Introduction
The World Health Organization (WHO) predicts that
lung cancer will become the leading cause of death not only among
cancers, but also all diseases by 2060 (1). The most common type of epithelial lung
cancer is non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), including lung
adenocarcinoma (LADC), which accounts for ~85% of all lung cancer
diagnoses (2). Although our
understanding of the epidemiology of lung cancer and the
development of strategies for its prevention have advanced in the
past 10 years, it is still the primary cause of cancer-related
death regardless of sex and age (3). The diagnosis of lung cancer in its
early stages continues to be a challenge because numerous
techniques and methodologies currently in use, such as low-dose CT,
X-rays, sputum examinations, bronchoscopy and lung tissue biopsies,
are often only effective at detecting cancer in its advanced stage
(4).
NSCLC exhibits a complex genomic landscape, with
various genetic and epigenetic mechanisms being implicated in its
development, and it has diverse genomic alterations (5). Tumor protein p53 and LDL receptor
related protein 1B mutations are prevalent across all subtypes of
NSCLC. However, LADC shows higher rates of somatic mutations in
genes, such as Kirsten rat sarcoma (RAS) viral oncogene homolog,
EGFR, Kelch-like ECH associated protein 1, serine/threonine kinase
11, mesenchymal epithelial transition factor receptor, V-Raf murine
sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, anaplastic lymphoma kinase, human
EGFR2, Ret proto-oncogene and Ros proto-oncogene 1, receptor
tyrosine kinase. These mutations primarily affect the RAS-MAPK
kinase-ERK, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase
catalytic subunit alpha-mTOR and MAPK pathways (6–10).
Epigenetic changes, including DNA methylation, are
present in all human cancers and contribute not only to the
initiation, but also the progression of diseases, particularly
cancer (11). Hypermethylation
silences critical tumor suppressor genes or regulatory regions
within the genome. This silencing may lead to the dysregulation of
cell proliferation or modify responses to cancer therapy (12).
The hypermethylation of numerous genes has been
reported in numerous cases of lung cancer, with the majority being
detected in promoter sequences (13,14).
Genes such as cyclin-dependent kinase-2, adenomatous polyposis
coli, cadherin-13, p16 (also known as cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitor 2A) and Ras-association domain family protein1 isoform A
are hypermethylated, and this methylation has been linked to a
higher likelihood of relapse after the surgical resection of stage
I NSCLC (15,16). Previous studies by our group
revealed that the hypermethylation of the glutamate decarboxylase 1
and dipeptidyl protease-like 6 genes was associated with poor
outcomes in patients with LADC (17,18).
Therefore, DNA methylation may contribute to the development of
biomarkers to detect cancer in the early stages and predict patient
outcomes.
In a previous study by our group, the paired
tumorous and non-tumorous tissues of 12 LADC samples were subjected
to genome-wide screening for aberrantly methylated CpG islands
(CGIs), and the top 10 significantly methylated genes were listed,
including zinc finger protein (ZNF)577 (19). Individual gene studies were then
performed to examine the methylation and expression of ZNF577 and
their relationships with the clinical characteristics of patients.
However, only a small number of studies have examined ZNF577,
particularly in lung cancer (13),
and therefore, further research is needed.
ZNF577 belongs to the Krüppel-associated box (KRAB)
C2H2-type ZNF family (20). ZNFs have a crucial role in the
regulation of gene transcription (21,22).
While the specific function of ZNF577 remains unclear and requires
further investigation, other individual ZNFs are frequently
subjected to hypermethylation and subsequent silencing in various
types of tumors. These findings indicate that the disrupted
epigenetic pathway involving ZNFs is a common occurrence in cancer
progression (22).
Numerous studies have recognized specific ZNFs as
potential tumor suppressors that are responsible for controlling
cellular proliferation through the inhibition of MAPK signaling and
the repression of various oncogenes (23). Oxidative stress is a potential
mechanism contributing to the hypermethylation of ZNFs during
malignant transformation because it disrupts the interaction
between CCCTC-binding factor and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1,
consequently leading to increases in DNA methylation (24).
To assess the potential of ZNF577 as a
prognostic marker for LADC, the present study set out to
investigate its DNA methylation, gene expression and tissue
expression in resected LADC tissues.
Materials and methods
Patients and tissue samples
The present study was conducted using a
retrospective, observational design. A total of 149 LADC tumor
samples and 27 paired tumor-matched normal lung tissue samples were
acquired from patients surgically treated at Tokushima University
Hospital (Tokushima, Japan) between April 1999 and November 2013.
Tissue samples were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen and then stored
at −80°C for the later extraction of DNA and RNA. All samples were
subjected to an IHC analysis to detect tissue expression of ZNF577.
Of the 149 samples, 73 tumor and 27 paired tumor-matched samples
were examined by methylation analysis and reverse
transcription-quantitative (RT-q)PCR. The 7th edition of the
tumor-nodes-metastasis classification for lung cancer was used to
grade the stages of tumors in samples (25). Tumors were also categorized
according to the predominant histological subtype proposed by the
2015 WHO classification (26). A
total of 162 patients with LADC were followed up for a mean
duration of 48 months (range, 0.6–147 months). Recurrence was
detected in 45 patients (27.8%) and there were 34 deaths (21.0%).
The patients' age ranged from 43 to 84 years, with a median age of
66 years.
The present study was approved by The Ethics
Committee of the University of Tokushima (Tokushima University
Hospital, Tokushima, Japan; approval no. 4071-1) and procedures
were performed in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of
Helsinki. Written informed consent, which included the key elements
of a research study and what their participation will involve, was
obtained from all patients.
