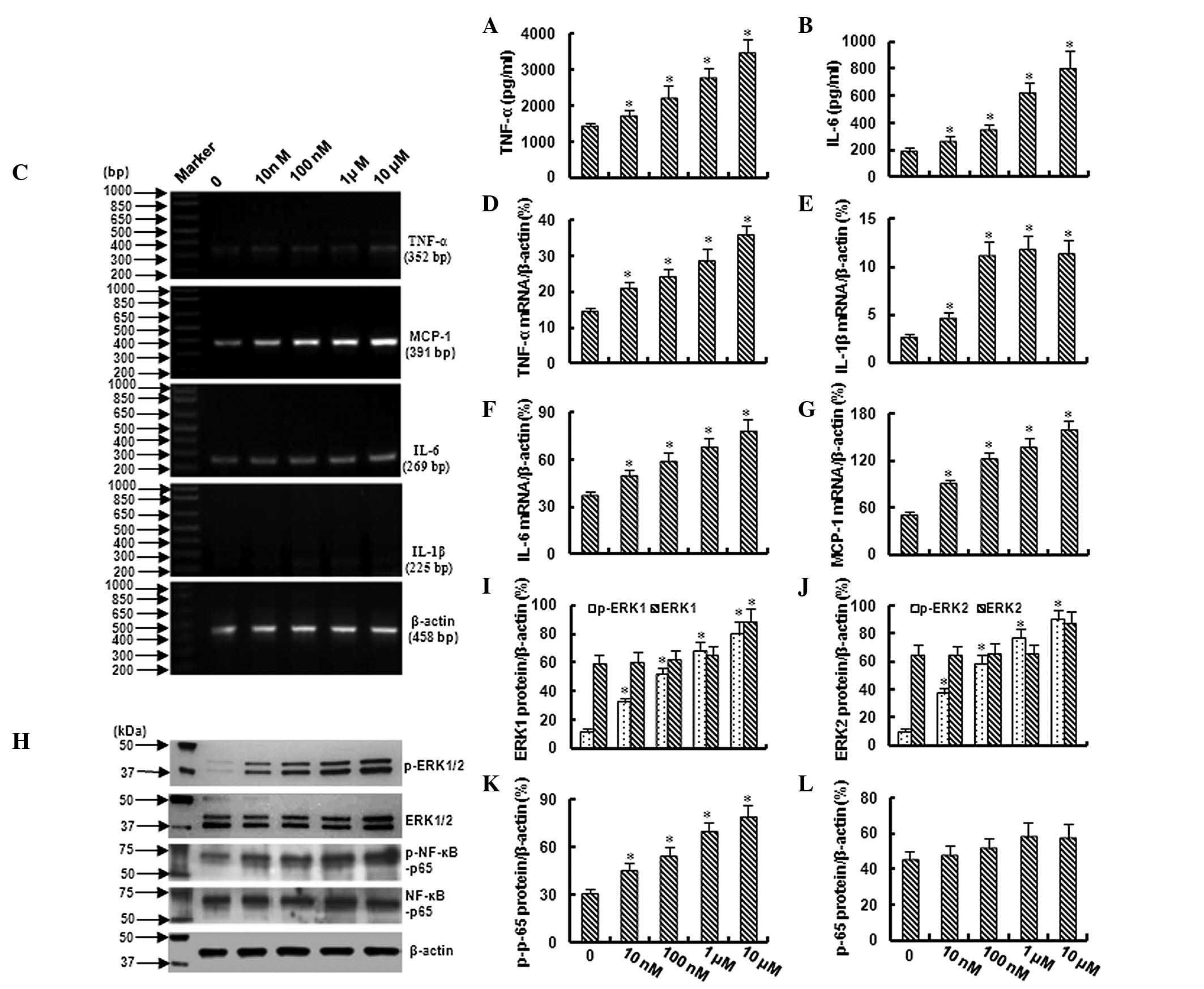
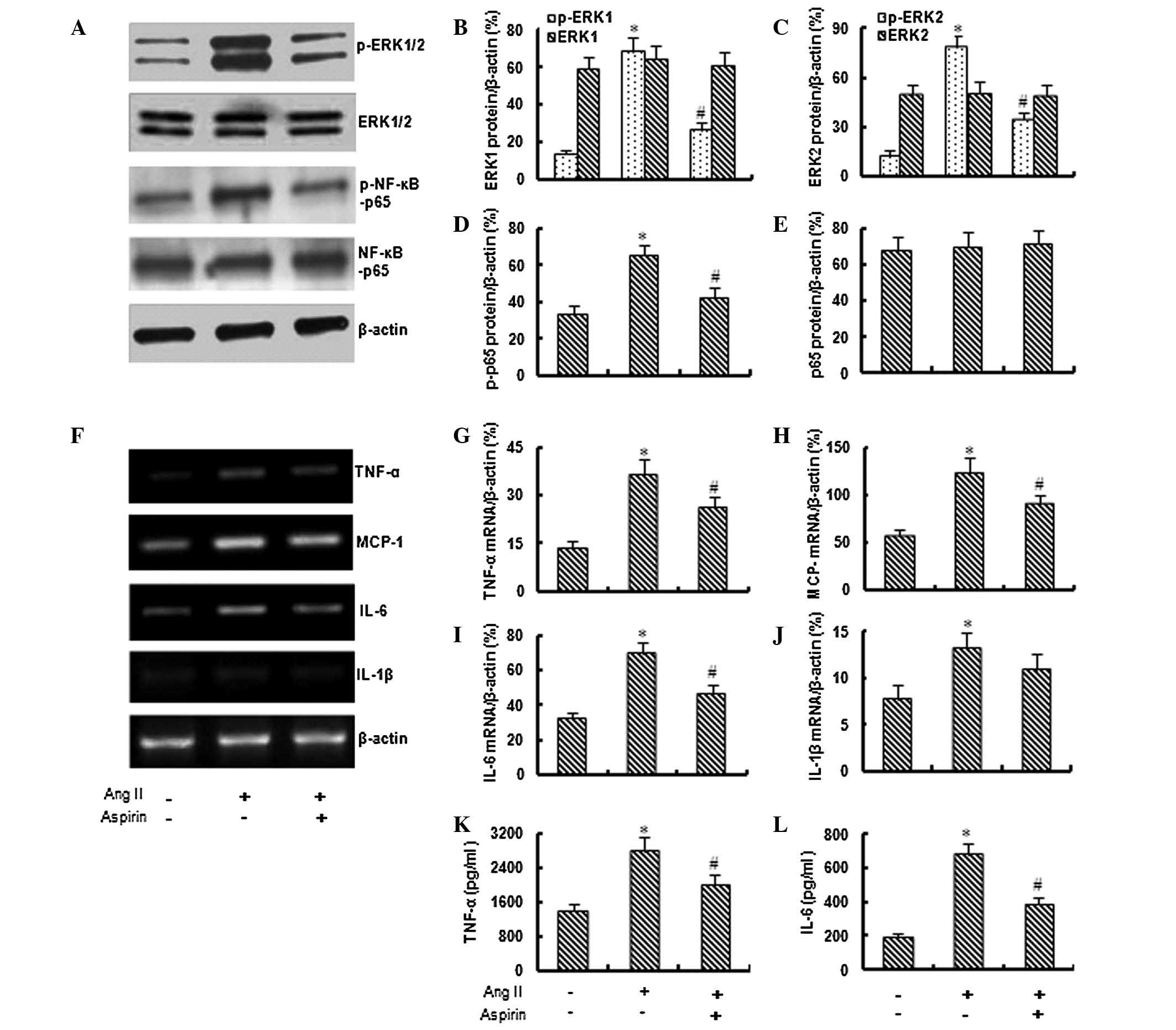
|
1
|
Rostovskaya M and Anastassiadis K:
Differential expression of surface markers in mouse bone marrow
mesenchymal stromal cell subpopulations with distinct lineage
commitment. PLoS One. 7:e512212012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jackson L, Jones DR, Scotting P, et al:
Adult mesenchymal stem cells: differentiation potential and
therapeutic applications. J Postgrad Med. 53:121–127. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mehta PK and Griendling KK: Angiotensin II
cell signaling: physiological and pathological effects in the
cardiovascular system. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 292:C82–C97.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xing Y, Lv A, Wang L, et al: The
combination of angiotensin II and 5-azacytidine promotes
cardiomyocyte differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 360:279–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matsushita K, Wu Y, Okamoto Y, et al:
Local renin angiotensin expression regulates human mesenchymal stem
cell differentiation to adipocytes. Hypertension. 48:1095–1102.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim YM, Jeon ES, Kim MR, et al:
Angiotensin II-induced differentiation of adipose tissue-derived
mesenchymal stem cells to smooth muscle-like cells. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 40:2482–2491. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhan Y, Brown C, Maynard E, et al: Ets-1
is a critical regulator of Ang II-mediated vascular inflammation
and remodeling. J Clin Invest. 115:2508–2516. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang X, Lu J, Khaidakov M, et al: Aspirin
