Introduction
Male breast cancer is an uncommon neoplasm,
accounting for 0.6% of all breast carcinomas and <1% of
malignancies in men (1,2). Carcinoma in situ and invasive
carcinoma may occur in the male breast. Ductal carcinoma in
situ is reported in ≤10% of breast carcinomas in males
(1). Invasive ductal carcinoma of
no special type is the most common type of male breast carcinoma,
accounting for ~90%. Mucinous carcinoma, also referred to as
colloid carcinoma or gelatinous carcinoma, is histopathologically
characterized by the presence of clusters of neoplastic cells
suspended in extensive extracellular mucin, and accounts for ~2% of
female breast carcinomas (3).
However, its occurrence in the male breast is extremely rare
(2,4,5).
Mucinous carcinoma is histopathologically subclassified into pure
and mixed types. The pure form is defined as a lesion with a
mucinous carcinoma component of >90% of the tumor; the mixed
type is defined as having mucinous and conventional invasive ductal
carcinoma components (3). It is
well-recognized that pure mucinous carcinoma is generally
associated with low rates of recurrence and excellent survival
rates. In the present study, we report a case of pure mucinous
carcinoma occurring in a male breast and review the
clinicopathological features of this extremely rare tumor.
Furthermore, we also discuss the subclassification of mucinous
carcinoma and the immunohistochemical differences between male and
female breast cancer.
Case report
Case presentation
A 63-year-old Japanese male without a history of
carcinoma, including in the gastrointestinal tract, presented to
Shiga University of Medical Science (Otsu, Japan) with a gradually
enlarged nodule in the right breast. Physical examination revealed
a relatively well-circumscribed nodule, measuring 15×10 mm in
diameter, in the right breast. Total resection of the breast nodule