Global methylation analysis
In a previous study by our group to detect
aberrantly methylated CGIs in a genome-wide manner (18), 12 paired tumorous/non-tumorous LADC
sample sets from freshly frozen specimens were screened using the
Illumina HumanMethylation450 K Bead Chip (Illumina, Inc.). The
findings obtained revealed 17 differentially hypermethylated CGI
sites in the ZNF577 gene. The false discovery rate was
<0.05 and the β difference (tumor vs. non-tumorous tissue) was
>0.22. CGI sites in ZNF577 ranked 3rd amongst
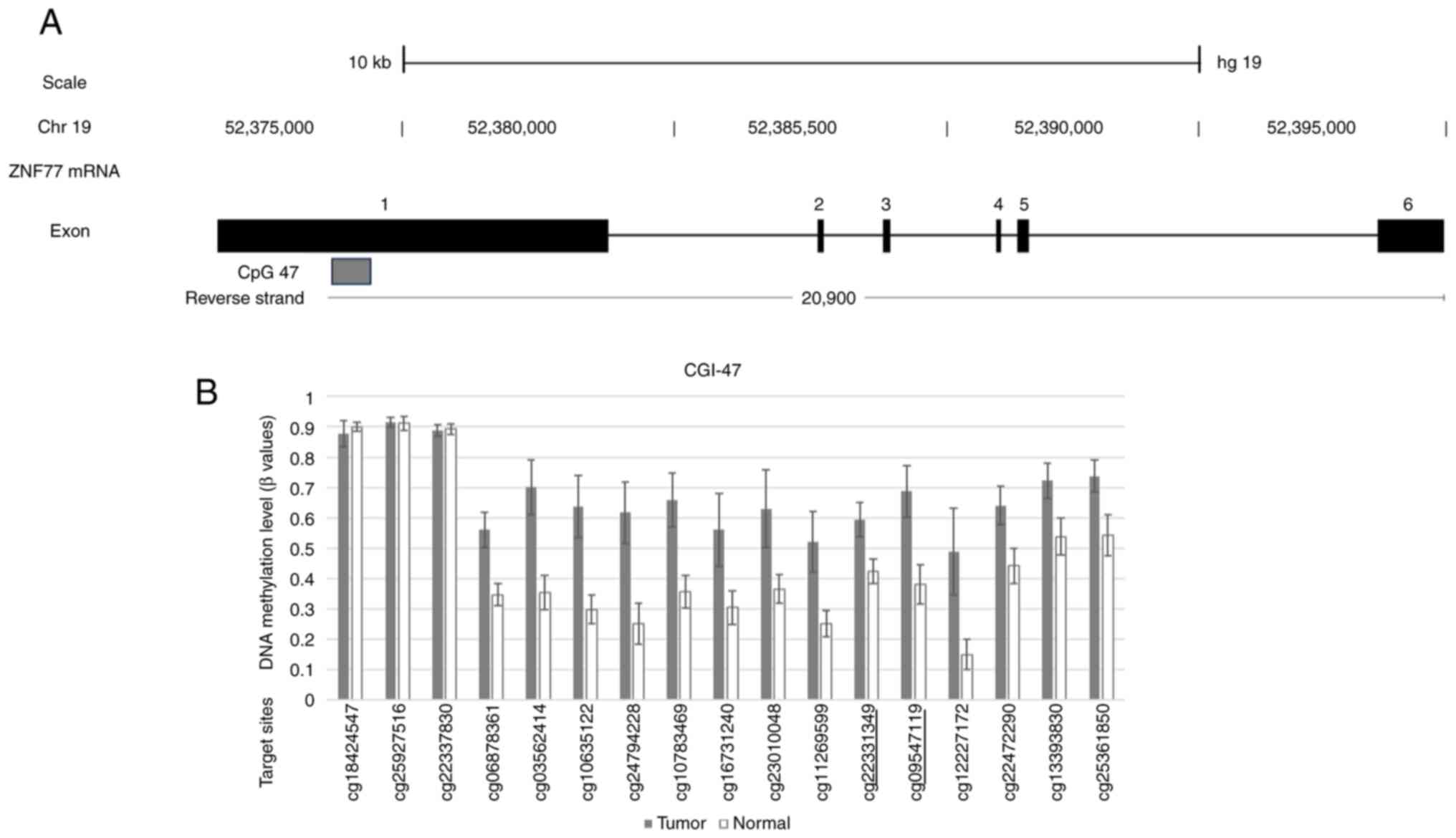
differentially methylated CGIs with a low P-value. Fig. 1A shows a schematic of the mRNA
structure of ZNF577. Among the 6 (4 coding and 2 non-coding)
exons of ZNF577 mRNA, CGIs were located around exon 1. The
array-based methylation status of each CpG site within
ZNF577 is shown in Fig. 1B.
Two DNA methylation sites in CpG47 of the ZNF577 gene,
cg09547119 and cg22331349, which were underlined, were subsequently
analyzed.
Nucleic acid isolation
The QIAamp DNA Mini Kitand RNeasy Mini kit (Qiagen
GmbH) were used to isolate DNA and RNA from frozen tissue,
respectively, using the protocols described by the
manufacturer.
Bisulfite conversion and
pyrosequencing
The EpiTect Bisulfite Kit 48 (Qiagen GmbH) was used
to convert genomic DNA to bisulfite according to the manufacturer's
protocols. Prior to pyrosequencing, the PyroMark PCR-Kit 200
(Qiagen GmbH) was used according to the manufacturer's protocols to
amplify the transformed DNA by PCR using the following primers:
Forward, 5′-GGGAAGTTTGTTGGGAGTAGTTAT-3′ and reverse,
(Biotin)-5′-ATATTACAAAACCAAAATCTAACAATTCAC-3′ (target sequence
before bisulfite treatment: Forward,
5′-CCTACTGCCGTAGAGCAGGCGGAGTCCCTCTTTTCGCGCCTTAGACAGGTTCTG A-3′ and
reverse,
3′-CCTACTACTGCCGTAGAGCAGGCGGAGTCCCTCTTTTCGCGCCTTAAGACAGGTAGGTTCTGA-5′).
The ZNF577 PyroMark Custom Assay Design 2.0 (Qiagen
GmbH) was employed to develop the following sequencing primer
according to the manufacturer's intstructuions:
5′-GTTGGGAGTAGTTATTTTTAAT-3′.
In order to assess the mean methylation rate of CpG
sites, pyrosequencing was conducted using PSQ 96MA (Qiagen GmbH)
according to the manufacturer's protocols. PyroQ-CpG 1.0.9 was used
to calculate the methylation rate at each CpG.
RT-qPCR
iScript™ Reverse Transcription Supermix
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) was used for RT. Real-time PCR was
conducted with SsoAdvanced Universal SYBR® Green
Supermix (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.) and the PrimePCR™
SYBR® Green Assay (cat. no. 10025716; Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.) for ZNF577 and GAPDH (cat. no. 10025637;
Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). The internal control gene was
GAPDH. All the reagents were used and reactions were
performed according to the manufacturer's protocols. The
quantification of qPCR data was performed according the
2−ΔΔCq method (27).
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
IHC staining was performed on paraffin-embedded
sections using anti-ZNF577 rabbit polyclonal antibodies (cat. no.
HPA046761; 1:50 dilution; Atlas Antibodies) overnight at 4°C. The
tissue samples were incubated at room temperature for 1 h with
EnVision + Dual Link System-HRP secondary antibody (cat. no. K4063;
Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc.). Antigen retrieval was conducted
by heating dewaxed and dehydrated sections in Dako Real Target
Retrieval Solution (Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc.), pH 9 at 98°C
for 30 min. A total of 149 tumor samples were analyzed, excluding
positive control and normal tissues. IHC images were evaluated and
grouped as follows: Negative (intensity: Not stained or weakly
stained in a small area) or positive (intensity: Moderate to strong
with ≥30% area).
Statistical analysis
Comparisons between paired samples, when data were
and were not normally distributed, were performed using the paired
t-test and the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, respectively. The
relationships between methylation and mRNA expression levels and
clinical characteristics, including tumor stage, histological
patterns, smoking history, blood vessel invasion, lymph vessel
invasion, pleural invasion and lymph node metastasis, were
investigated using the unpaired t-test for normally distributed
data and the Mann-Whitney U-test for data that were not normally
distributed. One-way analysis of variance was employed for
multiple-group comparisons and was followed by Tukey's
multiple-comparisons test for normally distributed data and the
Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple-comparisons test
for non-normally distributed data. Overall survival (OS) and
disease-free survival (DFS) rates were compared between high/low
methylation, high/low mRNA expression and ZNF577 negative/positive
expression using Kaplan-Meier analysis with the log-rank
(Mantel-Cox) test. Cut-off values were selected from receiver
operating characteristic (ROC) curves. Multivariate survival
analyses were performed using the likelihood ratio test of the
stratified Cox proportional hazard regression analysis. GraphPad
Prism version 5.00 (GraphPad; Dotmatics) and SPSS (version 24.0;
IBM Corp.) were used for all statistical analyses.
