Introduction
A clear cell carcinoma of the colorectum is a rare
oncologic entity and, thus, the clinical and imaging features of
such have not been adequately investigated. Thus far, only 13 cases
have been documented in the English literature, according to the
results of searches using PubMed. The majority of reported primary
colonic clear cell adenocarcinomas are located in the left colon
and are more common in elderly men (1–2).
Clinical and imaging features have not been adequately investigated
due to its rarity. Considerable diagnostic difficulties may arise
when distinguishing primary colonic clear cell adenocarcinoma and
metastatic carcinomas from sites such as the kidney and testis
(3). In the majority of cases
colonic clear cell adenocarcinomas are treated by a polypectomy or
segmental resection. Clinical data regarding tumor-associated
mortality and disease-free survival in patients with primary clear
cell adenocarcinoma of the colorectum is limited. In this study, a
new case of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colon in a 26-year-old
male is presented. The aim of this study was to investigate the
clinical and computed tomography (CT) features of the neoplasm.
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient’s
family.
Case report
Clinical data
A 26-year-old male was admitted to Yantai
Yuhuangding Hospital (Yantai, China) with a palpable abdominal
mass, which had gradually increased in size for three months. The
patient had no history of abdominal pain, melena, body weight loss
or change in bowel habits. Standard blood tests and chest X-rays
revealed no abnormalities. Ultrasound of the abdomen showed no
abnormal findings from the liver and gall bladder, pancreas, testes
and genital tract or kidneys. General examination was negative,
with the exception of an extensive, immobile mass (13 cm in
diameter) in the left upper quadrant of the abdomen.
Imaging results
CT examination of the abdomen was performed prior to
and following the administration of an intravenous contrast agent.
Sagittal and coronal reformatted images were obtained. Abdominal CT
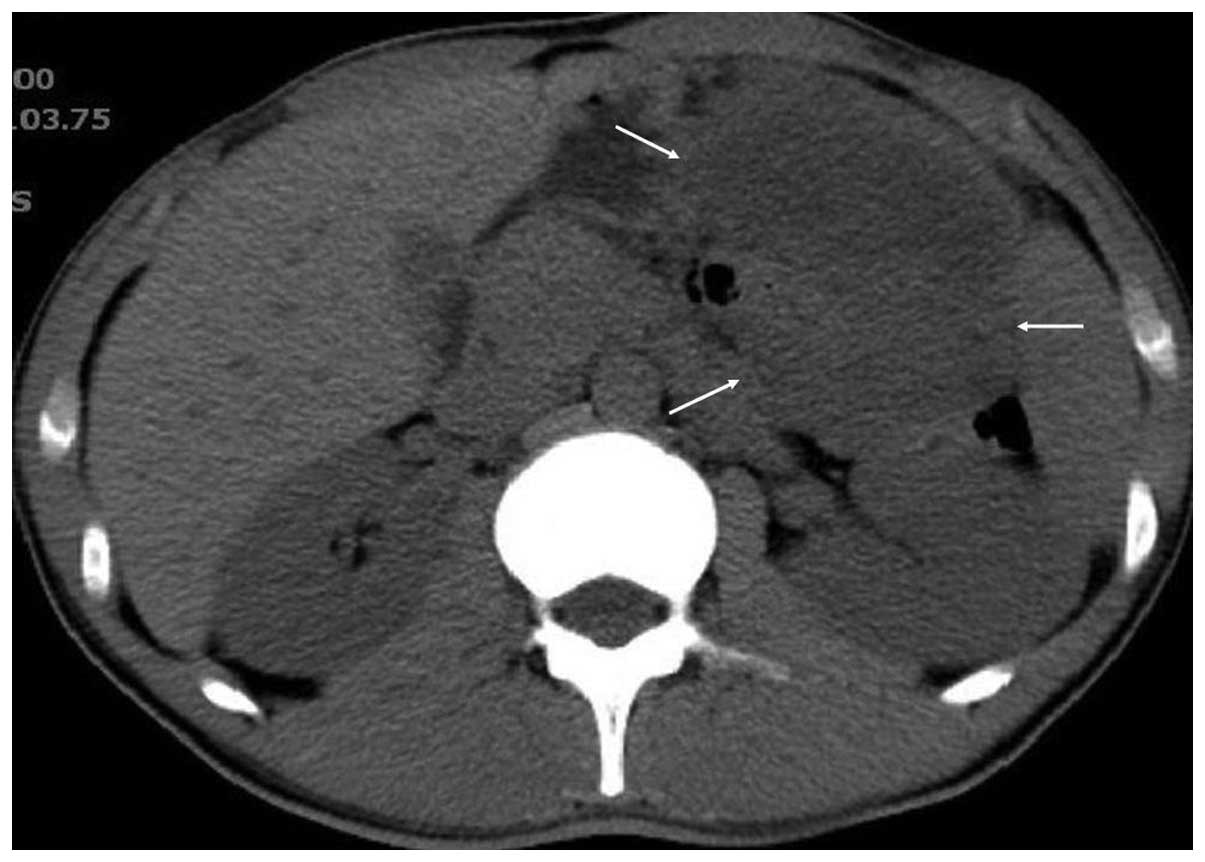
revealed an ill-defined mass (12×10 cm in size) located in the left
upper quadrant. On unenhanced images the mass was hypo-attenuated
in relation to the liver (Fig. 1).
