Introduction
Lymphoepithelial carcinoma (LEC) of salivary gland
origin is an undifferentiated carcinoma accompanied by a prominent
non-neoplastic lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate; LEC exhibits
morphological characteristics identical to those of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma (1). It has a significant
racial predilection for Inuit and Southeast Asian populations
(1,2). An association between LEC and
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection has been previously reported
(1,2). The majority of cases of LEC arise in
major salivary glands, with the parotid being most commonly
affected (~80% of cases) (2). LEC
presents as slowly growing mass which may exhibit a rapid increase
in size with or without pain. Cervical lymph node involvement is
present in ~40% of patients at presentation (2,3). Due
to the lack of distinctive clinical and radiographical features and
the rarity of the tumor, the diagnosis of LEC is initially based on
histology. Clinical evaluation for possible primary nasopharyngeal
carcinoma must be performed in all patients. At present, treatment
for LEC includes complete surgical excision and adjuvant
radiotherapy. To the best of our knowledge, only three cases of LEC
have been reported in the English language literature as arising
from the minor salivary gland (4–6). The
current study presents the fourth such case of LEC originating from
the minor salivary gland of the hard palate, and reviews the
clinicopathological characteristics of this uncommon tumor.
Case report
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of
The Second Xiangya Hospital, Central South University (Hunan,
China) and written informed consent was obtained from the
patient.
A 38-year-old Chinese female was admitted to the
Department of Stomatology at the Second Xiangya Hospital, of
Central South University (Changsha, China) with a painless mass in
her left palate. The patient stated that the mass was initially
identified approximately one month previously. Intraoral
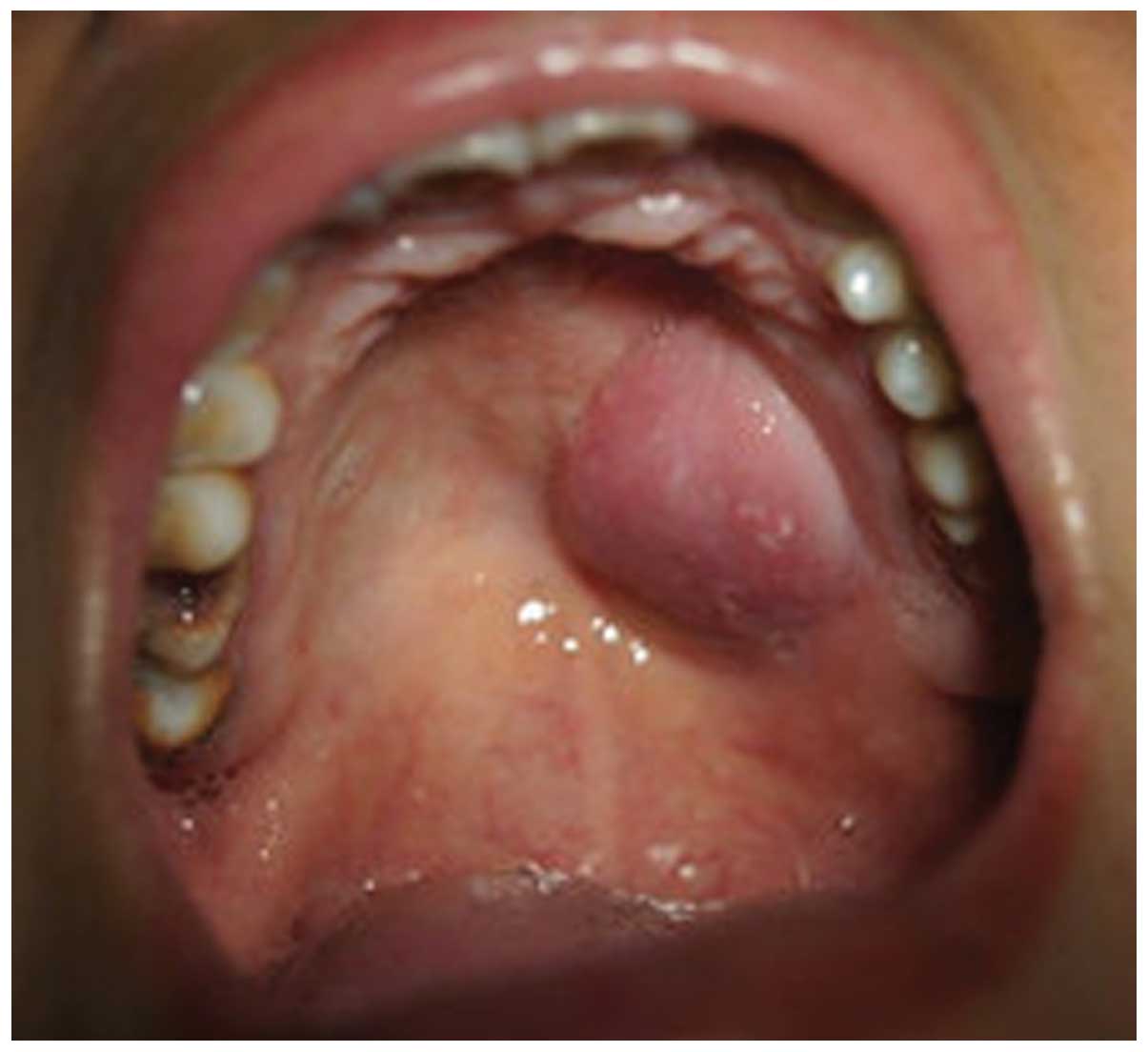
examination revealed a well-defined, nodular mass in the left side
of the hard palate (Fig. 1). The
mass was non-tender and soft to palpation, with areas of
fluctuance. The surface mucosa was red in color with no erosion,
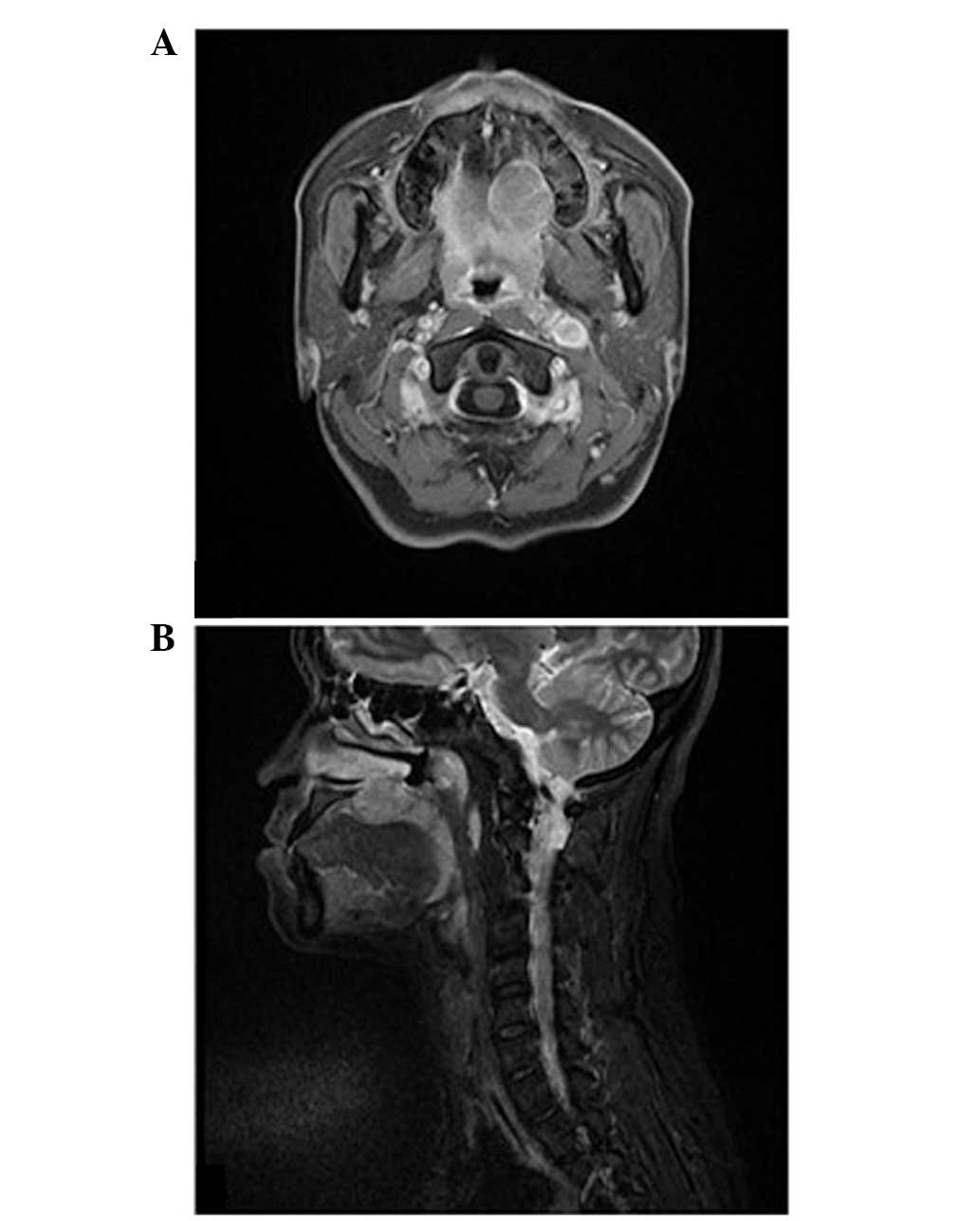
bleeding or ulceration. Magnetic resonance imaging delineated a
mass lesion of 26 × 24 × 17 mm in size, located on the left hard
palate with invasion into the nasal cavity (Fig. 2). The tumor exhibited isointensity
on T1-weighted images and hyperintensity on T2-weighted images,
with a moderately enhanced effect. No marked lymphadenopathy was
identified according to imaging features and clinical examination.
The patient was otherwise well, with no significant events in the
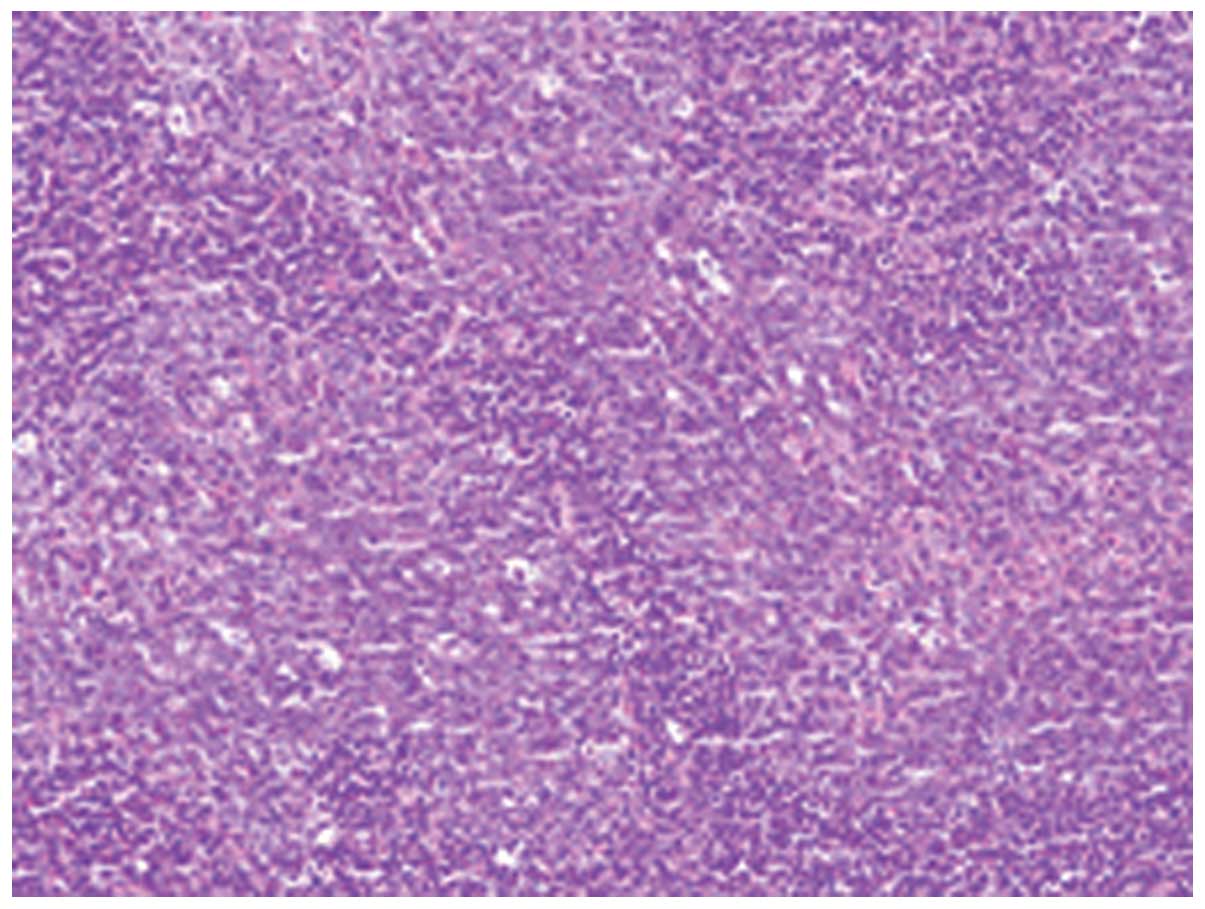
