Introduction
A total of ~20 million people worldwide succumb
every year due to AS with the increased of the incidence rate of
atherosclerosis (AS) (1). In 2018,
the death induced by cardiovascular disease was the first cause of
death among urban and rural residents in China (2). Of note, vascular endothelial cells
are lined up in the inner surface of blood vessels, are in direct
contact with the metabolite-related endogenous danger signals in
the circulatory system. Consequently, the impairment and
dysfunction of vascular endothelial cells would impair vasodilation
and increase endothelium-dependent permeability, which is strongly
correlated with the development of AS. Reactive oxygen species
(ROS) is the key factor that contributes to the injury of vascular
endothelial cells (3). Therefore,
protecting endothelial cells from the damage of ROS is one of the
effective strategies to prevent AS. As H2O2
is a well-known ROS, it is often used as a stimulant of in
vitro model for oxidative injury in AS which presented as
ROS-intermediated destruction of lipids and proteins contributing
to damage of the membrane in a series of cells (4).
It is known that soy is the main source of
high-quality proteins (5) and the
nutritional value of soy is mainly attributed to the content of
phytochemical content, particularly the uniquely rich content of
isoflavone (6). Particularly,
Genistein (GEN), the most active soy isoflavone, is a potent
antioxidant and anti-browning agent both in vivo and in
vitro, which exhibit preventive and therapeutic effects on
cancer, post-menopausal syndrome, osteoporosis and a series of
cardiovascular diseases (7,8). GEN
pretreatment significantly attenuated
H2O2-induced peroxide formation and inhibited
ischemia-induced ROS production, including enhancement of
superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx)
activity in Caco-2 cells and cerebral ischemia mouse (9,10).
Moreover, GEN can also attenuate apoptosis by reversing the ratio
of Bcl-2 to Bax and inhibiting the activity of the pro-apoptotic
caspase-9 and caspase-3 in the primary rat neurons (11).
However, the effect of GEN on endothelial cells
after oxidative damage remains obscure and the mechanism by which
GEN attenuates oxidative stress-induced endothelial cell injury
also needs further study to verify. Therefore, the present study
aimed to further determine the effect of GEN on the oxidative
damage of human vascular endothelial cells (HUVECs) caused by
H2O2 and further elucidated its potential
associated signaling pathways.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
HUVECs were provided by the Basic Medical College of
Jilin University (Changchun, China). In brief, HUVECs were cultured
in RPMI-1640 medium (P004-1, Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering
Institute) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (F8318, Gibco) and 1%
penicillin in a 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator. The treatment
conditions of H2O2 and GEN (cat. no.
HY-14596; MedChemExpress) were determined according to previous
studies (10,12). Subsequent experiments were divided
into four groups: control group, GEN treatment group,
H2O2 treatment group and a combined treatment
group of GEN and H2O2.
Cell viability assay
H2O2 (130 µM) was used to
induce oxidation injury in HUVECs (1×105 cells per well
was seeded) according to pre-experiments and previous studies
(10,12). GEN with different concentrations
(100 nM, 1 µM, 10 µM) were pretreated to reduce the oxidant injury
of H2O2. The CCK-8 kit (ck04, Dojindo, the
absorbance values at 450 nm were recorded) was used to detect cell
viability referring to operating instructions. A total of 10 µl
CCK-8 solution was added to each well and incubated at 37°C with 5%
CO2 in incubator for 2 h. An optimal dose of GEN was
utilized for its antioxidant effect and for observing its
antioxidant mechanism.
Intracellular ROS assay
HUVECs were seeded in six-well plates at a density
of 1.2×105/ml per well for 24 h. Then,
Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) Assay (cat. no.
S0033S; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) was implemented. A
total of 10 µmol/l GEN was added to the GEN and GEN +
H2O2 group for 1 h; 130 µmol/l
H2O2 was added to the GEN +
H2O2 group and the H2O2
group for 1 h. After the treatment was completed, the six-well
plates were taken out from the incubator and washed by adding 1 ml
of PBS to each well once, then the PBS was discarded. The DCFH-DA
probes were diluted with the serum-free RPMI-1640 culture medium at
the ratio of 1:1,000. The discarded culture medium from the
six-well plates was aspirated, and the cells were washed three
times with 1 ml of serum-free RPMI-1640 culture medium per well to
avoid eluting the cells from the wall. After aspirating the culture
medium used for washing, 1 ml of prepared DCFH-DA probe was added
to each well and the six-well plate loaded with the probe was
incubated in the incubator for 40 min to prevent degradation and
inactivation of the probe, and the HUVECs were washed with
serum-free cell RPMI-1640 culture medium for 3 times after 40 min
to wash away the DCFH-DA that had not entered into the cells. Then,
200 µl of 0.25% trypsin was added to each well, the digestion was
terminated, centrifugation followed and the supernatant was
discarded. A total of 200 µl of PBS was added to each tube and was
blown several times to make a single-cell suspension, which was
transferred to a flow tube protected from light, and put on a flow
cytometer (C6, BD, USA, 488 nm excitation light and 525 nm emission
used) for ROS detection.
Apoptosis assay
Apoptosis was detected using Annexin V-FITC kit
(cat. no. C1062L; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) (13). In brief, HUVECs were seeded in
six-well plates at a density of 1.2×105/ml per well for
24 h. Then, the desired concentrations of GEN and
H2O2 were added and washed once with PBS
according to previous description. After that, cells were collected
and supplemented with Annexin V-FITC conjugate. The flow tubes were
incubated for 20 min in a dark place at room temperature and
analyzed immediately by a flow cytometer (C6 and BD Accuri™ C6
Software, version 227.4).
Determination of intracellular enzyme
activity
Cells in logarithmic growth phase were cultured in
5-mm cell culture dishes, and cell samples were collected after
adding GEN and H2O2. The cells were removed
from the incubator, placed in an ice bath, and the adherent cells
were collected in 1.5 ml EP tubes by scraping with a cell scraper.