with right sentinel lymph node dissection was performed. The
patient provided written informed consent.
Immunohistochemistry
The formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue blocks
of the resected breast specimen and lymph nodes were cut into
3-μm-thick sections, deparaffinized and rehydrated. Each section
was stained with hematoxylin and eosin, and then used for
immunostaining. Immunohistochemical analyses were performed using
an autostainer (XT system Benchmark; Ventana Medical System,
Tucson, AZ, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The
following primary antibodies were used: mouse monoclonal antibody
against estrogen receptor (ER; clone 6F11; Novocastra Laboratories,
Ltd., Newcastle upon Tyne, UK) and mouse monoclonal antibody
against progesterone receptor (PgR; clone PgR636; DakoCytomation;
Dako, Glostrup, Denmark). In addition, immunohistochemical analysis
for c-erbB-2 (HER2) oncoprotein was performed using Dako HercepTest
II (Dako).
Histopathological results
Histopathological study of the resected breast
tissue revealed a relatively well-circumscribed nodular lesion in
the breast. Clusters of uniform neoplastic cells with slightly
enlarged round nuclei containing small nucleoli were suspended
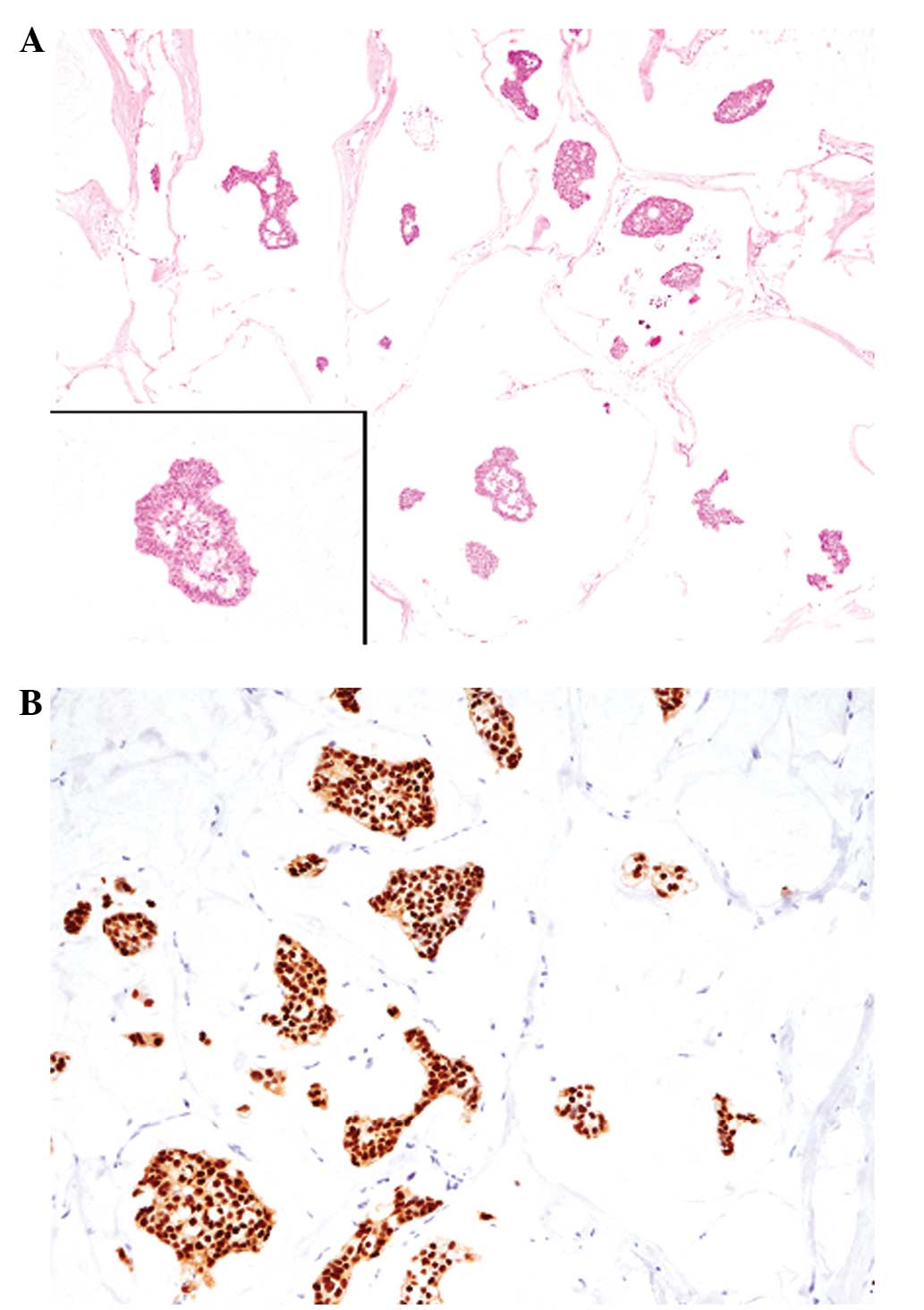
within rich mucinous material (mucous lake; Fig. 1A). The tumor had invaded into the
surrounding fatty tissue, however, no skin involvement was
observed. Neither conventional invasive carcinoma nor intraductal
components were present.
Immunohistochemical results
Immunohistochemical analysis showed that the tumor
cells were diffusely positive for ER (Fig. 1B), but negative for PgR. The HER2
score was 0. The sentinel lymph nodes had no metastatic carcinoma.
Therefore, an ultimate diagnosis of pure mucinous carcinoma
occurring in the male breast was made.
