Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second most
common cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide and is the most
prevalent type of primary liver cancer, accounting for ~85% of all
malignant liver tumors. Clinically, surgical resection and ablation
are commonly used for treatment, but the recurrence rate within
five years remains high at 40–70% (1). The advent of targeted immunotherapies
has largely mitigated disease progression in patients with HCC
(2). However, medication alone does
not function as well (3). By
contrast, immunotherapy in combination with targeted inhibitors
offers greater clinical benefits for patients with HCC and
represents a new direction for future HCC treatment (4,5).
Therefore, it is important to study the pathogenesis of HCC and
explore new therapeutic targets.
The transcriptional repressor homeobox containing 1
(HMBOX1) was first isolated from a human pancreatic cDNA library
and is widely expressed in various human organ tissues. As a novel
transcriptional repressor, there is relatively little research on
the biological activity of HMBOX1, mainly involving studies on cell
differentiation and development, immune regulation, cellular
autophagy and aging, and tumor pathology (6). As previously reported, HMBOX1 exerts
distinct regulatory effects on different types of tumors. For
instance, in osteosarcoma, cervical cancer and ovarian cancer,
HMBOX1 impedes tumor cell immune evasion and malignant
proliferation (7,8). Conversely, in gastric cancer, it can
facilitate tumor growth and metastasis, underscoring the intricate
regulatory mechanisms of HMBOX1 in tumorigenesis (9). Preliminary research found that the
expression level of HMBOX1 in liver cancer tissue is significantly
decreased (10), but the specific
regulatory mechanism and its effect on tumor growth are still
unclear.
Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Non-receptor type 1
(PTPN1), also known as PTP1B, is a member of the protein tyrosine
phosphatase (PTP) family. It plays an important role in different
physiological processes, especially insulin and leptin sensitivity
(11). Therefore, PTPN1 may be an
effective target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. As the
research continues, PTPN1 has also been shown to play an important
role in tumor-related studies. However, the specific role of PTPN1
activation in promoting or suppressing tumors is not consistent
across different tumors (12–15).
In HCC, PTPN1 has also been reported to have both a tumor-promoting
effect (16) and a possible
tumor-inhibiting effect (17).
However, the specific regulatory effects and mechanisms of PTPN1 in
tumors, especially HCC, remain unclear, and its regulatory
relationship with HMBOX1 has not yet been reported.
In the present study, it was identified, for the
first time to the best of the authors' knowledge, the important
role of HMBOX1-mediated activation of the PTPN1/AKT signaling
pathway in HCC malignant biological behaviors, such as
proliferation and migration. Importantly, these molecular events
account for the protective effects of HMBOX1 on HCC development,
thereby providing a new potential target for the clinical diagnosis
and treatment of HCC.
Materials and methods
Data sources
GEPIA2 (18)
(http://gepia2.cancer-pku.cn/) was used
to compare the expression level of genes in tumor and normal
tissues and to perform correlation analysis of the expression of
two genes. Kaplan-Meier plotter (https://kmplot.com/analysis/) was used to compare
differences in the survival of patients with different gene
expression levels (19).
Metascape database (https://metascape.org/) was used for Gene ontology
(GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway
enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes screened by
proteomics (20). STRING database
(https://cn.string-db.org/) is used to
analyze protein-protein interactions (21). cBioPortal database (http://www.cbioportal.org/) was used to analyze the
effect of clinical interventions on the expression of HMBOX1 and
PTPN1 in tumor tissues of patients with HCC (22). JASPAR (https://jaspar.elixir.no/) was used to predict
potential HMBOX1-binding sites within the 2-kb region upstream of
the transcription start site of PTPN1 (23). The use of patient sample data from
the public databases was approved by the Ethics Committee of
Shandong First Medical University (approval no. R202403040155;
Jinan, China).
Cell lines and culture
Mouse hepatoma cell line Hepa1-6 (cat. no. CL-0105;
Procell Life Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) and human hepatoma
cell line Huh-7 (cat. no. CL-0120; Procell Life Science &
Technology Co., Ltd.) were cultured in high-glucose Dulbecco's
Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; cat. no. PM150210; Procell Life
Science & Technology Co., Ltd.) with 10% fetal bovine (cat. no.
11011-8611; Zhejiang Tianhang Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) and 1%
penicillin/streptomycin (cat. no. PB180120; Procell Life Science
& Technology Co., Ltd.) at 37°C and 5% CO2 in a cell
culture incubator. In some experiments, the Akt activator SC79
(cat. no. HY-18749; MedChemExpress) at a concentration of 4 µΜ was
used to treat Hepa1-6 cells for different times. All cell
experiments were completed within two months after
transfection.
Vector constructs, lentivirus
production and cell transduction
Lentiviral particles were produced by transfecting
293T cells with the transfer plasmid
(pLV3-CMV-MCS-3flag-EF1-ZsGreen-T2A-PURO, Research Cloud Biology)
containing the HMBOX1 transcrip, along with the packaging plasmid
(psPAX2) and the envelope plasmid (pMD2.G), using PEI at a mass
ratio of 4:3:1 at 37°C and 5% CO2 in a cell culture
incubator. Supernatants containing viral particles were collected
at 48 h post-transfection, filtered, and concentrated. To generate
stable HMBOX1-overexpressing cell lines, target HCC cells were then
transduced with the virus in the presence of 8 µg/ml Polybrene
(cat. no. C0351; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) at 37°C and
5% CO2 in a cell culture incubator. The multiplicity of
infection values used to transduce Hepa1-6 and Huh-7 cells were 5
and 10, respectively. After transduction for 24 h, the culture
medium containing the lentivirus was washed, and changed to fresh
complete medium to continue culture for 48 h. Finally, cell lines
were selected using complete medium containing the appropriate
concentration of puromycin for seven days (Hepa1-6 2.2 µg/ml and
Huh-7 1.0 µg/ml).
Cell proliferation assay
Cells were seeded into 96-well plates at a density
of 1,000 cells/well. Cell viability was determined using a Cell
Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8; cat. no. BS350B; Biosharp Life Sciences)
following the instructions. At 6, 24, 48 and 72 h respectively, 10
µl/well CCK-8 reagent was added in each well and incubated at 37°C
for 4 h. Absorbance was measured at 450 nm using a multimode reader
(SpectraMax i3×) to assess cell viability.
Colony formation assay
Cells were seeded into 6-well plates at a density of
1,000 cells/well. 2 ml of DMEM was added to each well, and the
medium was changed every two days. After 10 days, the cells were
fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde at 25°C for 15 min and stained with
0.1% crystal violet solution at 25°C for 7 min. The number of
colonies (minimum number of cells forming a colony equals to 50)
formed was counted using ImageJ software (Version 1.54f; National
Institutes of Health).
Wound healing assay
The cells were seeded into a 6-well plate overnight
and allowed to proliferate to 90% density. To minimize the
influence of cell proliferation on wound closure, cells were
serum-starved by incubating in serum-free DMEM for 12 h prior to
creating the scratch. Then, a uniform scratch wound was then
created in the center of each well using a 10-µl sterile pipette
tip. The plate was washed three times with PBS to remove scraped
cells, and 2 ml of 2% serum DMEM was added per well. At 0, 48 and
72 h, images were captured under bright-field illumination usingan
inverted phase-contrast microscope (IX73; Olympus Corporation). The
width of the wound was assessed utilizing ImageJ software in order
to determine the relative rate of healing. The relative healing
rate was calculated using the following formula:
(S0h-Sah)/S0h ×100% (where ah is
the scratch area time).
Proteomic analysis
The protein expression of the two groups (Vector and
Over-HMBOX1) of Hepa1-6 cells were detected by liquid
chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.). The sample processing and analysis methods have been
described in a recent study by the authors (24). In brief, Hepa1-6 cells were lysed
with RIPA protein lysate containing 1% PMSF (cat. no. P0013B;
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) to extract total cell protein,
according to the manufacturer's instructions. The protein
concentration was determined using a BCA protein concentration
detection reagent kit (cat. no. ZJ101; Epizyme, Inc.). The protein
samples are pre-treated and then then further tests be conducted
using a mass spectrometry instrument. Mass spectra were searched
against the mouse UniProt database
(organism_id_10090_2022_07_15.fasta; http://www.uniprot.org/) using Proteome Discoverer
version 2.4.
