Introduction
Breast cancer is the most common type of malignancy
in females, accounting for 25% of all female cases and resulting in
>1.67 million cases worldwide in 2012. It is also the most
common cause of cancer-related mortality in females with ~522,000
mortalities in 2012 (1). For the
treatment of breast cancer, identification of the intrinsic subtype
is important, as well as the anatomical staging (2). Axillary lymph node (LN) metastasis,
which indicates established cancerous dissemination, is one of the
most important prognostic factors for the survival of breast cancer
(3). It is a multifactorial event
determined by the patient and tumor characteristics. The
correlation between LN metastasis and T category has previously
been investigated in a certain case series (4). At present, the initial treatment
approach is to define the intrinsic subtype, as it is significant
in determining medical treatments, as well as being a prognostic
factor (2). However, the intrinsic
subtype is not known to predict the frequency of LN metastasis. The
aim of the present study was to evaluate the frequency of LN
metastasis with regard to tumor size according to intrinsic subtype
at the Aichi Cancer Center Hospital (Nagoya, Aichi).
Patients and methods
Patient characteristics and
procedures
A total of 776 patients with primary breast cancer
who underwent surgical resection between 2010 and 2011 at the Aichi
Cancer Center were included in the present study. A Consolidated
Standards of Reporting Trials diagram is shown in Fig. 1 to avoid patient bias in this
retrospective study. Patients who received neoadjuvant medical
treatment and patients who had not undergone an LN biopsy were
excluded. Therefore, the clinical and pathological data were
analyzed for 654 patients who underwent an axillary LN dissection
or sentinel LN (SLN) biopsy for primary breast cancer. In
clinically LN-negative cases, an SLN biopsy was performed. The SLN
was bisected along its major axis and a diagnosis was determined
from frozen sections obtained during surgery. If the SLN indicated
LN positivity, patients were treated with a standard level one and
two axillary dissection. Clinically LN-positive (i.e. cytologically
positive) patients underwent an axillary dissection. The SLN
section was routinely stained with hematoxylin and eosin for
examination. Patients provided written informed consentand the
study was approved by the ethics committee of Aichi Cancer
Center.
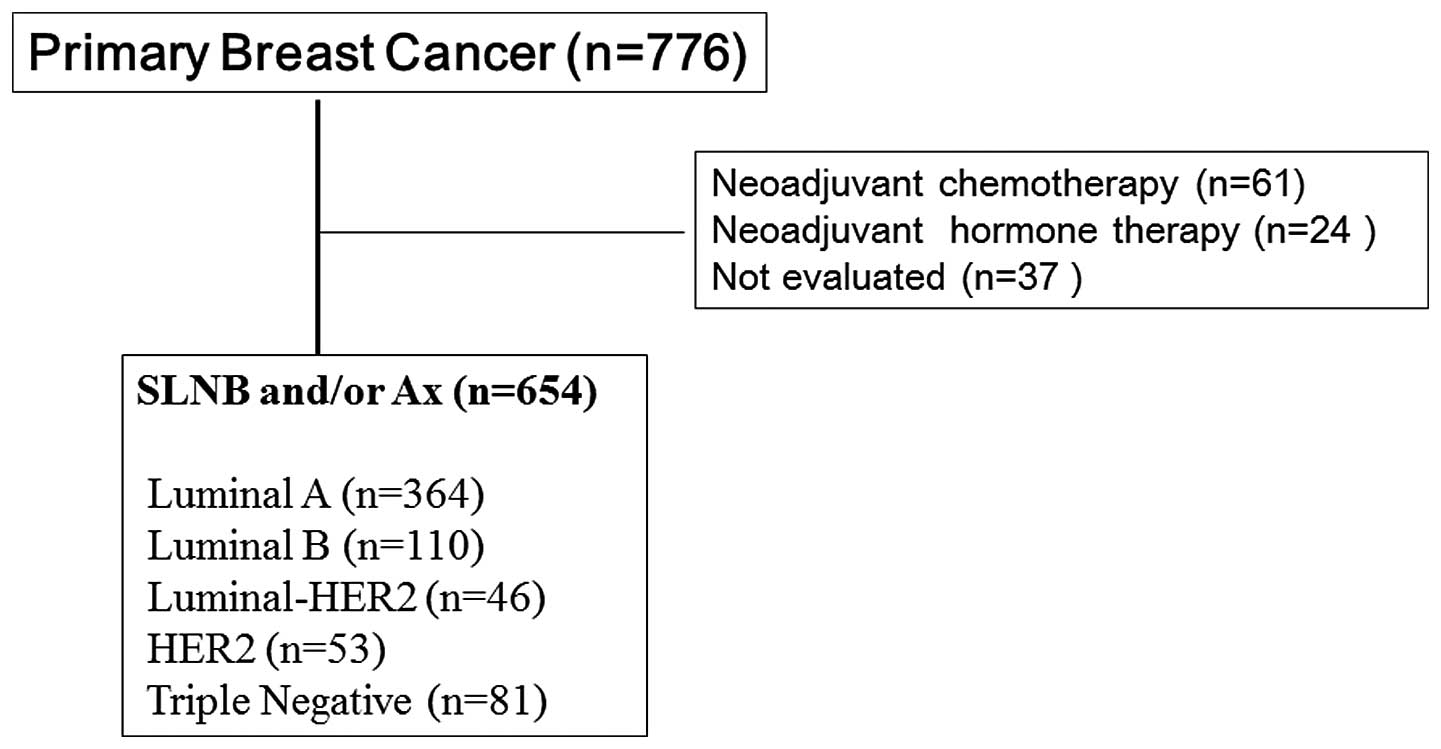 | Figure 1Consolidated Standards of Reporting
Trials diagram. Patients with primary breast cancer, who underwent
surgical resection between 2011 and 2012 at the Aichi Cancer Center
(Nagoya, Japan) were included in the present study. Patients who
had received neoadjuvant medical treatment and those who had not
undergone a lymph node biopsy were excluded. The subtypes were
classified as follows: Luminal A, ER- and/or PgR-positive,
HER2-negative and Ki-67 of ≤20%; luminal B, ER- and/or
PgR-positive, HER2-negative and Ki-67 of >20%; luminal-HER2, ER-
and/or PgR-positive and HER2-positive; HER2, ER- and PgR-negative,
and HER2-positive; and triple-negative, ER-, PgR- and
HER2-negative. SLNB, sentinel lymph node biopsy; Ax, axillary
dissection; ER, estrogen receptor; PgR, progesterone receptor;
HER2, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. |
Extent of the primary tumor
Lesions were identified preoperatively by palpation,
measured using ultrasound and the largest diameter was recorded as
the T category according to the tumor, necrosis, metastasis
classification (UICC, Sixth Edition, 2002) (5). The tumors were categorized as follows:
Tis, carcinoma in situ; T1mic, microinvasion of ≤0.1 cm;
T1a, tumor of >0.1 to ≤0.5 cm; T1b, tumor of >0.5 to ≤1 cm;
T1c, tumor of >1 to ≤2 cm; T2, tumor of >2 to ≤5 cm; T3,
tumor of >5 cm; and T4, any size with direct extension to the
chest wall or skin. When the primary tumor could not be assessed or
when there was no evidence of a primary tumor, the clinical T size
was determined as Tis.