A total of 100 µl of cell lysate was added to each tube and placed
in liquid nitrogen for 3 min, 37°C water bath for 3 min, and
repeated three times. The cells were pre-cooled at 4°C in advance
in a centrifuge and centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 10 min, and the
supernatant was taken for the assay of enzyme activity. The
intracellular enzyme activity was detected according to the
instructions of GPx kits (cat. no. S0058; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology) (14), SOD kits
(cat. no. BC0175; Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co.,
Ltd.) (15), and reduced
glutathione (GSH) kits (cat. no. BC1175; Beijing Solarbio Science
& Technology Co., Ltd.), respectively (16).
RNA extraction and reverse
transcription-quantitative (RT-q) PCR
RNA [An RNA extraction kit was used (12183018A,
PureLink™ RNA; Thermo Fisher)] was extracted from HUVECs and qPCR
[The TBGreen® Premix Ex Taq (Takara) was used] was
conducted after reverse transcription according to the reagent
manufacturer's instructions (T2210, Solarbio, China). GAPDH was
used as a reference gene. Primer sequences are listed in Table I. Thermocycling conditions were as
follows: Initial denaturation at 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40
cycles including denaturation at 95°C for 10 sec, annealing at 55°C
and extension at 72°C for 30 sec. A standard measure of mRNA
expression (2-ΔΔ cycle threshold) was calculated (17).
 | Table I.Primer sequences used in reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR. |
Table I.
Primer sequences used in reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR.
| Gene name | Primer sequences
(5′→3′) |
|---|
| Nuclear factor
erythroid 2-related | F:
AGTCCAGAAGCCAAACTGACAGAAG |
| factor 2 | R:
GGAGAGGATGCTGCTGAAGGAATC |
| Superoxide | F:
ATCCTCTATCCAGAAAACACGG |
| dismutase 1 | R:
GCGTTTCCTGTCTTTGTACTTT |
| Heme
oxygenase-1 | F:
CCTCCCTGTACCACATCTATGT |
|
| R:
GCTCTTCTGGGAAGTAGACAG |
| Bax | F:
CGAACTGGACAGTAACATGGAG |
|
| R:
CAGTTTGCTGGCAAAGTAGAAA |
| Bcl-2 | F:
GACTTCGCCGAGATGTCCAG |
|
| R:
GAACTCAAAGAAGGCCACAATC |
| Caspase-3 | F:
CCAAAGATCATACATGGAAGCG |
|
| R:
CTGAATGTTTCCCTGAGGTTTG |
| GAPDH | F:
AGATCCCTCCAAAATCAAGTGG |
|
| R:
GGCAGAGATGATGACCCTTTT |
Western blot analysis
A total of 50 µg of cell protein were collected from
four groups [Negative control (NC), GEN, GEN +
H2O2, H2O2] with a cell
scraper and lysed with RIPA (cat. no. P0013B; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology) and 1% PMSF (cat. no. ST506; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology). Electrophoresis was carried out, placing 50 µg of
protein in each well, using 10% preformed gel. After transferring
the proteins to the membrane (PVDF), it was blocked with 5% skimmed
milk powder at room temperature for 2 h. Subsequently, the membrane
was incubated overnight at 4°C with the following primary
antibodies (all diluted at 1:1,000): Nuclear factor
erythroid2-related factor 2 (Nrf2; cat. no. 12721S), heme oxygenase
(HO-1; cat. no. 43966), SOD1 (37385S), Bax (cat. no. 5023S; all
from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.), Caspase-3 (cat. no. 14220S;
Abcam) and Bcl-2 (cat. no. orb10173; Biorbyt, Ltd). Following the
primary incubation, the membrane was incubated with horseradish
peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody (1:3,000; cat. no.
7074S; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.) for 1 h at room
temperature. As the same grouping (NC, GEN, GEN +
H2O2, H2O2) in western
blot detection, the same GAPDH (cat. no. AC001; ABclonal Biotech
Co., Ltd.) was used as control in each experiment which was
repeated at least three times. ImageJ software (1.52a, National
Institutes of Health) was used to analyze the grey value of each
resulting image, and the control protein was used to normalize the
grey values of the target protein for statistical analysis.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad
Prism 8 (Dotmatics). One way ANOVA was used for multiple group
comparisons, corrected by Bonferroni's method. Two independent
samples unpaired t-test was used for comparison between two groups.