Western blotting
Cells were lysed with RIPA (cat. no. P0013B;
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) containing 1% PMSF to extract
total cell protein. The protein concentration was determined by BCA
kit. The detection quantity for each sample was 25 micrograms of
protein. β-actin was used as the loading control. Protein samples
were separated using 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and transferred to a PVDF membrane
(MilliporeSigma). Membranes were blocked and incubated with primary
antibodies overnight at 4°C. The following antibodies were used:
anti-HMBOX1 (1:1,000; cat. no. 16123-1-AP; Proteintech Group,
Inc.), anti-PTPN1 (1:2,000; cat. no. 11334-1-AP; Proteintech Group,
Inc.), anti-AKT1 (1:2,000; cat. no. A17909; ABclonal Biotech Co.,
Ltd.), anti-phospho-AKT1-S473 (1:1,000; cat. no. AP0637; ABclonal
Biotech Co., Ltd.), and anti-β-actin (1:10,0000; cat. no. AC026;
ABclonal Biotech Co., Ltd.). Incubation with the horseradish
peroxidase-labeled secondary antibody (1:1,000; cat. no. A0208;
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) at 37°C for 1 h was performed
to test the binding of the antibodies. Finally, the proteins were
visualized on a chemiluminescence instrument (5200Multi; Tanon
Science and Technology Co., Ltd.) using an ultrasensitive ECL
chemiluminescence kit (cat. no. P0018AS; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology). ImageJ software (Version 1.54f; National Institutes
of Health) was used for densitometric analysis.
Identification of HMBOX1 binding
molecules by Co-IP and mass spectrometry
Protein samples from Hepa1-6 cells overexpressing
HMBOX1 were carried out using the Immunoprecipitation Kit with
Protein A+G Magnetic Beads kit (cat. no. P2179; Beyotime Institute
of Biotechnology) in accordance with the manufacturer's
instructions. Briefly, following thorough cell lysis with lysis
buffer, the lysate was centrifuged at 12,000 × g for 5 min at 4°C.
Then the protein concentration was detected using the BCA kit. The
HMBOX1 antibody (cat. no. 16123-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.) was
incubated overnight with the protein sample at 4°C at 0.5–4.0 ug
for 1.0–3.0 mg of total protein lysate. The Protein A+G Magnetic
Beads were co-incubated with the protein-antibody complex at room
temperature for 2 h. After incubation was completed, the mixture
was placed on a Magnetic Separation Rack (cat. no. FMS004; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology) for 10 sec and the supernatant was
removed. The magnetic beads were washed three times with the lysis
buffer containing the inhibitor. The protein samples were eluted
using SDS-PAGE loading buffer elution. Subsequently, the samples
were tested using western blotting. The SDS-PAGE gel was stained
with Coomassie Blue Staining Solution (cat. no. P0003S; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology), and gels were collected for mass
spectrometry analysis to identify the protein molecules interacting
with HMBOX1.
Animal models
Animal studies were approved by the Institutional
Animal Care Committee of Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong
First Medical University (approval no. W202403040279; Jinan,
China). The experimental procedures were in accordance with the
ARRIVE guidelines. Wild type male C57BL/6j mice (6-week-old;
weight, 20±2g) were purchased from Beijing HFK Bioscience Co. Ltd.
All mice were housed in the Laboratory Animal Center Central
Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University in a
specific pathogen-free (SPF) conditions. The temperature of the
raising environment was controlled at 22±2°C, and the humidity was
50%±10%. A 12/12-h light/dark cycle was adopted. Animals could
freely consume standard experimental feed and drink sterile water.
To evaluate the antitumor effect of HMBOX1 overexpression in
vivo, Hepa1-6 cells overexpressing HMBOX1 (Over-HMBOX1) or
transfected with an empty vector (Vector, as Ctrl group) were used
to construct a mouse subcutaneous tumor-bearing model. A total of
12 mice were involved in the experiment and randomly divided into 2
groups using completely random design, with 6 mice in each group,
every mouse is an experimental unit. Hepa1-6 cells
(5×106, Over-HMBOX1 or Vector) were mixed with Matrigel
(cat. no. 256234; Corning, Inc.) in a total volume of 100 µl. Cells
were subcutaneously injected into the right subaxillary region of
every C57BL/6 mouse. Tumor sizes of every mouse were measured every
three days using a Vernier caliper, and tumor volume
(mm3)=a × b2/2 (where a is the largest and b
is the smallest tumor diameter). At the endpoint, all mice were
euthanized by carbon dioxide overdose inhalation which was carried
out in accordance with the Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals
made by American Veterinary Medical Association. A gradual fill
method was employed, where the chamber was initially filled to 30%
CO2, followed by a maintained flow rate of 50% of the
chamber volume per min until respiratory arrest and confirmed
death. Tumors from individual mice were isolated to compare tumor
weights.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP
assay)
ChIP experiments were performed using a ChIP Assay
Kit (cat. no. P2078; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). The
cells were collected after cross-linking the protein and genomic
DNA using DMEM containing 1% formaldehyde. DNA was cleaved into
200-1,000 kb fragments using sonication after cell lysis.
Anti-HMBOX1 (cat. no. 16123-1-AP; Proteintech Group, Inc.) was
added and incubated overnight at 4°C, followed by Protein A+G
Agarose/Salmon Sperm DNA slowly rotated at 4°C for 60 min to
precipitate the protein DNA complex recognized by the primary
antibody. After removing the cross-links between the protein and
DNA and PCR amplification of the PTPN1 promoter sequence, the
binding of HMBOX1 to the PTPN1 promoter was verified through 2%
agarose gel electrophoresis. The gel was stained with Goldview
Nucleic acid dye (cat. no. BS357A; Biosharp Life Sciences) and
visualized under UV light using a gel documentation system
(5200Multi; Tanon Science and Technology Co., Ltd.). Primers were
designed based on possible binding sites predicted by JASPAR. The
primer sequences were as follows: PTPN1-1 forward,
5′-CTCTTCCAGGTTTTCAAACCTC-3′ and reverse,
5′-GATGAGACCCGGAATCTGCAT-3′; and PTPN1-2 forward,
5′-CCTCAAAATAGCACAAGTGTCC-3′ and reverse,
5′-TGATTTCCCAAGCAGACCGTT-3′.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
HCC tissue chips (cat. no. D097Lv01;
Bioaitech®; http://www.bioaitech.com/) containing tumor and
matched adjacent non-tumor tissues from 48 patients with HCC were
used to evaluate the expression levels of HMBOX1 and PTPN1. The use
of the tissue chips was approved by the Ethics Committee of
Shandong First Medical University (approval no. R202403040155;
Jinan, China). For immunohistochemical staining, the tissue chips
were incubated at 60°C for 30–60 min and then subjected to
deparaffinization. Briefly, the slides were incubated in xylene
twice for 10 min each to completely dissolve the paraffin.
Subsequently, the slides were rehydrated through a graded ethanol
series: 100% ethanol twice for 5 min each, followed by 95% ethanol
for 5 min, 80% ethanol for 5 min and finally 70% ethanol for 5 min.
After rehydration, the slides were rinsed thoroughly in water for 5
min. Repaired the antigen with citric acid and then blocked the
endogenous peroxidase activity with 3%
H2O2-methanol. After incubation with
anti-HMBOX1 (1:200; cat. no. 16123-1-AP) or anti-PTPN1 (1:200; cat.
no. 11334-1-AP; both from Proteintech Group, Inc.) at 4°C for 16 h
and secondary antibodies (1:50; cat. no. A0208; Beyotime Institute
of Biotechnology), streptavidin-peroxidase was added dropwise.
Images were captured under bright-field illumination using an
upright microscope (BX53; Olympus Corporation) to analyze the
positivity rate, and the expression of HMBOX1 and PTPN1 was
compared between the patient's liver cancer tissue and adjacent
tissues.
Statistical analysis
All experiments were repeated at least three times.