Clinicopathological definition of
intrinsic subtype
The intrinsic subtypes of primary tumors were
classified by immunohistochemical (IHC) examination of
paraffin-embedded thin sections as follows: Luminal A subtype,
estrogen receptor (ER)- and/or progesterone receptor
(PgR)-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
(HER2)-negative and Ki-67 of ≤20%; luminal B subtype, ER- and/or
PgR-positive, HER2-negative and Ki-67 of >20%; luminal-HER2
subtype, ER- and/or PgR-positive and HER2-positive; HER2 subtype,
ER-negative, PgR-negative and HER2-positive; and triple-negative
subtype, ER-, PgR- and HER2-negative. In the proposed
classification, the Ki-67 labeling index was particularly
significant for distinguishing between the luminal A and B
(HER2-negative) subtypes (2).
IHC assessment
The expression of ER and PgR was scored using the
Allred score (6–8). In brief, the following proportion
score was assigned, which represented the estimated proportion of
positively stained tumor cells: 0, None; 1, <1/100; 2, 1/100 to
1/10; 3, 1/10 to 1/3; 4, 1/3 to 2/3; and 5, >2/3. Next, the
following intensity score was assigned, which represented the
average intensity of positive tumor cells as follows: 0, None; 1,
weak; 2, intermediate; and 3, strong. The sum of the proportion and
intensity scores provided the total score, which ranged between 0
and 8 (7). The scores were regarded
as positive if the total score was >3. HER2 was considered to be
positive if a score of 3+ (uniform, intense membrane staining of
>30% of invasive tumor cells) was obtained according to the
manufacturer’s instructions for the HercepTest® (Dako,
Carpinteria, CA, USA). Fluorescence in situ hybridization
was performed when a score of 2+ was obtained and gene
amplification was assessed. The ratio of HER2 to chromosome 17
centromere was ≥2.2, which was considered to be positive (9). The Ki-67 expression was quantified
using a visual grading system. The percentage of Ki-67-positive
cells among the total number of counted neoplastic cells was
determined at a magnification of ×400 using an eye-piece graticule
(BX51®; Olympus Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) at areas in
which Ki67 staining was particularly prevalent (10,11) An
estimated percentage of Ki-67-positive cells was determined, and
scored according to two categories that were organized by
increasing percentage intervals of 0–20% and >20%. For the
present study, >20% of Ki-67-positive cells was regarded as
positive (10). The slides were
scored independently by two pathologists.
Results
Patients and intrinsic subtype
A total of 654 patients were included in the present
study and the patient characteristics are demonstrated in Table I. Of the 654 patients, 157 patients
(24.0%) exhibited LN metastasis. The proportion of intrinsic
subtypes in the present study was as follows: Luminal A, n=364
(55.7%); luminal B, n=110 (16.8%); luminal-HER2, n=46 (7.0%); HER2,
n=53 (8.1%); and triple-negative, n=81 (12.4%).
 | Table IPatient characteristics. |
Table I
Patient characteristics.
| Variable | Subjects | Lymph node
positivity |
|---|
| Total, n (%) | 654 (100) | 157 (24.0) |
| Age, years |
| Median | 54.5 | - |
| Range | 20–85 | - |
| Clinical T stage, n
(%) |
| Tis | 83 (12.7) | 3 (3.6) |
| T1a | 12 (1.8) | 1 (8.3) |
| T1b | 110 (16.8) | 14 (12.7) |
| T1c | 251 (38.4) | 58 (23.1) |
| T2 | 172 (26.3) | 70 (40.7) |
| T3 | 21 (3.2) | 8 (38.1) |
| T4 | 5 (0.8) | 3 (60.0) |
| Pathological T stage,
n (%) |
| Tis | 107 (16.4) | 0 (0.0) |
| T1mic | 13 (2.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| T1a | 47 (7.2) | 4 (8.5) |
| T1b | 108 (16.5) | 14 (13) |
| T1c | 241 (36.9) | 69 (28.6) |
| T2 | 130 (19.9) | 65 (49.6) |
| T3 | 8 (1.2) | 5 (62.5) |
| T4 | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Intrinsic subtype, n
(%) |
| Luminal A | 364 (55.7) | 63 (17.3) |
| Luminal B | 110 (16.8) | 43 (39.1) |
| HER2-luminal | 46 (7.0) | 14 (30.4) |
| HER2 | 53 (8.1) | 15 (28.3) |
| Triple-negative | 81 (12.4) | 22 (27.2) |
| Histological
classification, n (%) |
| Non-invasive
carcinoma | 107 (16.4) | 0 (0.0) |
| Papillotubular
carcinoma | 169 (25.8) | 44 (26.0) |
| Solid-tubular
carcinoma | 57 (8.7) | 22 (38.6) |
| Scirrhous
carcinoma | 260 (39.8) | 81 (31.2) |
| Special types | 61 (9.3) | 10 (16.4) |
Lymph node positivity by T category in
all patients
LN positivity was evaluated according to T category
in all patients (n=654; Fig. 2). In
all patients, pT1a (n=47), pT1b (n=108), pT1c (n=241), pT2 (n=130)
and pT3 (n=8) exhibited 8.5, 13, 28.6, 50.0 and 62.5% LN
positivity, respectively. A larger tumor size was found to
correlate with a higher proportion of LN positivity with regard to
the pT category.