Discussion
Mucinous carcinoma is histopathologically
subclassified into pure and mixed types (3). The pure form is defined as a lesion
with a mucinous carcinoma component in more than 90% of the tumor,
and the mixed type has both mucinous and conventional invasive
carcinoma components (3). In the
present case, a diagnosis of pure mucinous carcinoma was made since
no conventional invasive ductal carcinoma component was present. It
has been reported that the prognosis of pure mucinous carcinoma is
more favorable than that of mixed type in females. Pure mucinous
carcinoma in females is associated with a low incidence of nodal
metastasis (2–4%) (6,7), and the 10-year overall survival ranges
from 80 to 100% (3). Therefore,
certain researchers have suggested that axillary lymph node
dissection may be unnecessary for pure mucinous carcinoma, and they
recommend sentinel lymph node dissection instead for patients with
this form of tumor (6). However,
certain cases of pure mucinous carcinoma with axillary lymph node
metastasis in the male breast have been reported (5,8,9), and a
case of pure mucinous carcinoma with lung metastasis in the male
breast has also been documented (10). Thus, sentinel lymph node technique
and clinical follow-up are considered necessary for patients with
mucinous carcinoma.
Cytological examination by fine needle aspiration
(FNA) is an easy and useful procedure for the diagnosis of breast
tumors. The cytological features of mucinous carcinoma include the
presence of relatively uniform neoplastic cells with slightly
enlarged round to oval nuclei containing small nucleoli arranged in
cords or small nests, within a rich mucinous material (11). A few cases of mucinous carcinoma of
the male breast successfully diagnosed by FNA have been reported
(8,12–14),
although FNA was not performed in the present case. Recently, Ingle
et al documented a case of pure mucinous carcinoma with
axillary lymph node metastasis in a 75-year-old male (8). The authors reported that the breast
tumor and lymph node metastasis were successfully diagnosed as
mucinous carcinoma by preoperative FNA (8). These results suggest that FNA is also
a useful tool for detecting male mucinous carcinoma, even in cases
with lymph node metastasis.
Capella et al classified mucinous carcinoma
based on structural and cytological features as type A
(paucicellular; a tumor showing a ribbon, annular or cribriform
growth pattern with prominent extracellular mucin) and type B
(hypercellular; a tumor showing clump- or sheet-like structures
with reduced extracellular mucin) (15). According to this classification, the
present case falls into the category of type A. It is well-known
that type B mucinous carcinoma frequently shows neuroendocrine
differentiation (15,16). Until now, only a few cases of
neuroendocrine carcinoma with a mucinous carcinoma component within
the same tumor have been reported in the female breast (17,18),
although this type of tumor has not been documented yet in the male
breast. This phenomenon is suggested to represent the same genetic
background present in both type B mucinous carcinoma and
neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast, since Weigelt et al
clearly revealed that no differences in gene expression were
present in these two types of tumors using genome-wide
oligonucleotide microarrays (19).
The immunoprofiles of mucinous carcinoma in males
are fundamentally the same as those in females. More than 90% of
cases show positive immunoreactivity for ER and/or PgR, and HER2
expression is not amplified, as observed in the present case
(5,8,9).
However, Muir et al reported that breast cancer in males is
more frequently positive for ER than in females (male 81% vs.
female 69%) and has lower HER2 overexpression (5% vs. 17%,
respectively), but no significant difference in PgR (63% vs. 56%,
respectively) (20). Postmenopausal
women have been identified to present with breast cancer that is
more likely to have hormone receptor expression. One possibility is
that hormone receptor-positive breast cancer is a consequence of
aberrant steroid receptor upregulation in the estrogen-starved
postmenopausal setting (20).
Therefore, the high rate of hormone receptor-positive breast cancer
in males is also likely due to similar conditions as breast cancer
in postmenopausal women. The pathogenesis of male breast carcinoma,
including mucinous carcinoma, remains unclear; therefore,
additional clinicopathological studies are required.
References
|
1
|
Reiner A and Badve S: Carcinoma of the
male breast. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of
the Breast. Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH and van de
Vijver MJ: IARC Press; Lyon, France: pp. 168–169. 2012
|
|
2
|
Giordano SH, Cohen DS, Buzdar AU, Perkins
G and Hortobagyi GN: Breast carcinoma in men: a population-based
study. Cancer. 101:51–57. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bussolati G and Sapino A: Mucinous
carcinoma and carcinomas with signet-ring cell differentiation.