Results
Patient characteristics
Table I shows the
clinical characteristics of the 73 patients with LADC examined by
PCR and methylation analysis, including survival data, and their
basic characteristics, such as sex (male, 52%; female, 47.9%), age
at diagnosis (66.3±9.7 years; range, 43–84 years). The clinical
characteristics of the 149 patients with LADC evaluated by IHC,
including survival data, and their basic characteristics, such as
sex (male, 45%; female, 55%), age at diagnosis (66.9±9.1 years;
range, 43–84 years) are provided in Table SI.
 | Table I.Patient characteristics (n=73). |
Table I.
Patient characteristics (n=73).
| Item | Value |
|---|
| Sex |
|
|
Male | 38 (52.0) |
|
Female | 35 (47.9) |
| Age, years | 66.3±9.7 (43–84) |
| Smoking status |
|
|
Non-smoker | 36 (49.3) |
|
Smoker | 37 (50.6) |
| Brinkman
indexa | 381.3±501.8 |
| Pathology |
|
|
Lepidic | 26 (35.6) |
|
Papillary | 26 (35.6) |
|
Solid | 3 (4.1) |
|
Acinar | 5 (6.8) |
| Mixed
or others | 13 (17.8) |
| Surgery |
|
|
Pneumonectomy | 1 (1.36) |
|
Lobectomy | 68 (93.1) |
|
Segmentectomy | 1 (1.36) |
|
Lobectomy + segmentectomy | 3 (4.1) |
|
Complete resection | 73 (100) |
| Preoperative
chemotherapy | 1 (1.4) |
| Postoperative
chemotherapy | 20 (27.4) |
|
Cisplatin-based | 6 |
|
UFT | 13 |
|
Other | 1 |
| Pathological
stageb |
|
| IA | 38 (52.1) |
| IB | 20 (27.4) |
|
IIA | 9 (12.3) |
|
IIB | 4 (5.5) |
|
III | 2 (2.7) |
| pN factor |
|
| 0 | 65 (89.0) |
| 1 | 6 (8.2) |
| 2 | 2 (2.7) |
| Pl
factor-positive | 14 (19.1) |
| V factor-positive
(n=72) | 12 (16.6) |
| Ly
factor-positive | 12 (16.4) |
| EGFR mutation
(n=25) | 11 (44) |
ZNF577 methylation and mRNA expression
levels in LADC tissues and paired normal tissues
ZNF577 methylation and mRNA expression levels
in LADC tissues were assessed in comparison with 27 matched
samples. ZNF577 methylation levels in LADC and normal lung
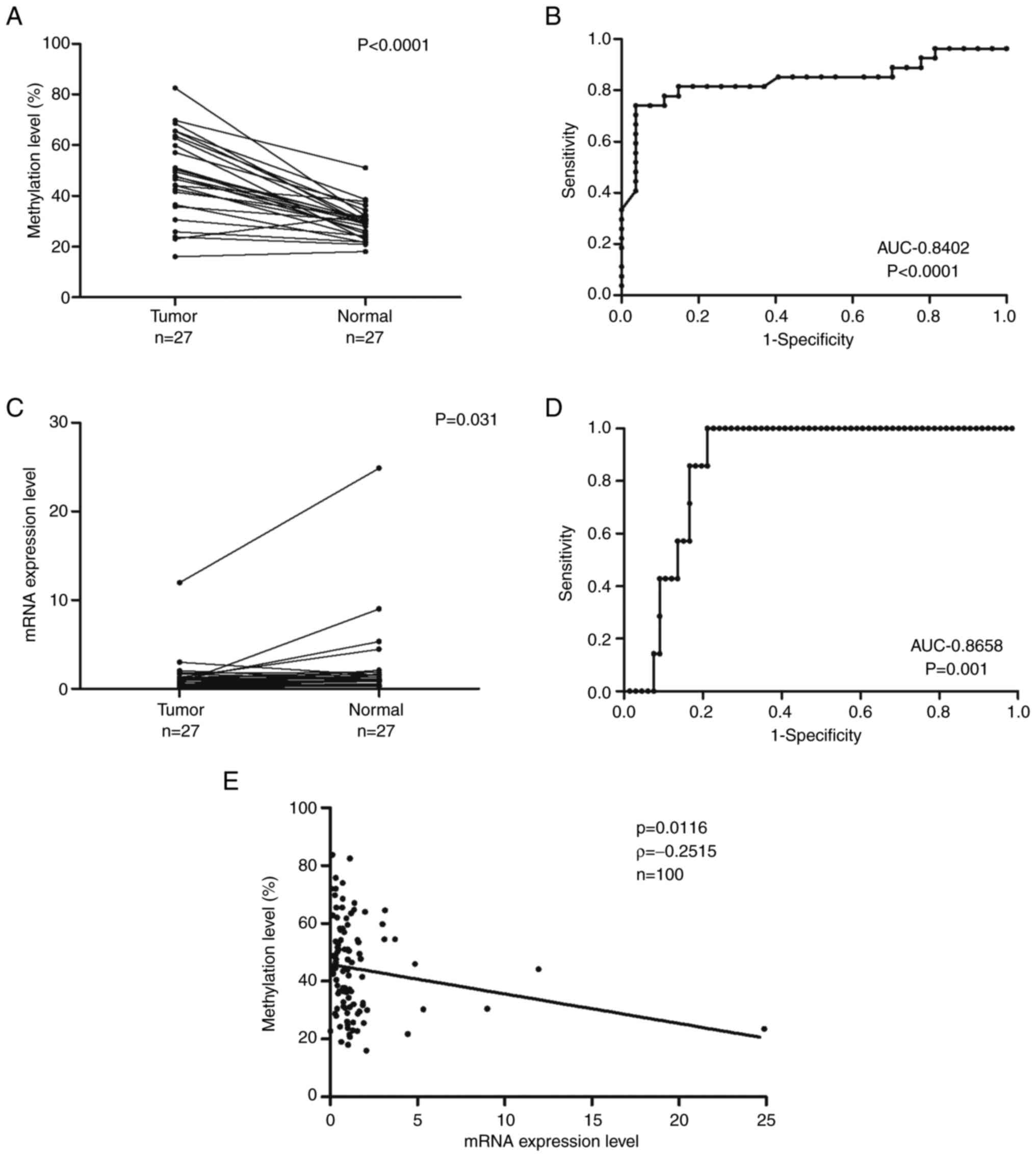
tissues are presented in Fig. 2A.
Tumor samples had significantly higher DNA methylation levels than
normal samples (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P<0.0001). ROC curves
were used to evaluate the ability of ZNF577 methylation levels and
mRNA expression levels to discriminate tumor tissue from non-tumor
tissue. Fig. 2B presents the ROC
for methylation levels between tumor and normal samples with an
area under the curve (AUC) of 0.8402. ZNF577 mRNA expression
levels in LADC and normal lung tissues are shown in Fig. 2C. Tumor samples had significantly
lower mRNA expression levels than normal samples (Wilcoxon
signed-rank test, P<0.031). Fig.
2D shows the ROC for ZNF577 mRNA expression levels in
tumor and normal samples with an AUC of 0.8658.
Spearman's rank correlation analysis was used to
investigate the relationship between ZNF577 DNA methylation
and mRNA expression levels in 100 samples (73 tumors and 27 normal
tissues) (Fig. 2E). The results
obtained showed that methylation levels were inversely correlated
with mRNA expression levels (P=0.0116, ρ=−0.2515).
