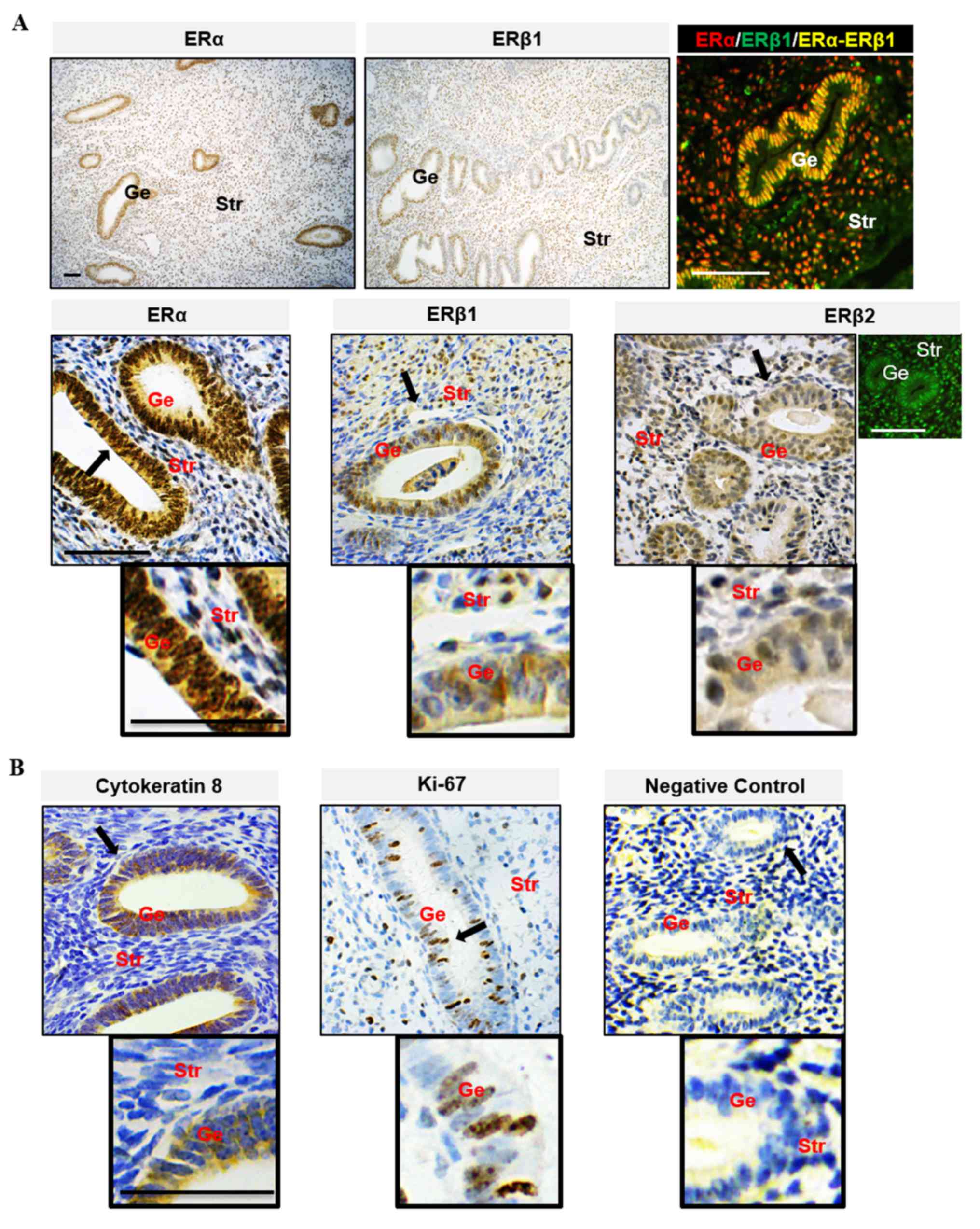
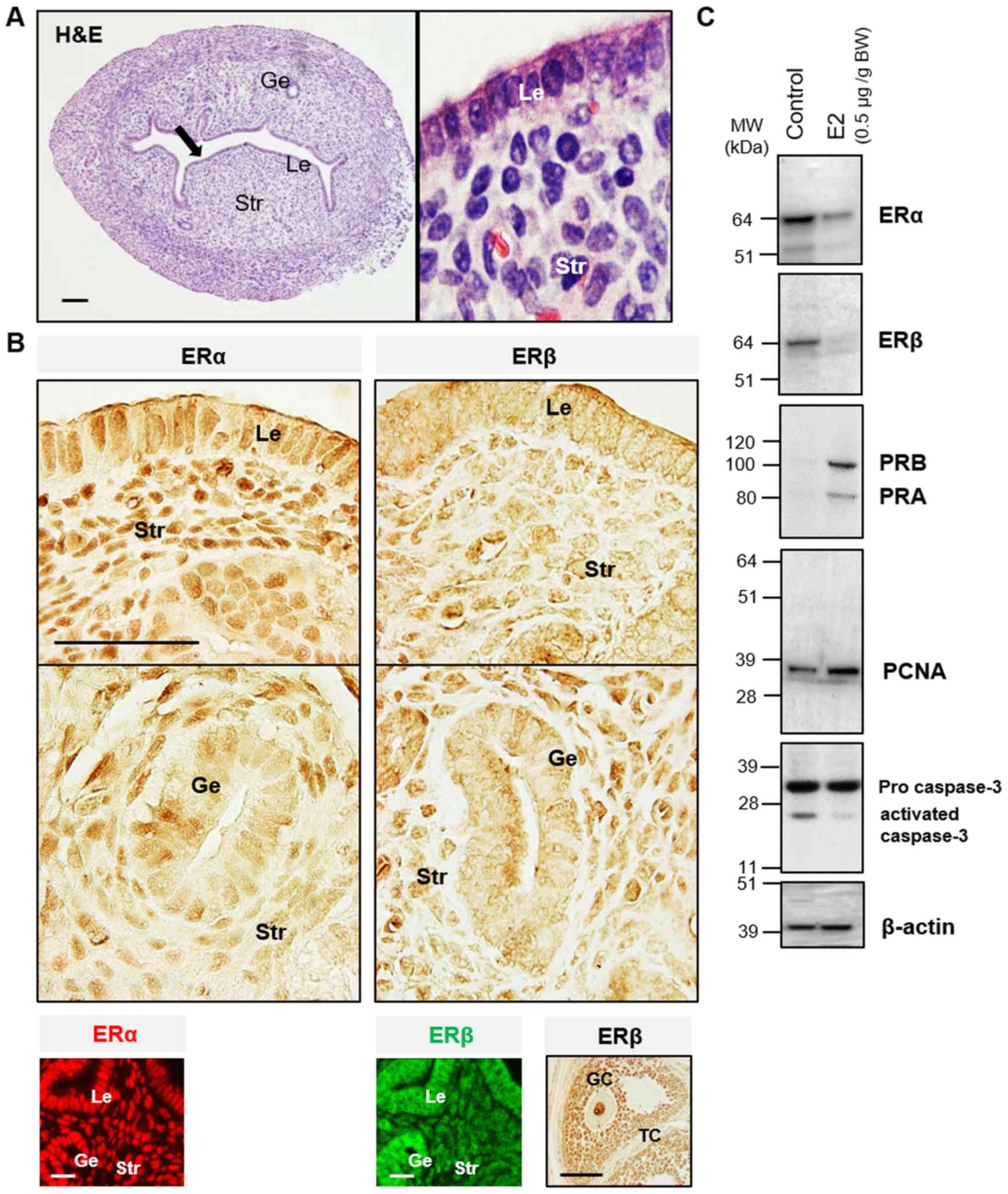
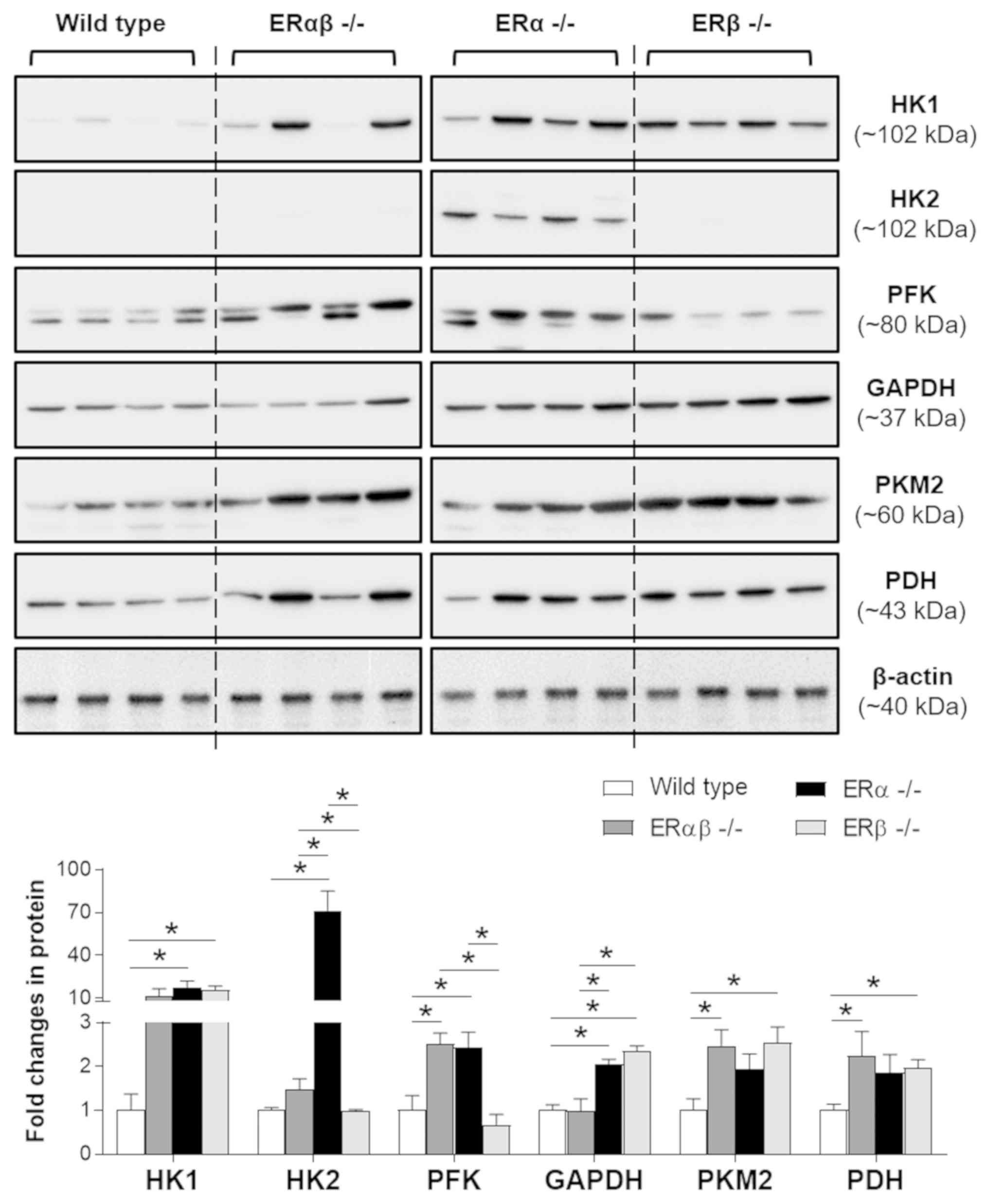
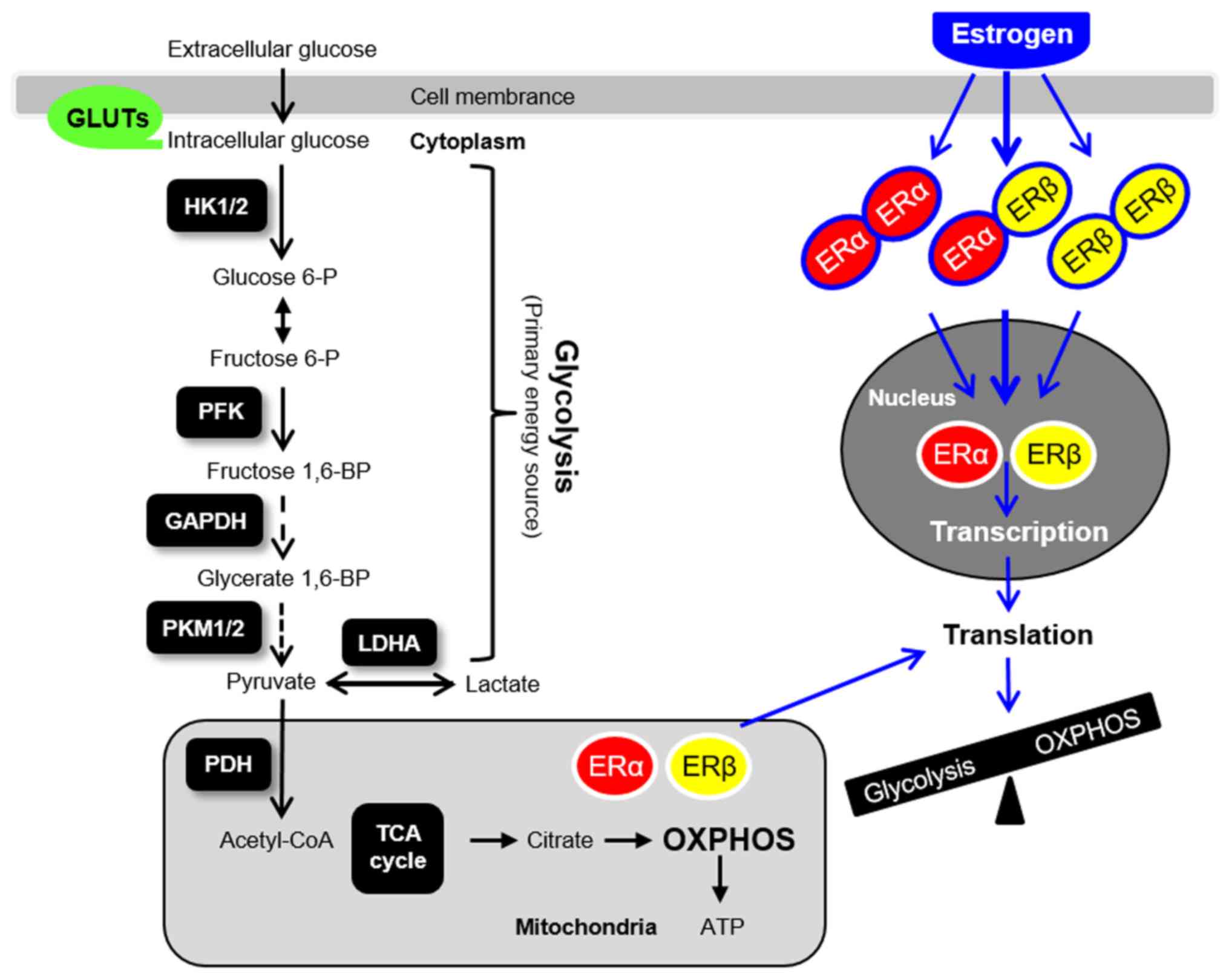
|
1
|
Hamilton KJ, Hewitt SC, Arao Y and Korach
KS: Estrogen hormone biology. Curr Top Dev Biol. 125:109–146.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Barros RP and Gustafsson JÅ: Estrogen
receptors and the metabolic network. Cell Metab. 14:289–299.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hewitt SC, Winuthayanon W and Korach KS:
What's new in estrogen receptor action in the female reproductive
