124 sequences revealed binding of MCUR1 enhancer to miR-124
(Fig. 4A). FISH at the cellular
level revealed the entry of miR-124 into the nucleus (Fig. 4B), which may have increased MCUR1
expression.
The present study revealed the key role of miR-124
in both cardiomyocyte apoptosis and MI and its underlying
mechanism. The findings further demonstrated that MCUR1 was a novel
target of miR-124, and that the miR-124-MCUR1 axis modulated
cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by H2O2. The
findings were consistent with the hypothesis that the expression
level of miR-124 increases during oxidative stress and that miR-124
enters the nucleus to combine with the MCUR1 enhancer. The
subsequent high expression level of MCUR1 confers resistance to
apoptosis in cardiomyocytes (Fig.
4C). Thus, miR-124 may be a biomarker of myocardial injury and
MI. Increasing the expression of MCUR1 may provide a new pathway to
decrease effects of MI and subsequent dysfunction.
miR-124 has been reported to be involved in various
cellular physiological and pathological processes (62–64).
Accumulating evidence has indicated that the expression of miR-124
facilitates cell death and differentiation under pathological
stress (41,46). Increasing evidence has shown that
miR-124 is associated with cardiovascular disease (39,65,66).
miR-124 modulates cardiomyocyte differentiation into bone
marrow-derived stem cells (65).
miR-124 overexpression decreased oxidative stress in
doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury and was a hopeful therapeutic
target in doxorubicin-related cardiomyopathy (47). Previous studies have described the
marked increase of miR-124 expression in smokers and patients with
acute coronary syndrome, suggesting that miR-124 may be a biomarker
of coronary heart disease (42,43).
miR-124 has been proposed to be a cell cycle regulator that
regulates cell survival and apoptosis (67–69),
consistent with the finding of the current study that miR-124
regulated cardiomyocyte apoptosis.
MCUR1 is a regulatory protein of the MCU that plays
an important role in mitochondrial
Ca2+[(Ca2+)m] uptake and maintenance of
normal cellular bioenergy (18).
MCUR1 knockout in HeLa cells causes a decrease in ATP synthesis,
which is dependent on protein kinase activity and leads to
autophagy (70). In addition,
knockout of MCU and MCUR1 in vascular endothelial cells impaired
[Ca2+]m uptake, thus weakened mitochondrial biosynthesis
and cell migration, decreases cell proliferation and induces
autophagy (71). Disorders in
mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostasis are associated with
occurrence and development of various types of tumour such as
melanoma and MCUR1 plays an important role in mitochondrial
Ca2+ homeostasis (72).
The role of MCU in I/R has attracted increasing interest (73). In the present study, MCUR1
expression increased, leading to resistance to apoptosis induced by
oxidative stress.
miRNAs negatively regulate gene expression primarily
by targeting the 3′-UTR of mRNA transcripts in cytoplasm to achieve
instability or translation inhibition (74–76).
Nuclear miRNAs exert gene activation functions. Human miR-373 was
the first activator of gene transcription, which induced both
E-cadherin (CDH1) and cold-shock domain-containing protein 2
(CSDC2) transcription (77). The
analysis of 1302 breast cancer samples indicated that miRNAs and
neighbouring genes may be positively associated (78). Thus, miRNAs have the dual
functional ability to activate transcription in the nucleus and
inhibit transcription in the cytoplasm. A number of studies have
shown that microRNAs at enhancer sites exert transcriptional
activation functions (48,79,80).
miR-24-1 activates enhancer RNA (eRNA) expression and promotes the
enrichment of p300 and RNA Pol II at enhancer sites (48). Nuclear miRNAs serve as enhancer
triggers by modifying chromatin states that facilitate activation
of transcriptional genes (81).
miR-24-1 activates gene transcription by targeting enhancers
(81). The present study
identified a novel mechanism for the miR-124-MCUR1 axis during
cardiac injury in cardiomyocytes. The present results revealed the
mechanism of MCUR1 activation by miR-124 binding to MCUR1 enhancers
and supported the hypothesis that miR-124 alters chromatin status
and increases MCUR1 expression, leading to apoptosis resistance and
inhibition of MI. However, further investigation is required to
confirm these preliminary results. Further studies should
investigate the interaction between miR-124 and MCUR1 and how
miR-124 affects the chromosomal status of MUCR1 enhancers.
In summary, the present study demonstrated that high
expression of miR-124 was induced under oxidative stress
conditions. miR-124 enters the nucleus and combines with the
enhancer of MCUR1 to activate expression of MCUR1. Mitochondrial
Ca2+ environment remodelling significantly promotes
resistance of cardiomyocytes to proliferation and apoptosis.