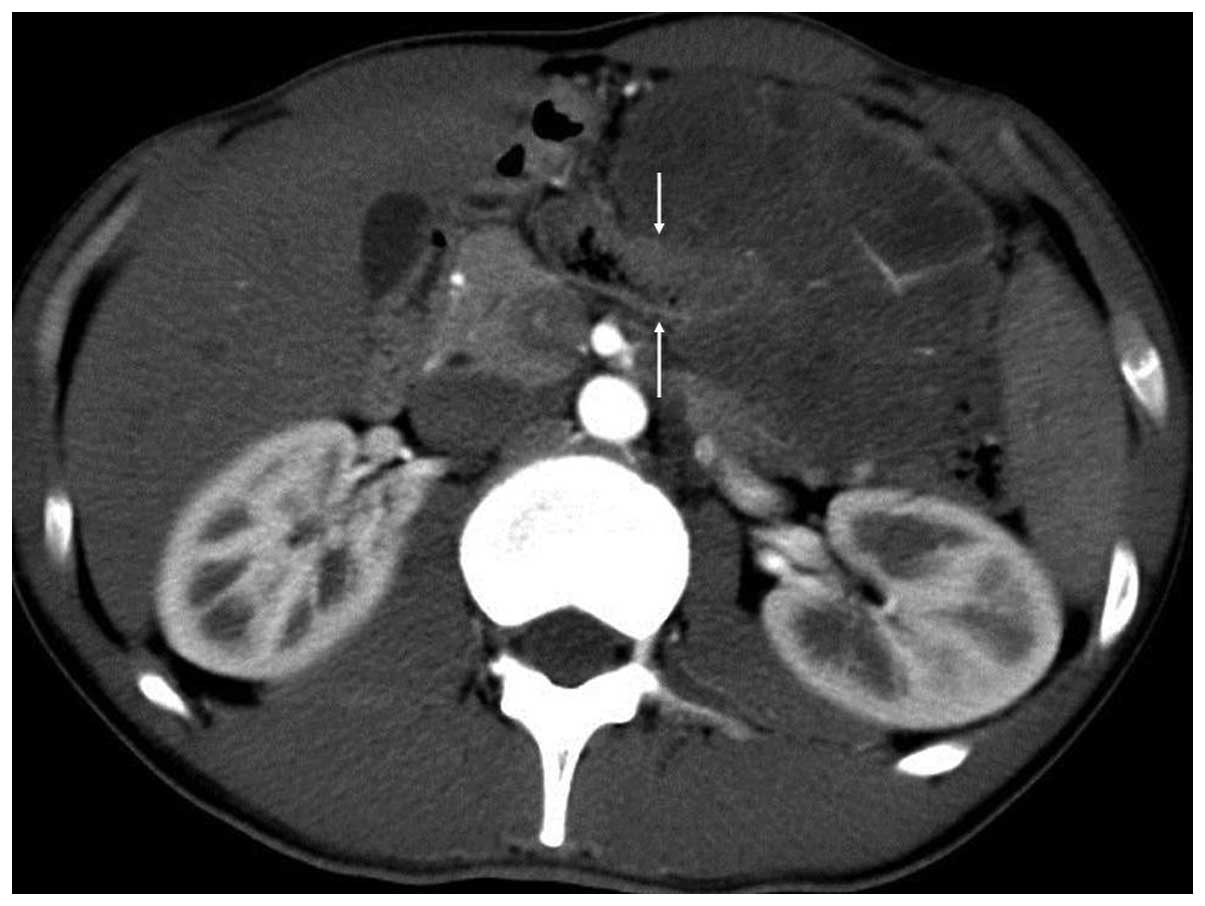
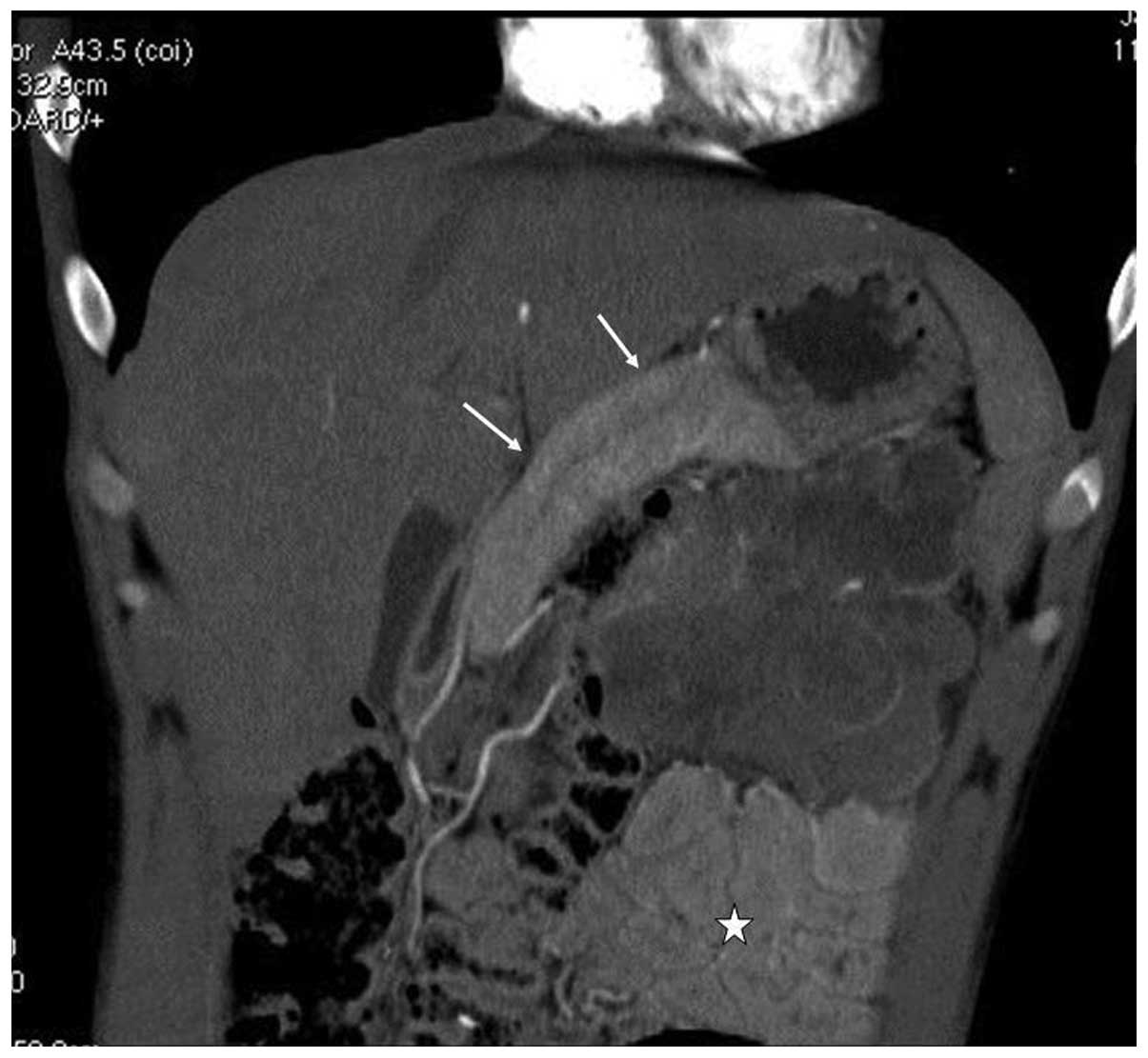
The mass exhibited heterogeneous moderate enhancement following
contrast material administration. The mass encased the left part of
the transverse colon, displaced the loop of small bowel inferiorly
and the pancreas superiorly, and invaded the spleen (Figs. 2–4).
