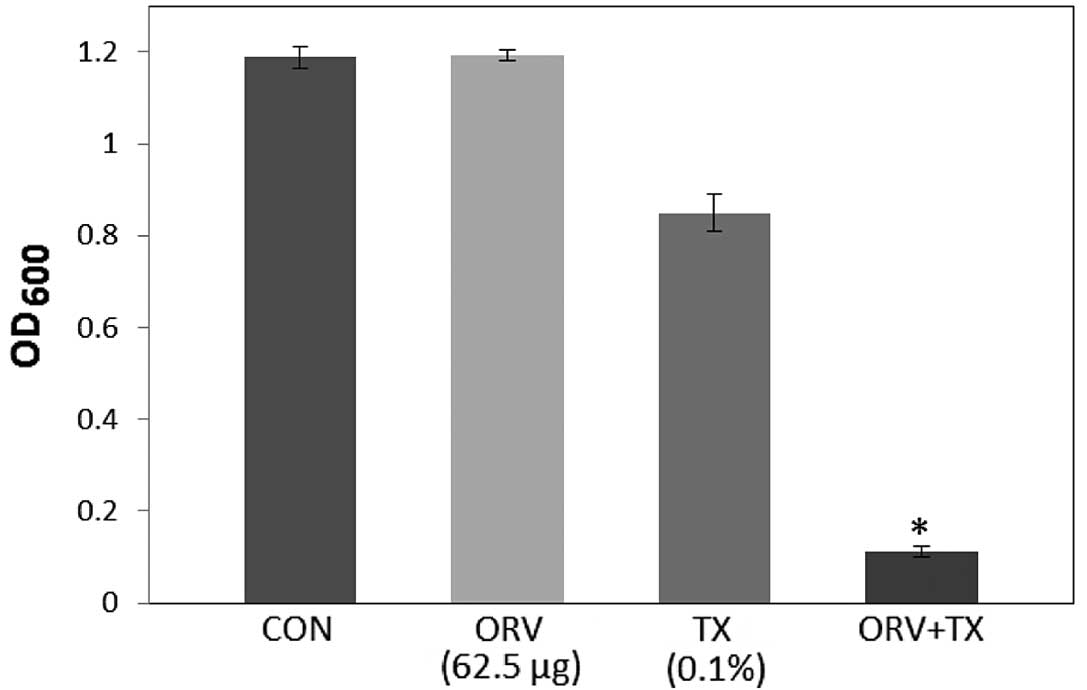
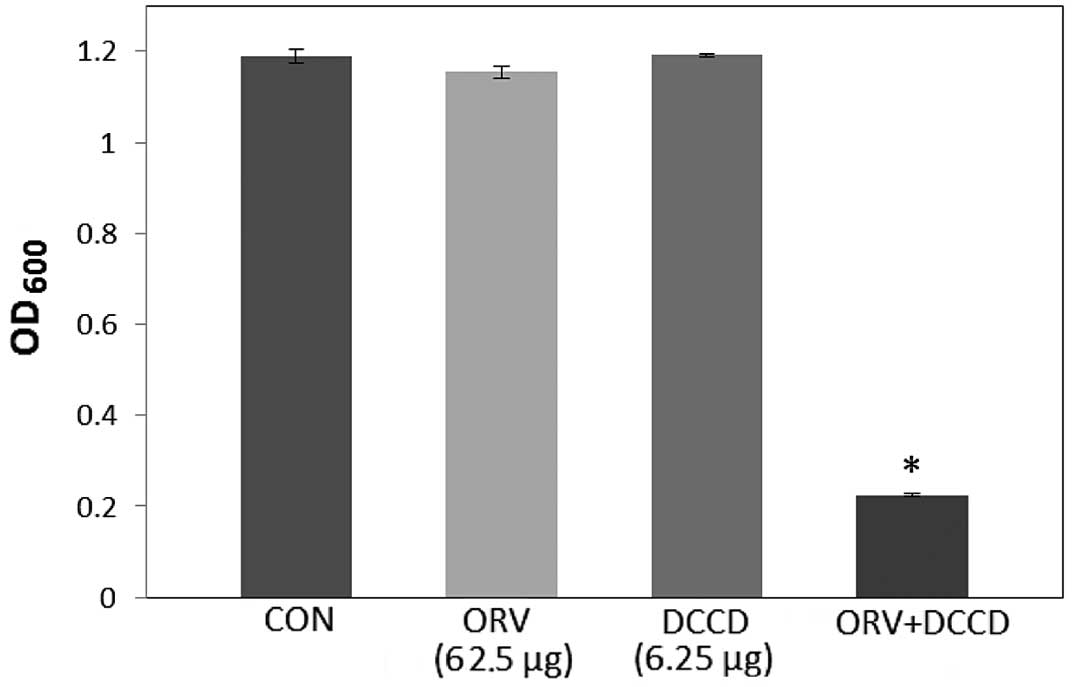
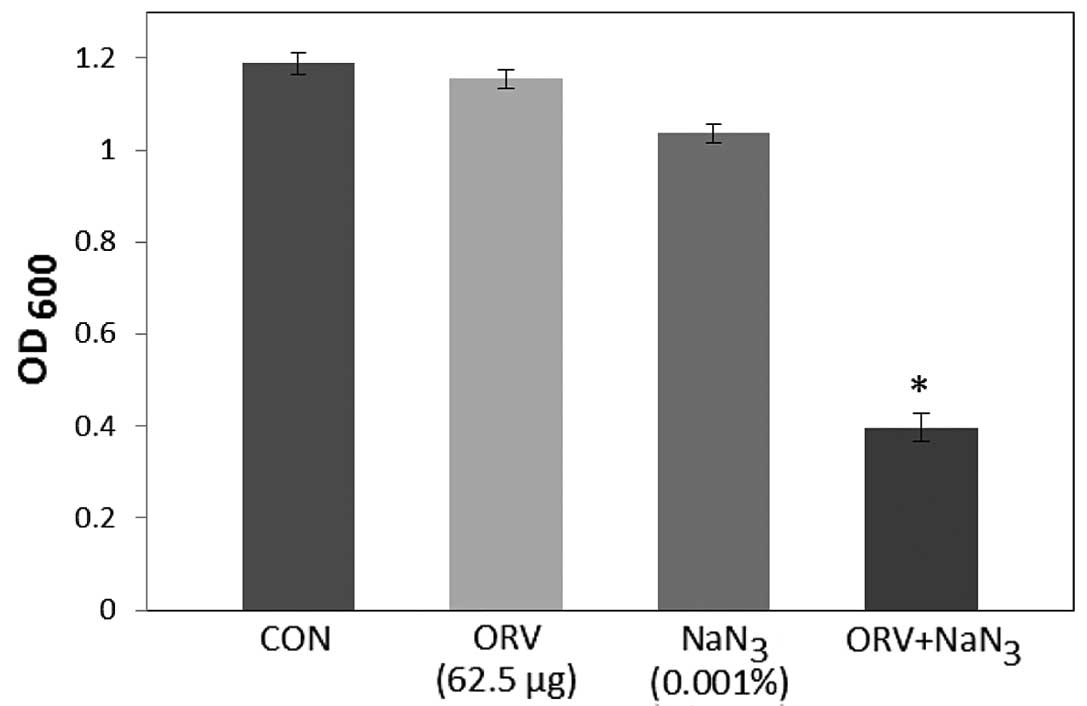
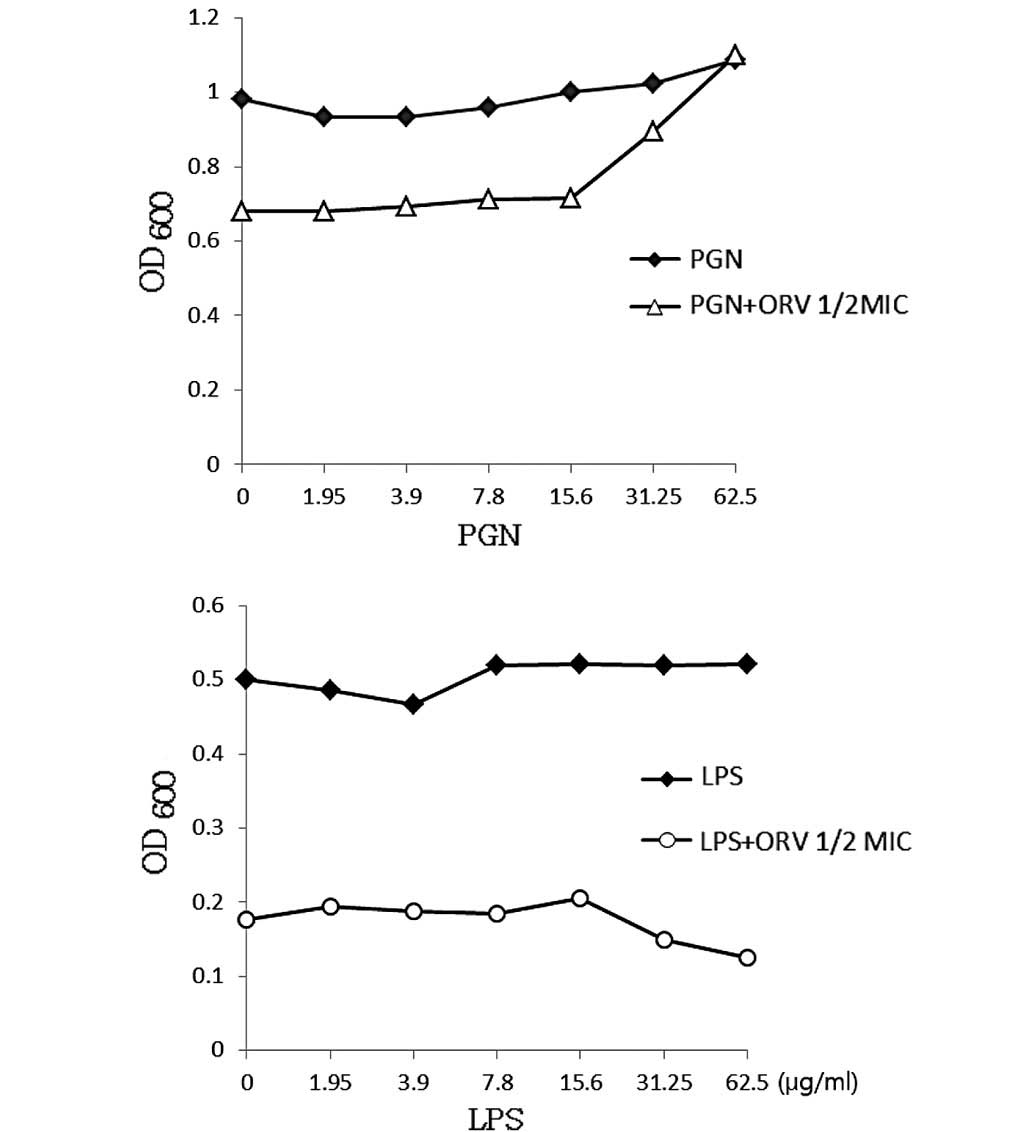
|
1
|
Mun SH, Kang OH, Joung DK, Kim SB, Choi
JG, Shin DW and Kwon DY: In vitro anti-MRSA activity of
carvone with gentamicin. Exp Ther Med. 7:891–896. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Whitby M, McLaws ML and Berry G: Risk of
death from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
bacteraemia: A meta-analysis. Med J Aust. 175:264–267.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bozic KJ and Ries MD: The impact of
infection after total hiparthroplasty on hospital and surgeon
resource utilization. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 8:1746–1751. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gracia E, Fernández A, Conchello P,
Laclériga A, Paniagua L, Seral F and Amorena B: Adherence of
Staphylococcus aureus slime-producing strain variants to
biomaterials used in orthopaedic surgery. Int Orthop. 21:46–51.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seghrouchni K, van Delden C, Dominguez D,
Benkabouche M, Bernard L, Assal M, Hoffmeyer P and Uçkay I:
Remission after treatment of osteoarticular infections due to
Pseudomonas aeruginosa versus Staphylococcus aureus:
A case-controlled study. Int Orthop. 36:1065–1071. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
De Lucas-Villarrubia JC, Lopez-Franco M,
Granizo JJ, De Lucas-Garcia JC and Gomez-Barrena E: Strategy to
control methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus
post-operative infection in orthopaedic surgery. Int Orthop.
28:16–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aqil F, Ahmad I and Owais M: Evaluation of
anti-methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
activity and synergy of some bioactive plant extracts. Biotechnol
J. 1:1093–1102. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Iqbal S, Younas U, Sirajuddin Chan KW,
Sarfraz RA and Uddin K: Proximate composition and antioxidant
potential of leaves from three varieties of Mulberry (Morus sp.): A
comparative study. Int J Mol Sci. 13:6651–6664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singab AN, El-Beshbishy HA, Yonekawa M,
Nomura T and Fukai T: Hypoglycemic effect of Egyptian Morus
alba root bark extract: Effect on diabetes and lipid
peroxidation of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 100:333–338. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin WY, Na MK, An RB, Lee HY, Bae KH and
Kang SS: Antioxidant compounds from twig of Morus alba. Nat Prod
Sci. 13:129–132. 2002.
|
|
11
|
Chung KO, Kim BY, Lee MH, Kim YR, Chung
HY, Park JH and Moon JO: In-vitro and in-vivo
anti-inflammatory effect of oxyresveratrol from Morus alba
L. J Pharm Pharmacol. 55:1695–1700. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sritularak B, De-Eknamkul W and
Likhitwitayawuid K: Tyrosinase inhibitors form Artocarpus lakoocha.
Thai J Pharm Sci. 22:149–155. 1998.
|
|
13
|
Likhitwitayawuid K, Sritularak B and
Benchanak K: Phenolics with antiviral activity from Millettia
erythrocalyx and Artocarpus lakoocha. Nat Prod Res. 19:177–182.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chuanasa T, Phromjai J, Lipipun V,
Likhitwitayawuid K, Suzuki M, Pramyothin P, Hattori M and Shiraki
K: Anti-herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) activity of oxyresveratrol
derived from Thai medicinal plant: Mechanism of action and
therapeutic efficacy on cutaneous HSV-1 infection in mice.