Not applicable.
The present study was supported by the Project of Shandong
Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (grant
nos. J18KA250 and J18KA127), research project of Qingdao University
Medical Group (grant no. YLJT20202039), Major Research Program of
the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no.
91849209), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no.
81602353), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (grant
no. BK20171145), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (grant nos.
2019M652314 and 2020T130333), Qingdao Applied Basic Research
Project (grant no. 19-6-2-39-cg) and Major Science and Technology
Project of Wenzhou Institute and University of Chinese Academy of
Sciences (grant no. WIUCASQD2021028).
The datasets used and/or analysed in the current
study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable
request.
LG and HD conceptualized the study. LG and HD
confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. CL and CJ designed
the methodology. LHHA used software to process the data. LG, HD and
YG performed experiments, wrote the manuscript and supervised the
study. HD and YG collected data and reviewed and edited the
manuscript. YD and CL analyzed and interpreted the data. All
authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
|
1
|
De Luca G, Suryapranata H, Ottervanger JP
and Antman EM: Time delay to treatment and mortality in primary
angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: Every minute of delay
counts. Circulation. 109:1223–1225. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Heusch G: Cardioprotection: Chances and
challenges of its translation to the clinic. Lancet. 381:166–175.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumfu S, Chattipakorn S, Fucharoen S and
Chattipakorn N: Mitochondrial calcium uniporter blocker prevents
cardiac mitochondrial dysfunction induced by iron overload in
thalassemic mice. Biometals. 25:1167–1175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sripetchwandee J, Sanit J, Chattipakorn N
and Chattipakorn SC: Mitochondrial calcium uniporter blocker
effectively prevents brain mitochondrial dysfunction caused by iron
overload. Life Sci. 92:298–304. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
De Marchi E, Bonora M, Giorgi C and Pinton
P: The mitochondrial permeability transition pore is a dispensable
element for mitochondrial calcium efflux. Cell Calcium. 56:1–13.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giorgi C, Bonora M, Sorrentino G,
Missiroli S, Poletti F, Suski JM, Galindo Ramirez F, Rizzuto R, Di
Virgilio F, Zito E, et al: p53 at the endoplasmic reticulum
regulates apoptosis in a Ca2+-dependent manner. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:1779–1784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cortassa S, Aon MA, Marbán E, Winslow RL
and O'Rourke B: An integrated model of cardiac mitochondrial energy
metabolism and calcium dynamics. Biophys J. 84:2734–2755. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vieira HL and Kroemer G: Pathophysiology
of mitochondrial cell death control. Cell Mol Life Sci. 56:971–976.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moreau B, Nelson C and Parekh AB: Biphasic
regulation of mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake by cytosolic
Ca2+ concentration. Curr Biol. 16:1672–1677. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Marchi S, Patergnani S, Missiroli S,
Morciano G, Rimessi A, Wieckowski MR, Giorgi C and Pinton P:
Mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum calcium homeostasis and
cell death. Cell Calcium. 69:62–72. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Granatiero V, De Stefani D and Rizzuto R:
Mitochondrial calcium handling in physiology and disease. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 982:25–47. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pan S, Ryu SY and Sheu SS: Distinctive
characteristics and functions of multiple mitochondrial
Ca2+ influx mechanisms. Sci China Life Sci. 54:763–769.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Drago I, Pizzo P and Pozzan T: After half
a century mitochondrial calcium in- and efflux machineries reveal
themselves. EMBO J. 30:4119–4125. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kirichok Y, Krapivinsky G and Clapham DE:
The mitochondrial calcium uniporter is a highly selective ion
channel. Nature. 427:360–364. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baughman JM, Perocchi F, Girgis HS,
Plovanich M, Belcher-Timme CA, Sancak Y, Bao XR, Strittmatter L,
Goldberger O, Bogorad RL, et al: Integrative genomics identifies
MCU as an essential component of the mitochondrial calcium
uniporter. Nature. 476:341–345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
De Stefani D, Raffaello A, Teardo E, Szabò
I and Rizzuto R: A forty-kilodalton protein of the inner membrane
is the mitochondrial calcium uniporter. Nature. 476:336–340. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Docampo R and Lukeš J: Trypanosomes and
the solution to a 50-year mitochondrial calcium mystery. Trends
Parasitol. 28:31–37. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mallilankaraman K, Doonan P, Cárdenas C,
Chandramoorthy HC, Müller M, Miller R, Hoffman NE, Gandhirajan RK,
Molgó J, Birnbaum MJ, et al: MICU1 is an essential gatekeeper for
MCU-mediated mitochondrial Ca(2+) uptake that regulates cell
survival. Cell. 151:630–644. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mallilankaraman K, Cardenas C, Doonan P,
Chandramoorthy H, Irrinki K, Golenar T, Csordas G, Madireddi P,
Yang J, Miller R, et al: MCUR1 is an essential component of
mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake that regulates cellular
metabolism. Biophys J. 104:616a2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Plovanich M, Bogorad RL, Sancak Y, Kamer
KJ, Strittmatter L, Li AA, Girgis HS, Kuchimanchi S, De Groot J,
Speciner L, et al: MICU2, a paralog of MICU1, resides within the
mitochondrial uniporter complex to regulate calcium handling. PLoS
One. 8:e557852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Calderon MR, Verway M, Benslama RO, Birlea
M, Bouttier M, Dimitrov V, Mader S and White JH: Ligand-dependent
corepressor contributes to transcriptional repression by C2H2
zinc-finger transcription factor ZBRK1 through association with
KRAB-associated protein-1. Nucleic Acids Res. 42:7012–7027. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kastenhuber ER and Lowe SW: Putting p53 in
context. Cell. 170:1062–1078. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tian C, Xing G, Xie P, Lu K, Nie J, Wang
J, Li L, Gao M, Zhang L and He F: KRAB-type zinc-finger protein
Apak specifically regulates p53-dependent apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol.