World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of the Breast.
Lakhani SR, Ellis IO, Schnitt SJ, Tan PH and van de Vijver MJ: IARC
Press; Lyon, France: pp. 60–61. 2012
|
|
4
|
Goss PE, Reid C, Pintilie M, Lim R and
Miller N: Male breast carcinoma: a review of 229 patients who
presented to the Princess Margaret Hospital during 40 years:
1955–1996. Cancer. 85:629–639. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dragoumis DM, Assimaki AS and Tsiftsoglou
AP: Pure mucinous carcinoma with axillary lymph node metastasis in
a male breast. Breast Cancer. 19:365–368. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paramo JC, Wilson C, Velarde D, Giraldo J,
Poppiti RJ and Mesko TW: Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast: is
axillary staging necessary? Ann Surg Oncol. 9:161–164. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kamitani K, Ono M, Toyoshima S, Mitsuyama
S, Anan K and Ikeda Y: Isoechoic axillary lymph node metastases of
mucinous carcinoma of the breast: a case report. Breast Cancer.
13:382–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ingle AP, Kulkarni AS, Patil SP,
Kumbhakarna NR and Bindu RS: Mucinous carcinoma of the male breast
with axillary lymph node metastasis: Report of a case based on fine
needle aspiration cytology. J Cytol. 29:72–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hammedi F, Trabelsi A, Abdelkrim SB, et
al: Mucinous carcinoma with axillary lymph node metastasis in a
male breast: A case report. N Am J Med Sci. 2:111–113.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kertmen N, Dogan E and Altundag K: Pure
mucinous breast carcinoma with lung metastasis in a young male
patient. Am Surg. 76:E1462010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Haji BE, Das DK, Al-Ayadhy B, et al:
Fine-needle aspiration cytologic features of four special types of
breast cancers: mucinous, medullary, apocrine, and papillary. Diagn
Cytopathol. 35:408–416. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nayak SK, Naik R, Upadhyaya K, Raghuveer
CV and Pai MR: FNAC diagnosis of mucinous carcinoma of male breast
- a case report. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 44:355–357.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aggarwal R, Rajni, Khanna G and Beg S:
Mucinous carcinoma in a male breast. J Cytol. 28:84–86. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gupta RK, Naran S, Lallu S and Fauck R:
Needle aspiration cytodiagnosis of mucinous (colloid) carcinoma of
male breast. Pathology. 35:539–540. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Capella C, Eusebi V, Mann B and Azzopardi
JG: Endocrine differentiation in mucoid carcinoma of the breast.
Histopathology. 4:613–630. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scopsi L, Andreola S, Pilotti S, et al:
Mucinous carcinoma of the breast. A clinicopathologic,
histochemical, and imunocytochemical study with special reference
to neuroendocrine differentiation. Am J Surg Pathol. 18:702–711.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ishida M, Umeda T, Abe H, Tani T and Okabe
H: Neuroendocrine carcinoma of the breast with mucinous carcinoma
component: a case report with review of the literature. Oncol Lett.
4:29–32. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
López-Bonet E, Alonso-Ruano M, Barraza G,
Vazquez-Martin A, Bernadó L and Menendez JA: Solid neuroendocrine
breast carcinomas: incidence, clinico-pathological features and
immunohistochemical profiling. Oncol Rep. 20:1369–1374.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weigelt B, Geyer FC, Horlings HM, Kreike
B, Halfwerk H and Reis-Filho JS: Mucinous and neuroendocrine breast
carcinomas are transcriptionally distinct from invasive ductal
carcinomas of no special type. Mod Pathol. 22:1401–1414. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Muir D, Kanthan R and Kanthan SC: Male
versus female breast cancers. A population-based comparative
immunohistochemical analysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 127:36–41.
2003.
|