Introduction
Viral infections are important causes of morbidity
and mortality following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell
transplantation (HSCT). Patients who have undergone transplantation
are susceptible to primary viral infections and to the reactivation
of latent viruses, including the polyomavirus BK virus (BKV)
(1).
Hemorrhagic cystitis (HC) is characterized by
hemorrhagic inflammation of the bladder mucosa, leading to painful
micturition with hematuria. HC is commonly associated with
immunosuppression caused by chemotherapy, radiotherapy or HSCT.
Clinically, HC ranges from mild and brief (Grade I) to severe,
prolonged and life threatening (Grade IV). Although BKV has been
found to be an important etiological agent for late-onset HC, until
now, therapy has been predominantly symptomatic with disappointing
results achieved using conventional antiviral drugs (2).
The present study reports the clinical and molecular
activity of levofloxacin in patients with severe BK-associated
hemorrhagic cystitis (BKHC) that is refractory to ciprofloxacin and
other supportive measures. Patients provided written informed
consent.
Case report
Patient presentation
The present study describes the cases of three
patients who presented with severe BKHC within 100 days of
undergoing HSCT. The patients received a full myeloablative
conditioning regimen and routine ciprofloxacin prophylaxis (500 mg,
orally) twice daily from the day of stem cell infusion until
neutrophil engraftment (Table I).
In September 2006, patient 1, a 40-year-old male, was diagnosed
with standard cytogenetic risk acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) at
the Marmara University Hospital (Istanbul, Turkey). In 2008,
following 3+7 (12 mg/m2/day idarubicin on days one to
three, and 100 mg/m2/day cytarabine on days one to seve,
for one cycle) induction and high dose cytarabine (3
g/m2 every 12 h on days one, three and five)
consolidation chemotherapy (three cycles), the patient underwent
autologous HSCT as the patient did not have a matched donor. By
post-transplant day 77, the patient experienced gross hematuria. In
February 2008, patient 2, a 37-year-old male was treated with 3+7
and high dose cytarabine chemotherapy due to standard risk AML at
the Marmara University Hospital. In October 2008, the patient
underwent a sibling donor HSCT. Gross hematuria was observed on
post-transplant day 49. Patient 3, a 45-year-old female, was
referred to Marmara University Hospital following a sibling donor
HSCT following a diagnosis of standard risk AML at the
Transplantation Unit, Erciyes University Hospital (Kayseri, Turkey)
in 2008. The patient reported gross hematuria on post-transplant
day 48. All patients presented with gross hematuria, as well as
dysuria and painful micturition.
 | Table ICharacteristics of patients with with
BKHC. |
Table I
Characteristics of patients with with
BKHC.
| Patient | Diagnosis:
FAB/Cytogenetic risk group | Gender | Age (years) | HSCT | Post-HSCT day | IS/GVHD | Therapies given for
HC | IS dose
reduction |
|---|
| 1 |
AML-M2/intermediate | M | 40 | Autologous | +77 | NA/none | Ciprofloxacin, IV
risperidone | NA |
| 2 |
AML-M7/intermediate | M | 37 | Matched sibling,
MA | +49 | cSA/none | Ciprofloxacin, IV
risperidone | None |
| 3 |
AML-M4/intermediate | F | 45 | Matched sibling,
MA | +48 | cSA/none | Ciprofloxacin, IV
risperidone, HOT, EIAE | None |
Diagnosis
Routine microscopic analyses and bacterial cultures
revealed no specific pathogenic organisms. Furthermore, analyses
for adenovirus, cytomegalovirus, mycoplasma and ureaplasma were all
negative. However, BKV was detected to varying degrees using
reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis
in the urine of the patients. Adenovirus, cytomegalovirus,
mycoplasma, BKV and ureaplasma-associated HC were included in the
differential diagnosis.
Treatment
All of the patients exhibited severe HC which
required continuous intravesical irrigation due to gross hematuria
and urinary obstruction caused by blood clots. All patients
received ciprofloxacin for two weeks, as well as intravesical
instillation of risperidone in order to control the bleeding.
Hyperbaric oxygen and subsequent external iliac artery embolization
were performed in one patient; however, no improvement was
observed. All patients were treated with levofloxacin (500 mg a
day, orally), which was administered for eight weeks, and urine BKV
copies were monitored every four weeks.