Relationship between ZNF577
methylation and mRNA expression levels and clinical characteristics
of patients with LADC
To establish whether the malignancy and progression
of LADC were affected by the hypermethylation of ZNF577, the
methylation and mRNA expression levels were measured in 73 samples
and compared with histology patterns and stage grading.
The IA group had slightly lower ZNF577
methylation levels than the other, advanced-stage groups but it was
not statistically significant. Furthermore, the IA group had
significantly higher ZNF577 mRNA expression levels
(Mann-Whitney U-test, P=0.0184; Fig. 3A
and B). Samples with the lepidic pattern had significantly
lower ZNF577 methylation levels than those with the other
patterns (unpaired t-test, P=0.0217; Fig. 3C). However, ZNF577 mRNA
expression levels did not significantly differ between samples with
the lepidic and other histological patterns (Mann-Whitney U-test;
Fig. 3D).
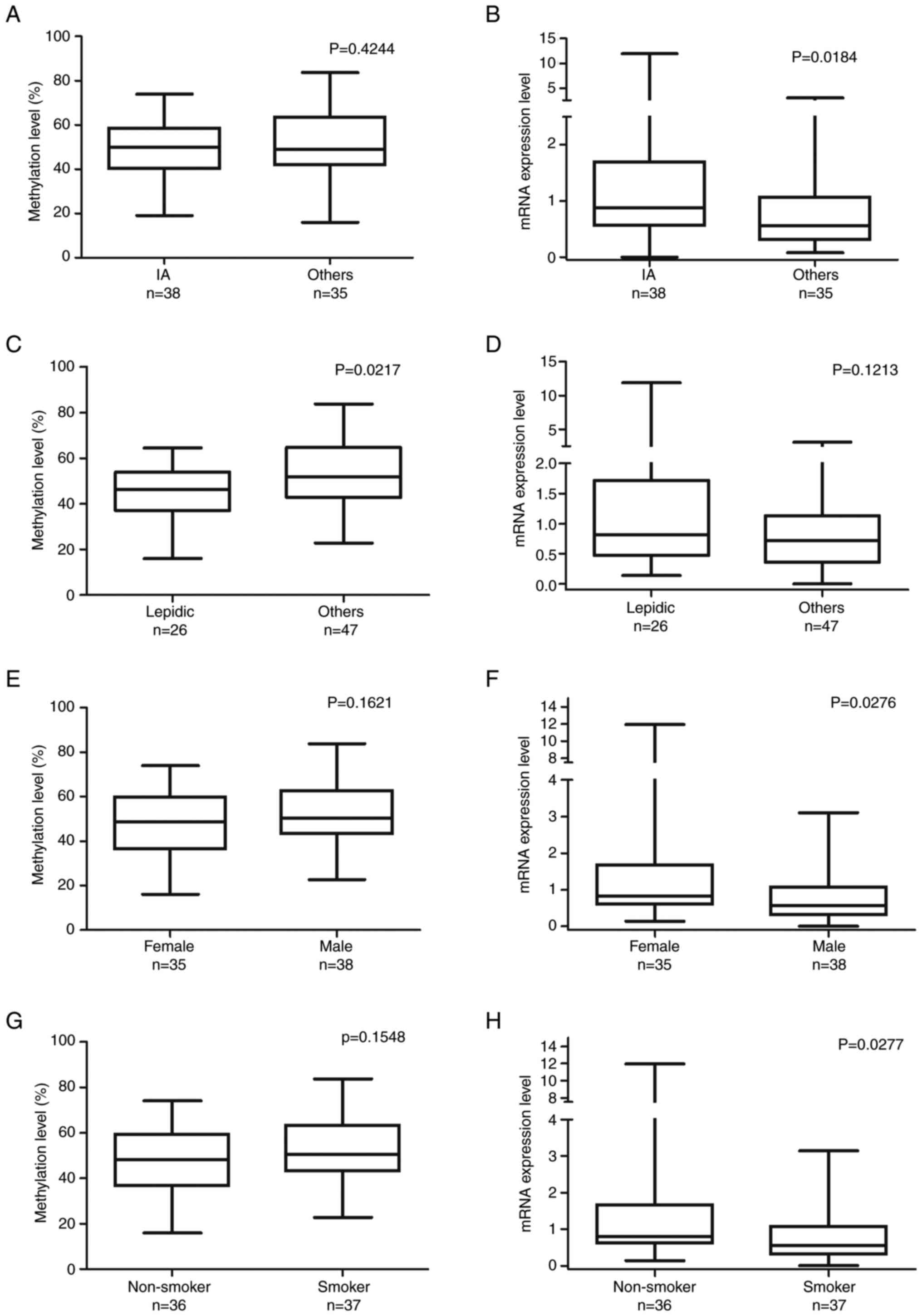 | Figure 3.Comparison of ZNF577 DNA methylation
and mRNA expression levels with patient characteristics. ZNF577
methylation and mRNA expression levels were analyzed in lung
adenocarcinoma tumor samples (n=73) using pyrosequencing and
reverse transcription-quantitative PCR, respectively. (A) ZNF577
methylation (%) and (B) mRNA expression levels in lung cancer
stages categorized by the World Health Organization histological
classification (IA, n=38; others: IB, n=21; IIA, n=9; IIB, n=4;
IIIA, n=1). (C) ZNF577 methylation (%) and (D) mRNA expression
levels in lung cancer with different histological patterns
(lepidic, n=26; others: Papillary, n=26; acinar, n=5; solid, n=3;
mixed, n=13). (E) ZNF577 methylation (%) and (F) mRNA expression
levels according to sex. (G) ZNF577 methylation (%) and (H) mRNA
expression levels according to smoking status. ZNF, zinc finger
protein. |
To examine differences in the hypermethylation and
mRNA expression levels of ZNF577 between the sexes and
individuals with different smoking statuses, methylation and mRNA
expression levels were assessed in 73 samples. ZNF577
methylation levels were slightly lower in females (unpaired t-test,
P=0.1621) and non-smokers (unpaired t-test, P=0.1548; Fig. 3E and F) but the differences were not
statistically significant. However, mRNA expression levels of
ZNF577 were significantly higher in females (Mann-Whitney
U-test, P=0.0276) and non-smokers (Mann-Whitney U-test, P=0.0277;
Fig. 3G and H).