All experimental data were presented as the mean ± standard. ANOVA
was used for comparisons among multi-group and if a statistically
significant difference was found, Tukey's post hoc test was applied
for multiple comparisons between all groups. Paired t-test was used
for comparisons between two groups in IHC assay results and
unpaired t-test was used for comparisons between two groups in
other results. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference. GraphPad Prism 8 (Dotmatics) was used for
all statistical analyses.
Results
HMBOX1 expression is downregulated in
tumor tissues and correlates with poor prognosis in patients with
HCC
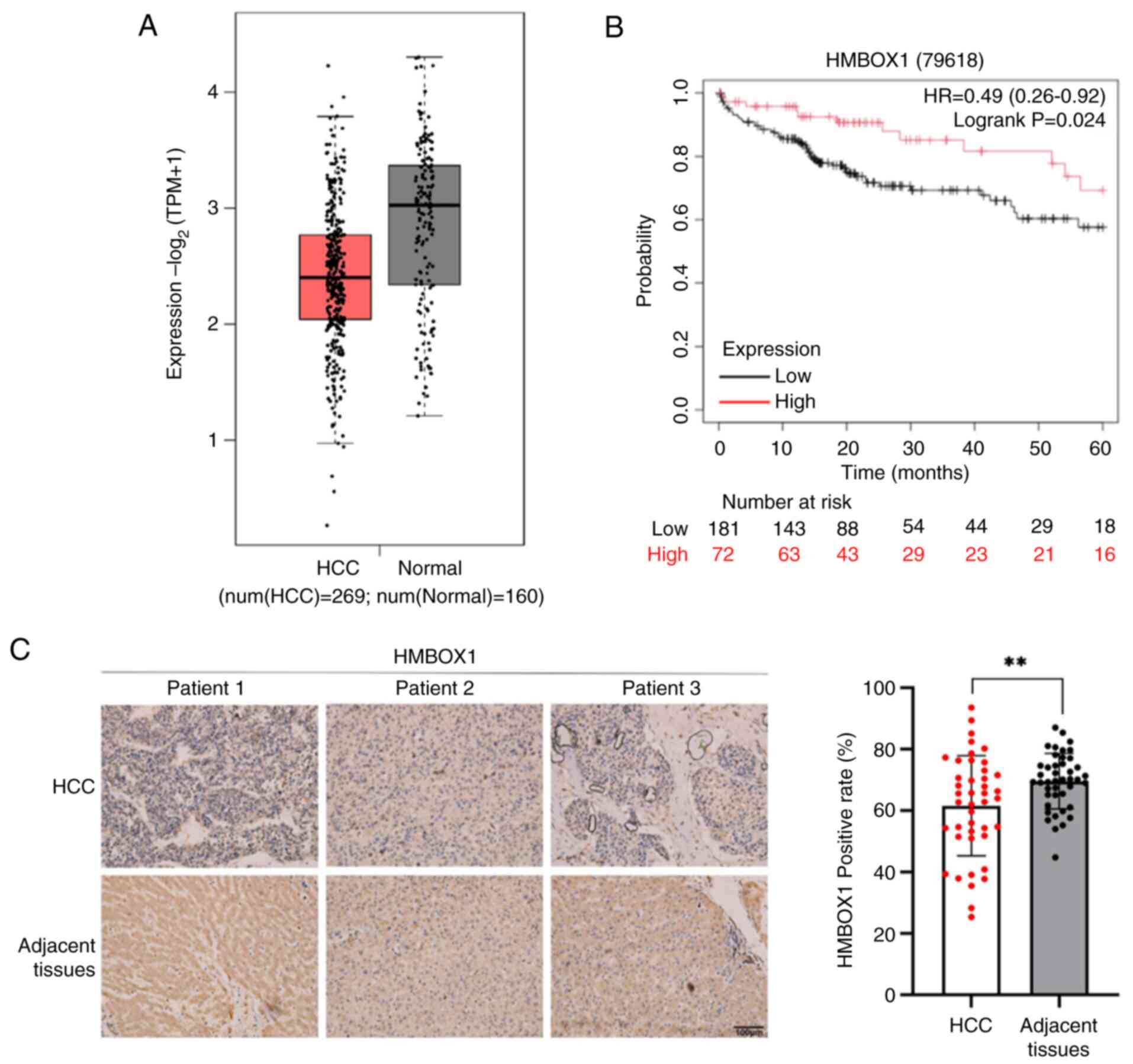
Analysis of clinical data from the TCGA database
revealed that HMBOX1 expression was significantly downregulated in
HCC tumor tissues (Fig. 1A).
Survival analysis conducted using the Kaplan-Meier Plotter database
also suggested a negative correlation between HMBOX1 levels and the
survival rate of patients with HCC (Fig. 1B). To further confirm the expression
pattern of HMBOX1 in HCC tumor tissues, IHC analysis was performed
using tissue microarray from patients with HCC. The results showed
that the expression of HMBOX1 in tumor tissues of was significantly
downregulated compared with that in non-tumor tissues (Fig. 1C). These results suggested that
HMBOX1 is downregulated in HCC, which is associated with a poor
prognosis. In addition, the expression of HMBOX1 in tumor tissues
of patients at different stages was further analyzed through the
GEPIA2 database. Although there was no statistical difference, it
could be observed that the expression of HMBOX1 in tumor tissues of
patients at stage IV was significantly downregulated compared with
patients at stage I–III (Fig. S1A and
B). The expression of HMBOX1 was not significantly correlated
with that of the HCC marker molecule AFP (Fig. S1C and D). Moreover, there was no
significant difference in the expression of HMBOX1 in tumor tissues
between patients who received treatment and those who did not
(Fig. S1E-H).
HMBOX1 inhibits HCC cell
proliferation, migration and colony formation in vitro
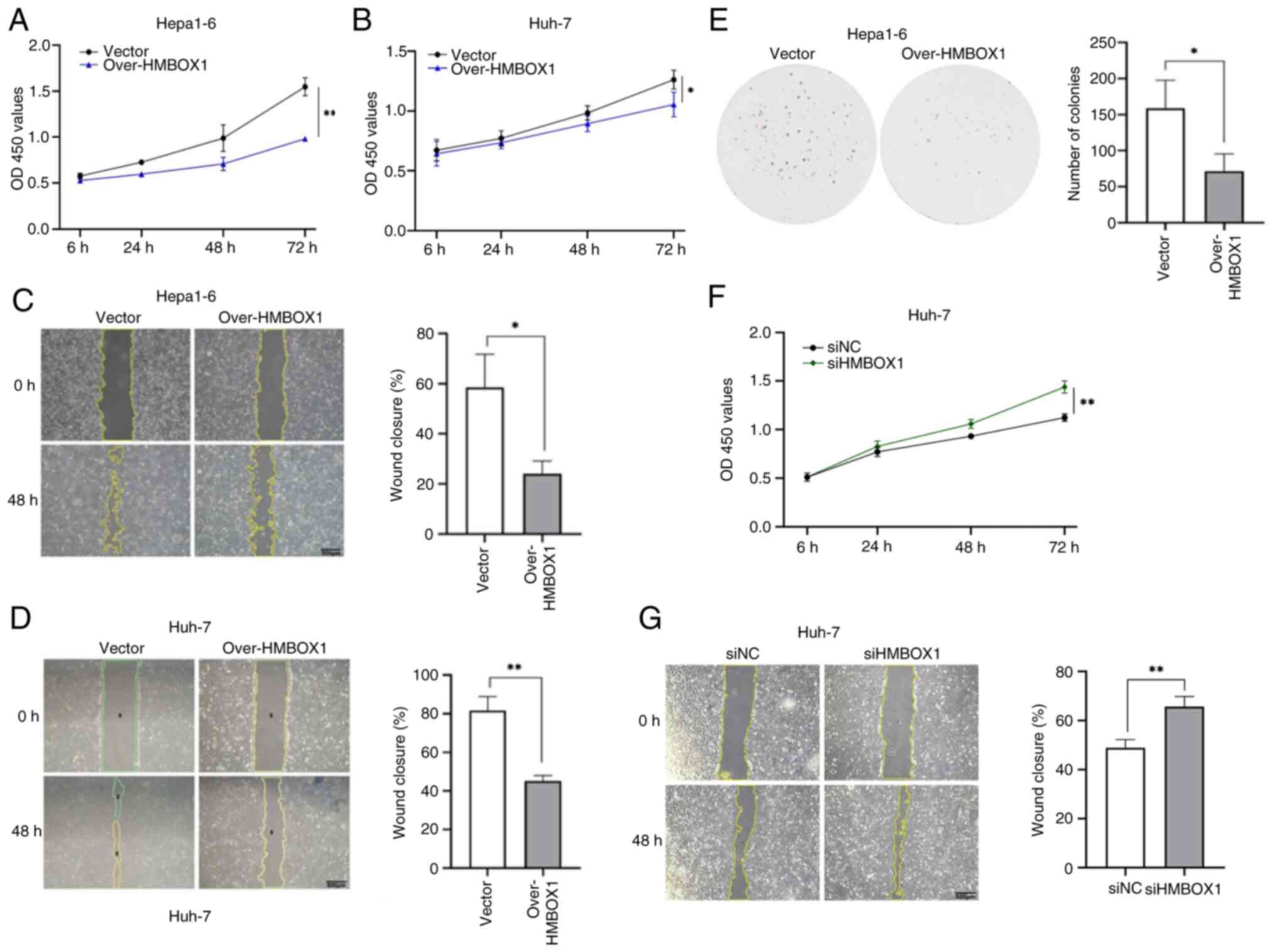
The potential role of HMBOX1 in HCC progression was
explored. Lentiviral infection was used to overexpress HMBOX1 in
Hepa1-6 and Huh-7 cells and the overexpression effect was verified
using western blotting (Fig. S2A and
B). The CCK-8 assay was utilized for the assessment of cellular
proliferation. The growth curves indicated that HMBOX1
overexpression impeded the proliferation of HCC cells (Fig. 2A and B). Wound healing assay was
used to explore the effect of HMBOX1 on the migration ability of
HCC cells. It was found that HMBOX1 overexpression significantly
inhibited the migration ability of Hepa1-6 cells (Fig. 2C and D). The colony formation assays
showed that exogenous HMBOX1 consistently inhibited colony
formation in HCC cells (Fig. 2E).
