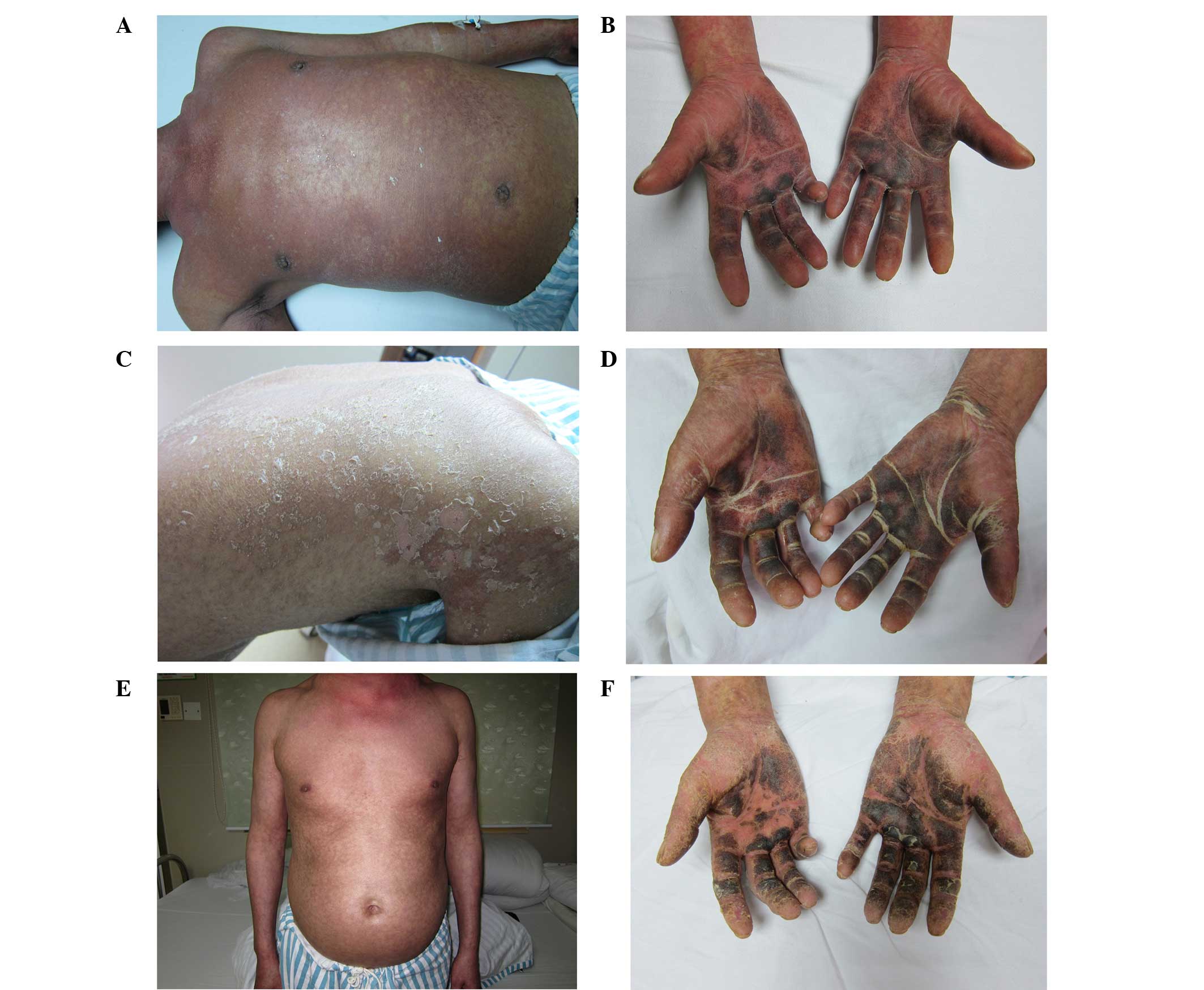
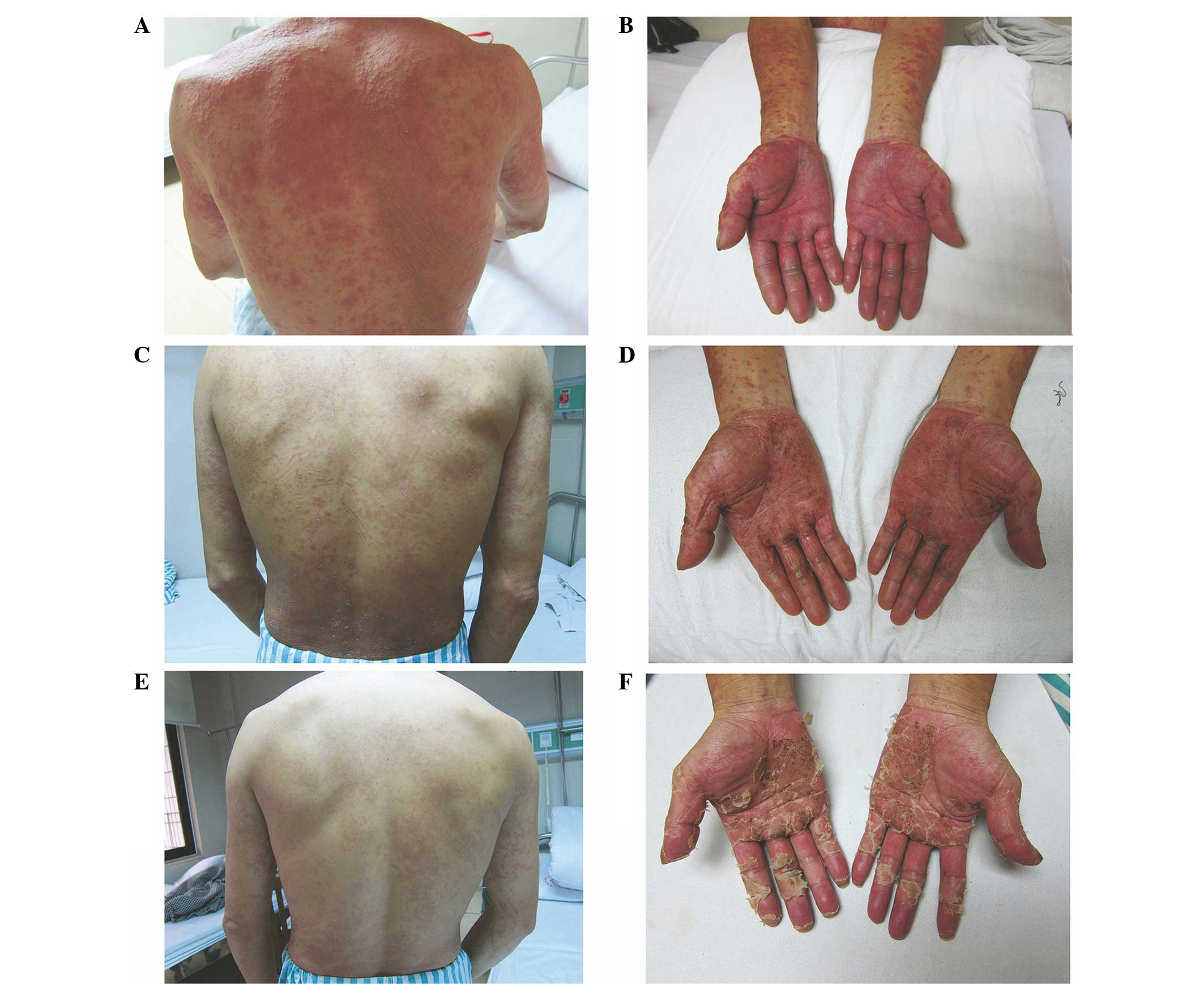
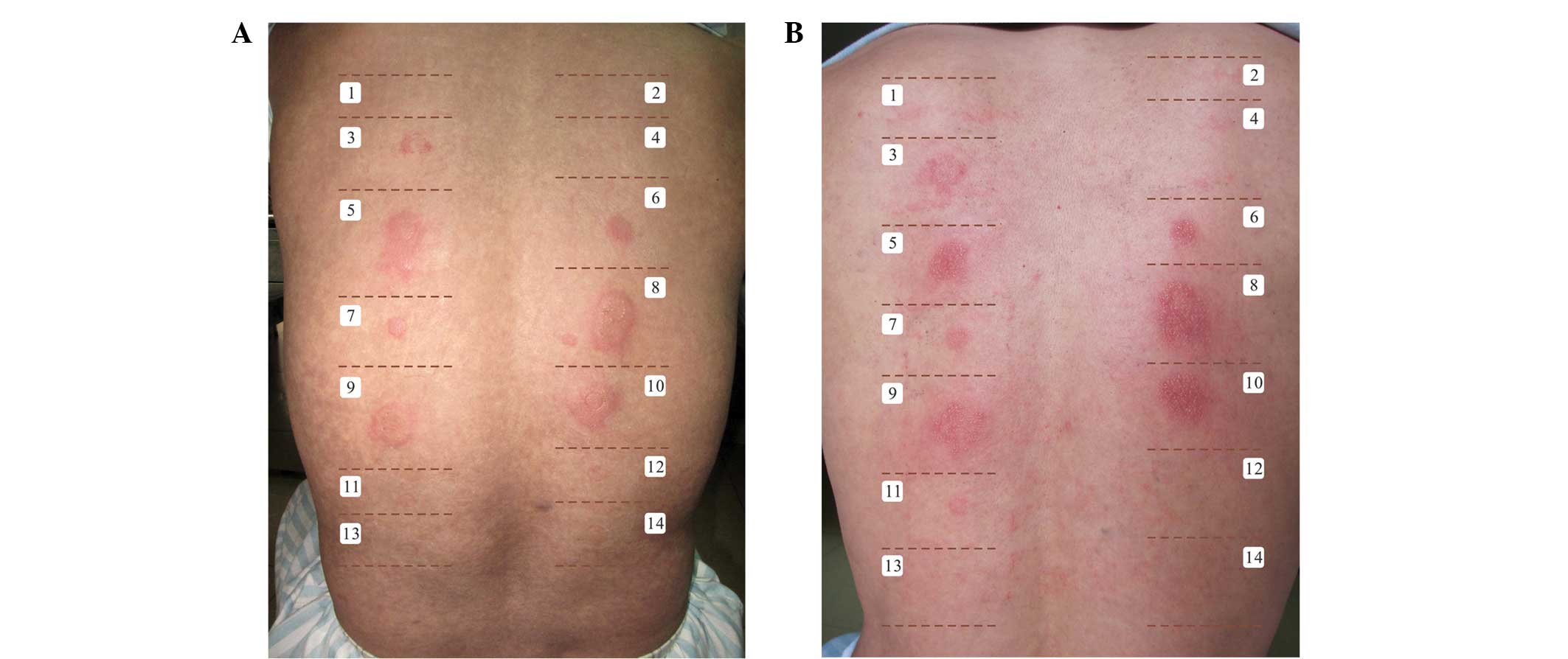
|
1
|
Huang Z, Yue F, Yang X, Xia L, Chen C, Qiu
X, Huang J, Li L, Kamijima M, Nakajima T and Huang H: Upregulation
of calprotectin and downregulation of retinol binding protein in
the serum of workers with trichloroethylene-induced
hypersensitivity dermatitis. J Occup Health. 54:299–309.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xu X, Yang R, Wu N, Zhong P, Ke Y, Zhou L,
Yuan J, Li G, Huang H and Wu B: Severe hypersensitivity dermatitis
and liver dysfunction induced by occupational exposure to
trichloroethylene. Ind Health. 47:107–112. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kamijima M, Hisanaga N, Wang H and
Nakajima T: Occupational trichloroethylene exposure as a cause of
idiosyncratic generalized skin disorders and accompanying hepatitis
similar to drug hypersensitivities. Int Arch Occup Environ Health.
80:357–370. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li H, Dai Y, Huang H, Li L, Leng S, Cheng
J, Niu Y, Duan H, Liu Q, Zhang X, et al: HLA-B* 1301 as a biomarker
for genetic susceptibility to hypersensitivity dermatitis induced
by trichloroethylene among workers in China. Environ Health
Perspect. 115:1553–1556. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang X, Que B, Song X, Li S, Yang X, Wang
H, Huang H, Kamijima M, Nakajima T, Lin Y and Li L:
Characterization of liver injury associated with hypersensitive
skin reactions induced by trichloroethylene in the guinea pig
maximization test. J Occup Health. 50:114–121. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kamijima M, Wang H, Yamanoshita O, Ito Y,
Xia L, Yanagiba Y, Chen C, Okamura A, Huang Z, Qiu X, et al:
Occupational trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome: Human
herpesvirus 6 reactivation and rash phenotypes. J Dermatol Sci.