All experiments were repeated more than 3 times. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
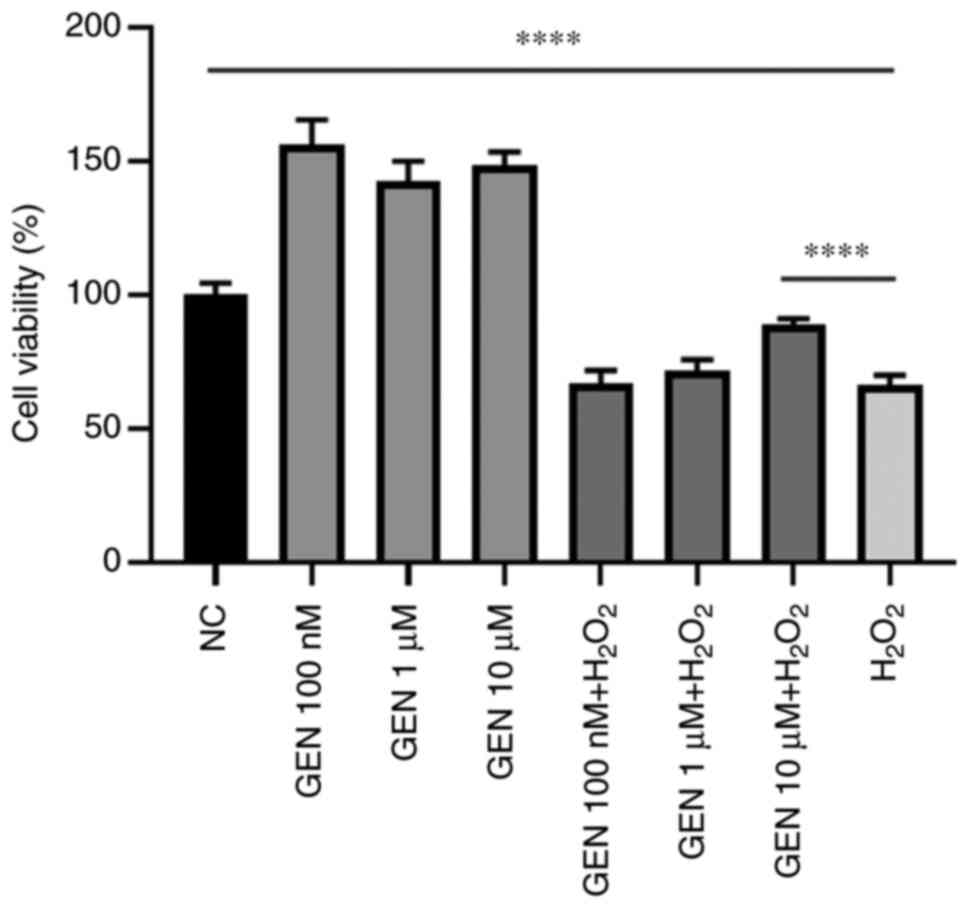
Effect of GEN on the viability of
HUVECs after H2O2 stress
To determine whether GEN could play a protective
role against H2O2-induced cell damage, in
combination with H2O2 stress for 1 h, HUVECs
were pretreated with GEN (100 nM, 1 and 10 µM) for 1 h. As
demonstrated in Fig. 1, the cell
viability increased significantly after pretreatment of GEN
compared with control group (****P<0.0001). Thus, 10 µM GEN
pretreatment for 1 h was used as the treatment condition for the
following experiments.
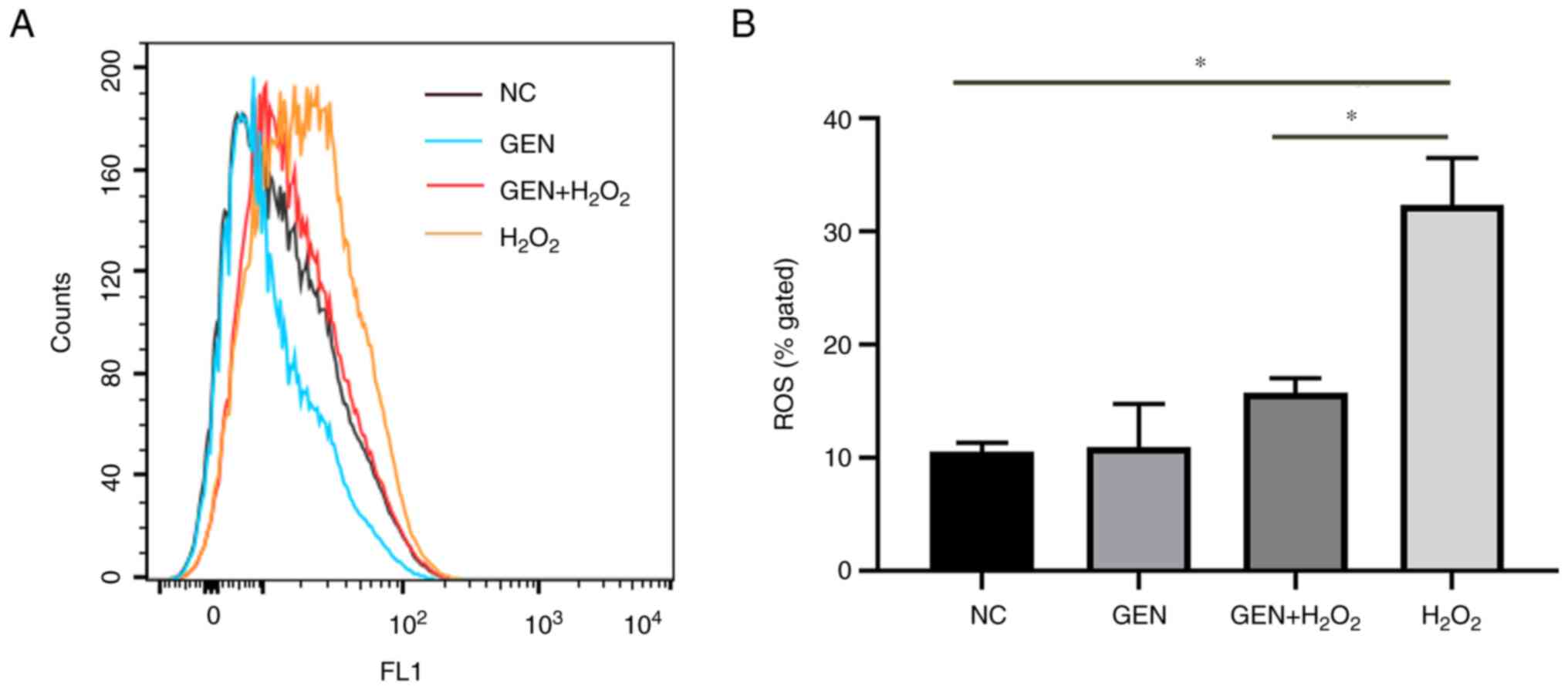
Effect of GEN on oxidative
injury-induced intracellular ROS
To investigate whether GEN could reduce the level of
intracellular ROS, DCFH-DA fluorescent probe was used to detect the
intracellular ROS in the labeled cells. As revealed in Fig. 2, intracellular ROS levels increased
significantly after H2O2 stress (*P<0.05).
By contrast, after GEN pretreatment, the intracellular ROS levels
reduced significantly (*P<0.05).