Antiviral Res. 80:62–70. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lipipun V, Sasivimolphan P, Yoshida Y,
Daikoku T, Sritularak B, Ritthidej G, Likhitwitayawuid K,
Pramyothin P, Hattori M and Shiraki K: Topical cream-based
oxyresveratrol in the treatment of cutaneous HSV-1 infection in
mice. Antiviral Res. 91:154–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sasivimolphan P, Lipipun V,
Likhitwitayawuid K, Takemoto M, Pramyothin P, Hattori M and Shiraki
K: Inhibitory activity of oxyresveratrol on wild-type and
drug-resistant varicella-zoster virus replication in vitro.
Antiviral Res. 84:95–97. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim YM, Yun J, Lee CK, Lee H, Min KR and
Kim Y: Oxyresveratrol and hydroxystilbene compounds. Inhibitory
effect on tyrosinase and mechanism of action. J Biol Chem.
227:16340–16344. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lorenz P, Roychowdhury S, Engelmann M,
Wolf G and Horn TF: Oxyresveratrol and resveratrol are potent
antioxidants and free radical scavengers: Effect on nitrosative and
oxidative stress derived from microglial cells. Nitric Oxide.
9:64–76. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saowakon N, Tansatit T, Wanichanon C,
Chanakul W, Reutrakul V and Sobhon P: Fasciola gigantica:
Anthelmintic effect of the aqueous extract of Artocarpus lakoocha.
Exp Parasitol. 122:289–298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qiu F, Komatsu K, Kawasaki K, Saito K, Yao
X and Kano Y: A novel stilbene glucoside, oxyresveratrol
3′-O-beta-glucopyranoside, from the root bark of Morus alba.
Planta Med. 62:559–561. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mun SH, Joung DK, Kim SB, Park SJ, Seo YS,
Gong R, Choi JG, Shin DW, Rho JR, Kang OH and Kwon DY: The
mechanism of antimicrobial activity of sophoraflavanone B against
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Foodborne
Pathog Dis. 11:234–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Institute: Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility
Testing; Twenty-Fourth Informational Supplement. CLSI document
M100-S24. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. (Wayne, PA).
2014.
|
|
23
|
Cordwell SJ, Larsen MR, Cole RT and Walsh
BJ: Comparative proteomics of Staphylococcus aureus and the
response of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-sensitive strains
to Triton X-100. Microbiology. 148:2765–2781. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shibata H, Saito H, Yomota C, Kawanishi T
and Okuda H: Alterations in the detergent-induced membrane
permeability and solubilization of saturated
phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol liposomes: Effects of poly(ethylene
glycol)-conjugated lipid. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 60:1105–1111.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Linnett PE and Beechey RB: Inhibitors of
the ATP synthetase system. Methods Enzymol. 55:472–518. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jung HJ and Lee DG: Synergistic
antibacterial effect between silybin and
N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in clinical Pseudomonas
aeruginosa isolates. J Microbiol. 46:462–467. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao WH, Hu ZQ, Okubo S, Hara Y and
Shimamura T: Mechanism of synergy between epigallocatechin gallate
and beta-lactams against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 45:1737–1742. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Al-Habib A, Al-Saleh E, Safer AM and Afzal
M: Bactericidal effect of grape seed extract on
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). J
Toxicol Sci. 35:357–364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Joung DK, Choi SH, Kang OH, Kim SB, Mun
SH, Seo YS, Kang DH, Gong R, Shin DW, Kim YC and Kwon DY:
Synergistic effects of oxyresveratrol in conjunction with
antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus. Mol Med Rep. 12:663–667. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Komatsuzawa H, Ohta K, Sugai M, Fujiwara
T, Glanzmann P, Berger-Bächi B and Suginaka H: Tn551-mediated
insertional inactivation of the fmtB gene encoding a cell
wall-associated protein abolishes methicillin resistance in
Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 45:421–431.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Farca AM, Nebbia P and Re G: Potentiation
of antibiotic activity by EDTA-tromethamine against three
clinically isolated gram-positive resistant bacteria. An in vitro
investigation. Vet Res Commun. 18:1–6. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lorian V and Atkinson B: Effect of serum
on gram-positive cocci grown in the presence of penicillin. J
Infect Dis. 138:865–871. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Muthaiyan A, Martin EM, Natesan S,
Crandall PG, Wilkinson BJ and Ricke SC: Antimicrobial effect and
mode of action of terpeneless cold-pressed Valencia orange
essential oil on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus. J Appl Microbiol. 112:1020–1033. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|