To further validate these results, small interfering RNA (siRNA)
silencing of HMBOX1 was performed in Huh-7 cells (Fig. S2C) and it was found that
downregulation of HMBOX1 expression significantly enhanced the
proliferation and migration capabilities of Huh-7 cells (Fig. 2F and G).
Inhibitory effect of HMBOX1 on HCC is
dependent on the blocking of AKT1 phosphorylation
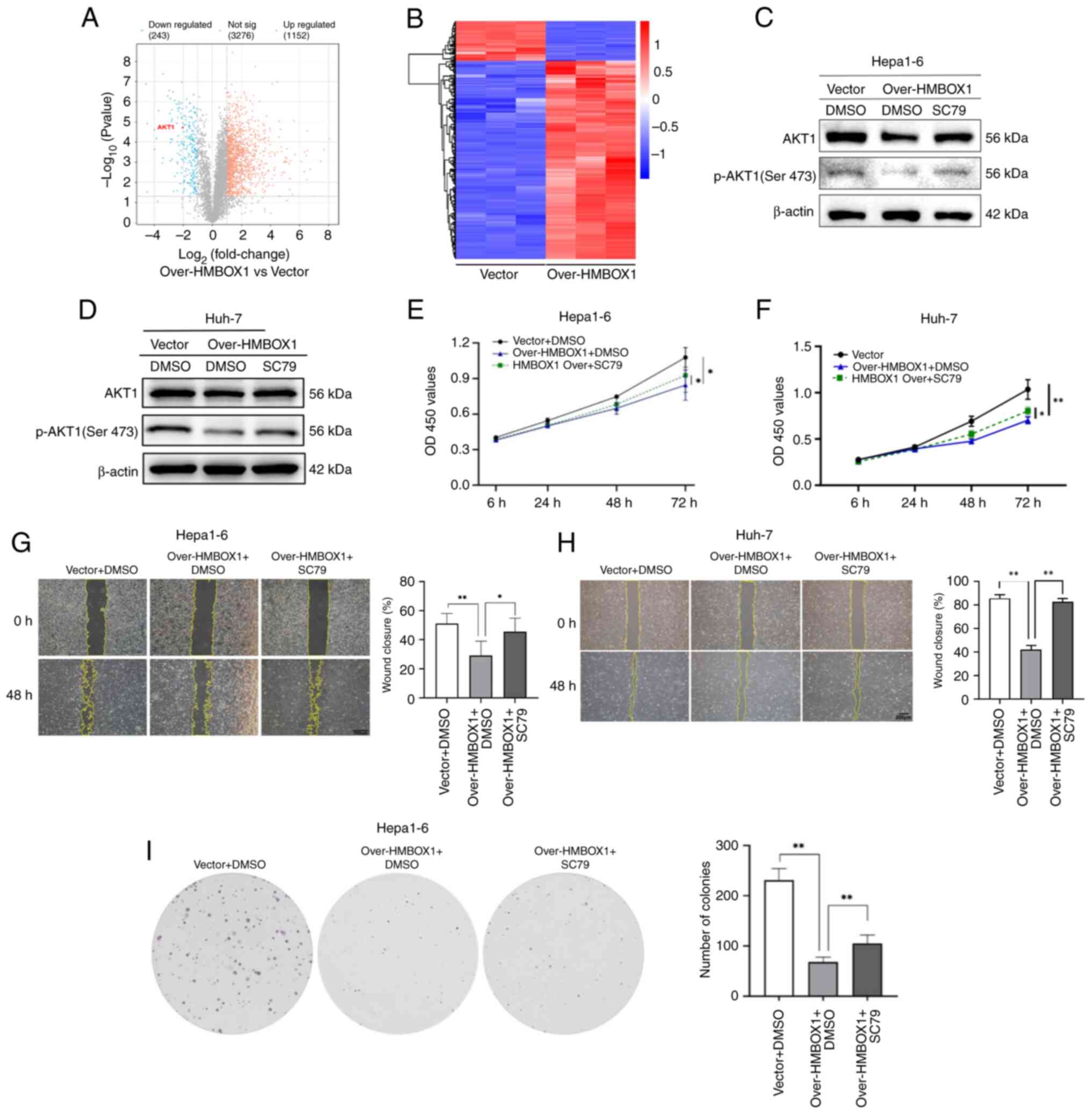
To explore the potential mechanisms by which HMBOX1
inhibits the malignant behavior of HCC cells, a proteomic analysis
of Hepa1-6 cells overexpressing HMBOX1 and control cells was
performed. The results revealed that, compared with the Vector
(Ctrl) group, there were 1,152 upregulated and 243 downregulated
protein molecules in the over-HMBOX1 group (Fig. 3A and B). GO and KEGG enrichment
analysis of the differential proteins was conducted using the
Metascape database (Fig. S3).
Among protein molecules with significant variations, it was found
that the expression of AKT1 was significantly downregulated in the
cells of the overexpression group. AKT1, as one of the effective
targets for HCC therapy, has been shown in numerous studies to
inhibit tumor growth both directly and indirectly through its
inhibitors (25,26). Among the phosphorylation sites of
AKT1, phosphorylation at Ser473 is critical for its functional
activity (27). However, whether
HMBOX1 regulates tumor progression by modulating AKT1 activation
has not been reported. A preliminary study was conducted on the
relationship between these two molecules. First, the expression
levels of AKT1 and its phosphorylated proteins were examined in
Hepa1-6 cells overexpressing HMBOX1 through western blotting. The
phosphorylation level of AKT1 at Ser473 was markedly downregulated
in Hepa1-6 and Huh-7 overexpressing HMBOX1 compared with control
cells infected with the empty vector (Fig. 3C and D). To further confirm the
impact of HMBOX1 on HCC through the AKT pathway,
HMBOX1-overexpressed Hepa1-6 cells were treated with the AKT
agonist SC79. The results demonstrated that the inhibition of
HMBOX1-overexpressed HCC cells on phosphorylated (p-)AKT1 (Ser473)
was reversed when these cells were treated with SC79 (Fig. 3C and D). Moreover, SC79 treatment
restored the inhibitory effects on HCC cell proliferation,
migration, and clone formation induced by HMBOX1 overexpression
(Fig. 3E-I). These results
suggested that the inhibitory effect of HMBOX1 overexpression on
the malignant biological behavior of HCC occurs through inhibition
of AKT signaling.