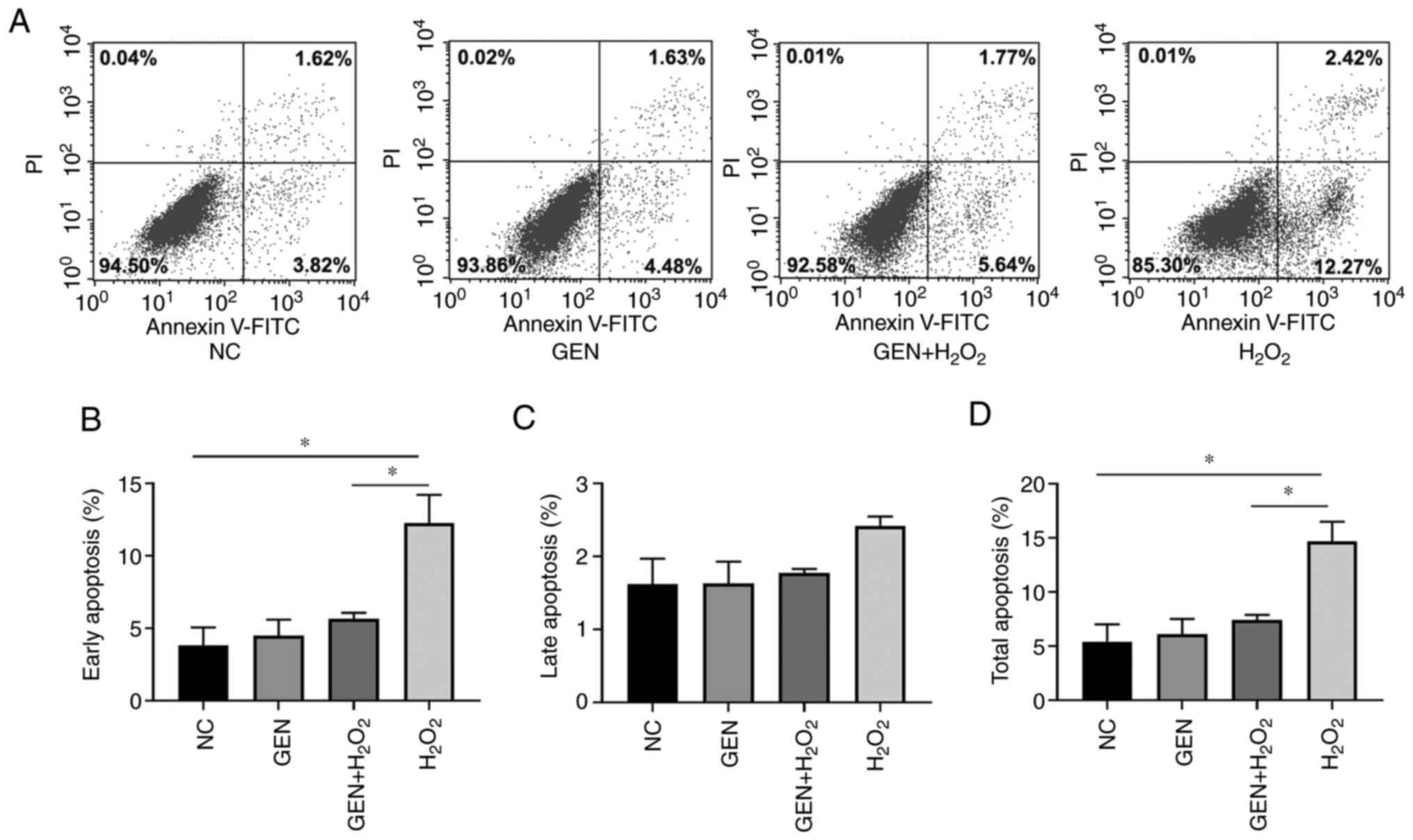
Effect of GEN on the apoptosis of
HUVECs after H2O2 stress
To verify whether GEN could further attenuate the
occurrence of apoptosis by attenuating the aggregation of ROS,
Annexin-V/FITC Assay was applied to stain cells pretreated with the
GEN. The apoptotic rates were counted separately for different
periods. As shown in Fig. 3, GEN
decreased the early apoptotic rate and the total apoptotic rate
significantly (P<0.05), while no effect was detected for the
late apoptotic rate.
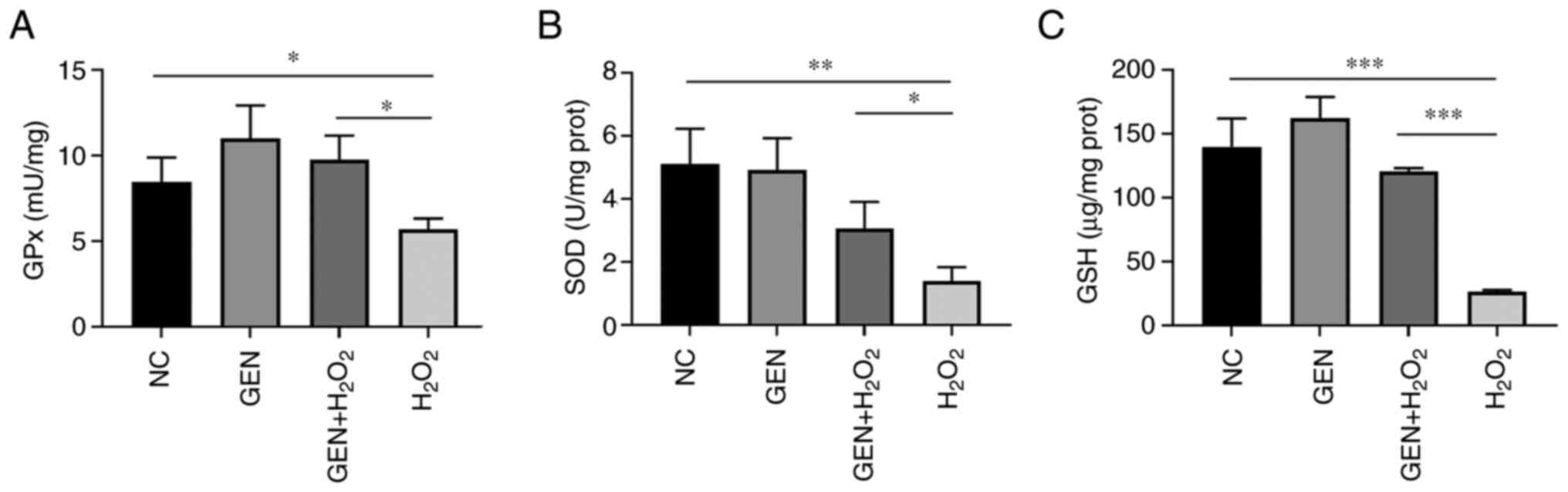
Effect of GEN on intracellular enzyme
activity of HUVECs after H2O2 stress
To further verify the mitigating effect of GEN on
the intracellular ROS, intracellular redox-responsive enzymes were
measured. As demonstrated in Fig.