suppresses cardiac fibroblast proliferation and collagen formation
through downregulation of angiotensin type 1 receptor
transcription. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 259:346–354. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wolak T, Kim H, Ren Y, et al: Osteopontin
modulates angiotensin II-induced inflammation, oxidative stress,
and fibrosis of the kidney. Kidney Int. 76:32–43. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen JW, Zhou SB and Tan ZM: Aspirin and
pravastatin reduce lectin-like oxidized low density lipoprotein
receptor-1 expression, adhesion molecules and oxidative stress in
human coronary artery endothelial cells. Chin Med J (Engl).
123:1553–1556. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Wu Y, Zhai H, Wang Y, et al:
Aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced intracellular ROS in BV2 microglia cells
by inhibiting the function of NADPH oxidase. Neurochem Res.
37:1690–1696. 2012.
|
|
12
|
Zhang F, Wang C, Jing S, et al:
Lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor-1 expresses in mouse bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and stimulates their
proliferation. Exp Cell Res. 319:1054–1059. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang F, Jing S, Ren T, et al:
microRNA-10b promotes the migration of mouse bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells and downregulates the expression of
E-cadherin. Mol Med Rep. Aug 6–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
van Velthoven CT, Kavelaars A and Heijnen
CJ: Mesenchymal stem cells as a treatment for neonatal ischemic
brain damage. Pediatr Res. 71:474–481. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pastore S, Mascia F, Mariotti F, et al:
ERK1/2 regulates epidermal chemokine expression and skin