Prognostic value of mRNA expression
and methylation levels of the ZNF577 gene in LADC
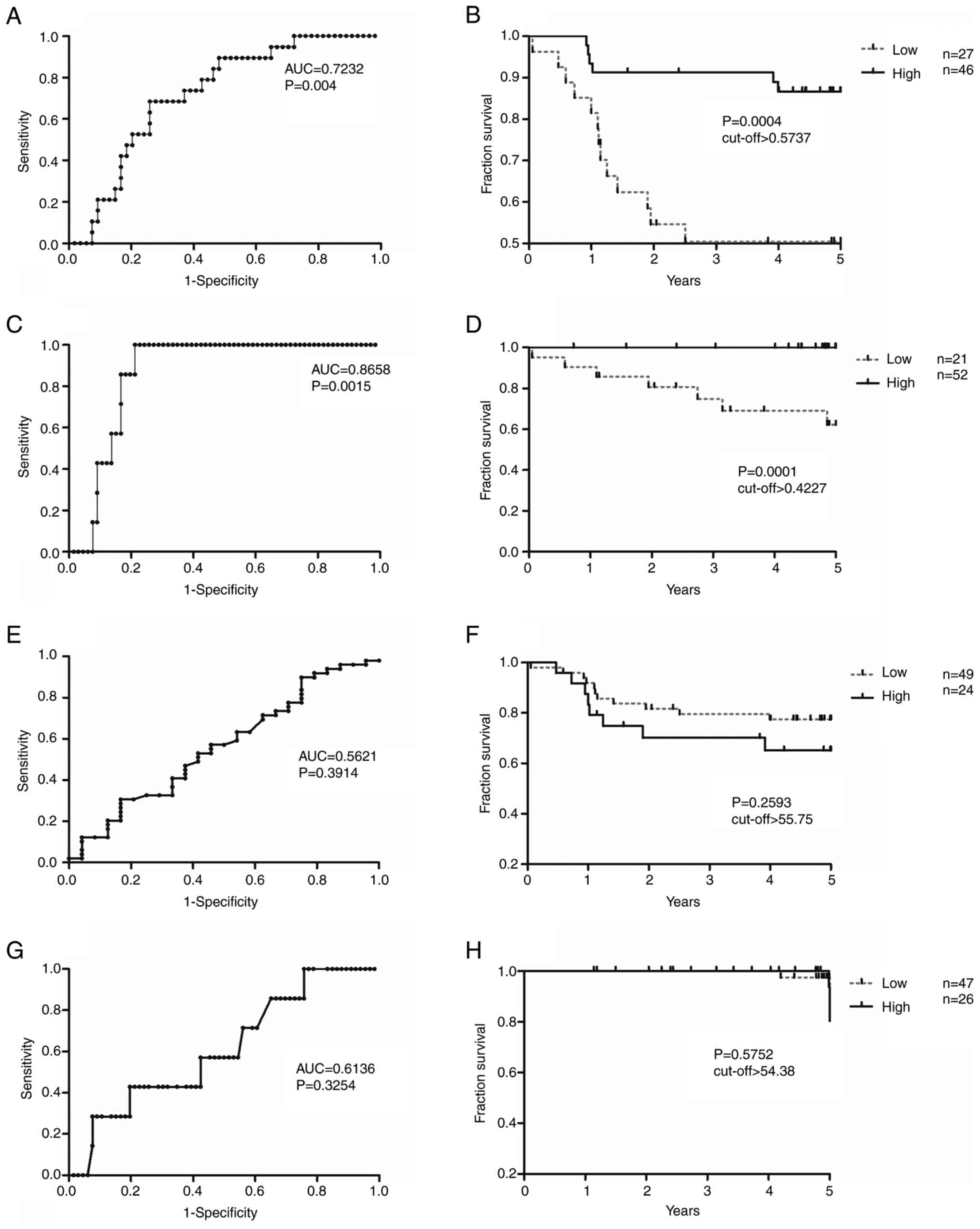
DFS and OS analyses of ZNF577 mRNA expression
and methylation levels were conducted (Fig. 4). Cut-off values obtained from ROC
curves were used to divide samples into those with high/low
expression and high/low methylation levels (Fig. 4A, C, E and G). Samples with high
ZNF577 mRNA expression levels had significantly higher DFS
and OS rates than those with low levels [DFS: Area under the ROC
curve (AUC)=0.7232; log-rank P=0.0004; cut-off value, 0.5737; and
OS: AUC=0.8658; log-rank P=0.0001; cut-off value, 0.4227; Fig. 4A-D]. However, no significant
differences were observed in DFS or OS between samples with high
and low ZNF577 methylation levels (DFS: Log-rank P=0.2593;
cut-off value, 55.75; and OS: Log-rank P=0.5752; cut-off value,
54.38) (Fig. 4E-H).
In the multivariate Cox regression analysis, ZNF577
mRNA expression levels [hazard ratio (HR): 3.917; 95% CI:
1.212–12.66; P=0.023], tumor stage (IA vs. others; HR: 0.159; 95%
CI: 0.041–0.612; P=0.007), smoking status (HR: 13.740: 95% CI:
1.778–106.1; P=0.012) and lymphovascular invasion (No vs. Yes; HR:
0.180; 95% CI: 0.037–0.888; P=0.035) were identified as independent
prognostic factors for DFS (Table
IIA). Patient age (HR: 0.022; 95% CI: 0.001–0.667; P=0.028),
tumor stage IA vs. others; HR: 0.021; 95% CI: 0.000–0.960; P=0.048)
and lymphovascular invasion (No vs. Yes; HR: 0.005; 95% CI:
0.000–0.729; P=0.037) were identified as independent prognostic
factors for OS (Table IIB).
 | Table II.Cox proportional hazard regression
analysis of DFS and OS in patients with lung adenocarcinoma
(n=73). |
Table II.
Cox proportional hazard regression
analysis of DFS and OS in patients with lung adenocarcinoma
(n=73).
| A, Disease-free
survival |
|---|
|
|---|
|
| Multivariate
analysis |
|---|
|
|
|
|---|
| Factor | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|
| Sex, female (n=35)
vs. male (n=38) | 0.264 | 0.043–1.605 | 0.148 |
| Age <67 (n=43)
vs. ≥67 (n=30) years | 0.364 | 0.106–1.253 | 0.109 |
| Smoking, smoker
(n=37) vs. non-smoker (n=36) | 13.740 | 1.778–106.1 | 0.012 |
| Stagea, IA (n=38) vs. others (n=35) | 0.159 | 0.041–0.612 | 0.007 |
| Metastasis, No
(n=65) vs. Yes (n=8) | 0.270 | 0.066–1.103 | 0.068 |
| LVI, No (n=61) vs.
Yes (n=12) | 0.180 | 0.037–0.888 | 0.035 |
| Pathology, lepidic
(n=26) vs. others (n=47) | 0.894 | 0.227–3.517 | 0.873 |
| ZNF577 mRNA
expression, Low (n=37) vs. High (n=36) | 3.917 | 1.212–12.660 | 0.023 |
| ZNF577 DNA
methylation, Low (n=36) vs. High (n=37) | 0.932 | 0.336–2.580 | 0.892 |
|
| B, OS |
|
| Sex, female (n=35)
vs. male (n=38) | 0.014 | 0.000–2.048 | 0.093 |
| Age,<67 (n=43)
vs. ≥67 (n=30) years | 0.022 | 0.001–0.667 | 0.028 |
| Smoking, smoker
(n=37) vs. smoker (n=36) | 356.2 | 0.802–158303 | 0.059 |
| Stagea, IA (n=38) vs. others (n=35) | 0.021 | 0.000–0.960 | 0.048 |
| Metastasis, No
(n=65) vs. Yes (n=8) | 11.90 | 0.248–570.8 | 0.210 |
| LVI, No (n=61) vs.