No signs of bowel obstruction were identified. The CT observations
indicated a malignant tumor, possibly of colonic origin. The
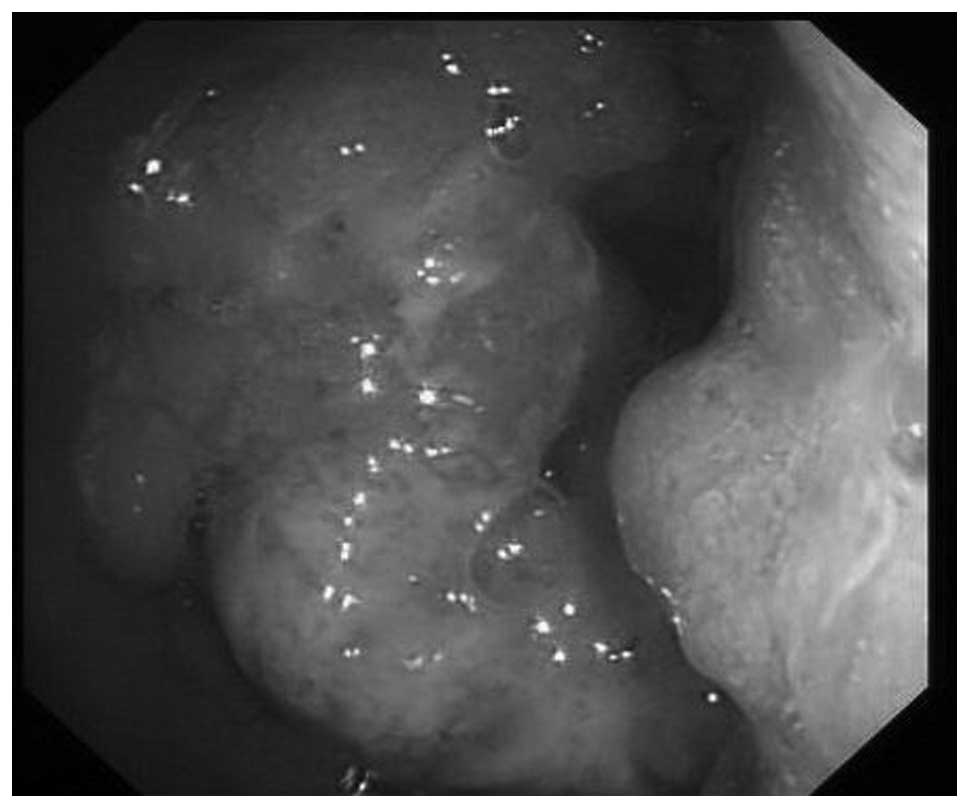
patient underwent subsequent colonoscopy, which revealed a stenotic
tumor mass in the transverse colon close to the spleen flexure
(Fig. 5).
Intraoperative observations
During surgery, an extensive mass, measuring 12 cm
maximally, was found arising from the transverse colon close to the
left colonic flexure, with invasion of the spleen. The tumor was
exophytic, with a lobulated and irregular surface. The cross
section revealed transmural invasion. The tumor and the spleen were
resected concurrently.
Pathological and immunohistochemical
observations
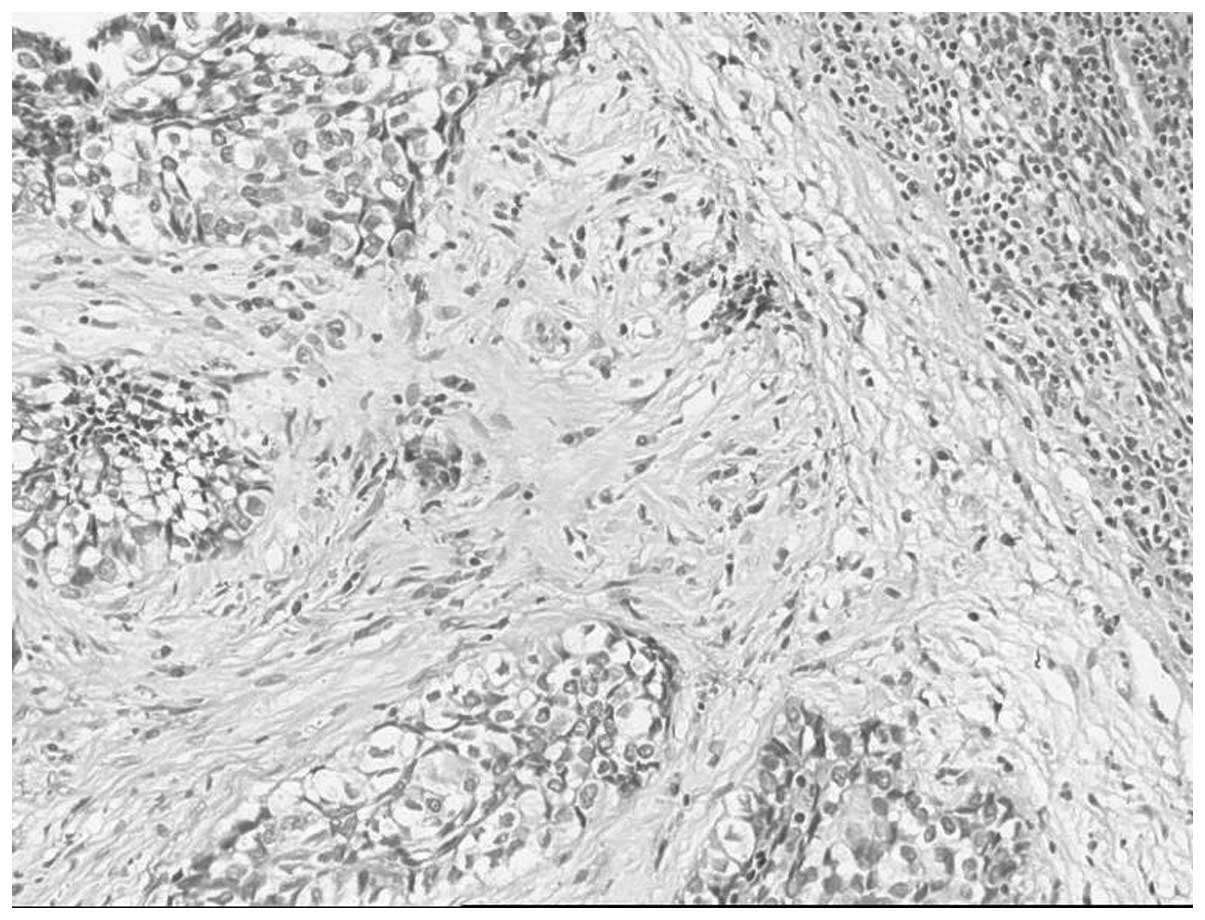
Histological examination of the resected specimen
revealed a tumor entirely composed of polygonal and oval cells
arranged in lobules, which were separated by fibrous septa
containing chronic inflammatory cells. The cells had abundant
cytoplasm, which varied from clear to eosinophilic. The nuclei
included one or more prominent vesicular and pleomorphic nucleoli
(Fig. 6). Immunohistochemical
staining revealed that the cells were positive for cytokeratin and
epithelial membrane antigen, and negative for vimentin and HMB45.
Based on the morphological and immunohistochemical observations,
clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colon was diagnosed.
Outcomes
The patient improved and was discharged 10 days
following surgery. However, one and a half years following surgery,
the tumor recurred in the peritoneal cavity, at the site of the
left colonic flexure. The patient succumbed to the disease three
years following surgery.
Discussion