4A, the enzyme activity of intracellular GPx was significantly
reduced in the H2O2 group (*P<0.05) and
increased after GEN pretreatment (*P<0.05). The intracellular
SOD activity was also significantly reduced (**P<0.01) and
increased after GEN pretreatment (*P<0.05; Fig. 4B). In addition, the activity of
intracellular GSH was significantly reduced in the
H2O2 group (***P<0.001) and increased
after GEN pretreatment (***P<0.001; Fig. 4C).
Effect of GEN on the expression of
Nrf2-related signaling pathway
To verify whether the protective effect of GEN on
oxidative damage after H2O2 stress was
mediated through the Nrf2 pathway, the expression of Nrf2
pathway-related molecules (Nrf2, HO-1 and SOD1) was detected. As
revealed in Fig. 5A, GEN
pretreatment increased the mRNA expression of Nrf2 (**P<0.01),
HO-1 (P<0.001) and SOD1 (**P<0.01) simultaneously under
H2O2 stress. As shown in Fig. 5B and C, compared with the control
group, the protein expression of Nrf2 (***P<0.001), HO-1
(***P<0.001) and SOD1 (****P<0.0001) significantly decreased
after H2O2 stress. Compared with the
H2O2 group, the protein expression of Nrf2
(*P<0.05), HO-1 (**P<0.01) and SOD1 (*P<0.05) increased
significantly after GEN pretreatment.
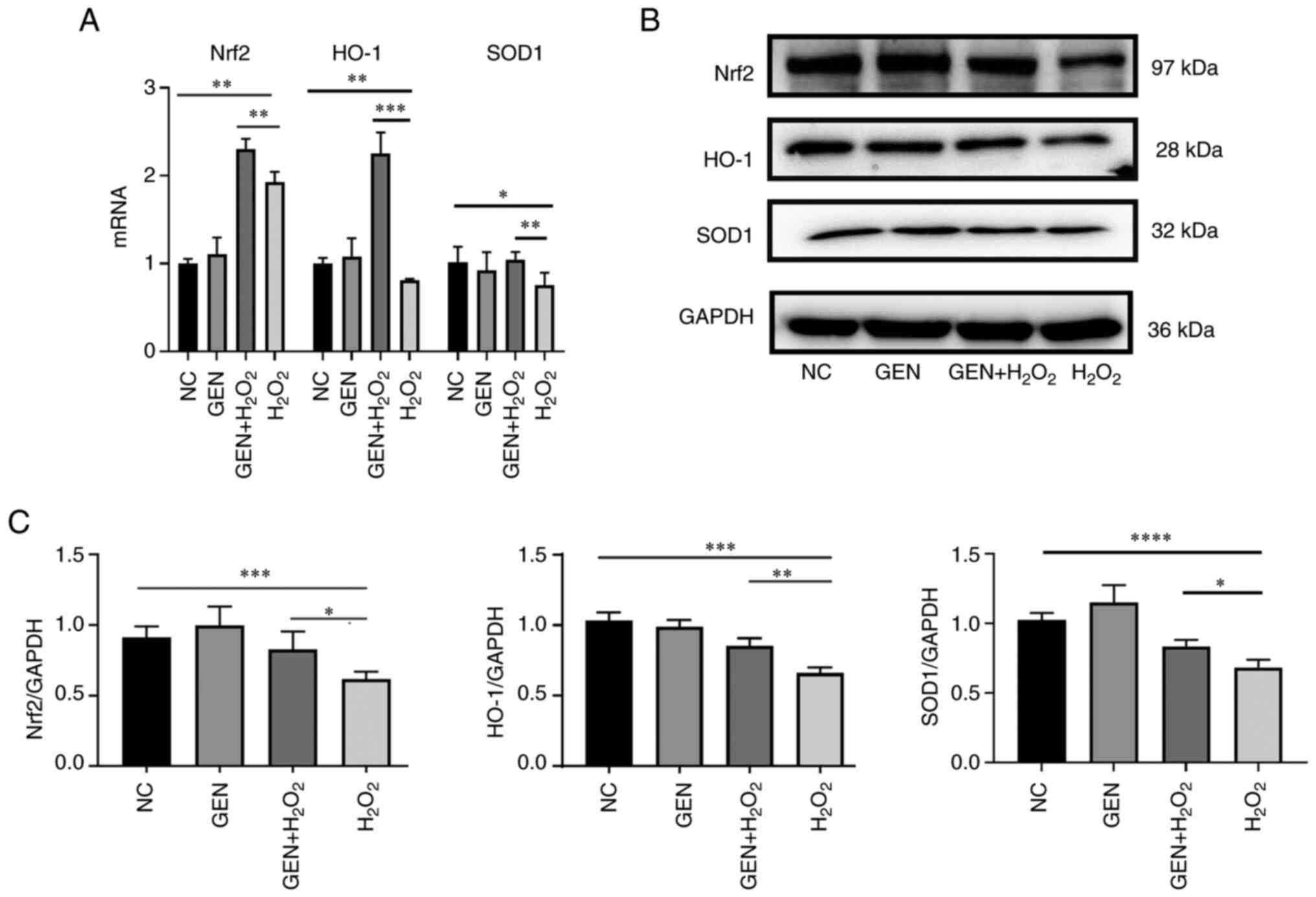 | Figure 5.mRNA and protein expression levels of
Nrf2, SOD1 and HO-1. (A) The mRNA transcription levels of Nrf2,
SOD1 and HO-1 in different groups. (B) Nrf2 pathway-related protein
were determined by western blotting. (C) Statistical results of
corresponding protein bands. GEN pretreatment increased the mRNA
transcription of Nrf2, HO-1 and SOD1 simultaneously under
H2O2 stress. Compared with the control group,
the protein expression of Nrf2, HO-1 and SOD1 decreased after
H2O2 stress. Compared with the
H2O2 group, the protein expression of Nrf2,
HO-1 and SOD1 increased significantly after GEN pretreatment.