PTPN1 may be a key regulator
downstream of HMBOX1
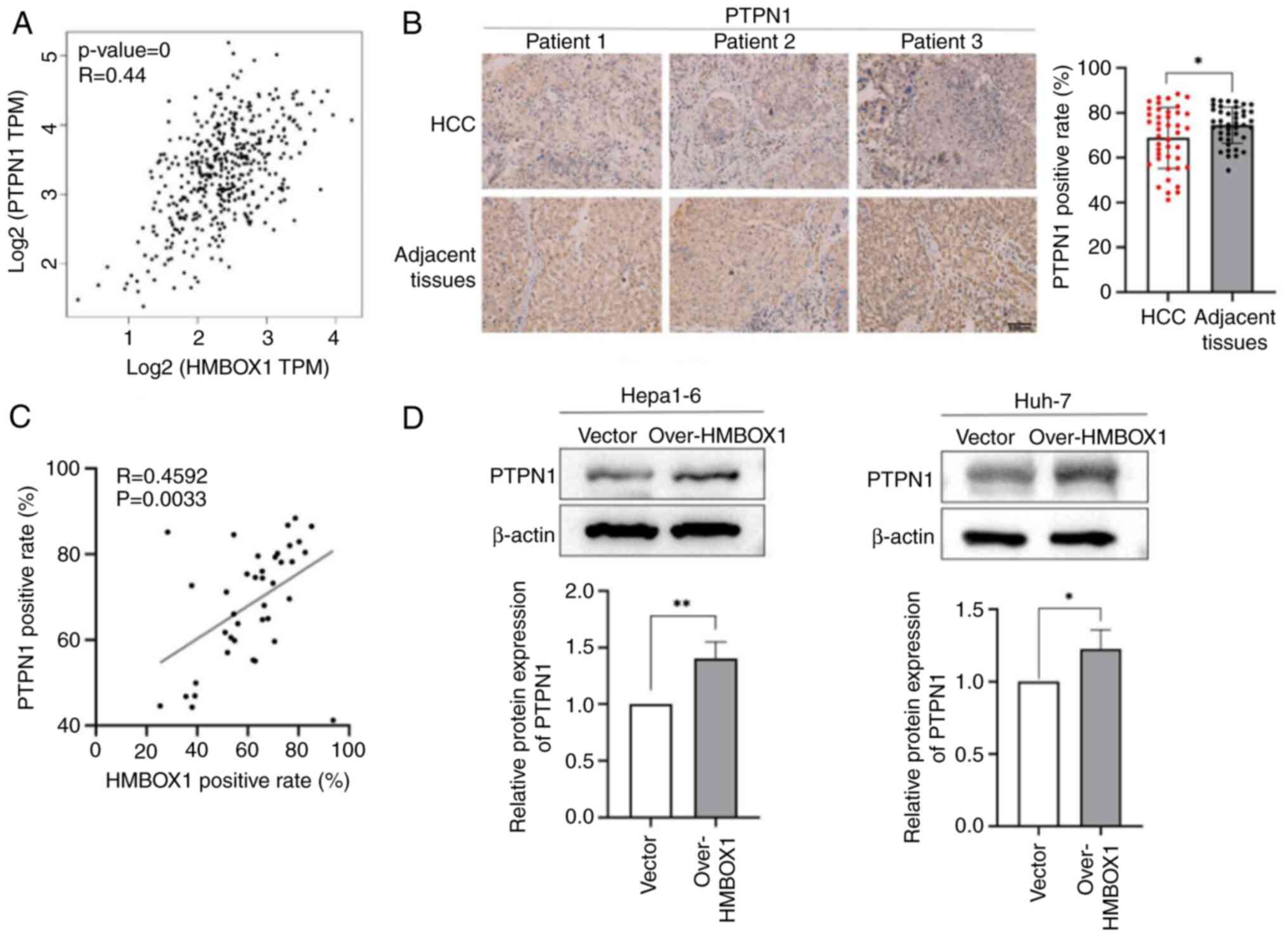
PTPN1 has been documented to play a significant role
in the modulation of AKT activation across various types of tumors
(28,29). PTPN1 is abnormally expressed in
liver cancer. Therefore, it was hypothesized that HMBOX1 may affect
AKT1 phosphorylation by regulating PTPN1 expression. Using the
GEPIA2 database, the correlation between HMBOX1 and PTPN1
expression levels was analyzed in HCC tissues, and it was found
that the expression levels of the two molecules are positively
correlated (Fig. 4A). In addition,
it could be observed that the expression of PTPN1 in tumor tissues
of patients at stage IV was significantly downregulated compared
with patients at stage I–III (Fig.
S1B). However, there is no significant correlation between the
expression of PTPN1 and that of AFP in tumor tissues (Fig. S1D). There was no significant
difference in the expression of PTPN1 in tumor tissues between
patients who received treatment and those who did not (Fig. S1F and H). The TMA of patients with
HCC was further used for IHC staining analysis. It was found that
PTPN1 expression in tumor was downregulated compared with that in
adjacent non-tumor tissues (Fig.
4B). Combined with the expression analysis of HMBOX1 in HCC
shown in Fig. 1C, the correlation
between the expression of HMBOX1 and PTPN1 was analyzed in the
tumor tissues of patients with HCC, and it was found that the
expression of these two proteins was positively correlated
(Fig. 4C). HMBOX1 overexpression
significantly upregulated the expression level of PTPN1 in Hepa1-6
and Huh-7cells (Fig. 4D and E).
These results suggested that PTPN1 may act as a downstream target
molecule of HMBOX1.
HMBOX1 inhibits HCC proliferation by
regulating PTPN1/AKT1 signaling
Building on previous findings that HMBOX1 inhibits
AKT1 phosphorylation and that PTPN1 may act as a downstream
regulator of HMBOX1, it was hypothesized that HMBOX1 may further
regulate the phosphorylation of AKT1 by modulating the expression
of PTPN1, which may contribute to the oncogenic suppression
activity of HMBOX1. To confirm the regulatory relationship between
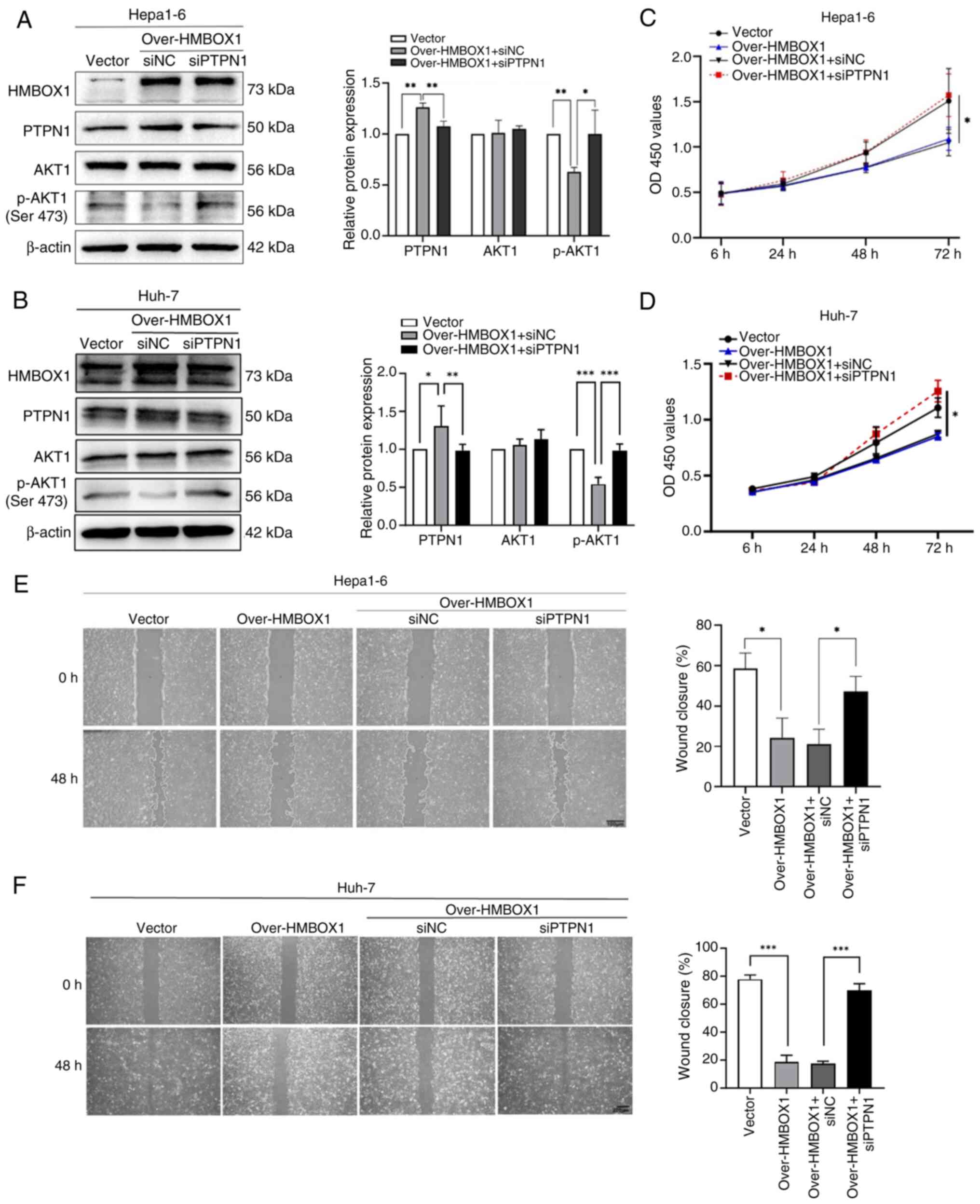
PTPN1 and AKT1, PTPN1 was silenced in HMBOX1-overexpressing HCC
cells using siRNA targeting PTPN1 (Fig. S2D and E) and it was found that
silencing of PTPN1 reversed the downregulation of AKT1
phosphorylation caused by the overexpression of HMBOX1 (Fig. 5A and B). Further functional studies
showed that silencing PTPN1 significantly restored the effect of
HMBOX1 overexpression on tumor cell proliferation and migration
(Fig. 5C-F).
