Introduction
Gastric cancer (GC) is the fifth most common
malignancy and the fourth leading cause of cancer-related mortality
worldwide, accounting for ~800,000 mortalities annually (1,2). Asia
has the highest global burden, with 820,000 novel cases and 576,000
mortalities reported in 2020 alone (3). Due to non-specific early symptoms
(such as epigastric discomfort or dull pain, loss of appetite,
early satiety, belching, acid reflux and nausea) (4,5),
delayed clinical presentation and limited sensitivity of current
tumor markers such as CD101 and Tim3 (6,7), the
majority of patients with GC are diagnosed at advanced stages,
precluding curative surgical resection. Current treatment
strategies, including chemotherapy, targeted therapy and
combination regimens (for example, 5-fluorouracil-based,
platinum-based and newer drug combinations), have markedly improved
over the past four decades. Nevertheless, persistent challenges
such as tumor invasion, metastasis and recurrence often lead to
treatment failure, markedly impairing patient survival and quality
of life (8–10). Therefore, elucidating the molecular
mechanisms underlying GC invasion and metastasis remains a key
research priority to improve therapeutic outcomes in the
future.
Increasing evidence indicates that dysregulated
activation of key signaling pathways, including
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), PI3K/AKT/mTOR,
Ras/Raf/ERK, Janus kinase/STAT and epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGFR)-mediated signaling, serves a key role in promoting malignant
progression (11–14). The aberrantly activated pathways
facilitate tumor aggressiveness by modulating downstream effector
molecules. EGFR is a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor that is
extensively expressed in mammalian epithelial cells, fibroblasts,
glial cells and keratinocytes. As a key regulator of cell
proliferation, survival and migration, the EGFR pathway is
implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple cancer types. EGFR
upregulation has been validated as a prognostic biomarker in breast
cancer progression (15). Previous
studies have reported that EGFR can be used as a marker in
predicting breast cancer progression and prognosis (16–18).
Furthermore, EGFR has been reported to be associated with the
metastasis of gallbladder, bladder, lung and colon cancer (19–22).
Notably, emerging studies have associated EGFR dysregulation with
the invasion and metastasis of GC, highlighting its potential as a
therapeutic target (23,24).
Postoperative recurrence, invasion and metastasis
are major challenges in GC management that markedly compromise
patient survival and quality of life (25,26).
Among the molecular mediators of these processes, matrix
metalloproteinases (MMPs) serve a well-established role in
facilitating GC progression (27,28).
MMP7, a key member of the MMP family, exhibits unique
characteristics despite its relatively simple structure. With a
molecular weight of only 19 kDa upon activation, MMP7 demonstrates
notably broad substrate specificity, degrading both extracellular
matrix (ECM) and non-ECM components to promote tumor invasion and
metastasis. Emerging evidence indicates that MMP7 is upregulated in
multiple malignancies, including GC, hepatocellular carcinoma and
colorectal cancer (29–31). Notably, MMP7 differs from other MMP
family members in its tumor cell-specific secretion pattern (vs.
stromal cell-derived production), making it a potential diagnostic
biomarker as well as a promising therapeutic target (32). The aforementioned findings
underscore the key involvement of MMP7 in GC recurrence, invasion
and metastasis.
Although the individual roles of EGFR and MMP7 in
cancer are well-recognized, their direct association and functional
interdependence in GC remain insufficiently explored.
Phosphorylation of EGFR at tyrosine 1068 (p-EGFR) is a
well-established indicator of its activation and downstream
signaling, with significant implications in tumor progression
(33–35). To clarify the clinical relevance of
this modification in the context of MMP7 co-expression, p-EGFR was
specifically assessed in the present study. The present study
integrated The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data with clinical
immunohistochemical (IHC) validation to assess their co-expression
as a hallmark of metastatic GC. Through comprehensive analysis of
the TCGA database, the expression profiles of EGFR and MMP7 and
their association with clinical outcomes in patients with GC were
examined. Furthermore, IHC analysis of clinical GC specimens was
conducted to explore the correlation between p-EGFR and MMP7
expression. Collectively, the present study aimed to establish
whether p-EGFR and MMP7 function as key mediators in GC metastasis,
thereby providing insights that could inform future therapeutic
strategies targeting GC invasion and metastasis.
Materials and methods
Tissue samples
This was a retrospective cohort study. GC tissue
samples (n=32) and their corresponding normal tissue samples
(samples taken at a distance of ≥2.5 cm from the cancer tissue)
were obtained from patients with GC who underwent surgery at The
First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University (Hefei,
China) from November 2022 to December 2023. Tumor classification
was based on the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of
Tumors, 5th edition (36). The
inclusion criteria were as follows: i) Underwent a definitive
surgical resection for primary GC between November 2022 to December
2023; ii) had a confirmed histopathological diagnosis of GC
according to the WHO Classification of Tumors, 5th edition; iii)
formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor tissue blocks with
sufficient quality and quantity were available for subsequent
molecular and IHC analyses; and iv) had complete
clinicopathological data and follow-up records that were accessible
from the institutional database. The exclusion criteria were as
follows: i) Received any form of neoadjuvant chemotherapy or
radiotherapy prior to surgical resection; ii) had a history of
other synchronous or metachronous active malignancies within 5
years prior to the diagnosis of the index tumor; iii) presented
with distant metastasis (Stage 4 disease) at the initial diagnosis;
iv) had insufficient clinical follow-up data (defined as <12
months post-surgery for surviving patients); and v) the available
tumor specimen was deemed inadequate for analysis due to extensive
necrosis or poor preservation upon central pathological review. The
patients had not received chemotherapy or radiotherapy previously.
Metastasis was defined by the histological confirmation of tumors
in the regional lymph nodes or distant organs at surgery. The tumor
samples included 17 metastatic and 15 non-metastatic samples. The
present study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First
Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University (approval no.
20231337; Hefei, China) and was conducted according to the
principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent
was obtained from all patients.
Reagents
p-EGFR (phospho-Y1068; cat. no. ab40815; 1:500) and
MMP7 (cat. no. ab207299; 1:1,000) were purchased from Abcam.
PV-9000 histochemical reagent kit (cat. no. PV-9000) was obtained
from Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao Biotechnology Co., Ltd. and DAB
(cat. no. P0201S) staining solution was obtained from Beyotime
Biotechnology.
Bioinformatics analysis
Publicly available databases and analytical tools
were employed to investigate gene expression correlations and
association with survival. The profile of gene upregulation in GC
was obtained from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Cancer
database (UALCAN; http://ualcan.path.uab.edu/cgi-bin/TCGAExHeatMap2.pl?size=25&cancer=STAD).
The transcript levels of MMP7 and EGFR were compared between tumor
and adjacent normal tissues using TCGA-stomach adenocarcinoma
(STAD) dataset within the UALCAN platform. The specific analysis
can be replicated using the following direct links: MMP7
(https://ualcan.path.uab.edu/cgi-bin/TCGAExResultNew2.pl?genenam=MMP7&ctype=STAD)
and EGFR (https://ualcan.path.uab.edu/cgi-bin/TCGAExResultNew2.pl?genenam=EGFR&ctype=STAD).