11:580–591. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan L, Tian C, Wang H, Song S, Li D, Xing
G, Yin Y, He F and Zhang L: Apak competes with p53 for direct
binding to intron 1 of p53AIP1 to regulate apoptosis. EMBO Rep.
13:363–370. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ren T, Wang J, Zhang H, Yuan P, Zhu J, Wu
Y, Huang Q, Guo X, Zhang J, Ji L, et al: MCUR1-mediated
mitochondrial calcium signaling facilitates cell survival of
hepatocellular carcinoma via reactive oxygen species-dependent P53
degradation. Antioxid Redox Signal. 28:1120–1136. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
García-Rivas Gde J, Carvajal K, Correa F
and Zazueta C: Ru360, a specific mitochondrial calcium uptake
inhibitor, improves cardiac post-ischaemic functional recovery in
rats in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 149:829–837. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Joiner MLA, Koval OM, Li J, He BJ,
Allamargot C, Gao Z, Luczak ED, Hall DD, Fink BD, Chen B, et al:
CaMKII determines mitochondrial stress responses in heart. Nature.
491:269–273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang N, Wang P, Wang S, Li S, Li Y, Wang
J and Wang M: Role of mitochondrial calcium uniporter in regulating
mitochondrial fission in the cerebral cortexes of living rats. J
Neural Transm (Vienna). 121:593–600. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang L, Gao X, Yuan X, Dong H, Zhang Z
and Wang S: Mitochondrial calcium uniporter opener spermine
attenuates the cerebral protection of diazoxide through apoptosis
in rats. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 23:829–835. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yan H, Zhang D, Hao S, Li K and Hang CH:
Role of mitochondrial calcium uniporter in early brain injury after
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol Neurobiol. 52:1637–1647.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liao Y, Hao Y, Chen H, He Q, Yuan Z and
Cheng J: Mitochondrial calcium uniporter protein MCU is involved in
oxidative stress-induced cell death. Protein Cell. 6:434–442. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Santulli G, Xie W, Reiken SR and Marks AR:
Mitochondrial calcium overload is a key determinant in heart
failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:11389–11394. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bell JR, Erickson JR and Delbridge LM:
Ca(2+)/calmodulin dependent kinase II: A critical mediator in
determining reperfusion outcomes in the heart? Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 41:940–946. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Icli B, Wara AKM, Moslehi J, Sun X, Plovie
E, Cahill M, Marchini JF, Schissler A, Padera RF, Shi J, et al:
MicroRNA-26a regulates pathological and physiological angiogenesis
by targeting BMP/SMAD1 signaling. Circ Res. 113:1231–1241. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu S, Huang M, Li Z, Jia F, Ghosh Z,
Lijkwan MA, Fasanaro P, Sun N, Wang X, Martelli F, et al:
MicroRNA-210 as a novel therapy for treatment of ischemic heart
disease. Circulation. 122 (11 Suppl):S124–S131. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang X, Yoon JY, Morley M, McLendon JM,
Mapuskar KA, Gutmann R, Mehdi H, Bloom HL, Dudley SC, Ellinor PT,
et al: A common variant alters SCN5A-miR-24 interaction and
associates with heart failure mortality. J Clin Invest.