Yes (n=12) | 0.005 | 0.000–0.729 | 0.037 |
| Pathology, lepidic
(n=26) vs. others (n=47) | 0.270 | 0.016–4.532 | 0.363 |
| ZNF577 mRNA
expression, Low (n=37) vs. High (n=36) | 3173475 | 0.000–2.658E+ | 0.949 |
| ZNF577 DNA
methylation, Low (n=36) vs. High (n=37) | 5.198 | 0.490–55.194 | 0.171 |
Tissue expression of ZNF577 in
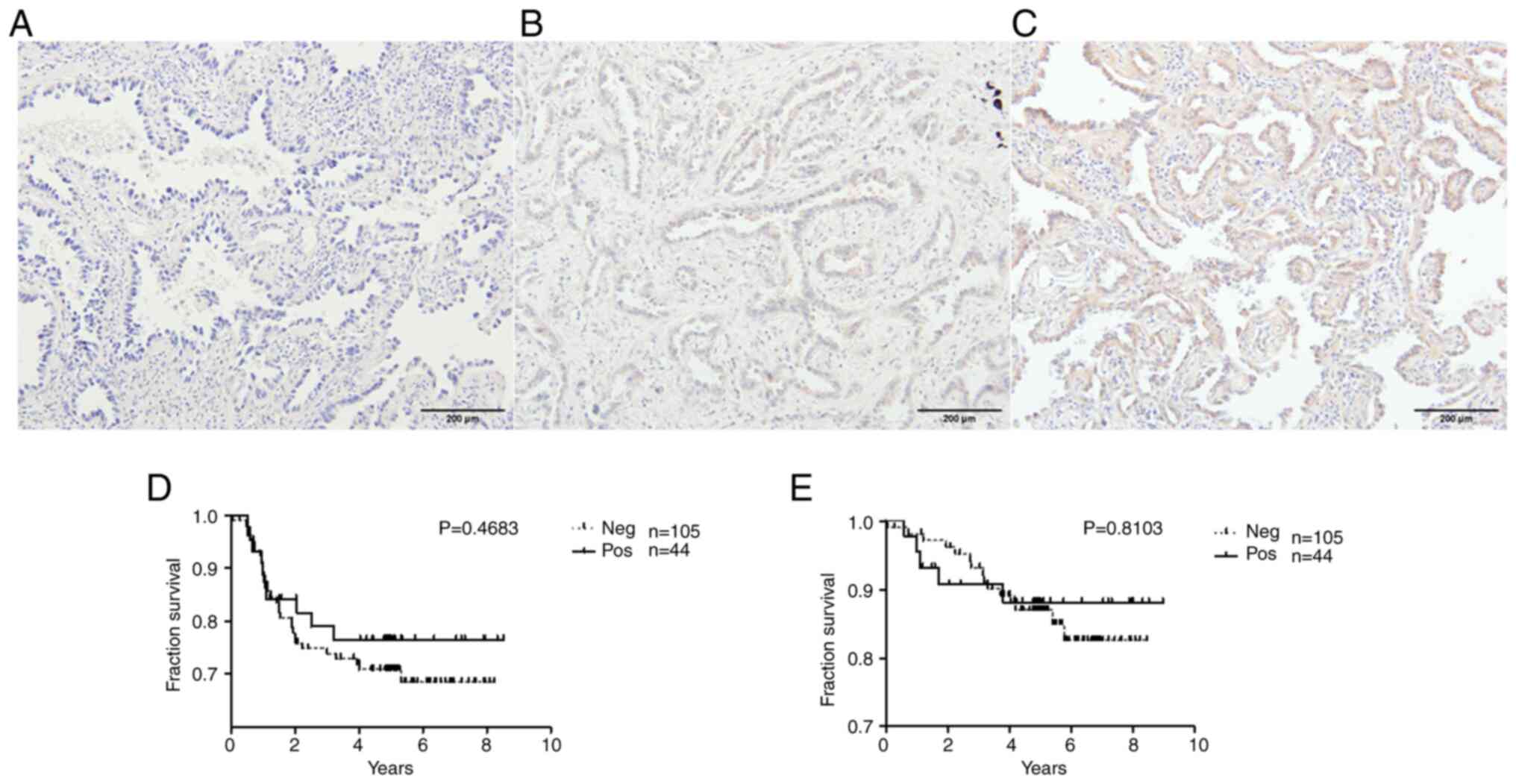
LADC
The tissue expression of ZNF577 was examined in 149
samples by IHC. In a total of 105 samples (70.5%), ZNF577 was not
expressed, while the remaining 44 (29.5%) showed positive IHC
staining. The staining indicated that the protein was located in
the cytoplasmic/membranous area. Representative images are shown in
Fig. 5A-C. In addition, the impact
of the tissue expression of ZNF577 on patient survival rates was
analyzed. Survival rates did not significantly differ (DFS:
Log-rank P=0.4683; OS: Log-rank P=0.8103) between the groups
(Fig. 5D and E).
Discussion
Methylation and gene expression analyses of the
ZNF577 gene in 73 patients with LADC were performed in the present
study. Tissue microarray was performed on 149 tumor samples to
detect ZNF577 expression in the tissue. To the best of our
knowledge, the present study was the first to report the
methylation and gene expression levels of ZNF577 and their
correlation with survival rates in patients with LADC.
In pyrosequencing and gene expression analyses,
significantly higher methylation levels and lower expression levels
of ZNF577 in tumor samples than in their matched normal tissues
were identified. The correlation analysis between the methylation
and expression of ZNF577 showed an inverse relationship, with
higher methylation levels being associated with lower expression
levels. These results confirm the property of DNA methylation that
silences or inhibits gene expression. Based on ROC curve data, the
present study revealed excellent efficiency for discriminating
between tumor and normal samples using the methylation and mRNA
levels of ZNF577. In addition, a previous study by our group
indicated that the mRNA expression level of ZNF577 was low in 10
out of 14 lung cancer cell lines. Furthermore, the demethylating
agents 5-aza-2-deoxycytidine and trichostatin effectively increased
its mRNA levels in lung cancer cell lines (19).
Rauch et al (13) identified 12 CpG islands that were
confirmed to be methylated in 85–100% of stage I lung squamous cell
carcinoma cases (n=5), including ZNF577. The group also tested
stage I LADC samples (n=8) to identify hypermethylated genes.
However, ZNF577 was not among the hypermethylated genes detected,
which may be attributed to the stage of the samples as well as the
small number of samples examined. Furthermore, certain studies
reported the hypermethylation of ZNF577 in aggressive prostate
cancer (28), breast cancer
(29,30), de-novo skin cancer (31) and polycythemia vera cases (32). On the other hand, hypomethylation
and overexpression of ZNF577 were observed in fetal alcohol
spectrum disorder (33). Based on
these studies, it may be predicted that ZNF577 is hypermethylated
in several types of tumors.
According to the present results, the mRNA
expression levels of ZNF577 were significantly higher in stage I
samples and non-smokers than in later stages and smokers. In
addition, lepidic samples had lower methylation levels of ZNF577
than advanced pathological patterns. These results clearly showed
that ZNF577 methylation and gene expression levels were affected by
sex, smoking status, cancer stage and the pathological pattern of
LADC. However, the expected (i.e., ‘high methylation-low
expression’ and ‘low methylation-high mRNA expression’) inverse
relationship between methylation and gene expression levels (i.e.,
‘high methylation-low expression’ and ‘low methylation-high mRNA
expression’), as seen in tumor vs. normal samples, was not observed
for these clinical characteristics.
The hypermethylation of ZNF577 has been associated
with obesity and post-menopause-related breast cancer (29,30).
Furthermore, higher methylation levels of ZNF577 were detected in
the leukocytes of women with breast cancer and greater adherence to
the Mediterranean diet or specific foods, such as vegetables and
fish. The present results showed that females had higher mRNA
expression levels of ZNF577 than males. However, the methylation
levels did not significantly differ between females and males. In
the present study, female patients were mostly menopausal and
post-menopausal, with ages ranging between 43 and 84 (median, 66)
years. Therefore, it was impossible to compare methylation and gene
expression levels between premenopausal and postmenopausal women in
this study. A relationship between obesity and aggressive prostate
cancer was previously reported (34). ZNF577 was hypermethylated in the
leukocytes of these patients, 49.1% of whom were obese and 36.8%
were overweight (28). Therefore, a
relationship may exist between the metabolic status and the ZNF577
methylation rate.