To ensure full reproducibility of the present analyses, a
comprehensive step-by-step protocol is provided in Data S1. Kaplan-Meier plotter (https://kmplot.com/analysis/) was used to examine the
associations between MMP7 or EGFR expression and overall survival.
All available datasets in the platform were included without any
dataset-specific restrictions. Cut-off values for gene expression
were determined automatically based on percentiles. Specifically,
the threshold corresponding to the 70th percentile was used for
MMP7 (absolute expression value, 1,486; range, 5–37,183), and the
threshold corresponding to the 75th percentile was used for EGFR
(absolute expression value, 53; range, 1–880). These thresholds
were applied to stratify patients into high and low expression
groups for subsequent survival analysis.
IHC analysis
Paraffin-embedded tissue sections were used for
immunohistochemistry. The source tissues had been previously fixed
in 10% neutral buffered formalin at room temperature for 24–48 h
during routine pathological processing. For IHC, 5 µm sections were
mounted on positively charged slides and dried in an oven at 60°C
for 1 h prior to staining. Tissue slides were deparaffinized using
xylene (100%, 15 min, 25°C, twice) and rehydrated through a graded
ethanol series (100% ethanol, 3 min, 25°C, twice; 95% ethanol, 3
min, 25°C; 90, 80 and 70% ethanol, 1 min each, 25°C). The tissue
slices were soaked in citrate buffer (0.01 M, 100°C) for antigen
retrieval. After boiling for 15 min, the samples were allowed to
cool. The effects of endogenous enzymes were eliminated after 20
min of treatment with H2O2 (reagent 1, 25°C).
Serum (10%) blocking was performed at 25°C for 20 min, followed by
incubation with p-EGFR or MMP7 primary antibodies at 4°C for 16 h.
Reaction-boosting solution (reagent 2) and secondary antibody
(reagent 3) were added sequentially and incubated for 20 min at
25°C. Reagents 1, 2 and 3 were included in the PV-9000
histochemical kit. DAB was used for 5 min for color development.
Nuclei were stained with hematoxylin (Beyotime Biotechnology) for 3
min at 25°C and sealed with neutral glue. Staining was
independently assessed by two experienced pathologists who were
blinded to the clinical data. Inter-observer variability was
quantitatively evaluated using Cohen's κ coefficient. A light
Panoramic MIDI scanner with Jetta JD801 (Jiangsu Jetta Technology
Development Co., Ltd.) was used to capture the images. A combined
score of staining intensity and distribution was used to
semi-quantitatively evaluate p-EGFR and MMP7 expression (37). For comparative analysis, patients
were stratified into low-(lowest 30%), moderate- and high-(highest
30%) expression cohorts. The average optical density was analyzed
using ImageJ software (version 1.44p; National Institutes of
Health).
Hematoxylin-eosin (H&E)
staining
Paraffin-embedded tissues were cut into 5 µm
sections and mounted on positively charged slides and dried in an
oven at 60°C for 1 h prior to staining. Tissue slides were
deparaffinized using xylene (100%, 15 min, 25°C, twice) and
rehydrated through a graded ethanol series (100% ethanol, 3 min,
25°C, twice; 95% ethanol, 3 min, 25°C; 90, 80 and 70% ethanol, 1
min each, 25°C). The nuclei were stained with hematoxylin for 3 min
at 25°C and the cytoplasm was stained with eosin for 1 min at 25°C
(Beyotime Biotechnology). Images were captured using a panoramic
scanner (Panoramic MIDI).
Statistical analysis
IHC staining for MMP7 or EGFR was performed on
sequential sections from 32 tissue samples, with each staining
procedure repeated in triplicate to ensure reproducibility. The
average optical density values were quantified using ImageJ
software. All data are presented as the mean ± SD. The primary
statistical analyses, including between two groups comparisons
using paired or unpaired two-tailed Student's t-tests and
correlation analysis using Pearson's correlation coefficient, were
performed using GraphPad Prism (version 8; Dotmatics), whereas the
results for Fig. 1, Fig. 2, Fig.
3 were obtained directly from TCGA analysis portal of the
UALCAN database without further modification by the authors.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
Bioinformatics analysis of MMP7
expression in GC
Gastric adenocarcinoma represents the primary form
of GC, with metastasis in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma
being a key determinant of their quality of life and survival. The
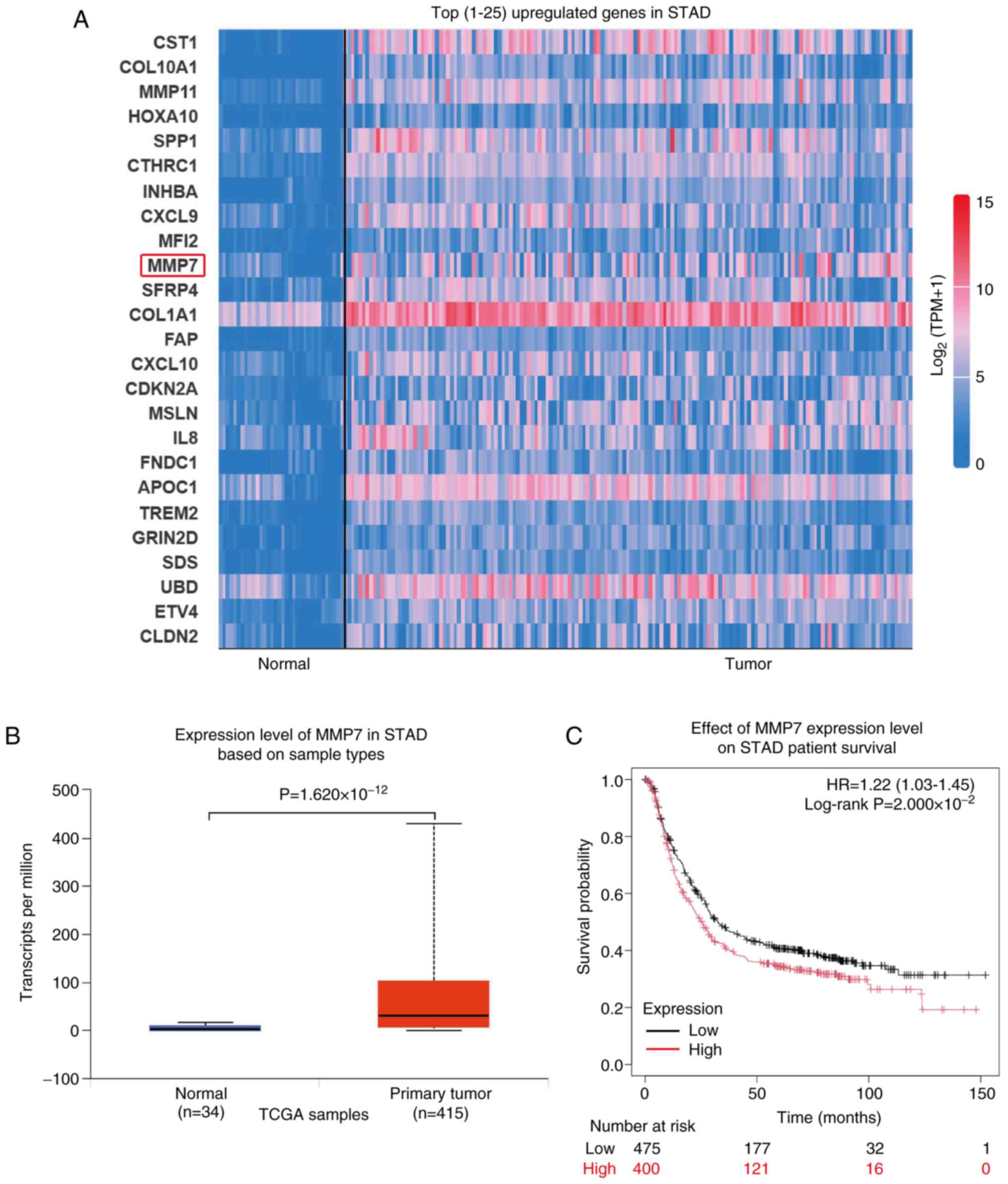
present study analyzed the top 25 upregulated genes in gastric
adenocarcinoma (Normal, n=34; Tumor, n=415) using data from TCGA
database and identified the expression levels of MMP11 and MMP7
elevated (both MMP7 and MMP11 were members of the MMPs family;
Fig. 1A). MMP7, specifically, is
secreted by cancer cells and possesses the ability to degrade the
ECM, facilitating the breach of the initial defensive barrier
during cancer cell metastasis.