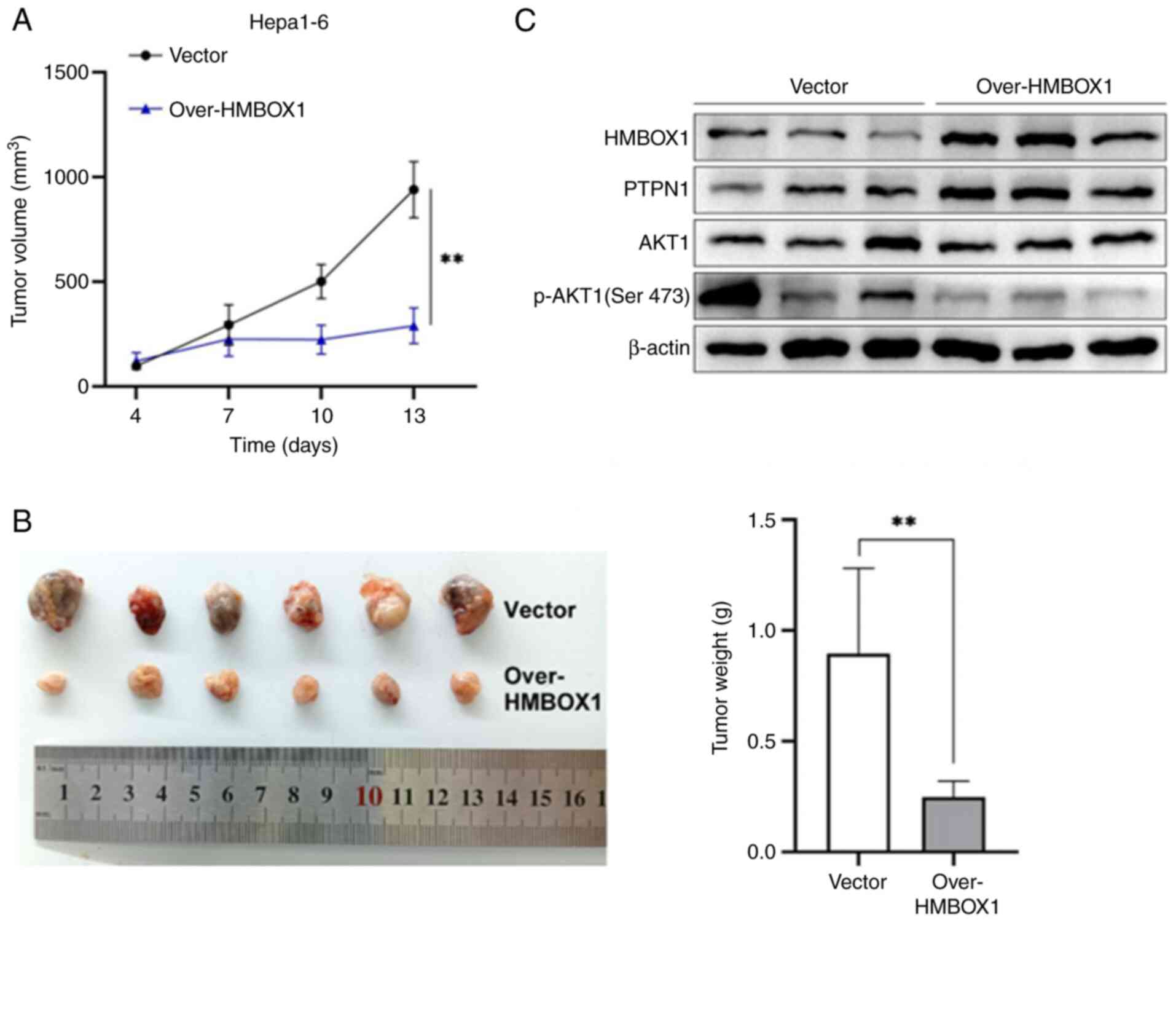
To further demonstrate the antitumor effect of
HMBOX1 in vivo, a subcutaneous tumor model was established
using HMBOX1-overexpressing (Over-HMBOX1) and control (Vector)
Hepa1-6 cells in mice of the same strain. It was found that HMBOX1
overexpression significantly inhibited the growth of subcutaneous
tumors in tumor-bearing mice (Fig. 6A
and B). The expression of related markers in tumor tissues was
analyzed, and it was found that HMBOX1 overexpression promoted
PTPN1 expression and inhibited AKT1 phosphorylation (Fig. 6C). Taken together, these results
indicated that HMBOX1 plays a vital role in the antitumor effects
of HCC by regulating the PTPN1/AKT pathway.
These results suggested that PTPN1 may be a
regulatory target of HMBOX1. To further clarify the relationship
between the two, a ChIP assay was performed. However, the results
showed that the regulation of PTPN1 by HMBOX1 may occur through an
indirect mode of action (Fig.
S4A-C). The CO-IP experiment was further used to analyze the
protein molecules that might interact with HMBOX1 and 69 protein
molecules interacting with HMBOX1 were further identified through
mass spectrometry (Fig. S4D). GO
enrichment analysis was conducted on PTPN1 and HMBOX1-interacting
proteins. GO terms containing PTPN1 in the enrichment analysis
results were selected to draw the Upset plots. It was found that
SOD2 repeatedly appears in 9 GO terms (Fig. S4E). Furthermore, the STRING
database was used to construct the interaction network between SOD2
and PTPN1. It was observed that SOD2 is directly associated with
PTPN1 through JAK2, APP and GHR and the remaining nodes form a
broader indirect interaction network (Fig. S4F). These results also suggested
that HMBOX1 may regulate the expression of PTPN1 through an
indirect regulatory approach, but the specific regulatory mechanism
still needs further exploration.
Discussion
In the present study, the low expression of HMBOX1
was confirmed in tumor tissues by searching a database and
analyzing tissue chips from patients with HCC, containing both
tumor and matched non-tumor liver tissues. Lentiviral infection was
used to overexpress HMBOX1 in HCC cell lines and observed its
effects on tumor progression through in vitro and in
vivo experiments. HMBOX1 overexpression significantly inhibited
the proliferation, migration and clonal formation of tumor cells,
and significantly inhibited tumor growth in mice. Further proteomic
analysis combined with experimental studies showed that HMBOX1
affected the phosphorylation of AKT1 by regulating the expression
of downstream PTPN1 indirectly, thus playing a role in inhibiting
HCC.