medical history. An incisional biopsy was performed, which revealed
irregular tumor nests of undifferentiated epithelial cells
intimately intermingled with lymphocytes and plasma cells. The
tumor cells exhibited a syncytial pattern with indistinct cell
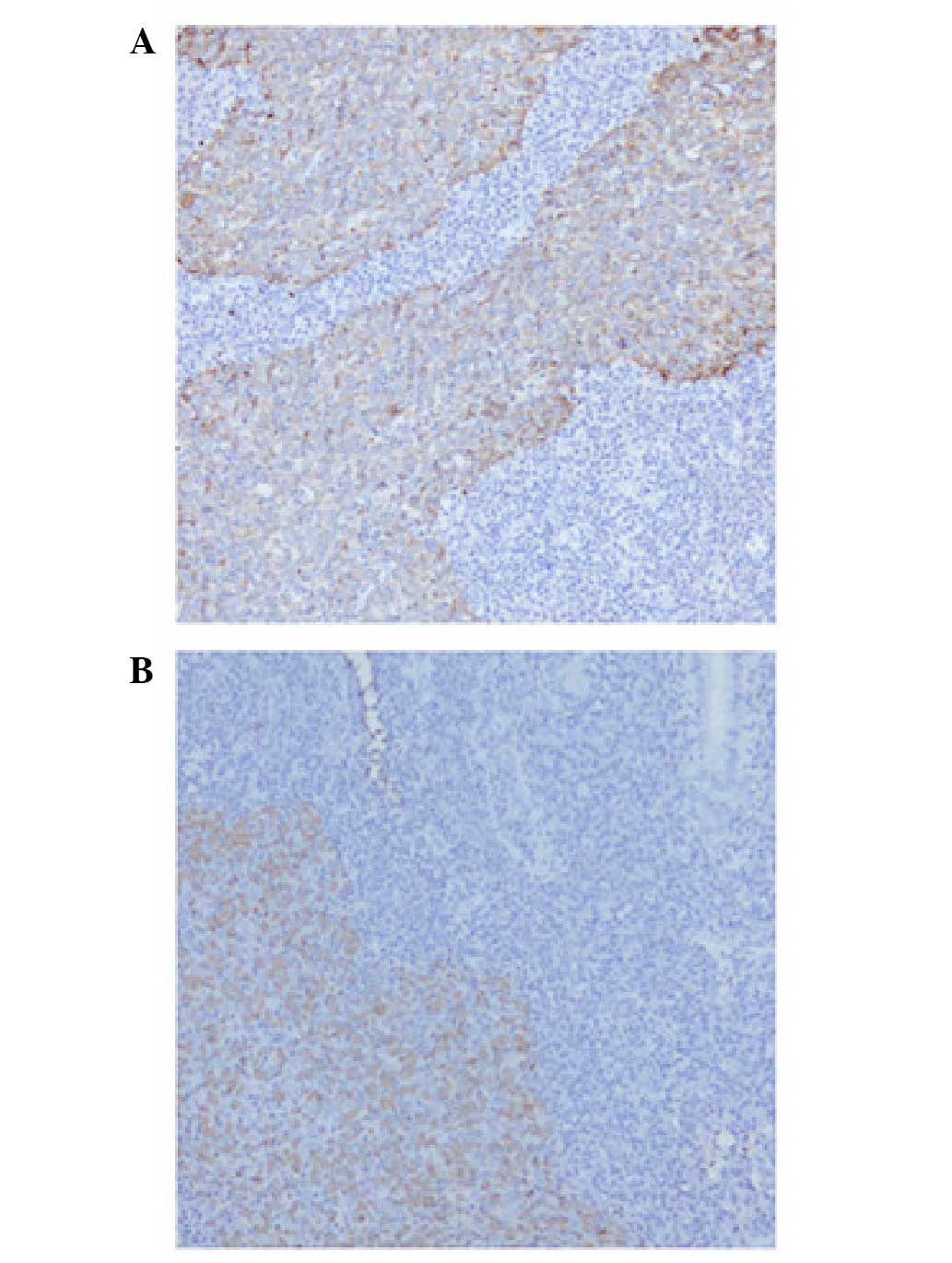
borders, vesicular nuclei, and large central nucleoli (Fig. 3). Immunohistochemically, the tumor
cells were diffusely positive for cytokeratin AE1/AE3 (Fig. 4A). In situ hybridization for
EBV-encoded RNA was diffusely positive in undifferentiated
carcinoma, however, it was negative in the surrounding lymphoid
stroma and adjacent salivary gland tissues (Fig. 4B). Endoscopy examination revealed a
thickening of the nasopharynx. Multiple biopsies from the
nasopharynx were subsequently performed, which were negative for
tumor cells. A final diagnosis of primary LEC was determined. The
patient underwent a partial maxillectomy without further surgical
neck dissection. Adjuvant radiotherapy was suggested, however this
was refused by the patient due to financial difficulties. The
patient showed no evidence of remission during the postoperative
follow-up of 12 months.
Discussion
According to the new World Health Organization
classification, undifferentiated carcinomas of the salivary gland
are separately classified into small-cell undifferentiated
carcinoma, large-cell undifferentiated carcinoma and LEC (1). LEC, is a rare and unique malignant