tract. J Mol Endocrinol. 56:R55–R71. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Matthews J, Wihlén B, Tujague M, Wan J,
Strom A and Gustafsson JA: Estrogen receptor (ER) beta modulates
ERalpha-mediated transcriptional activation by altering the
recruitment of c-Fos and c-Jun to estrogen-responsive promoters.
Mol Endocrinol. 20:534–543. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hapangama DK, Kamal AM and Bulmer JN:
Estrogen receptor β: The guardian of the endometrium. Hum Reprod
Update. 21:174–193. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rumi MA, Dhakal P, Kubota K, Chakraborty
D, Lei T, Larson MA, Wolfe MW, Roby KF, Vivian JL and Soares MJ:
Generation of Esr1-knockout rats using zinc finger
nuclease-mediated genome editing. Endocrinology. 155:1991–1999.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rodriguez AC, Blanchard Z, Maurer KA and
Gertz J: Estrogen signaling in endometrial cancer: A key oncogenic
pathway with several open questions. Horm Cancer. 10:51–63.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Azziz R, Carmina E, Chen Z, Dunaif A,
Laven JS, Legro RS, Lizneva D, Natterson-Horowtiz B, Teede HJ and
Yildiz BO: Polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2(16057)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Goodarzi MO, Dumesic DA, Chazenbalk G and
Azziz R: Polycystic ovary syndrome: Etiology, pathogenesis and
diagnosis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 7:219–231. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li X, Feng Y, Lin JF, Billig H and Shao R:
Endometrial progesterone resistance and PCOS. J Biomed Sci.