*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 and ****P<0.0001. Nrf2,
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; SOD1, superoxide
dismutase 1; HO-1, heme oxygenase-1; GEN, Genistein; NC, negative
control. |
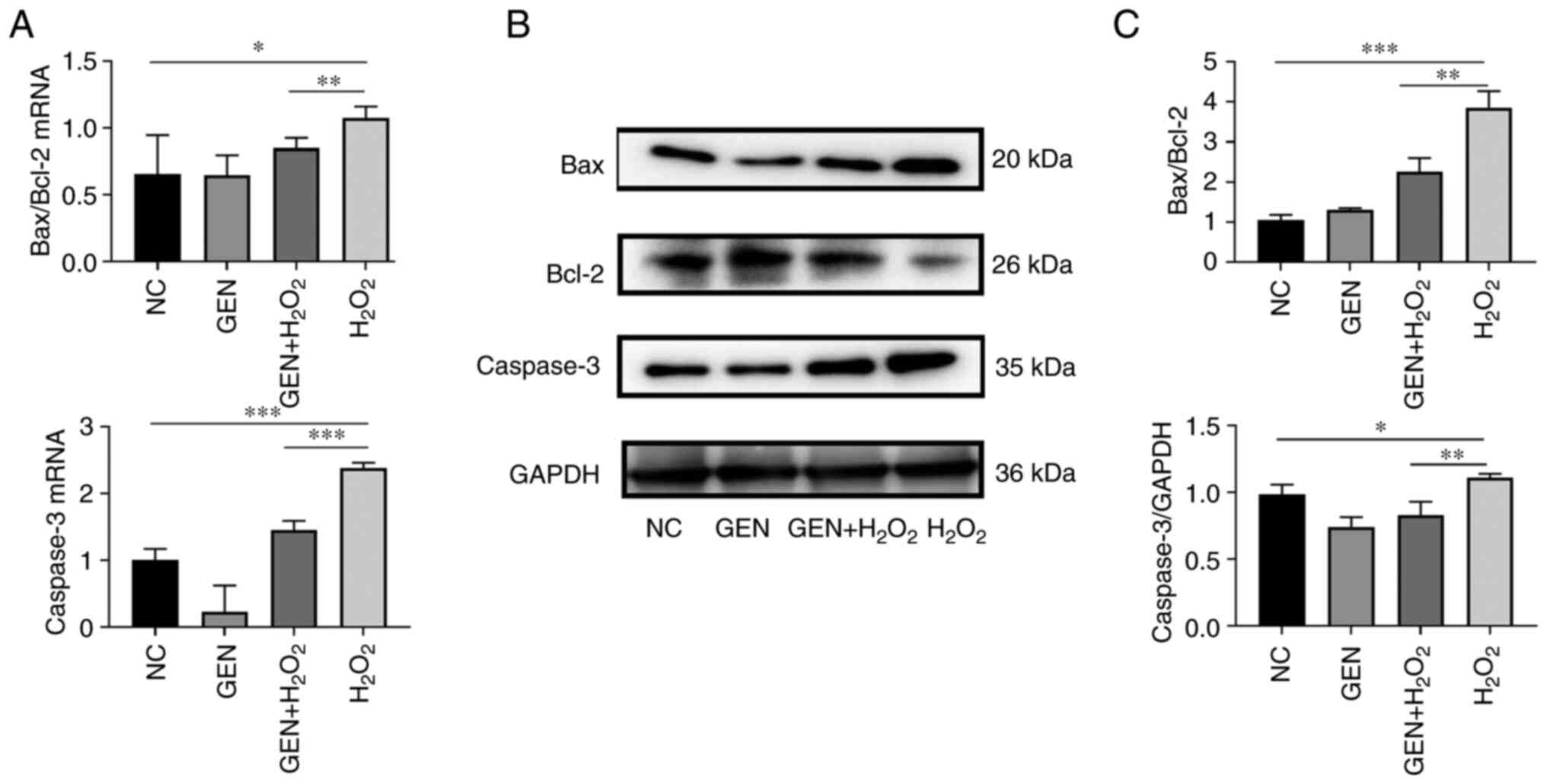
Effect of GEN on the expression of
apoptosis-related genes
To verify the expression of apoptosis-related genes
after GEN treatment, the expression of Bax, Bcl-2, and Caspase-3
were detected by RT-qPCR and western blotting, respectively. As
shown in Fig. 6A, compared with
the control group, the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 was significantly higher
after H2O2 stress (*P<0.05), which was
decreased after GEN pretreatment (**P<0.01). The expression of
Caspase-3 was also significantly higher in the
H2O2 group (***P<0.001), and lower in the
GEN pretreatment group (***P<0.001; Fig. 6B and C. Compared with the control
group, the ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 (***P<0.001) and the protein
expression of Caspase-3 were significantly higher (*P<0.05) in
the H2O2 group. However, the ratio of
Bax/Bcl-2 was decreased (P<0.01) and the expression of Caspase-3
was also decreased (**P<0.01) after GEN pretreatment.
Discussion
AS is a slowly progressive disease which is the
pathological basis of coronary heart disease (9,18).