DNA methylation patterns are linked to a greater
likelihood of developing cancer, a worse prognosis and a lower
chance of DFS (35). A relationship
between patient survival rates and ZNF577 expression levels has not
been reported. Significantly higher OS and DFS rates in the high
ZNF577 mRNA expression group than in the low expression group were
observed. Furthermore, the prediction of both OS and DFS rates by
the high and low ZNF577 mRNA expression groups was excellent (DFS:
AUC=0.7232; log-rank P=0.0004 and OS: AUC=0.8658; log-rank
P=0.0001).
The tissue expression of ZNF577 was also assessed
and slightly higher OS and DFS rates were found in the
ZNF577-positive group than in the ZNF577-negative group. There was
no relationship between the mRNA expression level and the IHC
H-score of ZNF577 (data not shown). Numerous factors, including
post-transcriptional and post-translational modifications and
microRNAs, can influence the abundance and stability of both mRNA
and proteins. Therefore, the abundance of mRNA and the protein
level may not always correlate. This may have affected the tissue
expression of ZNF577. And another reason could be the availability
of the ZNF577 antibody. Since this gene is less studied,
particularly by IHC, immunofluorescence and western blotting, there
are only a small number of antibody options. A couple of
commercially available antibodies were tried by our group, which
generally gave relatively weak signals. Furthermore, the tissue
expression of ZNF577 was not reported in previous studies.
ZNF577 is a KRAB C2H2-type
zinc-finger protein (20). The
presence of the KRAB domain, which has a potent transcriptional
repressor property, indicates that the majority of KRAB-ZNF family
members have roles in regulating various biological processes, such
as embryonic development, cell differentiation, cell proliferation,
apoptosis, neoplastic transformation and cell cycle regulation
(36). For instance, ZNF471, ZNF382
and ZNF545 have been reported as tumor suppressor genes and are
hypermethylated in several cancer types (37–43).
ZNF577 may be regarded as a relatively new gene that
has not been reported in many studies. The hypermethylation of
ZNF577 may interfere with immune responses under conditions such as
obesity, the post-menopausal stage and all of the aforementioned
cancer cases. This may be because ZNFs have significant roles in
regulating immune responses at both the transcriptional and
post-transcriptional levels and are involved in the onset and
progression of cancer (22,44).
The present study had certain limitations that need
to be addressed. First, the sample size examined was small due to
the limited source of collected samples. Furthermore, since ZNF577
is relatively less studied, there are only a couple of commercially
available antibodies to detect ZNF577. This limits our choice to
select a suitable antibody for IHC analysis. In addition, liquid
biopsy samples of patients were not available for analysis. This
prevented us from obtaining more profound data to compare and
support the present results.
In conclusion, ZNF577 may be a candidate biomarker
for the prognosis and screening of LADC as well as a therapeutic
target. Therefore, additional studies are required to obtain a more
detailed understanding of the functional role of ZNF577,
particularly its methylation status and expression levels, in
cancer biology. ZNF577 has potential in the diagnosis and outcome
predictions of lung cancer.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for
Scientific Research (grant no. 23K0829600) from the Ministry of
Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
SS, KK, HTa and BM analyzed DNA methylation using
pyrosequencing and interpreted the data. SS, BM and KK analyzed
mRNA expression using RT-qPCR and interpreted the data. KK, BT, HTo
and MY performed the IHC staining and interpreted the association
between the clinical data and the immunoreactivity. KK, HTa and BM
designed and conducted the present study. KK, NK and MY performed
the histological examination of LADC tumor samples. BM, KK and BT
were major contributors in writing the manuscript. BM and KK
checked and confirmed the authenticity of all the raw data. All
authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was performed in accordance with
the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. Following
the approval of all aspects of the present study by the local
Ethics Committee (Tokushima University Hospital; Tokushima, Japan;
approval no. 4071-1), formal written informed consent for the use
of their tissues and the publication of any associated data was
obtained from all patients.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Sleeman KE, Gomes B, de Brito M, Shamieh O
and Harding R: The burden of serious health-related suffering among
cancer decedents: Global projections study to 2060. Palliat Med.
35:231–235. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Padinharayil H, Varghese J, John MC,
Rajanikant GK, Wilson CM, Al-Yozbaki M, Renu K, Dewanjee S, Sanyal
R, Dey A, et al: Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC):
Implications on molecular pathology and advances in early
diagnostics and therapeutics. Genes Dis. 10:960–989. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bade BC and Dela Cruz CS: Lung cancer
2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med.
41:1–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nooreldeen R and Bach H: Current and
future development in lung cancer diagnosis. Int J Mol Sci.
22:86612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature.
511:543–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jordan EJ, Kim HR, Arcila ME, Barron D,
Chakravarty D, Gao J, Chang MT, Ni A, Kundra R, Jonsson P, et al:
Prospective comprehensive molecular characterization of lung
adenocarcinomas for efficient patient matching to approved and
emerging therapies. Cancer Discov. 7:596–609. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding L, Getz G, Wheeler DA, Mardis ER,
McLellan MD, Cibulskis K, Sougnez C, Greulich H, Muzny DM, Morgan
MB, et al: Somatic mutations affect key pathways in lung
adenocarcinoma. Nature. 455:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seo JS, Ju YS, Lee WC, Shin JY, Lee JK,
Bleazard T, Lee J, Jung YJ, Kim JO, Shin JY, et al: The
transcriptional landscape and mutational profile of lung
adenocarcinoma. Genome Res. 22:2109–2119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barbar J, Armach M, Hodroj MH, Assi S, El
Nakib C, Chamseddine N and Assi HI: Emerging genetic biomarkers in
lung adenocarcinoma. SAGE Open Med. 10:205031212211323522022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kan Z, Jaiswal BS, Stinson J, Janakiraman
V, Bhatt D, Stern HM, Yue P, Haverty PM, Bourgon R, Zheng J, et al:
Diverse somatic mutation patterns and pathway alterations in human
cancers. Nature. 466:869–873. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jha G, Azhar S, Rashid U, Khalaf H,
Alhalabi N, Ravindran D and Ahmad R: Epigenetics: The key to future
diagnostics and therapeutics of lung cancer. Cureus.