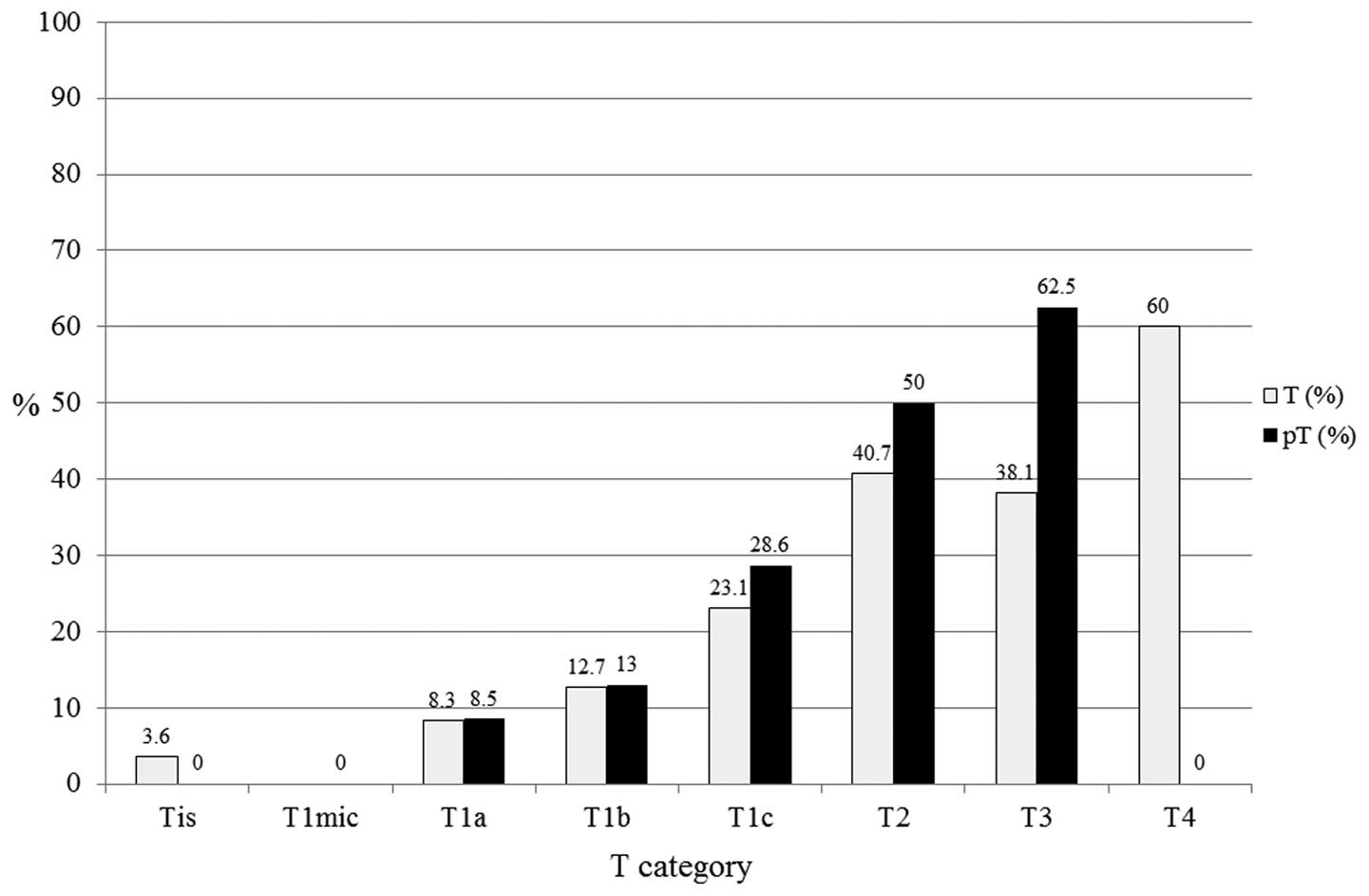 | Figure 2Lymph node (LN) positivity according
to the tumor size category of all patients (n=654). In all
patients, pT1a (n=47), pT1b (n=108), pT1c (n=241), pT2 (n=130) and
pT3 (n=8) exhibited 8.5, 13.0, 28.6, 50.0 and 62.5% LN positivity,
respectively. Larger tumor size correlated with a higher proportion
of LN positivity. T, tumor; pT, primary tumor; Tis, carcinoma in
situ; T1mic, microinvasion of ≤0.1 cm; T1a, tumor of >0.1 to
≤0.5 cm; T1b, tumor of >0.5 to ≤1 cm; T1c, tumor of >1 to ≤2
cm; T2, tumor of >2 to ≤5 cm; T3, tumor of >5 cm; T4, any
size with direct extension to the chest wall or skin. |
Lymph node positivity by T category in
each subtype
In the luminal A subtype (n=364; Fig. 3), pT1a (n=35), pT1b (n=71), pT1c
(n=125), pT2 (n=56) and pT3 (n=3) exhibited 5.7, 11.3, 21.6, 42.1
and 66.7% LN positivity, respectively. Larger tumor size was found
to correlate with a higher proportion of LN positivity. In the
luminal B subtypes (n=110), pT1a (n=2), pT1b (n=12), pT1c (n=55),
pT2 (n=34), and pT3 (n=2) exhibited 50.0, 8.3, 38.2, 55.9 and 50.0%
LN positivity, respectively (Fig.