The transcript levels of MMP7 in gastric
adenocarcinoma tissue samples (n=415) were significantly higher
compared with those in normal tissue samples (n=34;
P=1.620×10−12; Fig. 1B).
Furthermore, the survival prognosis curve revealed that increased
MMP7 expression was significantly associated with unfavorable
survival outcomes in patients (Fig.
1C; P=2.000×10−2).
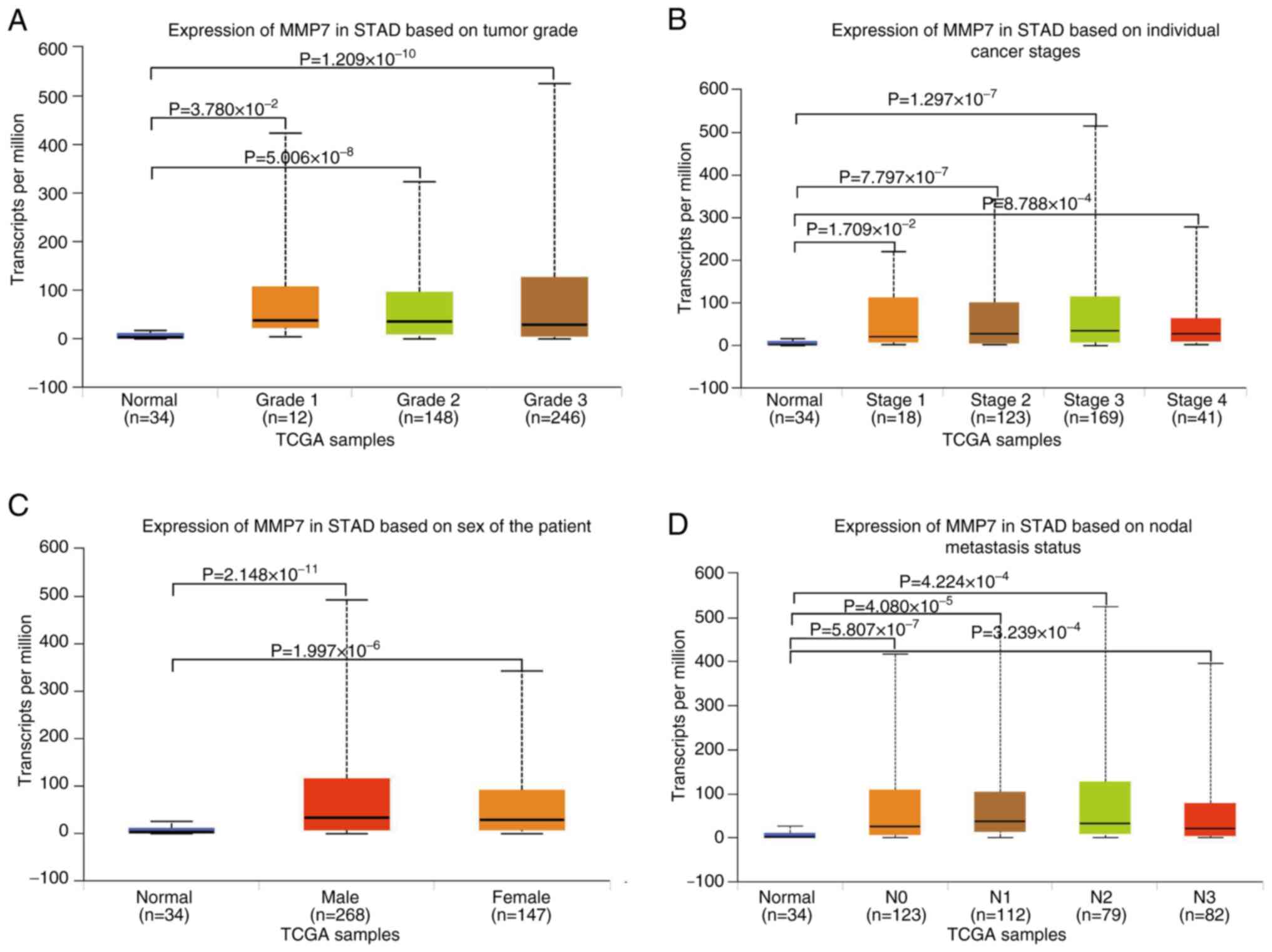
Next, the stage-specific analysis of MMP7 expression
in gastric adenocarcinoma revealed significantly elevated levels
across all tumor grades compared with that in normal tissues (Grade
1, P=3.780×10−2, n=12; Grade 2, P=5.006×10−8,
n=148; Grade 3, P=1.209×10−10, n=246), demonstrating
progressively increasing expression from well-differentiated to
poorly-differentiated tumors, although inter-grade differences did
not reach statistical significance (Fig. 2A). The present study findings
revealed that MMP7 is consistently upregulated in gastric
adenocarcinoma regardless of tumor grade, with a non-significant
increase accompanying loss of differentiation. The pattern supports
its involvement in both tumor initiation and progression. The
findings suggest that MMP7 upregulation occurs early in gastric
adenocarcinoma development and persists throughout tumor
progression, supporting its potential role as a consistent
molecular marker across different disease stages.
Furthermore, the present comprehensive analysis
revealed significant MMP7 upregulation across all clinical stages
of gastric adenocarcinoma compared with that in normal tissues
(n=34), with stage-specific elevations observed in Stage 1 (n=18;
P=1.709×10−2), Stage 2 (n=123; P=7.797×10−7),
Stage 3 (n=169; P=1.297×10−7) and Stage 4 (n=41;
P=8.788×10−4) tumors. Notably, while MMP7 expression
progressively increased from the early to advanced stages, the
inter-stage comparisons did not reach statistical significance
(Fig. 2B). The significant
upregulation of MMP7 across all clinical stages, compared with that
in normal tissue, establishes its broad association with gastric
tumorigenesis. The non-significant increasing trend with disease
progression possibly reflects the function of MMP7 as a sustained
driver of tumor aggressiveness. The consistent increase across all
stages underscores the potential utility of MMP7 as a reliable
biomarker and therapeutic target throughout the disease
continuum.