salivary gland tumor with morphological features identical to that
of undifferentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma, but which are not
shared by other salivary gland tumor types (1,2). This
neoplasm exhibits a strong racial prevalence for Inuit and
Southeast Asian individuals, however the reasoning for this remains
unknown. Within the Inuit population, LEC is the most common
malignant salivary gland tumor, representing 92% of all cases
(7). LEC accounts for 5.9 and 5.4%
of malignant salivary gland tumors in Southeast Chinese and
Taiwanese populations, respectively (3,8). In
nonendemic areas, LEC accounts for ~0.4% of malignant tumors in the
salivary gland (2). An association
between LEC and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection has also been
previously reported (1,2). In endemic areas, the association
between LEC occurring in the salivary glands and EBV infection is
~100% (3,6). The age range at presentation is
between 20 and 60 years, with a median age of 40 years. There is no
evident gender predilection (3).
Although LEC may occur in any salivary gland
location, the diagnosis of a primary LEC arising in a salivary
gland is largely restricted to the major glands due to difficulties
with differentiating LEC from tumors of primary mucosal origin. The
parotid gland is most frequently affected, followed by the
submandibular gland (2). Primary
LEC of minor salivary gland origin is extremely rare, being absent
in recent large cohort of salivary gland LECs and several previous
studies of minor salivary gland tumors (3,8–10). It
is conceivable, however, that the incidence of LEC of the minor
salivary glands may in fact be higher; this is due to difficulties
in reliably distinguishing them from tumors of primary mucosal
origin, therefore, by convention they are not included in the
majority of current salivary gland neoplasm classifications. In the
present case, the distance from the overlying nondysplastic
epithelium and close proximity to glandular tissue strongly
indicated a primary minor salivary gland origin. To the best of our
knowledge, only four cases of intraoral LEC of presumed minor
salivary gland origin, including the present case, have been
reported (4–6). The four cases involved three females
and one male; the mean age was 53 years and the age range was 38–69
years. Two cases arose in the cheek, and one each in the palate and
upper lip. The tumors varied in diameter from 0.5–2.6 cm, with a
mean diameter of 1.9 cm. Lymph node metastasis was observed in one
patient. Three patients were treated with surgery, and one was
treated with surgery followed by adjuvant radiotherapy. Patient
follow-up varied from 12–120 months. All patients were alive with
no evidence of disease or recurrence during follow-up. EBV
infection was identified in two patients who were from Southeast
Asia.