4). In the luminal-HER2 subtypes (n=46), pT1c (n=17), pT2
(n=10) and pT3 (n=1) exhibited 41.1, 60.0 and 100.0% LN positivity,
respectively (Fig. 5). In the HER2
subtypes (n=53), pT1a (n=6), pT1b (n=4), pT1c (n=15), and pT2
(n=10) exhibited 16.7, 25, 46.7 and 60.0% LN positivity,
respectively (Fig. 6). In the
triple-negative subtypes (n=81), pT1b (n=15), pT1c (n=29), pT2
(n=20) and pT3 (n=2) exhibited 26.7, 24.1, 50.0 and 50.0% LN
positivity, respectively (Fig.
7).
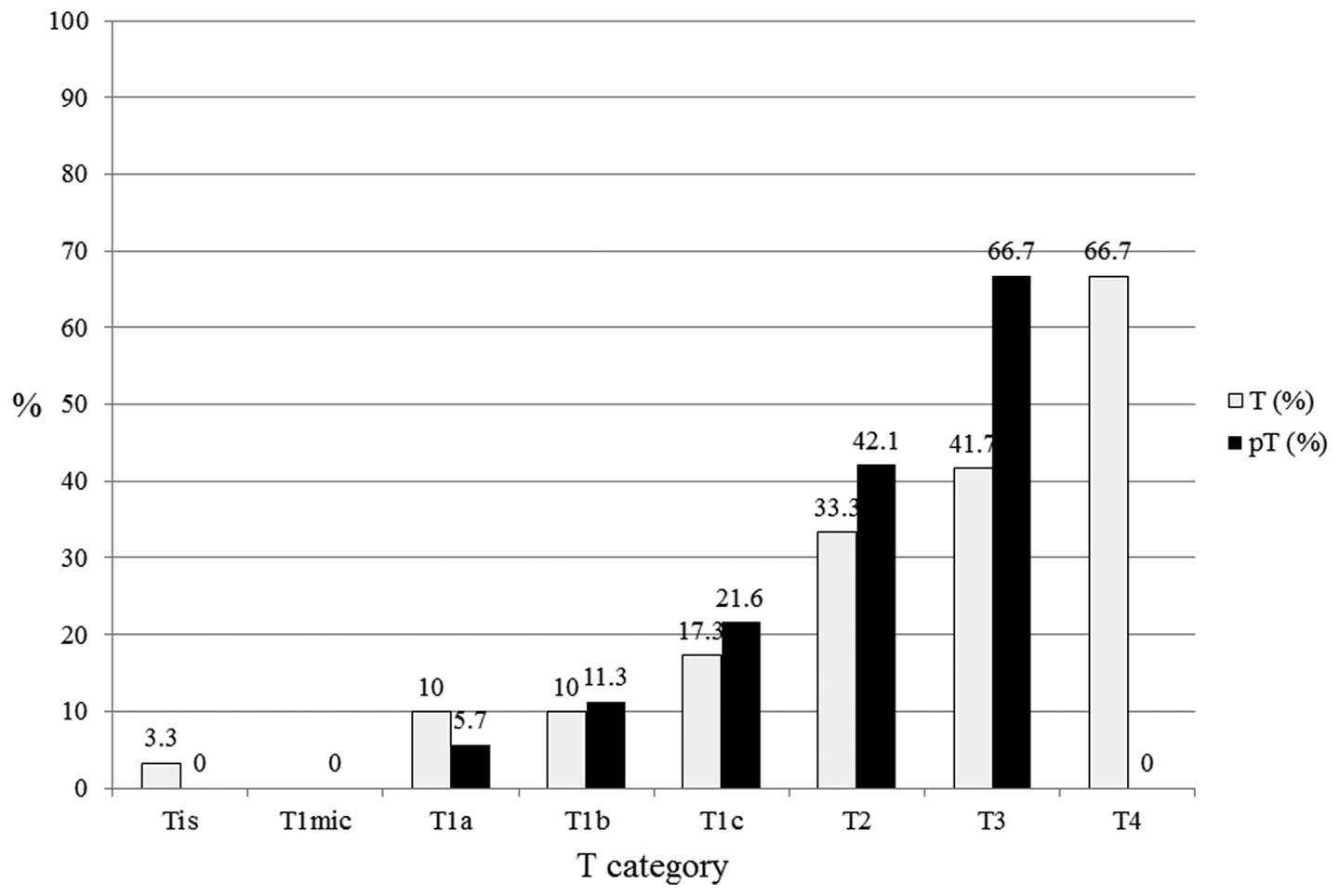 | Figure 3In luminal A subtypes (n=364), pT1a
(n=35), pT1b (n=71), pT1c (n=125), pT2 (n=56) and pT3 (n=3)
exhibited 5.7, 11.3, 21.6, 42.1 and 66.7% LN positivity,
respectively. Larger tumor size correlated with a higher proportion
of lymph node positivity. T, tumor; pT, primary tumor; Tis,
carcinoma in situ; T1mic, microinvasion of ≤0.1 cm; T1a,
tumor of >0.1 to ≤0.5 cm; T1b, tumor of >0.5 to ≤1 cm; T1c,
tumor of >1 to ≤2 cm; T2, tumor of >2 to ≤5 cm; T3, tumor of