After these analyses, the present study examined the
disparities in MMP7 levels in the gastric adenocarcinoma tissues of
male and female patients. The results indicated that compared with
normal tissues (n=34), MMP7 expression was elevated in both male
(n=268, P=2.148×10−11) and female (n=147,
P=1.996×10−6) patients, although no notable differences
were observed in the expression levels between male and female
patients, as shown in Fig. 2C.
The present study compared the MMP7 expression
differences in patients with gastric adenocarcinoma and lymph node
metastasis. The findings highlighted that compared with normal
tissues (n=34), MMP7 expression increased significantly in N0
(n=123; P=5.807×10−7), N1 (n=112;
P=4.080×10−5), N2 (n=79; P=4.224×10−4) and N3
(n=82; P=3.239×10−4), with no statistically significant
differences in the MMP7 expression levels between lymph node
metastasis grades (N0-N3), as depicted in Fig. 2D. The observations underscored the
key role of MMP7 in the metastasis of gastric adenocarcinoma and
emphasized the clinical significance of selecting MMP7 as a target
for further exploration and potential intervention.
Bioinformatics analysis of EGFR
expression in GC
Emerging evidence indicates that MMP7 expression is
modulated by upstream regulatory pathways (38,39).
Notably, EGFR-mediated regulation of MMP7 has been reported not
only in diabetic kidney disease (40), but also in the context of GC
metastasis (41), suggesting a
potentially conserved mechanism across inflammatory and malignant
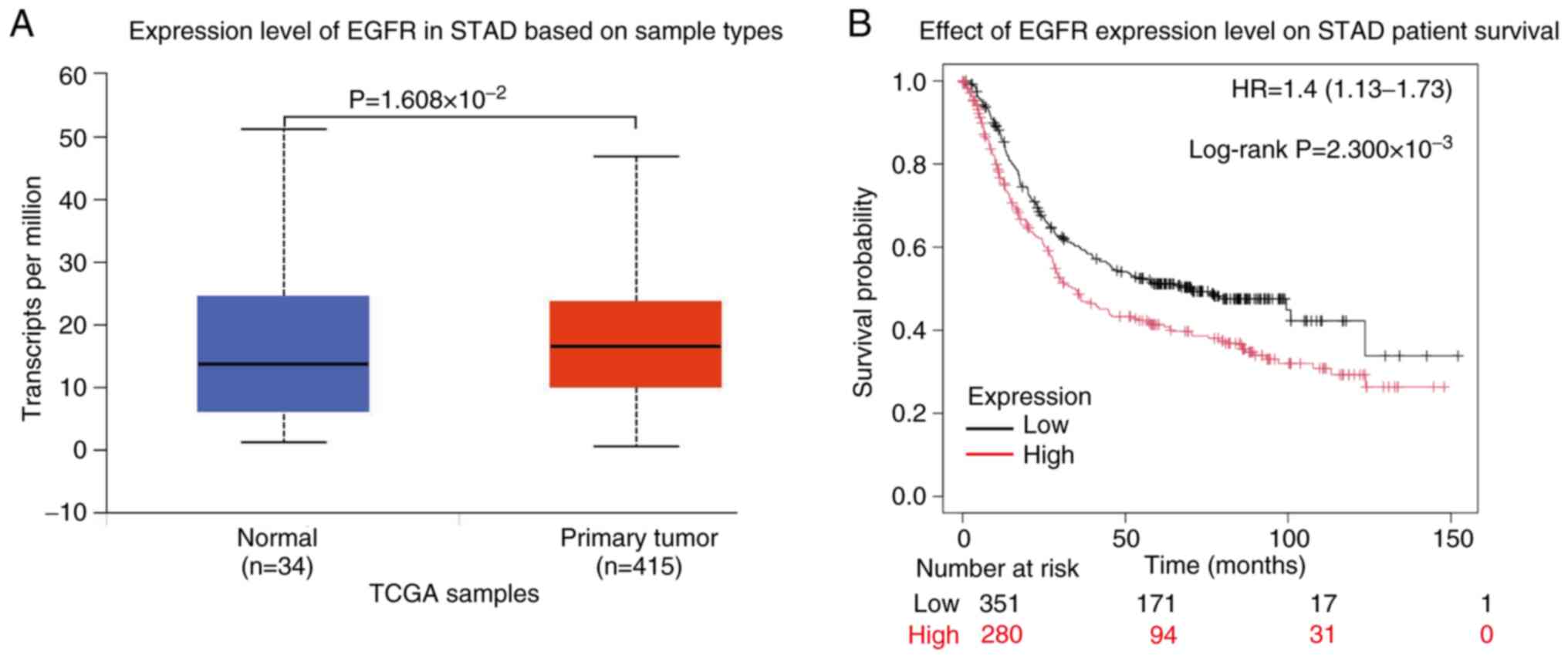
conditions. The present bioinformatic analysis of TCGA dataset
revealed significant differential expression level of EGFR between
normal gastric tissue and gastric adenocarcinoma, with notable
upregulation observed in malignant tissues
(P=1.608×10−2; Fig. 3A).
Survival analysis demonstrated that elevated EGFR expression is
significantly associated with worse clinical outcomes in patients
with gastric adenocarcinoma (P=2.300×10−3; Fig. 3B), highlighting its prognostic
relevance in GC progression.