72:218–224. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao N, Wang HL, Yue F, Zeng ZM, Li HL,
Huang YS and Chen RT: Studying the changes of the related serum
complement immune indexes in patients with occupational
medicamentosa-like dermatitis induced by trichloroethylene and
workers occupationally exposed to trichloroethylene. Zhonghua Lao
Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 30:284–288. 2012.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu J: Clinical analysis of seven cases of
trichloroethylene medicamentose-like dermatitis. Ind Health.
47:685–688. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xia LH, Huang HL, Kuang SR, Liu HF and
Kong LZ: A clinical analysis of 50 cases of medicament-like
dermatitis due to trichloroethylene. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng
Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 22:207–210. 2004.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chiu WA, Jinot J, Scott CS, Makris SL,
Cooper GS, Dzubow RC, Bale AS, Evans MV, Guyton KZ, Keshava N, et
al: Human health effects of trichloroethylene: Key findings and
scientific issues. Environ Health Perspect. 121:303–311. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chae H, Lee S, Lee K, Kim J, Lee S, Shin
D, et al: Exfoliative dermatitis and toxic hepatitis associated
with occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Korean J Occup
Environ Med. 15:111–117. 2003.(In Korean).
|
|
12
|
Chittasobhaktra T, Wannanukul W,
Wattanakrai P, Pramoolsinsap C, Sohonslitdsuk A and Nitiyanant P:
Fever, skin rash, jaundice and lymphadenopathy after
trichloroethylene exposure: A case report. J Med Assoc Thai.
80(Suppl 1): S144–S148. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Phoon WH, Chan MO, Rajan VS, Tan KJ,
Thirumoorthy T and Goh CL: Stevens-Johnson syndrome associated with
occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Contact Dermatitis.
10:270–276. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Conde-Salazar L, Guimaraens D, Romero LV
and Sanchez Yus E: Subcorneal pustular eruption and erythema from
occupational exposure to trichloroethylene. Contact Dermatitis.
9:235–237. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ohtoshi S, Kitami Y, Sueki H and Nakada T:
Utility of patch testing for patients with drug eruption. Clin Exp
Dermatol. 39:279–283. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang Y and Huang H: Research progress oil
immune injury resulted from occupational medicamentose-like
dermatitis induced by trichloroethylene. Zhong Guo Zhi Ye Yi Xue.
37:157–162. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Huang H, Kamijima M, Wang H, Li S,
Yoshikawa T, Lai G, Huang Z, Liu H, Chen J, Takeuchi Y, et al:
Human herpesvirus 6 reactivation in trichloroethylene-exposed
workers suffering from generalized skin disorders accompanied by
hepatic dysfunction. J Occup Health. 48:417–423. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu H, Wang Y, Dong N, Yang F, Lin Z, Shang
X and Li C: Meibomian gland dysfunction determines the severity of
the dry eye conditions in visual display terminal workers. PLoS
One. 9:e1055752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schrader S, Liu L, Kasper K and Geerling
G: Generation of two- and three-dimensional lacrimal gland
constructs. Dev Ophthalmol. 45:49–56. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong N, Li W, Lin H, Wu H, Li C, Chen W,
Qin W, Quyang L, Wang H and Liu Z: Abnormal epithelial
differentiation and tear film alteration in pinguecula. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:2710–2715. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lash LH, Fisher JW, Lipscomb JC and Parker
JC: Metabolism of trichloroethylene. Environ Health Perspect 108
Suppl. 2:177–200. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gawkrodger DJ: Patch testing in
occupational dermatology. Occup Environ Med. 58:823–828. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shear NH, Milpied B, Bruynzeel DP and
Phillips EJ: A review of drug patch testing and implications for
HIV clinicians. AIDS. 22:999–1007. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Slodownik D, Williams J, Frowen K, Palmer
A, Matheson M and Nixon R: The additive value of patch testing with
patients' own products at an occupational dermatology clinic.
Contact Dermatitis. 61:231–235. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Watanabe H, Tohyama M, Kamijima M,
Nakajima T, Yoshida T, Hashimoto K and Iijima M: Occupational
trichloroethylene hypersensitivity syndrome with human
herpesvirus-6 and cytomegalovirus reactivation. Dermatology.
221:17–22. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|