21(2)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li X and Shao R: PCOS and obesity: Insulin
resistance might be a common etiology for the development of type I
endometrial carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 4:73–79. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fearnley EJ, Marquart L, Spurdle AB,
Weinstein P and Webb PM: Australian Ovarian Cancer Study Group and
Australian National Endometrial Cancer Study Group: Polycystic
ovary syndrome increases the risk of endometrial cancer in women
aged less than 50 years: An Australian case-control study. Cancer
Causes Control. 21:2303–2308. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Sun X, Sun X, Meng F, Hu M, Li X,
Li W, Wu XK, Brännström M, Shao R and Billig H: Molecular
characterization of insulin resistance and glycolytic metabolism in
the rat uterus. Sci Rep. 6(30679)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kuyucu Y, Çelik LS, Kendirlinan Ö, Tap Ö
and Mete UÖ: Investigation of the uterine structural changes in the
experimental model with polycystic ovary syndrome and effects of
vitamin D treatment: An ultrastructural and immunohistochemical
study. Rep Biol. 18:53–59. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Brosens I and Benagiano G: Menstrual
preconditioning for the prevention of major obstetrical syndromes
in polycystic ovary syndrome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 213:488–493.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Leonhardt H, Gull B, Kishimoto K, Kataoka
M, Nilsson L, Janson PO, Stener-Victorin E and Hellström M: Uterine
morphology and peristalsis in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Acta Radiol. 53:1195–1201. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Villavicencio A, Bacallao K, Gabler F,
Fuentes A, Albornoz J, Casals A and Vega M: Deregulation of tissue
homeostasis in endometria from patients with polycystic ovarian
syndrome with and without endometrial hyperplasia. Gynecol Oncol.
104:290–295. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Piltonen TT: Polycystic ovary syndrome:
Endometrial markers. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 37:66–79.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Baracat MC, Serafini PC, Simões Rdos S,
Maciel GA, Soares JM Jr and Baracat EC: Systematic review of cell
adhesion molecules and estrogen receptor expression in the
endometrium of patients with polycystic ovary syndrome. Int J
Gynaecol Obstet. 129:1–4. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hu M, Zhang Y, Feng J, Xu X, Zhang J, Zhao
W, Guo X, Li J, Vestin E, Cui P, et al: Uterine progesterone
signaling is a target for metformin therapy in PCOS-like rats. J
Endocrinol. 237:123–137. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li SY, Song Z, Song MJ, Qin JW, Zhao ML
and Yang ZM: Impaired receptivity and decidualization in
DHEA-induced PCOS mice. Sci Rep. 6(38134)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Burns JS and Manda G: Metabolic pathways
of the warburg effect in health and disease: Perspectives of
choice, Chain or chance. Int J Mol Sci. 18pii.
(E2755)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Gellersen B and Brosens JJ: Cyclic
decidualization of the human endometrium in reproductive health and
failure. Endocr Rev. 35:851–905. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Baquer NZ and McLean P: The effect of
oestradiol on the profile of constant and specific proportion
groups of enzymes in rat uterus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
48:729–734. 1972.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Baquer NZ, Sochor M, Kunjara S and McLean
P: Effect of oestradiol on the carbohydrate metabolism of immature
rat uterus: The role of fructose-2, 6-bis-phosphate and of
phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 31:509–519.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reiss NA: Ontogeny and estrogen
responsiveness of creatine kinase and glycolytic enzymes in brain
and uterus of rat. Neurosci Lett. 84:197–202. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Singhal RL and Valadares JR: Estrogenic
regulation of uterine pyruvate kinase. Am J Physiol. 218:321–327.