>5 cm; T4, any size with direct extension to the chest wall or
skin. |
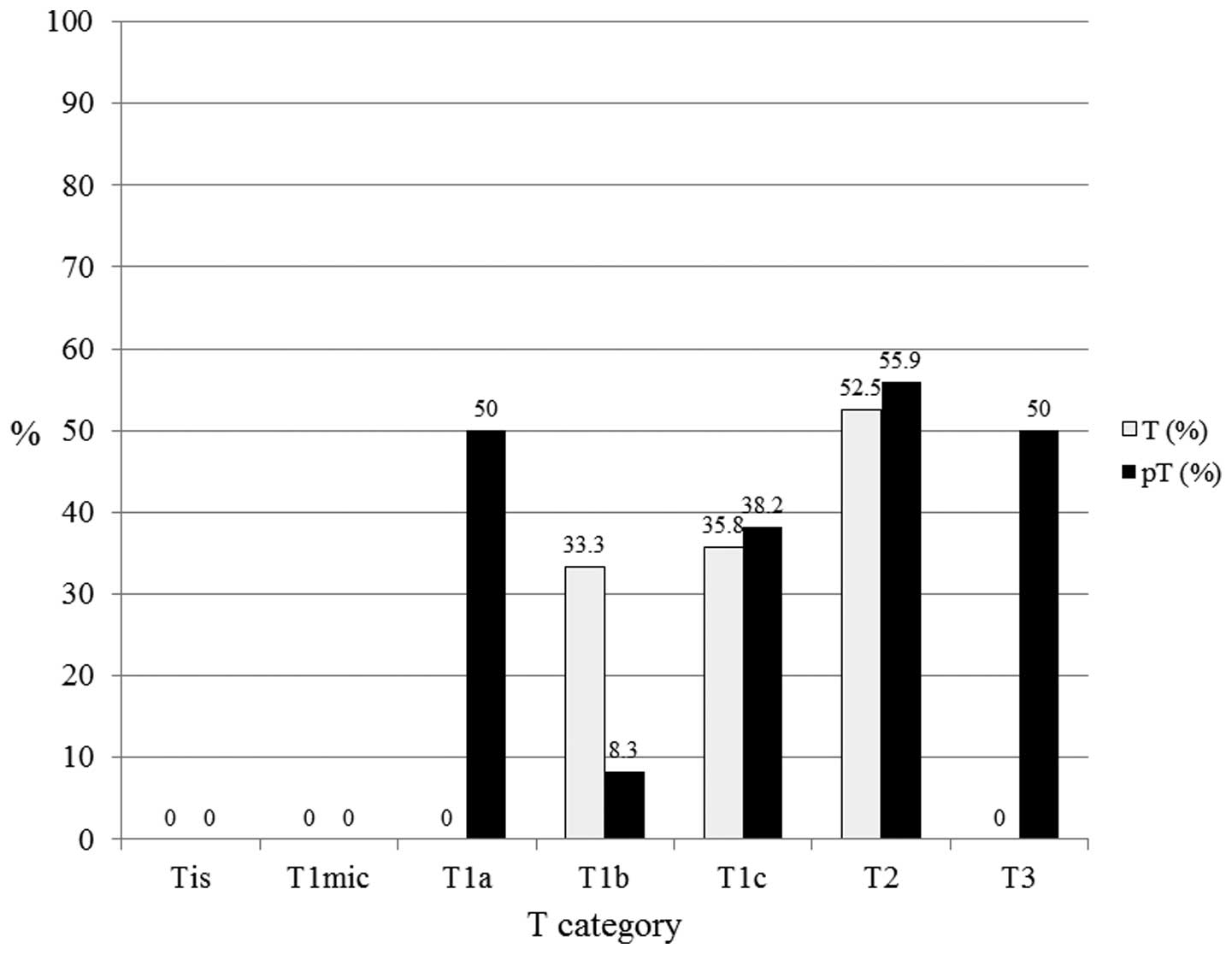 | Figure 4In luminal B subtypes (n=110), pT1a
(n=2), pT1b (n=12), pT1c (n=55), pT2 (n=34) and pT3 (n=2) exhibited
50, 8.3, 38.2, 55.9 and 50% lymph node positivity, respectively. T,
tumor; pT, primary tumor; Tis, carcinoma in situ; T1mic,
microinvasion of ≤0.1 cm; T1a, tumor of >0.1 to ≤0.5 cm; T1b,
tumor of >0.5 to ≤1 cm; T1c, tumor of >1 to ≤2 cm; T2, tumor
of >2 to ≤5 cm; T3, tumor of >5 cm. |
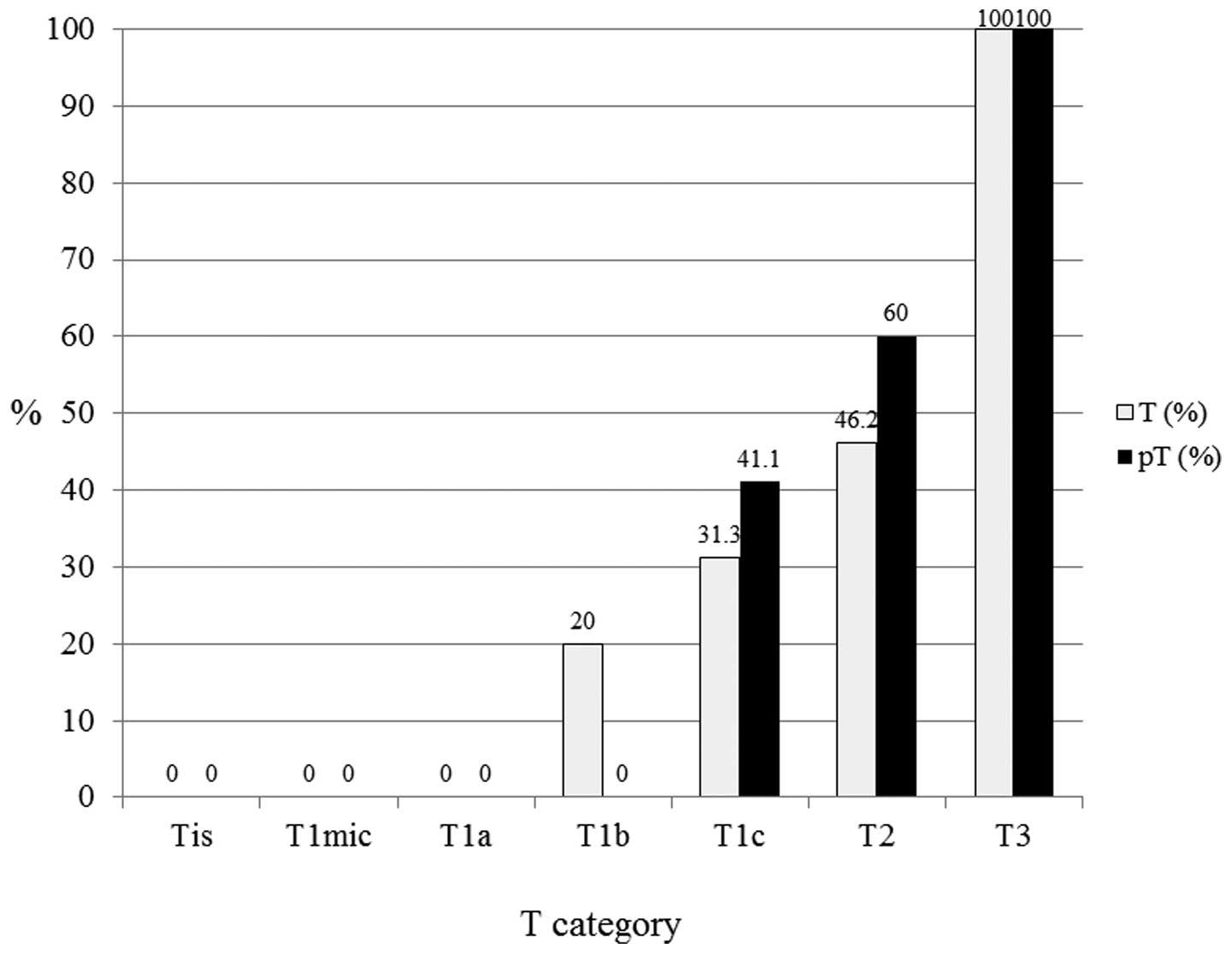 | Figure 5In human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2-luminal subtypes (n=46), pT1c (n=17), pT2 (n=10) and pT3
(n=1) exhibited 41.1, 60 and 100% lymph node positivity,
respectively. T, tumor; pT, primary tumor; Tis, carcinoma in
situ; T1mic, microinvasion of ≤0.1 cm; T1a, tumor of >0.1 to
≤0.5 cm; T1b, tumor of >0.5 to ≤1 cm; T1c, tumor of >1 to ≤2
cm; T2, tumor of >2 to ≤5 cm; T3, tumor of >5 cm. |