As a novel transcriptional suppressor, HMBOX1 is
widely expressed in various tissues of the human body. Previously,
in addition to the regulation of differentiation and development,
its role in tumors has gradually attracted attention. However, the
expression levels of HMBOX1 were not consistent among different
tumors. Differences in expression levels also imply diverse
functions (6,30). Our previous studies confirmed that
the expression of HMBOX1 is significantly downregulated in tumor
tissues and HCC cell lines, and that its expression level decreases
with disease progression (10). In
the present study, the LIHC dataset in the TCGA database and IHC
staining of tumor tissues of patients with HCC were further
analyzed, both of which confirmed that HMBOX1 had low expression in
tumor tissues compared with non-tumor tissues. Proteomic analysis
of Hepa1-6 cells overexpressing HMBOX1 (Over-HMBOX1) and the Vector
(Ctrl) showed that AKT1 expression in the Over-HMBOX1 group was
significantly downregulated compared with that in the Vector group.
The activation of AKT1 is significantly implicated in the
advancement of multiple types of malignant tumors, particularly HCC
(25,31). Consequently, it was hypothesized
that the overexpression of HMBOX1 could contribute to tumor
suppression by downregulating the expression and activation of
AKT1. The proteomic results were verified through western blotting,
and it was found that the expression of total AKT1 protein was not
significantly different between the two groups. However, the
phosphorylation level of AKT1 (Ser473) was significantly inhibited
in the HMBOX1 overexpression group. SC79 (AKT1 agonist) was used to
activate p-AKT1 (Ser473) and it was found that the inhibitory
effect of HMBOX1 on HCC could be reversed to a certain extent.
These results indicated that HMBOX1 could inhibit the
phosphorylation of AKT1. The downregulation of total AKT1 in
proteomics conflicts with the western blotting experiments,
probably because proteomic methods such as mass spectrometry are
generally more sensitive than western blotting and different
variant isoforms of AKT1 may affect the recognition of proteins by
antibodies in western blot experiments. The antibody used in the
present western blotting experiments is highly specific for the
AKT1 isoform and recognizes a single, defined epitope. By contrast,
bottom-up proteomics relies on the detection of tryptic peptides.
It is possible that the specific peptides quantified for ‘AKT1’ in
the current proteomic experiment were derived from a region whose
detectability was altered (for example, by a co-occurring
post-translational modification not related to the phosphorylation
studied, or by a sequence variant), leading to an apparent
downregulation. The western blotting, assessing the intact protein,
would be unaffected by such a localized change. However, the
downregulation of p-AKT1 expression was detected in
HMBOX1-overexpressing cells, suggesting that HMBOX1 inhibited the
activation of the AKT1 pathway.
PTPN1, a key post-translational mechanism in the
cellular processes of proliferation, migration, differentiation and
apoptosis (32), has attracted
attention for its abnormal expression in HCC tissues.
Overexpression of HMBOX1 upregulated the expression of PTPN1, and
the expression of PTPN1 in tumor tissues of patients with HCC was
downregulated, which is consistent with and correlated with the
changes in HMBOX1. In the present study, the rescue experiments
were only verified by silencing PTPN1 with siRNA in HCC cells
overexpressing HMBOX1; future gain-of-function studies will provide
complementary validation. Moreover, there is a significant positive
correlation between the expressions of HMBOX1 and PTPN1, that
suggests that there might be a regulatory role between the two
molecules. Further silencing of PTPN1 in HCC cells overexpressing
HMBOX1 can reverse the inhibition of AKT1 phosphorylation by
HMBOX1, which can to some extent explain the regulatory role among
these three molecules. Whereas the precise temporal sequence and
kinetics of these events remain to be fully elucidated by future
time-course studies. In addition, whether other isoform of AKT
(AKT2 and AKT3) are involved in signal regulation also remains to
be further explored as the function of different isoforms of AKT in
other tumor types is not redundant.
As a transcriptional suppressor, the positive
regulation of HMBOX1 on PTPN1 expression may be indirect. Through
the CHIP experiment, we also did not observe a direct interaction
between HMBOX1 and PTPN1. This suggests that other molecules may
play a regulatory role between HMBOX1 and PTPN1. The Co-IP
experiment was used to pull down the proteins interacting with
HMBOX1 and further identified 69 protein molecules interacting with
HMBOX1 through mass spectrometry (Fig.
S4D).
Using metascape database, GO enrichment analysis was
conducted on PTPN1 and HMBOX1-interacting proteins. GO terms
containing PTPN1 in the enrichment analysis results were selected
to draw the Upset plots. It was found that SOD2 repeatedly appears
in 9 GO terms (not in GO:0080135, GO:0071732 and GO:1901699)
(Fig. S4E). Further, by using the
STRING database to construct the interaction network between SOD2
and PTPN1. It can be seen that SOD2 is directly associated with
PTPN1 through JAK2, APP and GHR and the remaining nodes form a
broader indirect interaction network (Fig. S4F). The proteomics identification
results and bioinformatics analysis results also suggested that
HMBOX1 may regulate the expression of PTPN1 through an indirect
regulatory approach, but the specific regulatory mechanism still
needs further exploration. The precise temporal sequence and
kinetics of these events remain to be fully elucidated by future
time-course studies.
The effect of PTPN1 on tumors is not consistent, and
even in studies of the same tumor, the regulatory effect of PTPN1
is completely opposite in different research contexts (33,34).
Lessard et al (35) reviewed
the double-sided role of PTPN1 in tumors, demonstrating that PTPN1
has the potential to function as both a tumor suppressor and a
tumor promoter, contingent upon the specific substrate and the
surrounding cellular environment. Yuan et al (36) confirmed that in the highly
metastatic HCC cell line MHCC97-H, OP-B could inhibit the
activation of PI3K/AKT signaling by inhibiting the expression of
PTPN1, subsequently playing a role in inhibiting HCC. This is
inconsistent with the present findings that PTPN1 inhibits tumors
by inhibiting AKT activation. This could be attributed to the
utilization of various HCC cell lines. A previous study using liver
cancer cell line HepG2 also confirmed that decreased PTPN1 protein
expression can induce the activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway
(29). These findings suggest that
PTPN1 may play different regulatory roles in cells with different
genetic and molecular characteristics, even within the same tumor.
The fundamental function of a phosphatase is determined by its
interacting partners and substrates in a specific cellular context.
In the current HCC model, the expression and activity of PTPN1 are
driven by the transcription factor HMBOX1. Although this driving
effect is indirect, this unique upstream regulation might create a
specific signaling complex. The outcome of PTPN1 activity is likely
shaped by the specific signaling complex. Different binding
partners in different cell types could recruit PTPN1 to distinct
sets of substrates, leading to either activation or inhibition of
oncogenic pathways. On the other hand, it is possible that PTPN1
participates in a negative feedback loop to dampen excessive AKT
signaling, which is a common feature in cancers with hyperactive
PI3K/AKT. In this scenario, in the specific context of the HCC
model of the present study, the tumor-suppressive,
AKT-dephosphorylating function of PTPN1 becomes dominant and
unmasked. Whether PTPN1′s regulatory role on tumors is related to
the disease process remains to be further determined.
In the present study, the data suggested that HMBOX1
can inhibit HCC progression by upregulating the expression of
downstream PTPN1 and inhibiting the phosphorylation at Ser473 of
AKT1. These results confirmed the protective effect of HMBOX1 in
HCC development, and providing a new potential target for the
clinical diagnosis and treatment of HCC.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Natural Science
Foundation of China (grant no. 81901610), the Medical and Health
Science and Technology Development Project of Shandong Province
(grant no. 202402071098) and the Shandong Provincial Natural
Science Foundation (grant no. ZR2022QH294).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
HLZ conceptualized the study, reviewed and edited
the manuscript. CNZ conducted data curation and investigation. CNZ,
JHL, WYZ and JQ developed the methodology. YJ performed formal
analysis. HLZ and YJ were acquired funding, conducted project
administration and supervised the study. HLZ and QW validated data.