1970.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Das A, Mantena SR, Kannan A, Evans DB,
Bagchi MK and Bagchi IC: De novo synthesis of estrogen in pregnant
uterus is critical for stromal decidualization and angiogenesis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:12542–12547. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Tan J, Paria BC, Dey SK and Das SK:
Differential uterine expression of estrogen and progesterone
receptors correlates with uterine preparation for implantation and
decidualization in the mouse. Endocrinology. 140:5310–5321.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zuo RJ, Gu XW, Qi QR, Wang TS, Zhao XY,
Liu JL and Yang ZM: Warburg-like glycolysis and lactate shuttle in
mouse decidua during early pregnancy. J Biol Chem. 290:21280–21291.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kommagani R, Szwarc MM, Kovanci E, Gibbons
WE, Putluri N, Maity S, Creighton CJ, Sreekumar A, DeMayo FJ, Lydon
JP and O'Malley BW: Acceleration of the glycolytic flux by steroid
receptor coactivator-2 is essential for endometrial
decidualization. PLoS Genet. 9(e1003900)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lv H, Tong J, Yang J, Lv S, Li WP, Zhang C
and Chen ZJ: Dysregulated pseudogene HK2P1 may contribute to
preeclampsia as a competing endogenous RNA for hexokinase 2 by
impairing decidualization. Hypertension. 71:648–658.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shao R, Markström E, Friberg PA, Johansson
M and Billig H: Expression of progesterone receptor (PR) A and B
isoforms in mouse granulosa cells: Stage-dependent PR-mediated
regulation of apoptosis and cell proliferation. Biol Reprod.
68:914–921. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shao R, Zhang FP, Rung E, Palvimo JJ,
Huhtaniemi I and Billig H: Inhibition of small ubiquitin-related
modifier-1 expression by luteinizing hormone receptor stimulation
is linked to induction of progesterone receptor during ovulation in
mouse granulosa cells. Endocrinology. 145:384–392. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Shao R, Egecioglu E, Weijdegård B,
Kopchick JJ, Fernandez-Rodriguez J, Andersson N and Billig H:
Dynamic regulation of estrogen receptor-alpha isoform expression in
the mouse fallopian tube: Mechanistic insight into
estrogen-dependent production and secretion of insulin-like growth
factors. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 293:E1430–E1442.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Couse JF, Hewitt SC, Bunch DO, Sar M,
Walker VR, Davis BJ and Korach KS: Postnatal sex reversal of the
ovaries in mice lacking estrogen receptors alpha and beta. Science.
286:2328–2331. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lubahn DB, Moyer JS, Golding TS, Couse JF,
Korach KS and Smithies O: Alteration of reproductive function but
not prenatal sexual development after insertional disruption of the
mouse estrogen receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
90:11162–11166. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Krege JH, Hodgin JB, Couse JF, Enmark E,
Warner M, Mahler JF, Sar M, Korach KS, Gustafsson JA and Smithies
O: Generation and reproductive phenotypes of mice lacking estrogen
receptor beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:15677–15682.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Feng Y, Johansson J, Shao R, Mannerås L,
Fernandez-Rodriguez J, Billig H and Stener-Victorin E: Hypothalamic
neuroendocrine functions in rats with dihydrotestosterone-induced
polycystic ovary syndrome: Effects of low-frequency
electro-acupuncture. PLoS One. 4(e6638)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Noyes RW, Hertig AT and Rock J: Dating the
endometrial biopsy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 122:262–263.
1975.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Hu M, Meng F, Sun X, Xu H, Zhang
J, Cui P, Morina N, Li X, Li W, et al: Metformin ameliorates
uterine defects in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome.
EBioMedicine. 18:157–170. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hu M, Zhang Y, Guo X, Jia W, Liu G, Zhang
J, Li J, Cui P, Sferruzzi-Perri AN, Han Y, et al: Hyperandrogenism
and insulin resistance induce gravid uterine defects in association
with mitochondrial dysfunction and aberrant reactive oxygen species
production. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 316:E794–E809.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li X, Pishdari B, Cui P, Hu M, Yang HP,
Guo YR, Jiang HY, Feng Y, Billig H and Shao R: Regulation of
androgen receptor expression alters AMPK phosphorylation in the
endometrium: In vivo and in vitro studies in women with polycystic
ovary syndrome. Int J Bio Sci. 11:1376–1389. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Quaynor SD, Stradtman EW Jr, Kim HG, Shen
Y, Chorich LP, Schreihofer DA and Layman LC: Delayed puberty and
estrogen resistance in a woman with estrogen receptor alpha
variant. N Engl J Med. 369:164–171. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hamilton KJ, Arao Y and Korach KS:
Estrogen hormone physiology: Reproductive findings from estrogen
receptor mutant mice. Reprod Biol. 14:3–8. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kim JJ, Choi YM, Choung SH, Yoon SH, Lee
GH and Moon SY: Estrogen receptor beta gene +1730 G/A polymorphism
in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril.