LEC is a lymphoid rich tumor composed of sheets and
nests of large vesicular cells with prominent nucleoli and
syncytial cytoplasm. The principle differential diagnosis of the
present case is metastatic undifferentiated carcinoma, particularly
metastasis from the nasopharynx. Morphologically, LEC of the
salivary gland is indistinguishable from nasopharyngeal carcinoma,
which is much more common, and has very similar cytological and
architectural features, the same ethnic predilection, and a strong
association with EBV infections. Therefore, a careful examination
of the nasopharynx is mandatory and, if relevant, multiple
nasopharyngeal biopsies must be obtained (1,2).
LEC has a tendency to metastasize, and the reported
incidence of lymph node metastases of LECs originating from the
major salivary glands at presentation is 10–50% (1–3,8). In
20% of cases, local recurrences or lymph node metastases develop,
and ~20% eventually experience distant metastases within three
years of treatment. Appropriate therapy for LEC includes complete
surgical excision with negative surgical margins and adjuvant
radiation therapy to the tumor area and ipsilateral neck nodes. A
neck dissection is usually reserved for patients with clinically
positive lymph nodes. LECs appear to exhibit an improved prognosis
compared with other undifferentiated carcinomas of the salivary
glands, and the 5-year survival has been reported to range from
50–90% (1–3,8).
Due to the limited number of cases, no standardized
treatment policy for LEC of the oral cavity has been established to
date. We hypothesize that the initial treatment choice for oral LEC
should be complete local excision, accompanied by neck
lymphadenectomy (if cervical nodes are involved). Adjuvant
radiotherapy must be considered for LEC due to its high
sensitivity, particularly in patients with extensive soft tissue
invasion, in cases in which tumor-free margins are not possible, or
in patients with local recurrence.
References
|
1
|
Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P and
Sidransky D: World Health Organization Classification of Tumours
Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours. Lyon, France: IARC
Press; 2005
|
|
2
|
Schneider M and Rizzardi C:
Lymphoepithelial carcinoma of the parotid glands and its
relationship with benign lymphoepithelial lesions. Arch Pathol Lab
Med. 132:278–282. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ma H, Lin Y, Wang L, et al: Primary
lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of salivary gland: sixty-nine
cases with long-term follow-up. Head Neck. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Worley NK and Daroca PJ Jr:
Lymphoepithelial carcinoma of the minor salivary gland. Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 123:638–640. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lu SY, Huang CC, Hsiung CY, Eng HL and
Huang HY: Primary lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of minor
salivary gland: a case report with immunohistochemical and in situ
hybridization studies. Head Neck. 28:182–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Menditti D, Laino L, Milano M, et al:
Intraoral lymphoepithelial carcinoma of the minor salivary glands.
In Vivo. 26:1087–1089. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nielsen NH, Mikkelsen F and Hansen JP:
Incidence of salivary gland neoplasms in Greenland with special
reference to an anaplastic carcinoma. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand
A. 86:185–193. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang CP, Chang YL, Ko JY, et al:
Lymphoepithelial carcinoma versus large cell undifferentiated
carcinoma of the major salivary glands. Cancer. 101:2020–2027.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pires FR, Pringle GA, Almeida OP and Chen
SY: Intra-oral minor salivary gland tumors: a clinicopathological
study of 546 cases. Oral Oncol. 43:463–470. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Venkata V and Irulandy P: The frequency
and distribution pattern of minor salivary gland tumors in a
government dental teaching hospital, Chennai, India. Oral Surg Oral
Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 111:e32–e39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|