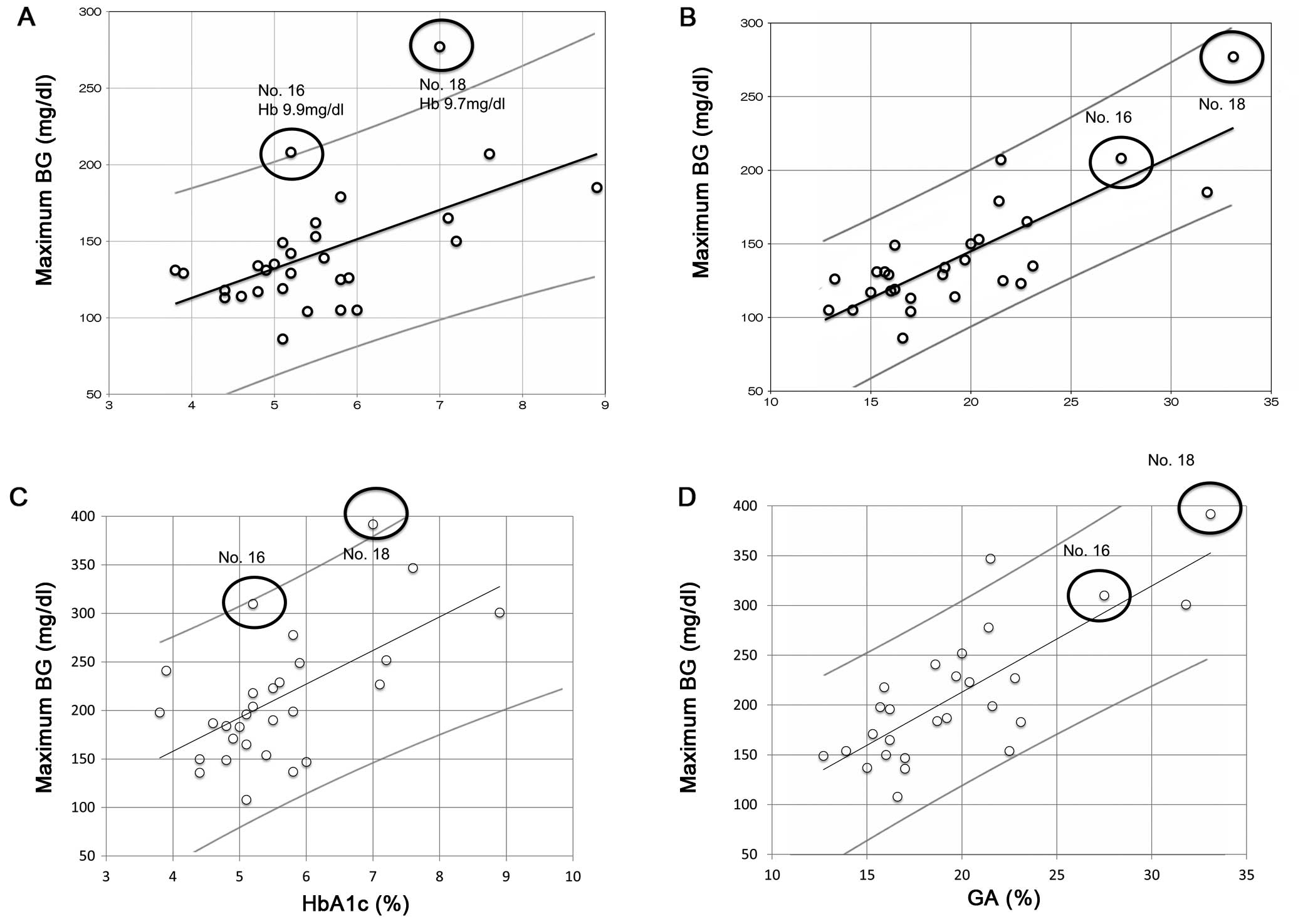
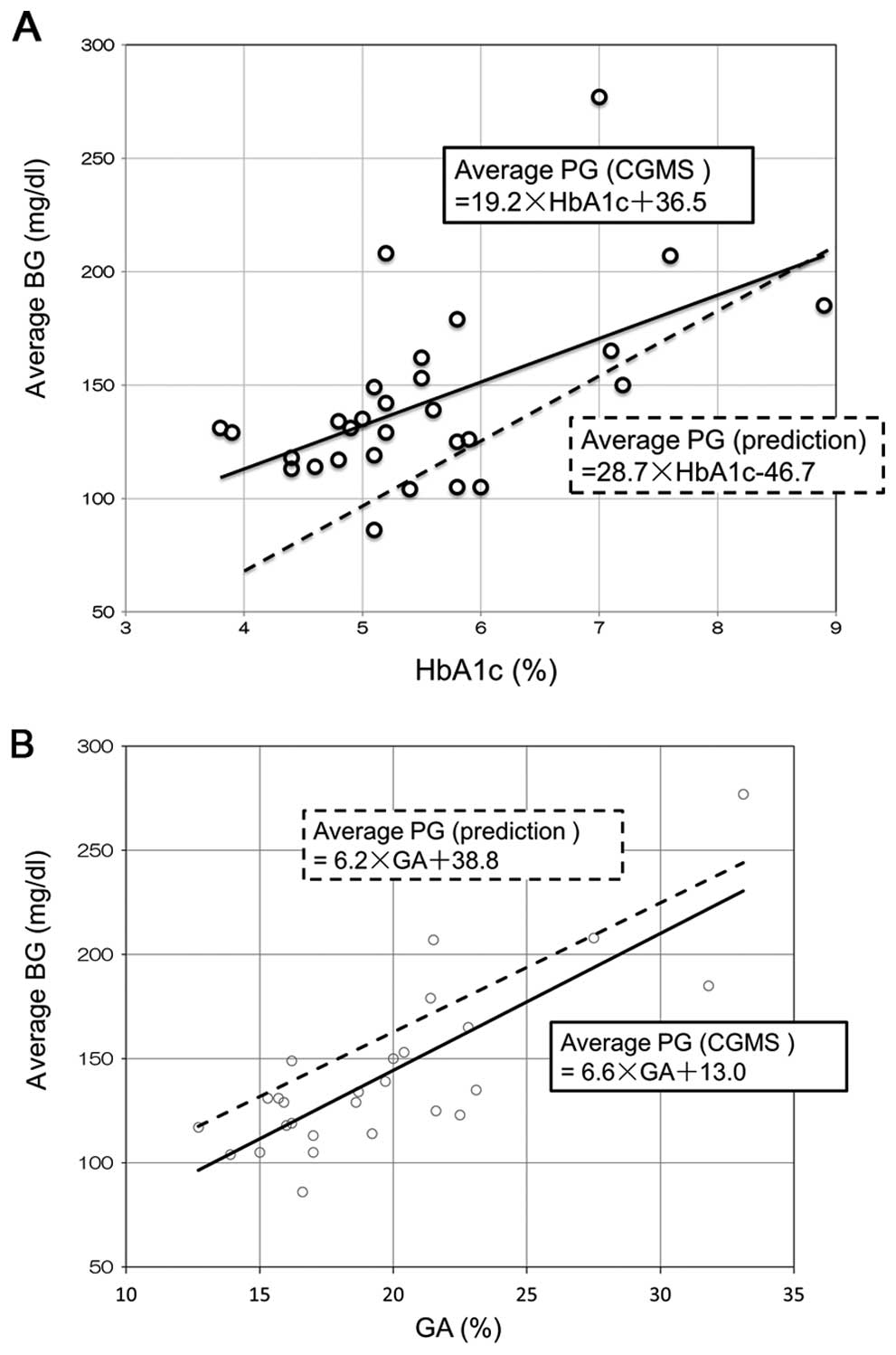
|
1
|
Kruszynska YT, Home PD and McIntyre N:
Relationship between insulin sensitivity, insulin secretion and
glucose tolerance in cirrhosis. Hepatology. 14:103–111. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Megyesi C, Samols E and Marks V: Glucose
tolerance and diabetes in chronic liver disease. Lancet.
2:1051–1056. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gillett MJ: International Expert Committee
report on the role of the A1c assay in the diagnosis of diabetes:
Diabetes Care 2009; 32(7): 1327–1334. Clin Biochem Rev. 30:197–200.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seino Y, Nanjo K, Tajima N, Kadowaki T,
Kashiwagi A, Araki E, Ito C, Inagaki N, Iwamoto Y, Kasuga M, et al:
Committee of the Japan Diabetes Society on the Diagnostic Criteria
of Diabetes Mellitus: Report of the committee on the classification
and diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Investig.
1:212–228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Garlick RL and Mazer JS: The principal
site of nonenzymatic glycosylation of human serum albumin in vivo.
J Biol Chem. 258:6142–6146. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Day JF, Ingebretsen CG, Ingebretsen WR Jr,
Baynes JW and Thorpe SR: Nonenzymatic glucosylation of serum
proteins and hemoglobin: Response to changes in blood glucose
levels in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 29:524–527. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koga M, Kasayama S, Kanehara H and Bando
Y: CLD (chronic liver diseases)-HbA1C as a suitable indicator for
estimation of mean plasma glucose in patients with chronic liver
diseases. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 81:258–262. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sterling K: The turnover rate of serum
albumin in man as measured by I131-tagged albumin. J Clin Invest.
30:1228–1237. 1951. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boyne MS, Silver DM, Kaplan J and Saudek
CD: Timing of changes in interstitial and venous blood glucose
measured with a continuous subcutaneous glucose sensor. Diabetes.
52:2790–2794. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nathan DM, Kuenen J, Borg R, Zheng H,
Schoenfeld D and Heine RJ: Alc-Derived Average Glucose Study Group:
Translating the A1C assay into estimated average glucose values.