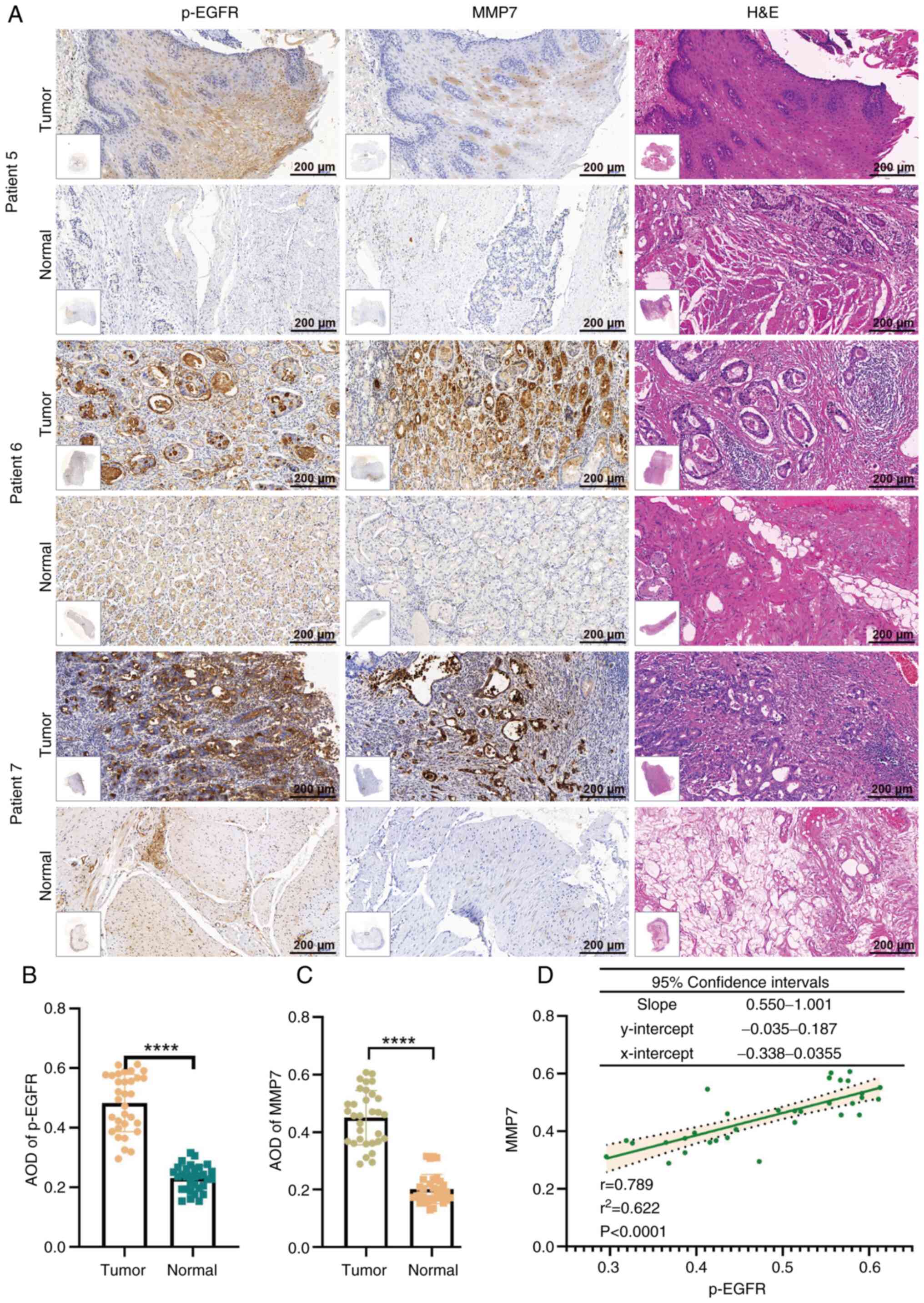
Expression levels of MMP7 and p-EGFR
are higher in metastatic gastric adenocarcinoma tissues
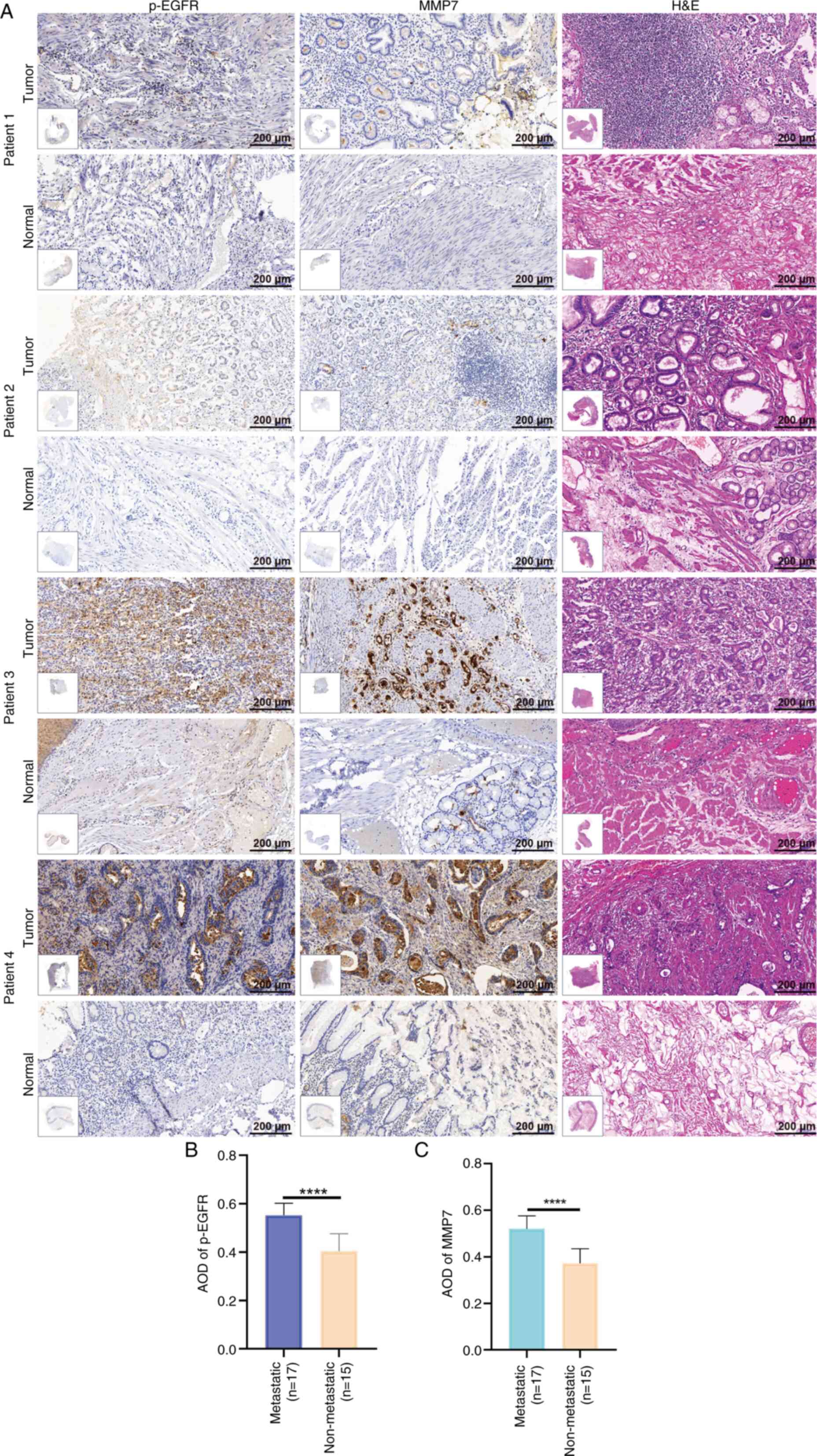
The present study utilized 32 matched pairs of
gastric adenocarcinoma and adjacent normal tissue samples,
including 17 metastatic and 15 non-metastatic cases. All specimens
underwent comprehensive histological evaluation using H&E
staining, coupled with IHC analysis of p-EGFR and MMP7 expression.
Fig. 4A displays representative IHC
results from 2 non-metastatic (patients 1 and 2) and 2 metastatic
(patients 3 and 4) cases.
Using GraphPad Prism, the present study performed a
comparative analysis of the protein expression patterns between the
metastatic and non-metastatic groups. The results demonstrated a
significantly elevated expression levels of both p-EGFR
(P<0.0001) and MMP7 (P<0.0001) in metastatic tissues compared
with that in the non-metastatic counterparts (Fig. 4B and C). The experimental findings
provided notable evidence for the involvement of p-EGFR and MMP7 in
gastric adenocarcinoma metastasis.
p-EGFR and MMP7 are positively
correlated in gastric adenocarcinoma tissue
IHC analysis of 17 metastatic GC cases revealed
differential MMP7 expression levels, ranging from low (patient 5),
moderate (patient 6) to high (patient 7) staining intensity
(Fig. 5A). Comparative evaluation
of all 32 matched tumor-normal tissue pairs demonstrated
significantly elevated expression levels of both p-EGFR
(P<0.0001) and MMP7 (P<0.0001) in gastric adenocarcinoma
tissues compared with that in their normal counterparts (Fig. 5B and C).