Clear cell adenocarcinomas are well characterized in
the kidneys (4), lower urinary
tract (5), ovaries (6), extraovarian endometriosis (7) and female genital tract (8). These organs originate from the
mullerian system, which may explain the occurrence of clear cell
adenocarcinoma in these systems (9). However, clear cell adenocarcinoma of
the colorectum is rare. Thus far, only 13 such cases have been
reported in the English literature. Therefore, this tumor type is
considered to be a rare malignancy and its ontogeny remains
unclear; however, certain clear cell adenocarcinomas form part of a
larger conventional adenoma or situate next to an adenoma (2,3), thus
supporting the theory that the adenoma-carcinoma sequence of
colorectal carcinogenesis is also valid for clear cell
adenocarcinoma.
Regarding the clinical characteristics, more male
patients exhibiting clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colorectum
have been reported, and the tumor tends to be located on the left
side (2), which is consistent with
the present case. However, the young age (27 years) of the patient
in the present case is noteworthy. Clear cell adenocarcinomas
generally affect elderly males with an average age of 62 years
(1).
In contrast to previous studies, the patient in the
current case presented with a palpable abdominal mass without
exhibiting any symptoms that indicated colonic adenocarcinoma,
including melena, a change in bowel habits or symptoms of bowel
obstruction. This may be associated with the exophytic growth
pattern of the tumor. Due to the absence of specific clinical
manifestations, the tumor was not identified until it had enlarged
enough to be palpated. This condition is uncommon for a primary
colonic adenocarcinoma.