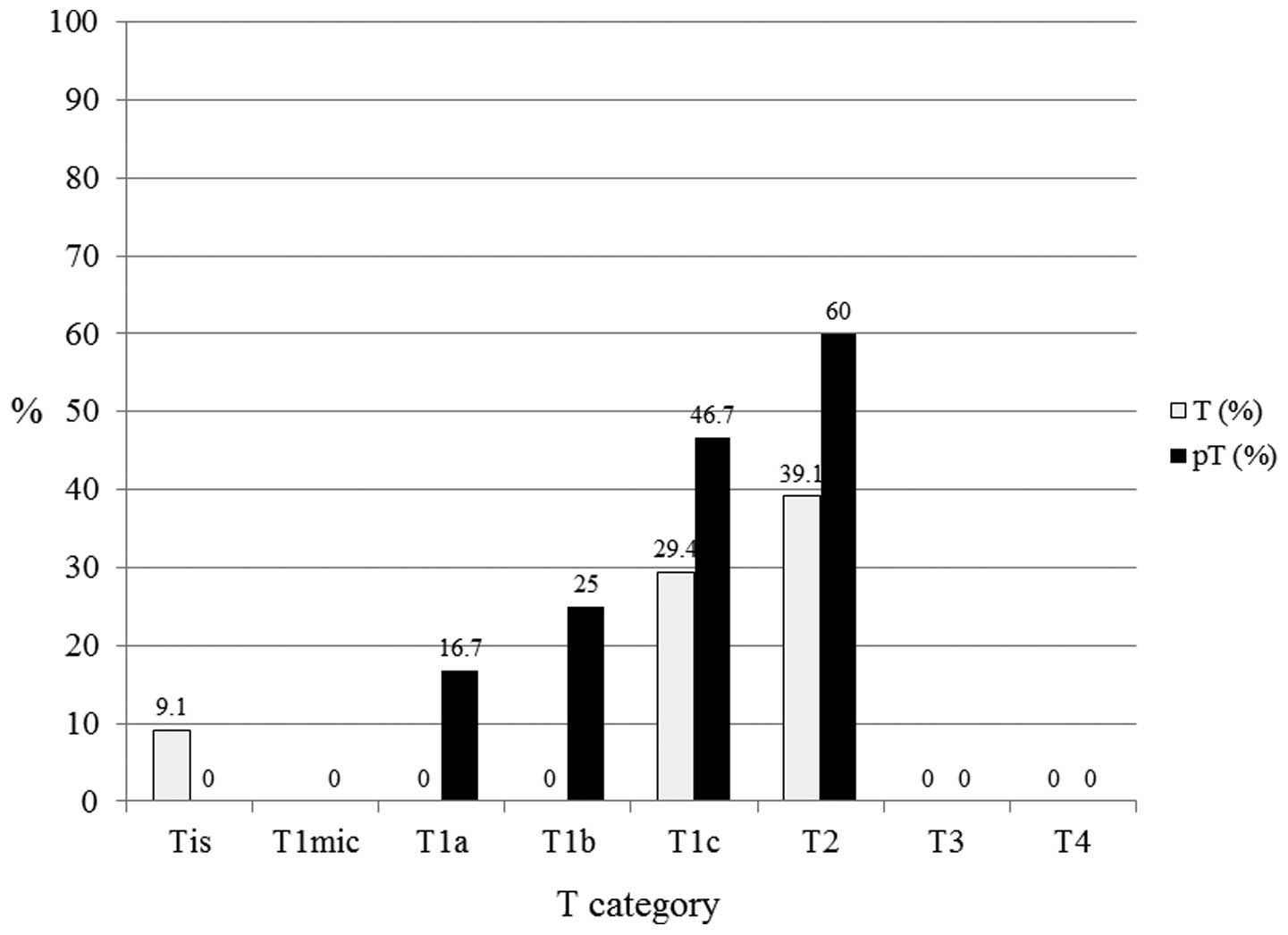 | Figure 6In human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2 subtypes (n=53), pT1a (n=6), pT1b (n=4), pT1c (n=15) and
pT2 (n=10) exhibited 16.7, 25, 46.7 and 60% lymph node positivity,
respectively. T, tumor; pT, primary tumor; Tis, carcinoma in
situ; T1mic, microinvasion of ≤0.1 cm; T1a, tumor of >0.1 to
≤0.5 cm; T1b, tumor of >0.5 to ≤1 cm; T1c, tumor of >1 to ≤2
cm; T2, tumor of >2 to ≤5 cm; T3, tumor of >5 cm; T4, any
size with direct extension to the chest wall or skin. |
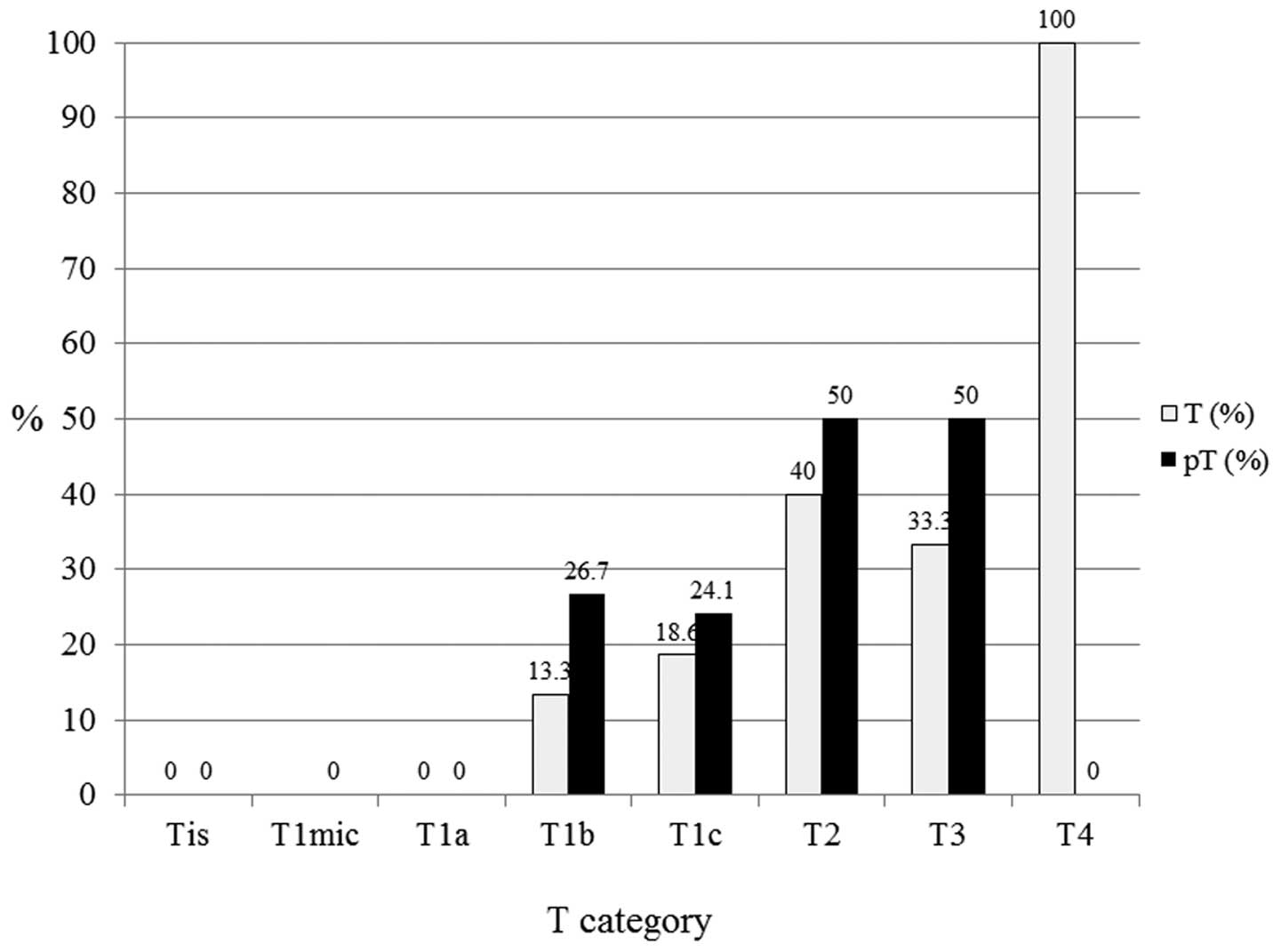 | Figure 7In triple-negative subtypes (n=81),
pT1b (n=15), pT1c (n=29), pT2 (n=20) and pT3 (n=2) exhibited 26.7,
24.1, 50 and 50% lymph node positivity, respectively. T, tumor; pT,
primary tumor; Tis, carcinoma in situ; T1mic, microinvasion
of ≤0.1 cm; T1a, tumor of >0.1 to ≤0.5 cm; T1b, tumor of >0.5
to ≤1 cm; T1c, tumor of >1 to ≤2 cm; T2, tumor of >2 to ≤5
cm; T3, tumor of >5 cm; T4, any size with direct extension to
the chest wall or skin. |
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first
report to investigate the likelihood of LN metastasis according to
intrinsic subtype and tumor size. The intrinsic subtypes of breast
cancer have, however, previously been analyzed by gene expression
arrays (12–14). These subtypes exhibit different
epidemiological risk factors (15),
natural histories (16), and
responses to systemic and local therapies (17). These differences imply that
clinicians managing breast cancer are required to consider cases
according to the various, distinct subtypes in order to properly
assess the relevant evidence and determine an appropriate
therapeutic strategy (2). As it is
not always feasible to obtain gene expression array data, a
simplified clinical classification has been adopted for performance
in the clinical setting (2,18). The subtypes defined by
clinicopathological criteria are similar, although not identical,
to the intrinsic subtypes and represent a convenient approximation
(2).