Although the progress of clinical treatment has reduced the risk of
cardiovascular events, AS and the complications from AS remain the
leading cause of death worldwide (10). Of note, the injury of endothelial
cells is the most important inducement of AS which is always
exacerbated by endothelial dysfunction caused by oxidative stress,
inflammation and other factors. Thus, inhibiting the oxidative
damage of vascular endothelial cells is an effective way to prevent
the occurrence and development of AS. It has been verified that GEN
can exabit an antioxidant effects in cancer, post-menopausal
syndrome, osteoporosis and a series of cardiovascular diseases
(8,11). In the present study, the results
further demonstrated that GEN reduced the oxidative damage of
HUVECs significantly through the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.
Cell viability can directly reflect the survival
status of cultured cells. In the present study, the results
demonstrated that the cell viability was significantly increased
after pretreatment with GEN. This result indicated that GEN inhibit
the injury induced by oxidation stress partly though the increase
of cell viability.
ROS play an important role in pathogen resistance
and cell signaling. However, ROS can also have deleterious effects
after excessive accumulation (19). Previous studies have shown that the
development of AS is closely related to oxidative stress, and
excessive ROS can accelerate the process of AS (20,21).
H2O2 is a common oxidizing agent that always
leads to an increase of intracellular ROS and a decrease in the
viability of numerous different cells (12). The present study further explored
the possible antioxidant effect of GEN. The results of the present
study revealed that GEN pretreatment could attenuate the
intracellular ROS aggregation under H2O2
treatment that is consistent with previous literature (10).
High concentrations of ROS not only cause damage to
macromolecules, including DNA (22), but also induces the opening of
mitochondrial membrane permeability transition pore to release more
ROS (23), which subsequently
induce the release of cytochrome C further to cause apoptosis
(24). These apoptotic cells will
promote the development and progression of coronary artery disease
(25). To determine the protective
role of GEN after oxidative injury, Annexin-V/FITC double staining
was used to further detect apoptosis. It was found that GEN
pretreatment could reduce the early and total apoptotic rate of
HUVECs after H2O2 stress. Meanwhile, the
Bcl-2/Bax ratio was increased and the expression of Caspase-3 was
correspondingly decreased in the GEN pretreatment group. It has
been identified that Caspase-3 is the critical caspase that is also
the main effector of the apoptotic program (26). Moreover, apoptosis can be resisted
though increased expression of anti-apoptotic proteins (such as
Bcl-2) or downregulated expression of pro-apoptotic proteins (such
as Bax) (7). Thus, the results of
the present study further confirmed that GEN could reduce the
apoptosis of HUVECs through decreased expression of Caspase-3 and
increased ratio of Bcl-2/Bax after H2O2
stress.
Moreover, the activity of SOD, GSH and GPx enzymes
was further detected to reveal the effect of GEN on the
anti-oxidative ability of vascular endothelial cells. SOD is an
enzyme that catalyzes the removal of superoxide radicals
(−O2-) and protects the organism from oxidative damage
during physiological aging (27).
GSH also plays a key role in protecting cells from oxidative damage
and toxicity from exogenous electrophiles to maintain redox
homeostasis (28). GPx is another
major member of the antioxidant enzyme family, which catalyzes the
reduction of peroxides by GSH, scavenges free radicals in the body
and thereby reducing the level of ROS. As hypothesized, the
activity of all these three enzymes was increased to some extent
after GEN pretreatment. These results indicated that
H2O2 induces the aggregation of intracellular
ROS accompanied by decreased activity of intracellular antioxidant
system enzymes. However, pretreatment of GEN increased the content
of intracellular antioxidant enzymes, which effectively reduced the
oxidative damage caused by ROS in cells.
Notably, Nrf2 is a critical cytoprotective factor
involved in regulating the expression of antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory and detoxification protein genes (29). Nrf2 also plays an integral role as
a transcription factor in the maintenance of cellular redox
homeostasis and phase II detoxification responses (30,31).
Keap1-Nrf2 pathway regulates the expression of a number of
cytoprotective genes, including the downstream gene HO-1 (32). HO-1 not only acts as an antioxidant
stressor but also regulates a series processes including
inflammation, apoptosis, cell proliferation, fibrosis and
angiogenesis (29). The present
study also revealed that the expression of Nrf2, HO-1 and SOD1 was
reduced after H2O2 stress. However, GEN
pretreatment could reverse the decreased expression of Nrf2, HO-1
and SOD1 significantly. These observations indicated that GEN
inhibit the antioxidation injury through the Nrf2/HO-1/SOD1 related
pathway.
In summary, the data provided in the present study
function as an insight that GEN can exhibit an effective
anti-oxidation role though ameliorating the decrease in cell
viability and antioxidant ability of vascular endothelial cells
after H2O2 stress. Moreover, the involvement
of Nrf2/HO-1/SOD1 related pathway was further verified to be in
H2O2-stessed vascular endothelial cells after
GEN pretreatment which may be clinically relevant. Understanding
the contribution of this molecular network within vascular
endothelial cells may provide new therapeutic approaches for the
treatment of oxidation damage in AS. The limitations of the present
study were the usage of singular cellular model and the lack of
in vivo experiments, which will be followed up by the
authors with an experimental study of an animal model.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the National Natural Science
Foundation of China (grant nos. 81600026,82070034 and 82173572),
the Hunan Natural Science Foundation (grant no. 2021JJ30898) and
the Research Project of Hunan Provincial Health Commission (grant
no B202303027804).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
KX and QQ carried out the experiments, analyzed and
interpreted the data, and drafted the manuscript. YY, LY, XD and KZ
performed the experiments and statistical analysis. QQ, XW and WW
analyzed and interpreted the data, provided the project funding and
revised the manuscript. CL analyzed and interpreted the data,
revised the manuscript. All authors provided critical feedback and
helped shape the research, analysis and manuscript. KX and CL
confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors read and
approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Libby P: The changing landscape of
atherosclerosis. Nature. 592:524–533. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang W, Liu YN, Yin P, Wang LJ, Liu JM, Qi
JL, You JL, Lin L and Zhou MG: Analysis on factors associated with
the place of death among individuals with cardiovascular diseases
in China, 2018. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 42:1429–1436.