On CT imaging, the present tumor appeared as an
extensive extracolic mass in the left upper quadrant, which encased
the left part of the transverse colon, displaced the loop of small
bowel and the pancreas, and invaded the spleen. It was difficult to
identify the origin of the mass due to its large size and prominent
extraluminal location. However, the tumor site and its association
with the transverse colon may provide an indication.
Noteworthy considerations in the differential
diagnosis of primary clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colon are
metastases from other organs, including the kidneys, lower urinary
tract, ovaries and female genital tract. The majority of reported
cases of clear cell adenocarcinoma in the colon have been
identified later as metastases originating from renal clear cell
malignancies, which may occur 16 years following resection
(10). In the present case, the
patient had no history or evidence of tumors elsewhere, on clinical
and imaging examination, which indicated its primary origin at this
site. Furthermore, the present tumor lacked the hypervascularity
usually observed in renal clear cell carcinoma, thus favoring the
diagnosis of a primary colonic clear cell carcinoma. Differential
diagnosis with other colonic tumors appears to be difficult based
on the preoperative imaging; however, the patient’s clinical
characteristics and the predominantly extraluminal growth pattern
of the tumor may provide useful information. Further reports are
required for the elucidation of this tumor.
Clinical data regarding tumor-associated mortality
and disease-free survival in patients with primary clear cell
adenocarcinoma of the colorectum is rare, as a result of the
short-term follow up and small number of cases. Previous studies
have indicated that the behavior of this tumor is not significantly
different from that of conventional intestinal carcinomas; however,
further studies are required to investigate this.
In conclusion, in this study, a rare case of clear
cell adenocarcinoma of the colon in a young male was presented. The
case was reported due to rarity, and the clinical and computed
tomography features were analyzed. The tumor presented as an
extensive extracolic mass, which is uncommon for a primary colonic
tumor. The predominantly extraluminal growth pattern exhibited by
the tumor, as well as the patient’s clinical characteristics, may
be key features of advanced colonic clear cell adenocarcinoma.
References
|
1
|
Furuya Y, Wakahara T, Akimoto H, et al:
Clear cell adenocarcinoma with enteroblastic differentiation of the
ascending colon. J Clin Oncol. 29:647–679. 2011.
|
|
2
|
Ko YT, Baik SH, Kim SH, et al: Clear cell
adenocarcinoma of the sigmoid colon. Int J Colorectal Dis.
22:1543–1544. 2007.
|
|
3
|
Soga K, Konishi H, Tatsumi N, et al: Clear
cell adenocarcinoma of the colon: a case report and review of
literature. World J Gastroenterol. 14:1137–1140. 2008.
|
|
4
|
Klatte T, Rao PN, de Martino M, LaRochelle
J, Shuch B, Zomorodian N, et al: Cytogenetic profile predicts
prognosis of patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 27:746–753. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Drew PA, Murphy WM, Civantos F and
Speights VO: The histogenesis of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the
lower urinary tract. Case series and review of the literature. Hum
Pathol. 27:248–252. 1996.
|
|
6
|
Kondi-Pafiti A, Papakonstantinou E,
Iavazzo C, Grigoriadis C, Salakos N and Gregoriou O:
Clinicopathological characteristics of ovarian carcinomas
associated with endometriosis. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 285:479–483.
2012.
|
|
7
|
McCluggage WG, Desai V, Toner PG and
Calvert CH: Clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colon arising in
endometriosis: a rare variant of primary colonic adenocarcinoma. J
Clin Pathol. 54:76–77. 2001.
|
|
8
|
He H, Zhou GX, Zhou M and Chen L: The
distinction of clear cell carcinoma of the female genital tract,
clear cell renal cell carcinoma, and translocation-associated renal
cell carcinoma: an immunohistochemical study using tissue
microarray. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 30:425–430. 2011.
|
|
9
|
Evans H, Yates WA, Palmer WE, Cartwright
RL and Antemann RW: Clear cell carcinoma of the sigmoid mesocolon:
a tumor of the secondary müllerian system. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
162:161–163. 1990.
|
|
10
|
Braumann C, Schwabe M, Ordemann J and
Jacobi CA: The clear cell adenocarcinoma of the colon: case report
and review of the literature. Int J Colorectal Dis. 19:264–267.
2004.
|