128:1154–1163. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Demkes CJ and van Rooij E: MicroRNA-146a
as a regulator of cardiac energy metabolism. Circulation.
136:762–764. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun Y, Luo ZM, Guo XM, Su DF and Liu X: An
updated role of microRNA-124 in central nervous system disorders: A
review. Front Cell Neurosci. 9:1932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bao Q, Chen L, Li J, Zhao M, Wu S, Wu W
and Liu X: Role of microRNA-124 in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy
induced by angiotensin II. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
63:23–27. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang L, Chen Q, An W, Yang F, Maguire EM,
Chen D, Zhang C, Wen G, Yang M, Dai B, et al: Novel pathological
role of hnRNPA1 (heterogeneous nuclear Ribonucleoprotein A1) in
vascular smooth muscle cell function and Neointima hyperplasia.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 37:2182–2194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Han F, Chen Q, Su J, Zheng A, Chen K, Sun
S, Wu H, Jiang L, Xu X, Yang M, et al: MicroRNA-124 regulates
cardiomyocyte apoptosis and myocardial infarction through targeting
Dhcr24. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 132:178–188. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
de Ronde MWJ, Kok MGM, Moerland PD, Van
den Bossche J, Neele AE, Halliani A, van der Made I, de Winther
MPJ, Meijers JCM, Creemers EE and Pinto-Sietsma SJ: High miR-124-3p
expression identifies smoking individuals susceptible to
atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis. 263:377–384. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Devaux Y, Dankiewicz J, Salgado-Somoza A,
Stammet P, Collignon O, Gilje P, Gidlöf O, Zhang L, Vausort M,
Hassager C, et al: Association of circulating MicroRNA-124-3p
levels with outcomes after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: A
substudy of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Cardiol. 1:305–313.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gilje P, Gidlöf O, Rundgren M, Cronberg T,
Al-Mashat M, Olde B, Friberg H and Erlinge D: The brain-enriched
microRNA miR-124 in plasma predicts neurological outcome after
cardiac arrest. Crit Care. 18:R402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gacoń J, Kabłak-Ziembicka A, Stępień E,
Enguita FJ, Karch I, Derlaga B, Żmudka K and Przewłocki T:
Decision-making microRNAs (miR-124, −133a/b, −34a and −134) in
patients with occluded target vessel in acute coronary syndrome.
Kardiol Pol. 74:280–288. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ghafouri-Fard S, Shoorei H, Bahroudi Z,
Abak A, Majidpoor J and Taheri M: An update on the role of miR-124
in the pathogenesis of human disorders. Biomed Pharmacother.
135:1111982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Ni J, Shu Y, Wang H and Hu T:
MiR-124 attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury via
inhibiting p66Shc-mediated oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 521:420–426. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhu P, Li H, Zhang A, Li Z, Zhang Y, Ren
M, Zhang Y and Hou Y: MicroRNAs sequencing of plasma exosomes
derived from patients with atrial fibrillation: miR-124-3p promotes
cardiac fibroblast activation and proliferation by regulating
AXIN1. J Physiol Biochem. 78:85–98. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hescheler J, Meyer R, Plant S, Krautwurst
D, Rosenthal W and Schultz G: Morphological, biochemical, and
electrophysiological characterization of a clonal cell (H9c2) line
from rat heart. Circ Res. 69:1476–1486. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shimada Y, Fischman DA and Moscona AA: The
fine structure of embryonic chick skeletal muscle cells
differentiated in vitro. J Cell Biol. 35:445–453. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Forero DA, González-Giraldo Y, Castro-Vega
LJ and Barreto GE: qPCR-based methods for expression analysis of
miRNAs. Biotechniques. 67:192–199. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shin S, Jung Y, Uhm H, Song M, Son S, Goo
J, Jeong C, Song JJ, Kim VN and Hohng S: Quantification of purified
endogenous miRNAs with high sensitivity and specificity. Nat
Commun. 11:60332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lewis BP, Shih IH, Jones-Rhoades MW,
Bartel DP and Burge CB: Prediction of mammalian microRNA targets.
Cell. 115:787–798. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lee Y and Gustafsson AB: Role of apoptosis
in cardiovascular disease. Apoptosis. 14:536–548. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bialik S, Geenen DL, Sasson IE, Cheng R,
Horner JW, Evans SM, Lord EM, Koch CJ and Kitsis RN: Myocyte
apoptosis during acute myocardial infarction in the mouse localizes
to hypoxic regions but occurs independently of p53. J Clin Invest.
100:1363–1372. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xiao M, Li J, Li W, Wang Y, Wu F, Xi Y,
Zhang L, Ding C, Luo H, Li Y, et al: MicroRNAs activate gene
transcription epigenetically as an enhancer trigger. RNA Biol.