Notably, as shown in Fig. 5A, as the MMP7 expression level
decreased (as seen in patient 5), p-EGFR expression decreased. By
contrast, when MMP7 expression was high (as observed in patient 7),
p-EGFR expression levels increased. Therefore, the present study
performed a correlation analysis between p-EGFR and MMP7 expression
in 32 gastric adenocarcinoma tissue samples and revealed a positive
correlation between p-EGFR and MMP7 expression
(r2=0.6219; P<0.0001), as shown in Fig. 5D. Furthermore, a correlational
analysis of EGFR and MMP7 expression, conducted via the Gene
Expression Profiling Interaction Analysis platform (https://gepia3.bioinfoliu.com/), identified a
statistically significant yet weak positive relationship (r=0.27;
P=4.4×10−12; Fig. S1).
The correlation underscores the association between p-EGFR and MMP7
in gastric adenocarcinoma, reinforcing their potential relevance in
disease progression.
Discussion
GC is one of the most lethal malignancies worldwide
and ranks among the leading causes of cancer-related mortality
(42). Its aggressive nature,
characterized by its pronounced invasive and metastatic potential,
poses notable clinical challenges. Although therapeutic advances
over the past decade have improved patient outcomes, persistent
issues of post-treatment recurrence and metastasis continue to
compromise patient prognosis. The unresolved clinical challenges
underscore the key need to identify the molecular targets involved
in GC metastasis, a key research priority that could markedly
enhance postoperative survival rates and quality of life in
affected individuals.
MMPs are key mediators of tumor metastasis, drawing
notable research interest due to their multifaceted roles in both
physiological and pathological processes. They were initially
characterized for their functions in embryonic development and
tissue remodeling (43,44). However, they are now recognized as
key contributors to cancer pathogenesis due to their ability to
degrade basement membrane components and ECM proteins (45). This proteolytic activity facilitates
key oncogenic processes, including tumor invasion, angiogenesis and
metastatic dissemination. Previous studies have reported that the
activity and expression levels of MMPs, such as MMP2, MMP3, MMP7
and MMP9, are increased in patients with GC and can reduce their
survival period, promote the metastasis and recurrence of cancer
and render a poor prognosis (46–48).
MMP7 exhibits unique clinical value as a
tumor-derived protease, thereby being distinct from other MMP
family members that are primarily secreted by stromal cells. This
tumor cell-specific expression pattern makes MMP7 an ideal
biomarker in monitoring cancer progression. Increasing evidence
demonstrates MMP7 upregulation in multiple malignancies, including
prostate and breast cancer, and its association with metastasis
(49,50). MMP7 can be used as a marker to
measure the prognosis of colon and esophageal cancer (51). Using bioinformatics analysis, the
present study demonstrated that MMP7 is upregulated in gastric
adenocarcinoma and is associated with a worse patient prognosis.
Notably, the IHC results of the present study revealed that MMP7
was highly expressed in gastric adenocarcinoma tissues with lymph
node metastasis, which demonstrated that MMP7 is associated with
cancer progression and is a tumor marker for the invasion,
metastasis and poor prognosis of GC. Therefore, it could be a
potential therapeutic target for the treatment of GC.
EGFR, a key member of the human EGFR family,
initiates downstream signaling cascades (for example, the PI3K/AKT,
STAT and MAPK pathways) upon ligand binding and phosphorylation.
These pathways notably regulate tumor cell survival, apoptosis,
invasion and metastasis (52–55).
Aberrant EGFR activation in GC is strongly implicated in the
promotion of metastatic progression (24,56).
Emerging evidence indicates that EGFR can directly modulate MMP7
transcription, as in lung cancer progression (57,58).
Using TCGA database analysis, the present study identified that the
upregulation of EGFR in GC is associated with a worse prognosis of
patients, consistent with a previous report. In addition, IHC
results suggested that p-EGFR and MMP7 were both expressed in
clinical GC samples. Notably, the present study identified that
p-EGFR and MMP7 are positively correlated in GC. To definitively
establish causality and elucidate the mechanism associating p-EGFR
with MMP7, a rigorous experimental follow-up would be required.
This would include genetic manipulation (small interfering
RNA/CRISPR) to confirm the functional necessity and sufficiency,
pharmacological inhibition to delineate the key downstream
signaling cascades (for example, MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT) and
chromatin immunoprecipitation assays to identify the transcription
factors (for example, activator protien-1 and E26
transformation-specific) that directly bind to the MMP7 promoter.
The current clinical evidence in the present study serves as a key
foundation for such targeted mechanistic studies.
Although the present study established an
association between p-EGFR and MMP7 in GC, the precise regulatory
mechanisms remain to be elucidated due to platform constraints.
Further investigation is warranted to elucidate a few points.
First, the association between p-EGFR and MMP7, although
significant in the present study, would require mechanistic
validation; whether p-EGFR directly regulates MMP7 transcription
and which specific signaling intermediates are involved remain to
be elucidated. Second, the prognostic and therapeutic potential of
this axis has not yet been fully defined. Future efforts should
focus on prospectively validating the combined p-EGFR/MMP7 profile
as a clinical biomarker for patient stratification and evaluation
of the efficacy of targeting this pathway. Lastly, the relatively
short follow-up period of the present study cohort limited a robust
overall survival analysis. Therefore, expanding the present study
to a larger, independent validation cohort with longer follow-up
period is a priority. Furthermore, investigating the potential
interplay among MMP7, p-EGFR and other upregulated proteins (for
example, collagen type I α 1 chain, ubiquitin D and cystatin 1)
would be a compelling avenue for future studies.
In summary, the present study systematically
elucidated the synergistic mechanism of p-EGFR and MMP7 in GC using
an integrated analysis of TCGA database and IHC detection of
clinical samples. The key findings were as follows: i) Significant
upregulation of both p-EGFR and MMP7 in GC tissues, which were
significantly associated with poor patient prognosis and metastatic
progression; and ii) to the best of our knowledge, IHC results
demonstrated for the first time a significant positive correlation
between p-EGFR and MMP7 expression in GC tissues. The findings not
only provide novel experimental evidence in understanding the
molecular mechanisms of GC metastasis, but, more notably, establish
the p-EGFR/MMP7 signaling axis as a potential dual target for
metastatic GC treatment, laying a key theoretical foundation for
the development of novel targeted therapies in the future.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by The Hefei Medical Research
Project (grant no. Hwk2023zc015) and The National Natural Science
Foundation of China (grant no. 81972266).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
BD and YWa conceived the present study, participated
in data analysis and drafted and wrote the manuscript. YWu, ZZ and
YM collected clinical tissue samples and conducted
immunohistochemical experiments. ZW, RJ and TL conceived the study,
led its design and contributed to the revision of the manuscript.