Follow-up
In patient 1, HC resolved completely after one month
of levofloxacin treatment. The other two patients also received the
same treatment and complete clinical responses were achieved. The
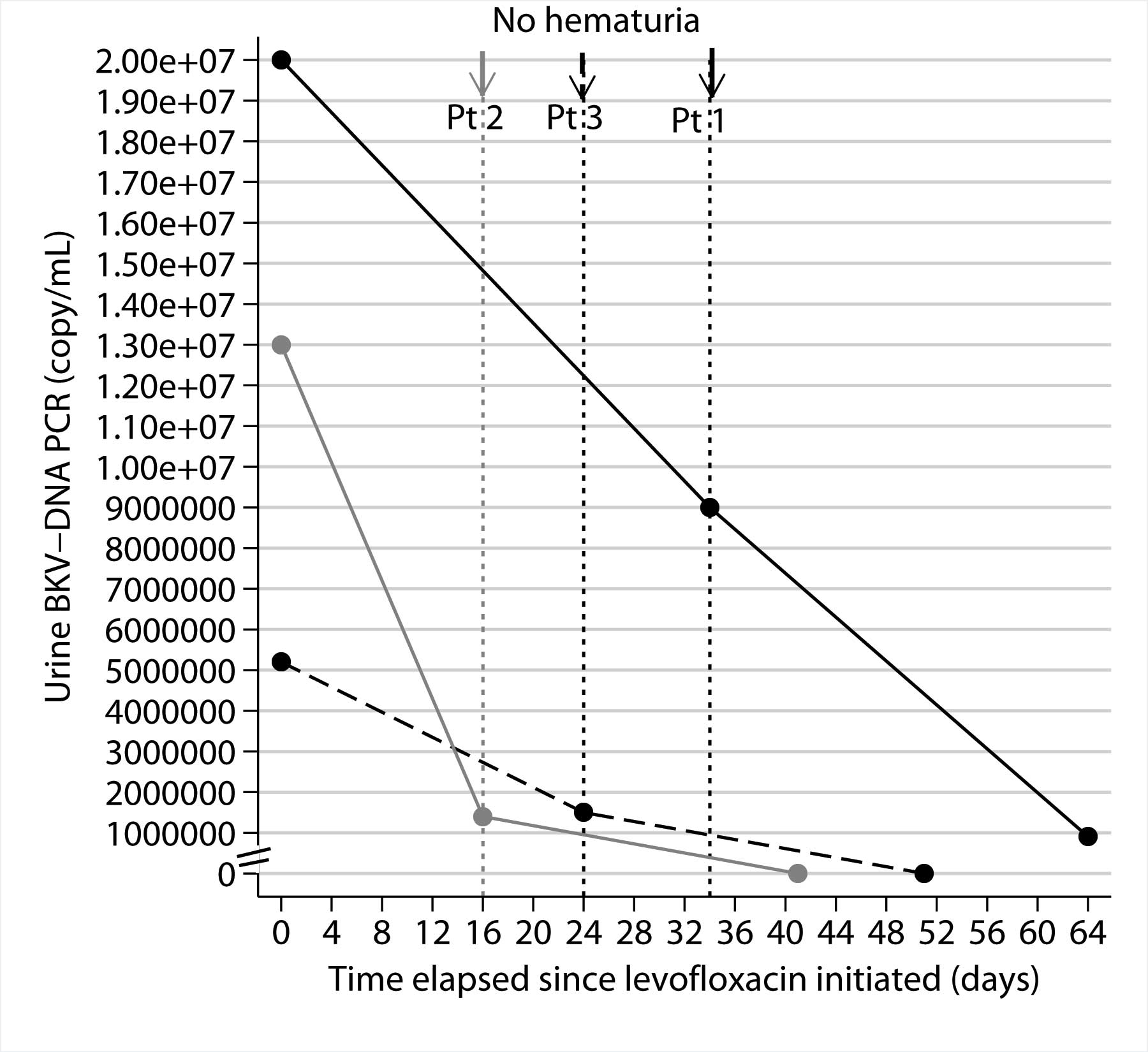
BKV copies in the urine were found to decrease by >90% at the
end of the eight weeks of levofloxacin treatment (Fig. 1).
Discussion
BKV is a member of the Polyomaviridae family of
viruses. BKV was first isolated in 1971 in the urine of a patient
who was asymptomatic and immunocompromised (3). Primary infection with BKV usually
occurs during childhood and is generally asymptomatic. Thereafter,
the virus remains latent in the host. BKV affects the epithelia of
the renal pelvis, ureter and urinary bladder. Common routes of
transmission have been proposed to be through respiratory or fecal
spread (2).
BKHC is defined by the co-occurrence of HC with
BK-viruria, which is detected using urinary RT-PCR analysis
targeting the BKV VP1 gene (4). The
presence of blood clots as a result of macroscopic hematuria, with
or without urinary retention, is defined as severe HC. Severe BKHC
is reported in ~15% of patients with BKHC and causes significant
morbidity among these patients (5).
Cidofovir has the highest specificity against BKV.
The majority of the evidence comes from non-randomized or
retrospective studies in renal transplantation settings. However,
its lack of availability in the majority of countries, high costs
and potential nephrotoxic effects limit the use of cidofovir.