14:1326–1334. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lu L, Zhou L, Chen EZ, Sun K, Jiang P,
Wang L, Su X, Sun H and Wang H: A novel YY1-miR-1 regulatory
circuit in skeletal myogenesis revealed by genome-wide prediction
of YY1-miRNA network. PLoS One. 7:e275962012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Lee BK, Bhinge AA and Iyer VR:
Wide-ranging functions of E2F4 in transcriptional activation and
repression revealed by genome-wide analysis. Nucleic Acids Res.
39:3558–3573. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Guimbellot JS, Erickson SW, Mehta T, Wen
H, Page GP, Sorscher EJ and Hong JS: Correlation of microRNA levels
during hypoxia with predicted target mRNAs through genome-wide
microarray analysis. BMC Med Genomics. 2:152009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xu J, Zheng Y, Wang L, Liu Y, Wang X, Li Y
and Chi G: miR-124: A promising therapeutic target for central
nervous system injuries and diseases. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
42:2031–2053. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Qin Z, Wang PY, Su DF and Liu X: miRNA-124
in immune system and immune disorders. Front Immunol. 7:4062016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yang J, Zhang X, Chen X, Wang L and Yang
G: Exosome mediated delivery of miR-124 promotes neurogenesis after
ischemia. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 7:278–287. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cai B, Li J, Wang J, Luo X, Ai J, Liu Y,
Wang N, Liang H, Zhang M, Chen N, et al: microRNA-124 regulates
cardiomyocyte differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cells via targeting STAT3 signaling. Stem Cells. 30:1746–1755.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Devaux Y and Stammet P:
Cardiolinc™ network: What's new in prognostication after
cardiac arrest: microRNAs? Intensive Care Med. 44:897–899. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Das E, Jana NR and Bhattacharyya NP:
MicroRNA-124 targets CCNA2 and regulates cell cycle in
STHdh(Q111)/Hdh(Q111) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
437:217–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Taniguchi K, Sugito N, Kumazaki M,
Shinohara H, Yamada N, Nakagawa Y, Ito Y, Otsuki Y, Uno B, Uchiyama
K and Akao Y: MicroRNA-124 inhibits cancer cell growth through
PTB1/PKM1/PKM2 feedback cascade in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett.
363:17–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liang YN, Tang YL, Ke ZY, Chen YQ, Luo XQ,
Zhang H and Huang LB: MiR-124 contributes to glucocorticoid
resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia by promoting
proliferation, inhibiting apoptosis and targeting the
glucocorticoid receptor. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 172:62–68.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Mallilankaraman K, Cárdenas C, Doonan PJ,
Chandramoorthy HC, Irrinki KM, Golenár T, Csordás G, Madireddi P,
Yang J, Müller M, et al: MCUR1 is an essential component of
mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake that regulates cellular
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 14:1336–1343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tomar D, Dong Z, Shanmughapriya S, Koch
DA, Thomas T, Hoffman NE, Timbalia SA, Goldman SJ, Breves SL,
Corbally DP, et al: MCUR1 is a scaffold factor for the MCU complex
function and promotes mitochondrial bioenergetics. Cell Rep.
15:1673–1685. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Romero-Garcia S and Prado-Garcia H:
Mitochondrial calcium: Transport and modulation of cellular
processes in homeostasis and cancer (review). Int J Oncol.
54:1155–1167. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kwong JQ: The mitochondrial calcium
uniporter in the heart: Energetics and beyond. J Physiol.
595:3743–3751. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Pasquinelli AE: MicroRNAs and their
targets: Recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal
relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 13:271–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Place RF, Li LC, Pookot D, Noonan EJ and
Dahiya R: MicroRNA-373 induces expression of genes with
complementary promoter sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:1608–1613. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Dvinge H, Git A, Gräf S, Salmon-Divon M,
Curtis C, Sottoriva A, Zhao Y, Hirst M, Armisen J, Miska EA, et al:
The shaping and functional consequences of the microRNA landscape
in breast cancer. Nature. 497:378–382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zou Q, Liang Y, Luo H and Yu W:
miRNA-mediated RNAa by targeting enhancers. Adv Exp Med Biol.
983:113–125. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Liu H, Lei C, He Q, Pan Z, Xiao D and Tao
Y: Nuclear functions of mammalian MicroRNAs in gene regulation,
immunity and cancer. Mol Cancer. 17:642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Vaschetto LM: miRNA activation is an
endogenous gene expression pathway. RNA Biol. 15:826–828.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|