All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
BD, YWa, YWu, ZZ, YM, ZW, RJ and TL confirm the authenticity of all
the raw data.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was conducted in accordance with
the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional
Review Board of First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical
University (Hefei, China; approval no. 20231337). Written informed
consent was obtained from all participants involved in the
study.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
GC
|
gastric cancer
|
|
IHC
|
immunohistochemical
|
|
EGFR
|
epidermal growth factor receptor
|
|
MMPs
|
matrix metalloproteinases
|
|
ECM
|
extracellular matrix
|
|
H&E
|
hematoxylin-eosin
|
References
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smyth EC, Nilsson M, Grabsch HI, van
Grieken NC and Lordick F: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 396:635–648.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I,
Parkin DM, Pineros M, Znaor A and Bray F: Cancer statistics for the
year 2020: An overview. Int J Cancer. Apr 5–2021.doi:
10.1002/ijc.33588. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shi AN, Zhou YB and Wang GH:
Immunotherapy: Progress and challenges of a revolutionary treatment
for gastric cancer. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 63:563–567. 2025.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen J, Ji Y, Liu Y, Cen Z, Chen Y, Zhang
Y and Li X and Li X: Exhaled volatolomics profiling facilitates
personalized screening for gastric cancer. Cancer Lett.
590:2168812024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng Z, Lu J, Chen Y, Cao W and Shao Q:
The role of CD101 and Tim3 in the immune microenvironment of
gastric cancer and their potential as prognostic biomarkers. Int
Immunopharmacol. 146:1138352025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Komekbay Z, Shirazi R, Yessultanova G,
Garifollin A, Tulyayeva A, Kereyeva N, Akhmetova S and Kaliev A:
Bibliometric analysis of tumor marker application in gastric cancer
diagnosis from 2019 to 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 12:15478502025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lordick F, Carneiro F, Cascinu S, Fleitas
T, Haustermans K, Piessen G, Vogel A and Smyth EC; ESMO Guidelines
Committee. Electronic address, : simpleclinicalguidelines@esmo.org:
Gastric cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 33:1005–1120. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Bentrem DJ, Chao J,
Cooke D, Corvera C, Das P, Enzinger PC, Enzler T, Fanta P, et al:
Gastric cancer, version 2.2022, NCCN clinical practice guidelines
in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 20:167–192. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bae SH, Kim DW, Kim MS, Shin MH, Park HC
and Lim DH: Radiotherapy for gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid
tissue lymphoma: Dosimetric comparison and risk assessment of solid
secondary cancer. Radiat Oncol J. 35:78–89. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang T, Jia L, Bian S, Chang X, Zhang Q,
Tang Q, Zhu J, Yang Z and Feng Z: TROP2 Down-regulated DSG2 to
promote gastric cancer cell invasion and migration by EGFR/AKT and
DSG2/PG/β-catenin pathways. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 22:691–702.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rong L, Li Z, Leng X, Li H, Ma Y, Chen Y
and Song F: Salidroside induces apoptosis and protective autophagy
in human gastric cancer AGS cells through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 122:1097262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kang X, Xu E, Wang X, Qian L, Yang Z, Yu
H, Wang C, Ren C, Wang Y, Lu X, et al: Tenascin-c knockdown
suppresses vasculogenic mimicry of gastric cancer by inhibiting
ERK-triggered EMT. Cell Death Dis. 12:8902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang YL, Liu P, Li D, Yang Q, Li B and
Jiang XJ: Stat-3 signaling promotes cell proliferation and
metastasis of gastric cancer through PDCD4 downregulation.
Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 36:244–249. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schlessinger J: Receptor tyrosine kinases:
Legacy of the first two decades. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
6:a0089122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Masuda H, Zhang D, Bartholomeusz C,
Doihara H, Hortobagyi GN and Ueno NT: Role of epidermal growth
factor receptor in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
136:331–345. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo D, Liu Y, Lu Z and Huang L: Targeted
therapy and immunotherapy for gastric cancer: Rational strategies,
novel advancements, challenges, and future perspectives. Mol Med.
31:522025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li S, Sun M, Cui Y, Guo D, Yang F, Sun Q,
Ding Y, Li M, Liu Y, Ou G, et al: Ephrin A1 functions as a ligand
of EGFR to promote EMT and metastasis in gastric cancer. EMBO J.
44:1464–1487. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ametller E, Garcia-Recio S, Pastor-Arroyo
EM, Callejo G, Carbo N, Gascon P and Almendro V: Differential
regulation of MMP7 in colon cancer cells resistant and sensitive to
oxaliplatin-induced cell death. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:4–13. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shen H, He M, Lin R, Zhan M, Xu S, Huang
X, Xu C, Chen W, Yao Y, Mohan M and Wang J: PLEK2 promotes
gallbladder cancer invasion and metastasis through EGFR/CCL2
pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:2472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou Z, Zhang Z, Chen H, Bao W, Kuang X,
Zhou P, Gao Z, Li D, Xie X, Yang C, et al: SBSN drives bladder
cancer metastasis via EGFR/SRC/STAT3 signalling. Br J Cancer.
127:211–222. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mittal S, Kamath A, Joseph AM and Rajala
MS: PLCgamma1-dependent invasion and migration of cells expressing
NSCLC-associated EGFR mutants. Int J Oncol. 57:989–1000.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lei ZN, Teng QX, Tian Q, Chen W, Xie Y, Wu
K, Zeng Q, Zeng L, Pan Y, Chen ZS and He Y: Signaling pathways and
therapeutic interventions in gastric cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 7:3582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cao T, Lu Y, Wang Q, Qin H, Li H, Guo H,
Ge M, Glass SE, Singh B, Zhang W, et al: A CGA/EGFR/GATA2 positive
feedback circuit confers chemoresistance in gastric cancer. J Clin
Invest. 132:e1540742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Huang L, Li L, Chen L, Chen P and
Chen X: The evaluation of gastric cancer lymphovascular invasion
using CT volume perfusion. Discov Med. 36:2037–2045. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu C, Xu J, Zhang Y, Zhang R, Pan S, Chen
J, Wang Y, Zhao Q, Wang Y, Zhu W, et al: Inhibition of glutathione
peroxidase 4 suppresses gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via
regulation of RCC2 homeostasis. Redox Biol. 80:1035192025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baghbanzadeh A, Rahmani S, Eslami S,
Ahmadpour Youshanlui M, Shafiee N, Shafiee A, Khalaji A and
Baradaran B: miR-146a-5p suppresses migration and downregulates
vimentin and MMP-9 expression in gastric cancer cells. Discov
Oncol. 16:10752025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
El-Sayed SF, Mahmoud SM, Samy W, Wahid RM,
Talaat A and Seada SG: Vitamin D3 mitigates aspirin-induced gastric
injury by modulating gastrokines, E-cadherin, and inhibiting NLRP3
and NF-κB/MMP-9 signaling pathway. Tissue Cell. 93:1027242025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wattanawongdon W, Bartpho TS and Tongtawee
T: Expression of matrix Metalloproteinase-7 predicts poor prognosis
in gastric cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2022:23009792022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yueh TC, Tsao HY, Chien WC, Tsai CW, Pei
JS, Wu MH, Chen CP, Chen CC, Wang ZH, Mong MC, et al: The
contribution of matrix Metalloproteinase-7 promoter genotypes to
hepatocellular carcinoma susceptibility. Anticancer Res.