13:e197702021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Belinsky SA, Nikula KJ, Palmisano WA,
Michels R, Saccomanno G, Gabrielson E, Baylin SB and Herman JG:
Aberrant methylation of p16(INK4a) is an early event in lung cancer
and a potential biomarker for early diagnosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:11891–11896. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rauch TA, Wang Z, Wu X, Kernstine KH,
Riggs AD and Pfeifer GP: DNA methylation biomarkers for lung
cancer. Tumour Biol. 33:287–296. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chao YL and Pecot CV: Targeting
epigenetics in lung cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
11:a0380002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brock MV, Hooker CM, Ota-Machida E, Han Y,
Guo M, Ames S, Glöckner S, Piantadosi S, Gabrielson E, Pridham G,
et al: DNA methylation markers and early recurrence in stage I lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 358:1118–1128. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sterlacci W, Tzankov A, Veits L, Zelger B,
Bihl MP, Foerster A, Augustin F, Fiegl M and Savic S: A
comprehensive analysis of p16 expression, gene status, and promoter
hypermethylation in surgically resected non-small cell lung
carcinomas. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1649–1657. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Munkhjargal B, Kondo K, Soejima S, Tegshee
B, Takai C, Kawakita N, Toba H and Takizawa H: Aberrant methylation
of dipeptidyl peptidase-like 6 as a potential prognostic biomarker
for lung adenocarcinoma. Oncol Lett. 25:2062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tsuboi M, Kondo K, Masuda K, Tange S,
Kajiura K, Kohmoto T, Takizawa H, Imoto I and Tangoku A: Prognostic
significance of GAD1 overexpression in patients with resected lung
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Med. 8:4189–4199. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kajiura K, Masuda K, Naruto T, Kohmoto T,
Watabnabe M, Tsuboi M, Takizawa H, Kondo K, Tangoku A and Imoto I:
Frequent silencing of the candidate tumor suppressor TRIM58 by
promoter methylation in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:2890–2905. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cards G: ZNF577 gene-zinc finger protein
577. Weizmann Institute of Science, 2024. https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=ZNF577#domains_families
|
|
21
|
Tan W, Zheng L, Lee WH and Boyer TG:
Functional dissection of transcription factor ZBRK1 reveals zinc
fingers with dual roles in DNA-binding and BRCA1-dependent
transcriptional repression. J Biol Chem. 279:6576–6587. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jen J and Wang YC: Zinc finger proteins in
cancer progression. J Biomed Sci. 23:532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sobocińska J, Molenda S, Machnik M and
Oleksiewicz U: KRAB-ZFP transcriptional regulators acting as
oncogenes and tumor suppressors: An overview. Int J Mol Sci.
22:22122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Severson PL, Tokar EJ, Vrba L, Waalkes MP
and Futscher BW: Coordinate H3K9 and DNA methylation silencing of
ZNFs in toxicant-induced malignant transformation. Epigenetics.
8:1080–1088. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Goldstraw P, Crowley J, Chansky K, Giroux
DJ, Groome PA, Rami-Porta R, Postmus PE, Rusch V and Sobin L;
International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer
International Staging Committee; Participating Institutions, : The
IASLC lung cancer staging project: Proposals for the revision of
the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the
TNM classification of malignant tumours. J Thorac Oncol. 2:706–714.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Burke AP, Marx A
and Nicholson AG: Introduction to the 2015 World Health
Organization classification of tumors of the lung, pleura, thymus,
and heart. J Thorac Oncol. 10:1240–1242. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu Y, Tsai CW, Chang WS, Han Y, Huang M,
Pettaway CA, Bau DT and Gu J: Epigenome-wide association study of
prostate cancer in African Americans identifies DNA methylation
biomarkers for aggressive disease. Biomolecules. 11:18262021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lorenzo PM, Izquierdo AG, Diaz-Lagares A,
Carreira MC, Macias-Gonzalez M, Sandoval J, Cueva J, Lopez-Lopez R,
Casanueva FF and Crujeiras AB: ZNF577 methylation levels in
leukocytes from women with breast cancer is modulated by adiposity,
menopausal state, and the mediterranean diet. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 11:2452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Crujeiras AB, Diaz-Lagares A, Stefansson
OA, Macias-Gonzalez M, Sandoval J, Cueva J, Lopez-Lopez R, Moran S,
Jonasson JG, Tryggvadottir L, et al: Obesity and menopause modify
the epigenomic profile of breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer.
24:351–363. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Peters FS, Peeters AMA, Mandaviya PR, van
Meurs JBJ, Hofland LJ, van de Wetering J, Betjes MGH, Baan CC and
Boer K: Differentially methylated regions in T cells identify
kidney transplant patients at risk for de novo skin cancer. Clin
Epigenetics. 10:812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Barrio S, Gallardo M, Albizua E, Jiménez
A, Rapado I, Ayala R, Gilsanz F, Martin-Subero JI and
Martinez-Lopez J: Epigenomic profiling in polycythaemia vera and
essential thrombocythaemia shows low levels of aberrant DNA
methylation. J Clin Pathol. 64:1010–1013. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Krzyzewska IM, Lauffer P, Mul AN, van der
Laan L, Yim AYFL, Cobben JM, Niklinski J, Chomczyk MA, Smigiel R,
Mannens MMAM and Henneman P: Expression quantitative trait
methylation analysis identifies whole blood molecular footprint in
fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD). Int J Mol Sci. 24:66012023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Allott EH, Masko EM and Freedland SJ:
Obesity and prostate cancer: Weighing the evidence. Eur Urol.
63:800–809. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hill VK, Ricketts C, Bieche I, Vacher S,
Gentle D, Lewis C, Maher ER and Latif F: Genome-wide DNA
methylation profiling of CpG islands in breast cancer identifies
novel genes associated with tumorigenicity. Cancer Res.
71:2988–2999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lupo A, Cesaro E, Montano G, Zurlo D, Izzo
P and Costanzo P: KRAB-zinc finger proteins: A repressor family
displaying multiple biological functions. Curr Genomics.
14:268–278. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cao L, Wang S, Zhang Y, Wong KC, Nakatsu
G, Wang X, Wong S, Ji J and Yu J: Zinc-finger protein 471
suppresses gastric cancer through transcriptionally repressing
downstream oncogenic PLS3 and TFAP2A. Oncogene. 37:3601–3616. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun R, Xiang T, Tang J, Peng W, Luo J, Li
L, Qiu Z, Tan Y, Ye L, Zhang M, et al: 19q13 KRAB zinc-finger
protein ZNF471 activates MAPK10/JNK3 signaling but is frequently
silenced by promoter CpG methylation in esophageal cancer.
Theranostics. 10:2243–2259. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tao C, Luo J, Tang J, Zhou D, Feng S, Qiu
Z, Putti TC, Xiang T, Tao Q, Li L and Ren G: The tumor suppressor
zinc finger protein 471 suppresses breast cancer growth and
metastasis through inhibiting AKT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Clin
Epigenetics. 12:1732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bhat S, Kabekkodu SP, Adiga D, Fernandes
R, Shukla V, Bhandari P, Pandey D, Sharan K and Satyamoorthy K:
ZNF471 modulates EMT and functions as methylation regulated tumor
suppressor with diagnostic and prognostic significance in cervical
cancer. Cell Biol Toxicol. 37:731–749. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bhat S, Kabekkodu SP, Jayaprakash C,
Radhakrishnan R, Ray S and Satyamoorthy K: Gene promoter-associated
CpG island hypermethylation in squamous cell carcinoma of the
tongue. Virchows Arch. 470:445–454. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cheng Y, Geng H, Cheng SH, Liang P, Bai Y,
Li J, Srivastava G, Ng MH, Fukagawa T, Wu X, et al: KRAB zinc
finger protein ZNF382 is a proapoptotic tumor suppressor that
represses multiple oncogenes and is commonly silenced in multiple
carcinomas. Cancer Res. 70:6516–6526. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheng Y, Liang P, Geng H, Wang Z, Li L,
Cheng SH, Ying J, Su X, Ng KM, Ng MH, et al: A novel 19q13
nucleolar zinc finger protein suppresses tumor cell growth through
inhibiting ribosome biogenesis and inducing apoptosis but is
frequently silenced in multiple carcinomas. Mol Cancer Res.
10:925–936. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rakhra G and Rakhra G: Zinc finger
proteins: Insights into the transcriptional and post
transcriptional regulation of immune response. Mol Biol Rep.
48:5735–5743. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|