Axillary LN metastasis is one of the most important
prognostic factors. However, prior to performing an SLN biopsy or
axillary dissection, it is not possible to determine whether the
patient is LN-negative. There are few studies that have been
reported to predict the frequency of LN metastasis according to
intrinsic subtype (19,20), however, the correlation between LN
metastasis and T category has been investigated in certain case
series (4). Multivariate predictive
models have been produced that incorporate tumor size, patient age,
S phase and PgR as independent predictors (21), however, these were not classified by
intrinsic subtype. The risk of LN metastasis is considered to be
significantly higher for palpable breast tumors (4), thus, clinical tumor size is important
for predicting LN metastasis. The likelihood of LN metastasis may
be predicted following a preoperative core needle biopsy using IHC
examination.
A limitation of the current study was that the
intrinsic subtype should have originally been identified by gene
expression array; however, a simplified clinicopathological
classification system was used in the clinical setting (2). Local quality control of Ki-67 staining
was considered to be a significant factor in the present study.
However, during IHC examination, the cut-off for the percentage of
Ki-67-positivity, for distinguishing between luminal A and B, was
controversial as it has been identified to be between 14 (18) and 20% (10). In the current study, few patients
with specific intrinsic subtypes were available for analysis. Few
patients exhibited stage T4 tumors, as almost all patients who had
undergone neoadjuvant medical treatment were excluded. Neoadjuvant
medical treatment is recommended to patients prior with stage T4
tumors (22).
In conclusion, the intrinsic subtype and tumor size
are important for predicting the frequency of LN metastasis in
breast cancer patients. By knowing the intrinsic subtype and tumor
size LN metastasis may be predicted prior to surgery.
Acknowledgements
The abstract was presented in part at the 13th
International Conference of Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer,
March 13–16, 2013 in St. Gallen, Switzerland.
References
|
1
|
Cancer Research UK. http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/cancer-info/cancerstats/types/breast/.
Accessed June 26, 2014
|
|
2
|
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ; Panel members. Strategies for
subtypes - dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: highlights
of the St. Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary
Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 22:1736–1747.
2011.
|
|
3
|
Cody HS III and Houssami N: Axillary
management in breast cancer: what’s new for 2012? Breast.
21:411–415. 2012.
|
|
4
|
Silverstein MJ, Gierson ED, Waisman JR,
Colburn WJ and Gamagami P: Predicting axillary node positivity in
patients with invasive carcinoma of the breast by using a
combination of T category and palpability. J Am Coll Surg.
180:700–704. 1995.
|
|
5
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind CH: Breast tumors.
TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. 6th edition. UICC,
Wiley-Liss; New York, NY: pp. 131–142. 2002
|
|
6
|
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M and Clark
GM: Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by
immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 11:155–168. 1998.
|
|
7
|
Harvey JM, Clark GM, Osborne CK and Allred
DC: Estrogen receptor status by immunohistochemistry is superior to
the ligand-binding assay for predicting response to adjuvant
endocrine therapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 17:1474–1481.
1999.
|
|
8
|
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, et al:
American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American
Pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical
testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 28:2784–2795. 2010.
|
|
9
|
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, et al;
American Society of Clinical Oncology; College of American
Pathologists. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of
American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
25:118–145. 2007.
|
|
10
|
Penault-Llorca F, André F, Sagan C, et al:
Ki67 expression and docetaxel efficacy in patients with estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 27:2809–2815.
2009.
|
|
11
|
Dowsett M, Nielsen TO, A’Hern R, et al;
International Ki-67 in Breast Cancer Working Group. Assessment of
Ki67 in breast cancer: recommendations from the International Ki67
in Breast Cancer working group. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:1656–1664.
2011.
|
|
12
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, et al:
Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 406:747–752.
2000.
|
|
13
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, et al:
Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor
subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:10869–10874. 2001.
|
|
14
|
Arpino G, Generali D, Sapino A, et al:
Gene expression profiling in breast cancer: a clinical perspective.
Breast. 22:109–120. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Millikan RC, Newman B, Tse CK, et al:
Epidemiology of basal-like breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
109:123–139. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Phipps AI, Buist DS, Malone KE, et al:
Reproductive history and risk of three breast cancer subtypes
defined by three biomarkers. Cancer Causes Control. 22:399–405.
2011.
|
|
17
|
Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, et al:
Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor,
progesterone receptor, and HER-2 is associated with local and
distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol.
26:2373–2378. 2008.
|
|
18
|
Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, et al: Ki67
index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 101:736–750. 2009.
|
|
19
|
Morrison DH, Rahardja D, King E, Peng Y
and Sarode VR: Tumour biomarker expression relative to age and
molecular subtypes of invasive breast cancer. Br J Cancer.
107:382–387. 2012.
|
|
20
|
Yoshihara E, Smeets A, Laenen A, et al:
Predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in early breast cancer
and their applicability in clinical practice. Breast. 22:357–361.
2012.
|
|
21
|
Ravdin PM, De Laurentiis M, Vendely T and
Clark GM: Prediction of axillary lymph node status in breast cancer
patients by use of prognostic indicators. J Natl Cancer Inst.
86:1771–1775. 1994.
|
|
22
|
NCCN guideline 2013. ver2. 2013,
http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf.
Accessed April 17, 2013
|





