93:1942–1947. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Frolova AI and Moley KH: Glucose
transporters in the uterus: An analysis of tissue distribution and
proposed physiological roles. Reproduction. 142:211–220.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Frolova AI and Moley KH: Quantitative
analysis of glucose transporter mRNAs in endometrial stromal cells
reveals critical role of GLUT1 in uterine receptivity.
Endocrinology. 152:2123–2128. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Frolova A, Flessner L, Chi M, Kim ST,
Foyouzi-Yousefi N and Moley KH: Facilitative glucose transporter
type 1 is differentially regulated by progesterone and estrogen in
murine and human endometrial stromal cells. Endocrinology.
150:1512–1520. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Cui P, Li X, Wang X, Feng Y, Lin JF,
Billig H and Shao R: Lack of cyclical fluctuations of endometrial
GLUT4 expression in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Evidence
for direct regulation of GLUT4 by steroid hormones. BBA Clin.
4:85–91. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Li X, Cui P, Jiang HY, Guo YR, Pishdari B,
Hu M, Feng Y, Billig H and Shao R: Reversing the reduced level of
endometrial GLUT4 expression in polycystic ovary syndrome: A
mechanistic study of metformin action. Am J Transl Res. 7:574–586.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Orostica L, Astorga I, Plaza-Parrochia F,
Vera C, Garcia V, Carvajal R, Gabler F, Romero C and Vega M:
Proinflammatory environment and role of TNF-α in endometrial
function of obese women having polycystic ovarian syndrome. Int J
Obes (Lond). 40:1715–1722. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Kim JY, Song H, Kim H, Kang HJ, Jun JH,
Hong SR, Koong MK and Kim IS: Transcriptional profiling with a
pathway-oriented analysis identifies dysregulated molecular
phenotypes in the endometrium of patients with polycystic ovary
syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 94:1416–1426. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Evans J, Salamonsen LA, Winship A,
Menkhorst E, Nie G, Gargett CE and Dimitriadis E: Fertile ground:
Human endometrial programming and lessons in health and disease.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 12:654–667. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hardiman P, Pillay OC and Atiomo W:
Polycystic ovary syndrome and endometrial carcinoma. Lancet.
361:1810–1812. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wang T, Zhang J, Hu M, Zhang Y, Cui P, Li
X, Li J, Vestin E, Brännström M, Shao LR and Billig H: Differential
expression patterns of glycolytic enzymes and
mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in PCOS patients with endometrial
hyperplasia, an early hallmark of endometrial cancer, in vivo and
the impact of metformin in vitro. Int J Biol Sci. 15:714–725.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Couse JF, Curtis SW, Washburn TF, Lindzey
J, Golding TS, Lubahn DB, Smithies O and Korach KS: Analysis of
transcription and estrogen insensitivity in the female mouse after
targeted disruption of the estrogen receptor gene. Mol Endocrinol.
9:1441–1454. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Schoneberg T, Kloos M, Brüser A,
Kirchberger J and Sträter N: Structure and allosteric regulation of
eukaryotic 6-phosphofructokinases. Biol Chem. 394:977–993.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Eto K, Sakura H, Yasuda K, Hayakawa T,
Kawasaki E, Moriuchi R, Nagataki S, Yazaki Y and Kadowaki T:
Cloning of a complete protein-coding sequence of human
platelet-type phosphofructokinase isozyme from pancreatic islet.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 198:990–998. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hannemann A, Jandrig B, Gaunitz F,
Eschrich K and Bigl M: Characterization of the human P-type
6-phosphofructo-1-kinase gene promoter in neural cell lines. Gene.
345:237–247. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Al Hasawi N, Alkandari MF and Luqmani YA:
Phosphofructokinase: A mediator of glycolytic flux in cancer
progression. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 92:312–321. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Hulchiy M, Nybacka Å, Sahlin L and
Hirschberg AL: Endometrial expression of estrogen receptors and the
androgen receptor in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: A
lifestyle intervention study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 101:561–571.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Shang K, Jia X, Qiao J, Kang J and Guan Y:
Endometrial abnormality in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
Reprod Sci. 19:674–683. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Hu M, Li J, Zhang Y, Li X, Brännström M,
Shao LR and Billig H: Endometrial progesterone receptor isoforms in
women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Am J Transl Res.
10:2696–2705. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|