Estrogens, leflunomide, hyperbaric oxygen, clotting factors (for
example factor VII and XIII), intravesical instillation of saline,
prostaglandin, risperidone, aluminum, formalin, growth factors,
immunosuppressive dose reduction, selective arterial embolization
and cystectomy have been used to treat patients with BKV, with
variable success rates. However, the majority of these procedures
have high costs, significant morbidity and limited activity
(2,6).
The in vitro and in vivo activity of
ciprofloxacin on BKV in prophylactic use has been shown by a
previous study with certain limitations (7). However, data with regard to the
efficacy of levofloxacin in patients with BKHC are limited in
prophylactic and therapeutic settings. Levofloxacin and other third
generation quinolones have high in vivo activity against
intracellular atypical pathogens compared with ciprofloxacin; thus,
levofloxacin may also have a unique in vivo antiviral
activity.
The current study presents three post-HSCT patients
fulfilling severe HC criteria, which was refractory to several
interventions mentioned in the literature previously (2,6).
Cidofovir is an active and safe treatment in post-HSCT
BKV-associated HC (8). However,
Cidofovir was not administered as it is not registered in Turkey.
The activity of levofloxacin in the setting of severe active
refractory HC can be explained by the probable antiviral effect of
levofloxacin. Two recent studies exploring the activity of
levofloxacin on BK-viremia in renal transplant recipients exhibited
conflicting results (9,10). A retrospective study, including 40
patients who received levofloxacin or ciprofloxacin, reported that
a one month course of fluoroquinolones, used with the intention to
treat other bacterial infections within three months following
renal transplant, was associated with a significant risk reduction
of one-year BK-viremia (9).
However, a more recent prospective, placebo-controlled,
double-blinded, randomized trial including 39 patients with
post-renal transplant BK viremia failed to verify such an effect
(10). To the best of our
knowledge, this is the first report to demonstrate the activity of
levofloxacin in the setting of refractory BK-associated HC in
post-HSCT patients. Since the plasma BK viral load was not measure,
a conclusion can not be determined with regard to its effect on
viremia. However, we hypothesize that levofloxacin exerts its main
activity on the urothelial epithelium by inhibiting BK-viral
replication, which results in symptomatic improvement and reduction
of BK-viruria. However, this hypothesis remains to be elucidated in
prospective studies.
Considering the high morbidity of severe BKHC and
the potential drawbacks of currently available treatment options,
levofloxacin (500 mg a day, orally) may present as an effective
treatment modality for achieving complete clinical and molecular
response in patients with refractory, severe BKHC. The use of
levofloxacin may prevent costly and invasive procedures.
References
|
1
|
Gratwohl A, Brand R, Frassoni F, et al:
Cause of death after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell
transplantation (HSCT) in early leukaemias: an EBMT analysis of
lethal infectious complications and changes over calendar time.
Bone Marrow Transplant. 36:757–769. 2005.
|
|
2
|
Harkensee C, Vasdev N, Gennery AR,
Willetts IE and Taylor C: Prevention and management of BK-virus
associated haemorrhagic cystitis in children following
haematopoietic stem cell transplantation - a systematic review and
evidence-based guidance for clinical management. Br J Haematol.
142:717–731. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Gardner SD, Field AM, Coleman DV, et al:
New human papovavirus (B.K.) isolated from urine after renal
transplantation. Lancet. 1:1253–1257. 1971.
|
|
4
|
Leung AY, Suen CK, Lie AK, Liang RH, Yuen
KY and Kwong YL: Quantification of polyoma BK viruria in
hemorrhagic cystitis complicating bone marrow transplantation.
Blood. 98:1971–1978. 2001.
|
|
5
|
Leung AY, Mak R, Lie AK, et al:
Clinicopathological features and risk factors of clinically overt
haemorrhagic cystitis complicating bone marrow transplantation.
Bone Marrow Transplant. 29:509–513. 2002.
|
|
6
|
Focosi D and Kast RE: Hyaluronate and
risperidone for hemorrhagic cystitis. Bone Marrow Transplant.
39:572007.
|
|
7
|
Leung AY, Chan MT, Yuen KY, et al:
Ciprofloxacin decreased polyoma BK virus load in patients who
underwent allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin
Infect Dis. 40:528–537. 2005.
|
|
8
|
Kwon HJ, Kang JH, Lee JW, Chung NG, Kim HK
and Cho B: Treatment of BK virus-associated hemorrhagic cystitis in
pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients with
cidofovir: a single-center experience. Transpl Infect Dis.
15:569–574. 2013.
|
|
9
|
Gabardi S, Waikar SS, Martin S, et al:
Evaluation of fluoroquinolones for the prevention of BK viremia
after renal transplantation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 5:1298–1304.
2010.
|
|
10
|
Lee BT, Gabardi S, Grafals M, et al:
Efficacy of levofloxacin in the treatment of BK viremia: a
multicenter, double-blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 9:583–589. 2014.
|