42:5275–5282. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen L and Ke X: MMP7 as a potential
biomarker of colon cancer and its prognostic value by
bioinformatics analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 100:e249532021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu L, Ma GQ, Liu XD, Sun RR, Wang Q, Liu M
and Zhang PY: Correlation between GDF15, MMP7 and gastric cancer
and its prognosis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:535–541.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nakatani K, Yamaoka T, Ohba M, Fujita KI,
Arata S, Kusumoto S, Taki-Takemoto I, Kamei D, Iwai S, Tsurutani J,
et al: KRAS and EGFR amplifications mediate resistance to
rociletinib and osimertinib in acquired Afatinib-resistant NSCLC
harboring exon 19 deletion/T790M in EGFR. Mol Cancer Ther.
18:112–126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gao S, Luan Y, Yu X, Wang L, Huang X, Yang
J and Liu W: TAIII suppresses the growth of T790M-mutant
non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting the EGFR/ERK signaling
pathway. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 18:14312025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang L, Lu YF, Wang CS, Xie YX, Zhao YQ,
Qian YC, Liu WT, Wang M and Jiang BH: HB-EGF activates the
EGFR/HIF-1α pathway to induce proliferation of Arsenic-transformed
cells and tumor growth. Front Oncol. 10:10192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Daum O, Daumova M and Svajdler M: Comments
on the 5th edition of WHO classification of digestive system
tumors-Part 1. Gastrointestinal tract. Cesk Patol. 56:194–206.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qiu S, Wang Q, Jiang H and Feng L:
Immunohistochemistry staining of Eag1 and p16/Ki-67 can help
improve the management of patients with cervical intraepithelial
Neoplasia after cold knife conversion. Diagn Pathol. 19:972024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang T, Du A, Peng Y, Yin J, Sun G, Yu Y,
Sun Z, Chang Q, Gong K, Han S, et al: DSG3 promotes bladder cancer
growth and metastasis via AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. J Transl
Med. 23:7292025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bai T, Li P, Liu Y, Cai B, Li G, Wang W,
Yan R, Zheng X and Du S: Knockdown of miR-411-3p induces M2
macrophage polarization and promotes colorectal cancer progression
by regulation of MMP7. Eur J Histochem. 69:41782025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hirohama D, Abedini A, Moon S, Surapaneni
A, Dillon ST, Vassalotti A, Liu H, Doke T, Martinez V, Md Dom Z, et
al: Unbiased human kidney tissue proteomics identifies matrix
metalloproteinase 7 as a Kidney disease biomarker. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 34:1279–1291. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu G, Jiang C, Li D, Wang R and Wang W:
MiRNA-34a inhibits EGFR-signaling-dependent MMP7 activation in
gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:9801–9806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Morgan E, Arnold M, Camargo MC, Gini A,
Kunzmann AT, Matsuda T, Meheus F, Verhoeven RHA, Vignat J,
Laversanne M, et al: The current and future incidence and mortality
of gastric cancer in 185 countries, 2020-40: A population-based
modelling study. EClinicalMedicine. 47:1014042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ge X, Lin F, Wu Z, Lin Y, Tang W, McKay
MJ, Sahu A, Lino-Silva LS, Tseng J and Li J: Role of ROR2 in
promoting gastric cancer metastasis by enhancing c-JUN-mediated
MMP3 transcription. Ann Transl Med. 10:11172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu HQ, Song S, Wang JH and Zhang SL:
Expression of MMP-3 and TIMP-3 in gastric cancer tissue and its
clinical significance. Oncol Lett. 2:1319–1322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dong Z, Guo S, Wang Y, Zhang J, Luo H,
Zheng G, Yang D, Zhang T, Yan L, Song L, et al: USP19 Enhances
MMP2/MMP9-mediated tumorigenesis in gastric cancer. Onco Targets
Ther. 13:8495–8510. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang HL, Zhou PY, Zhang Y and Liu P:
Relationships between abnormal MMP2 expression and prognosis in
gastric cancer: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Cancer Biother
Radiopharm. 29:166–172. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Choi EK, Kim HD, Park EJ, Song SY, Phan
TT, Nam M, Kim M, Kim DU and Hoe KL: 8-Methoxypsoralen induces
apoptosis by upregulating p53 and inhibits metastasis by
downregulating MMP-2 and MMP-9 in human gastric cancer cells.
Biomol Ther (Seoul). 31:219–226. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li T, Cao H, Wu S, Zhong P, Ding J, Wang
J, Wang F, He Z and Huang GL: Phosphorylated ATF1 at Thr184
promotes metastasis and regulates MMP2 expression in gastric
cancer. J Transl Med. 20:1692022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tregunna R: Serum MMP7 levels could guide
metastatic therapy for prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 17:6582020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sizemore ST, Sizemore GM, Booth CN,
Thompson CL, Silverman P, Bebek G, Abdul-Karim FW, Avril S and Keri
RA: Hypomethylation of the MMP7 promoter and increased expression
of MMP7 distinguishes the basal-like breast cancer subtype from
other triple-negative tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 146:25–40.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gao Y, Nan X, Shi X, Mu X, Liu B, Zhu H,
Yao B, Liu X, Yang T, Hu Y, et al: SREBP1 promotes the invasion of
colorectal cancer accompanied upregulation of MMP7 expression and
NF-κB pathway activation. BMC Cancer. 19:6852019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Janecka-Widla A, Majchrzyk K,
Mucha-Malecka A and Biesaga B: EGFR/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in head
and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients with different HPV
status. Pol J Pathol. 72:296–314. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lu X, An L, Fan G, Zang L, Huang W, Li J,
Liu J, Ge W, Huang Y, Xu J, et al: EGFR signaling promotes nuclear
translocation of plasma membrane protein TSPAN8 to enhance tumor
progression via STAT3-mediated transcription. Cell Res. 32:359–374.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Greenspan LJ, de Cuevas M, Le KH, Viveiros
JM and Matunis EL: Activation of the EGFR/MAPK pathway drives
transdifferentiation of quiescent niche cells to stem cells in the
Drosophila testis niche. Elife. 11:e708102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liang N, Bing Z, Wang Y, Liu X, Guo C, Cao
L, Xu Y, Song Y, Gao C, Tian Z, et al: Clinical implications of
EGFR-associated MAPK/ERK pathway in multiple primary lung cancer.
Clin Transl Med. 12:e8472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yu J, Fang T, Yun C, Liu X and Cai X:
Antibody-drug conjugates targeting the human epidermal growth
factor receptor family in cancers. Front Mol Biosci. 9:8478352022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hu DD, Chen HL, Lou LM, Zhang H and Yang
GL: SKA3 promotes lung adenocarcinoma metastasis through the
EGFR-PI3K-Akt axis. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR201943352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chang CH, Chen MC, Chiu TH, Li YH, Yu WC,
Liao WL, Oner M, Yu CR, Wu CC, Yang TY, et al: Arecoline promotes
migration of A549 lung cancer cells through activating the
EGFR/Src/FAK pathway. Toxins (Basel). 11:1852019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|