Diabetes Care. 31:1473–1478. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bedossa P: The French METAVIR Cooperative
Study Group: Intraobserver and interobserver variations in liver
biopsy interpretation in patients with chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatology. 20:15–20. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brunt EM, Janney CG, Di Bisceglie AM,
Neuschwander-Tetri BA and Bacon BR: Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A
proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. Am J
Gastroenterol. 94:2467–2474. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Inoue K, Tsujimoto T, Yamamoto-Honda R,
Goto A, Kishimoto M, Noto H, Kajio H, Doi S, Miyazaki S, Terauchi
Y, et al: A newer conversion equation for the correlation between
HbA1c and glycated albumin. Endocr J. 61:553–560. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Petersen KF, Krssak M, Navarro V,
Chandramouli V, Hundal R, Schumann WC, Landau BR and Shulman GI:
Contributions of net hepatic glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis to
glucose production in cirrhosis. Am J Physiol. 276:E529–E535.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tajika M, Kato M, Mohri H, Miwa Y, Kato T,
Ohnishi H and Moriwaki H: Prognostic value of energy metabolism in
patients with viral liver cirrhosis. Nutrition. 18:229–234. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Imano E, Kanda T, Nakatani Y, Motomura M,
Arai K, Matsuhisa M, Yamasaki Y and Hori M: Impaired splanchnic and
peripheral glucose uptake in liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol.
31:469–473. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nielsen MF, Caumo A, Aagaard NK,
Chandramouli V, Schumann WC, Landau BR, Schmitz O and Vilstrup H:
Contribution of defects in glucose uptake to carbohydrate
intolerance in liver cirrhosis: Assessment during physiological
glucose and insulin concentrations. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 288:G1135–G1143. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Petrides AS, Stanley T, Matthews DE, Vogt
C, Bush AJ and Lambeth H: Insulin resistance in cirrhosis:
Prolonged reduction of hyperinsulinemia normalizes insulin
sensitivity. Hepatology. 28:141–149. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cusin I, Terrettaz J, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F
and Jeanrenaud B: Metabolic consequences of hyperinsulinaemia
imposed on normal rats on glucose handling by white adipose tissue,
muscles and liver. Biochem J. 267:99–103. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Heaton JH and Gelehrter TD:
Desensitization of hepatoma cells to insulin action. Evidence for a
post-receptor mechanism. J Biol Chem. 256:12257–12262.
1981.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wardzala LJ, Hirshman M, Pofcher E, Horton
ED, Mead PM, Cushman SW and Horton ES: Regulation of glucose
utilization in adipose cells and muscle after long-term
experimental hyperinsulinemia in rats. J Clin Invest. 76:460–469.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bianchi G, Marchesini G, Zoli M, Bugianesi
E, Fabbri A and Pisi E: Prognostic significance of diabetes in
patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 20:119–125. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishida T, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Arimitsu S,
Haruna Y, Imano E, Suzuki M, Kanda T, Kawano S, Hiramatsu N, et al:
Oral glucose tolerance test predicts prognosis of patients with
liver cirrhosis. Am J Gastroenterol. 101:70–75. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Moreau R, Delègue P, Pessione F, Hillaire
S, Durand F, Lebrec D and Valla DC: Clinical characteristics and
outcome of patients with cirrhosis and refractory ascites. Liver
Int. 24:457–464. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jepsen P, Watson H, Andersen PK and
Vilstrup H: Diabetes as a risk factor for hepatic encephalopathy in
cirrhosis patients. J Hepatol. 63:1133–1138. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wlazlo N, van Greevenbroek MM, Curvers J,
Schoon EJ, Friederich P, Twisk JW, Bravenboer B and Stehouwer CD:
Diabetes mellitus at the time of diagnosis of cirrhosis is
associated with higher incidence of spontaneous bacterial
peritonitis, but not with increased mortality. Clin Sci (Lond).
125:341–348. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ariza X, Castellote J, Lora-Tamayo J,
Girbau A, Salord S, Rota R, Ariza J and Xiol X: Risk factors for
resistance to ceftriaxone and its impact on mortality in community,
healthcare and nosocomial spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. J
Hepatol. 56:825–832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheruvattath R and Balan V: Infections in
patients with end-stage liver disease. J Clin Gastroenterol.
41:403–411. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kawaguchi T, Itou M, Taniguchi E, Sakata
M, Abe M, Koga H, Oriishi T, Imamura Y, Kato T, Yamada K, et al:
Serum level of free fatty acids is associated with nocturnal
hypoglycemia in cirrhotic patients with HCV infection: A pilot
study. Hepatogastroenterology. 58:103–108. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hashiba M, Ono M, Hyogo H, Ikeda Y, Masuda
K, Yoshioka R, Ishikawa Y, Nagata Y, Munekage K, Ochi T, et al:
Glycemic variability is an independent predictive factor for
development of hepatic fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease. PLoS One. 8:e761612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kishimoto M and Noda M: Verification of
glycemic profiles using continuous glucose monitoring: Cases with
steroid use, liver cirrhosis, enteral nutrition, or late dumping
syndrome. J Med Invest. 62:1–10. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|