2021.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang W, Huang Q, Zeng Z, Wu J, Zhang Y
and Chen Z: Sirt1 inhibits oxidative stress in vascular endothelial
cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:75439732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu Y, Wang Y and Nabi X: Protective effect
of Ziziphora clinopodioides flavonoids against
H2O2-induced oxidative stress in HUVEC cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 117:1091562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hughes GJ, Ryan DJ, Mukherjea R and
Schasteen CS: Protein digestibility-corrected amino acid scores
(PDCAAS) for soy protein isolates and concentrate: Criteria for
evaluation. J Agric Food Chem. 59:12707–12712. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li P, Yao LY, Jiang YJ, Wang DD, Wang T,
Wu YP, Li BX and Li XT: Soybean isoflavones protect SH-SY5Y neurons
from atrazine-induced toxicity by activating mitophagy through
stimulation of the BEX2/BNIP3/NIX pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
227:1128862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Miyashita T, Krajewski S, Krajewska M,
Wang HG, Lin HK, Liebermann DA, Hoffman B and Reed JC: Tumor
suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in
vitro and in vivo. Oncogene. 9:1799–1805. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rahman Mazumder MA and Hongsprabhas P:
Genistein as antioxidant and antibrowning agents in in vivo and in
vitro: A review. Biomed Pharmacother. 82:379–392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhai X, Lin M, Zhang F, Hu Y, Xu X, Li Y,
Liu K, Ma X, Tian X and Yao J: Dietary flavonoid genistein induces
Nrf2 and phase II detoxification gene expression via ERKs and PKC
pathways and protects against oxidative stress in Caco-2 cells. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 57:249–259. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qian Y, Guan T, Huang M, Cao L, Li Y,
Cheng H, Jin H and Yu D: Neuroprotection by the soy isoflavone,
genistein, via inhibition of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis
pathways and reactive oxygen induced-NF-κB activation in a cerebral
ischemia mouse model. Neurochem Int. 60:759–767. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qian Y, Cao L, Guan T, Chen L, Xin H, Li
Y, Zheng R and Yu D: Protection by genistein on cortical neurons
against oxidative stress injury via inhibition of NF-kappaB, JNK
and ERK signaling pathway. Pharm Biol. 53:1124–1132. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park WH: The effect of MAPK inhibitors and
ROS modulators on cell growth and death of
H2O2-treated HeLa cells. Mol Med Rep.
8:557–564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song T, Xue Z, Zhang Z, Shen X and Li X:
Pan-BH3 mimetic S1 exhibits broad-spectrum antitumour effects by
cooperation between Bax and Bak. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol.
113:145–151. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhai X, Zhang C, Zhao G, Stoll S, Ren F
and Leng X: Antioxidant capacities of the selenium nanoparticles
stabilized by chitosan. J Nanobiotechnology. 15:42017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang K, Han L, Hong H, Pan J, Liu H and
Luo Y: Purification and identification of novel antioxidant
peptides from silver carp muscle hydrolysate after simulated
gastrointestinal digestion and transepithelial transport. Food
Chem. 342:1282752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu H, Wang H, Qi F, Xia T, Xia Y, Xu JF
and Zhang X: An activatable host-guest conjugate as a nanocarrier
for effective drug release through self-inclusion. ACS Appl Mater
Interfaces. 13:33962–33968. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Messina M: Soy foods, isoflavones, and the
health of postmenopausal women. Am J Clin Nutr. 100 (Suppl
1):423S–430S. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nathan C and Cunningham-Bussel A: Beyond
oxidative stress: An immunologist's guide to reactive oxygen
species. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:349–361. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen XH, Tan Y, Yu S, Lu L and Deng Y:
Pinitol protects against ox-low-density lipoprotein-induced
endothelial inflammation and monocytes attachment. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 79:368–374. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shan R, Liu N, Yan Y and Liu B: Apoptosis,
autophagy and atherosclerosis: Relationships and the role of Hsp27.
Pharmacol Res. 166:1051692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang S and Lian G: ROS and diseases: Role
in metabolism and energy supply. Mol Cell Biochem. 467:1–12. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zorov DB, Juhaszova M and Sollott SJ:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) and ROS-induced ROS
release. Physiol Rev. 94:909–950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE,
Didelot C and Kroemer G: Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from
mitochondria. Cell Death Differ. 13:1423–1433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang X, He T, Han S, Zhang X, Sun Y, Xing
Y and Shang H: The role of traditional Chinese medicine in the
regulation of oxidative stress in treating coronary heart disease.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:32314242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sakahira H, Enari M and Nagata S: Cleavage
of CAD inhibitor in CAD activation and DNA degradation during
apoptosis. Nature. 391:96–99. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yanase S, Onodera A, Tedesco P, Johnson TE
and Ishii N: SOD-1 deletions in Caenorhabditis elegans alter the
localization of intracellular reactive oxygen species and show
molecular compensation. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 64:530–539.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Forman HJ, Zhang H and Rinna A:
Glutathione: Overview of its protective roles, measurement, and
biosynthesis. Mol Aspects Med. 30:1–12. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Loboda A, Damulewicz M, Pyza E, Jozkowicz
A and Dulak J: Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative
stress response and diseases: An evolutionarily conserved
mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:3221–3247. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N and Biswal S:
Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the
Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:89–116.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mitsuishi Y, Motohashi H and Yamamoto M:
The Keap1-Nrf2 system in cancers: Stress response and anabolic
metabolism. Front Oncol. 2:2002012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Alam J, Stewart D, Touchard C, Boinapally
S, Choi AM and Cook JL: Nrf2, a Cap'n'Collar transcription factor,
regulates induction of the heme oxygenase-1 gene. J Biol Chem.
274:26071–26078. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|