YJ wrote the original draft of the manuscript. HLZ and CNZ confirm
the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors read and approved
the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Animal studies were approved by the Ethical
Committee of Central Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical
University (approval no. W202403040279; Jinan, China). Animal
experiments were performed in accordance with the ARRIVE
guidelines. The use of HCC tissue chips and the patient information
in the public database were approved by the Ethics Committee of
Shandong First Medical University (approval no. R202403040155;
Jinan, China).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yau T, Kang YK, Kim TY, El-Khoueiry AB,
Santoro A, Sangro B, Melero I, Kudo M, Hou MM, Matilla A, et al:
Efficacy and safety of nivolumab plus ipilimumab in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with
sorafenib: The CheckMate 040 Randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol.
6:e2045642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yau T, Park JW, Finn RS, Cheng AL,
Mathurin P, Edeline J, Kudo M, Harding JJ, Merle P, Rosmorduc O, et
al: Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
(CheckMate 459): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3
trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:77–90. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
No authors listed. Correction to Lancet
Oncol. 2021.22:977–90. Lancet Oncol. 22:e3472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Finn RS, Qin S, Ikeda M, Galle PR, Ducreux
M, Kim TY, Kudo M, Breder V, Merle P, Kaseb AO, et al: Atezolizumab
plus bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 382:1894–1905. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang Y, Mu H and Zhao H: HMBOX1, a member
of the homeobox family: Current research progress. Cent Eur J
Immunol. 48:63–69. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen S, Li Y, Zhi S, Ding Z, Wang W, Peng
Y, Huang Y, Zheng R, Yu H, Wang J, et al: WTAP promotes
osteosarcoma tumorigenesis by repressing HMBOX1 expression in an
m(6)A-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis. 11:6592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu YL, Diao NN, Li YZ, Meng XH, Jiao WL,
Feng JB, Liu ZP and Lu N: Low expression level of HMBOX1 in
high-grade serous ovarian cancer accelerates cell proliferation by
inhibiting cell apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 501:380–386.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Diao N, Li Y, Yang J, Jin C, Meng X, Jiao
W, Feng J, Liu Z and Lu N: High expression of HMBOX1 contributes to
poor prognosis of gastric cancer by promoting cell proliferation
and migration. Biomed Pharmacother. 115:1088672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao H, Jia H, Han Q and Zhang J: Homeobox
containing 1 inhibits liver cancer progression by promoting
autophagy as well as inhibiting stemness and immune escape. Oncol
Rep. 40:1657–1665. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Coronell-Tovar A, Pardo JP,
Rodriguez-Romero A, Sosa-Peinado A, Vasquez-Bochm L, Cano-Sanchez
P, Alvarez-Anorve LI and Gonzalez-Andrade M: Protein tyrosine
phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) function, structure, and inhibition
strategies to develop antidiabetic drugs. FEBS Lett. 598:1811–1838.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Monoe Y, Jingushi K, Kawase A, Hirono T,
Hirose R, Nakatsuji Y, Kitae K, Ueda Y, Hase H, Abe Y, et al:
Pharmacological Inhibition of miR-130 family suppresses bladder
tumor growth by targeting various oncogenic pathways via PTPN1. Int
J Mol Sci. 22:47512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jin T, Li D, Yang T, Liu F, Kong J and
Zhou Y: PTPN1 promotes the progression of glioma by activating the
MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways and is associated with poor patient
survival. Oncol Rep. 42:717–725. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xu Q, Wu N, Li X, Guo C, Li C, Jiang B,
Wang H and Shi D: Inhibition of PTP1B blocks pancreatic cancer
progression by targeting the PKM2/AMPK/mTOC1 pathway. Cell Death
Dis. 10:8742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee YJ, Song H, Yoon YJ, Park SJ, Kim SY,
Cho Han D and Kwon BM: Ethacrynic acid inhibits STAT3 activity
through the modulation of SHP2 and PTP1B tyrosine phosphatases in
DU145 prostate carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 175:1139202020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie L, Qi H, Tian W, Bu S, Wu Z and Wang
H: High-expressed PTPN1 promotes tumor proliferation signature in
human hepatocellular carcinoma. Heliyon. 9:e198952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng LY, Zhou DX, Lu J, Zhang WJ and Zou
DJ: Downregulated expression of the protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B
(PTP1B) is associated with aggressive clinicopathologic features
and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 420:680–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T and Zhang Z:
GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling
and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 47((W1)): W556–W560.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gyorffy B: Integrated analysis of public
datasets for the discovery and validation of survival-associated
genes in solid tumors. Innovation (Camb). 5:1006252024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10:15232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szklarczyk D, Kirsch R, Koutrouli M,
Nastou K, Mehryary F, Hachilif R, Gable AL, Fang T, Doncheva NT,
Pyysalo S, et al: The STRING database in 2023: Protein-protein
association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any
sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 51((D1)):
D638–D646. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
de Bruijn I, Kundra R, Mastrogiacomo B,
Tran TN, Sikina L, Mazor T, Li X, Ochoa A, Zhao G, Lai B, et al:
Analysis and visualization of longitudinal genomic and clinical
data from the AACR project GENIE biopharma collaborative in
cBioPortal. Cancer Res. 83:3861–3867. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rauluseviciute I, Riudavets-Puig R,
Blanc-Mathieu R, Castro-Mondragon JA, Ferenc K, Kumar V, Lemma RB,
Lucas J, Cheneby J, Baranasic D, et al: JASPAR 2024: 20th
anniversary of the open-access database of transcription factor
binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 52((D1)): D174–D182. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Du J, Yu X, Zhang W, Zhang X, Zhao H, Xu R
and Wen Q: Plasma biomarker screening based on proteomic signature
of patients with resistant hypertension. j Cardiovasc Transl Res.
17:1286–1294. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mroweh M, Roth G, Decaens T, Marche PN,
Lerat H and Macek Jilkova Z: Targeting Akt in hepatocellular
carcinoma and its tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci.
22:17942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Paskeh MDA, Ghadyani F, Hashemi M,
Abbaspour A, Zabolian A, Javanshir S, Razzazan M, Mirzaei S,
Entezari M, Goharrizi MASB, et al: Biological impact and
therapeutic perspective of targeting PI3K/Akt signaling in
hepatocellular carcinoma: Promises and Challenges. Pharmacol Res.
187:1065532023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liao Y and Hung MC: Physiological
regulation of Akt activity and stability. Am J Transl Res. 2:19–42.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen C, Xu R, Guo C, Li X, Zhao Y and Luo
D: Lanostane triterpenoids from Ganoderma calidophilum exhibit
potent antitumor activity by inhibiting PTP1B. Chem Biol Interact.
403:1112532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li H, Dusseault J and Larose L: Nck1
depletion induces activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway by attenuating
PTP1B protein expression. Cell Commun Signal. 12:712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dai J, Zhang C, Tian Z and Zhang J:
Expression profile of HMBOX1, a novel transcription factor, in
human cancers using highly specific monoclonal antibodies. Exp Ther
Med. 2:487–490. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu L, Wei J and Liu P: Attacking the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment
in human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 85:69–94. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chiarugi P and Buricchi F: Protein
tyrosine phosphorylation and reversible oxidation: Two
cross-talking posttranslation modifications. Antioxid Redox Signal.
9:1–24. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de Jong PR, Takahashi N, Harris AR, Lee J,
Bertin S, Jeffries J, Jung M, Duong J, Triano AI, Lee J, et al: Ion
channel TRPV1-dependent activation of PTP1B suppresses
EGFR-associated intestinal tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest.
124:3793–3806. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu S, Bjorge JD and Fujita DJ: PTP1B
contributes to the oncogenic properties of colon cancer cells
through Src activation. Cancer Res. 67:10129–10137. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lessard L, Stuible M and Tremblay ML: The
two faces of PTP1B in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804:613–661.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yuan F, Gao Q, Tang H, Shi J and Zhou Y:
Ophiopogonin-B targets PTP1B to inhibit the malignant progression
of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the PI3K/AKT and AMPK
signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep. 25:1222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|