inflammation. J Immunol. 174:5047–5056. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee WK, Chung KW, Kim GH, et al:
Gallotannin causes differentiation and inflammation via ERK-1/-2
and p38 kinase pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes. Mol Med
Rep. 7:701–707. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vartiainen N, Goldsteins G,
Keksa-Goldsteine V, et al: Aspirin inhibits p44/42
mitogen-activated protein kinase and is protective against
hypoxia/reoxygenation neuronal damage. Stroke. 34:752–757. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang YP, Wu Y, Li LY, et al:
Aspirin-triggered lipoxin A4 attenuates LPS-induced
pro-inflammatory responses by inhibiting activation of NF-κB and
MAPKs in BV-2 microglial cells. J Neuroinflammation.
8:952011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ke X, Chen J, Zhang X, et al: Qing Hua
Chang Yin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
response in human intestinal cells by inhibiting NF-κB activation.
Exp Ther Med. 6:189–193. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: Therapeutic
potential of inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in the treatment
of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest. 107:135–142. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Muller DN, Heissmeyer V, Dechend R, et al:
Aspirin inhibits NF-kappaB and protects from angiotensin II-induced
organ damage. FASEB J. 15:1822–1824. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Akyazi I, Eraslan E, Gulcubuk A, et al:
Long-term aspirin pretreatment in the prevention of
cerulein-induced acute pancreatitis in rats. World J Gastroenterol.
19:2894–2903. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|