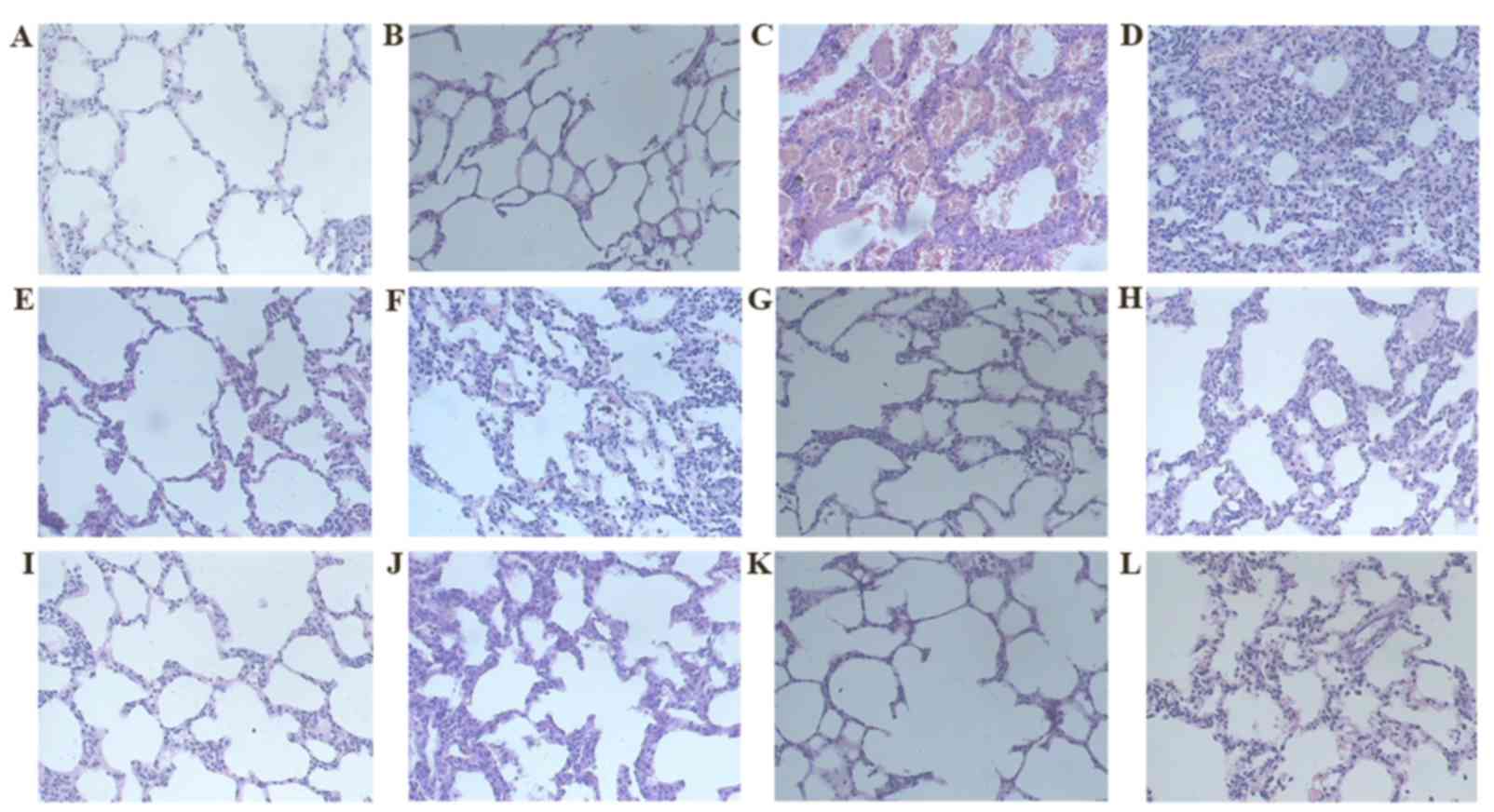
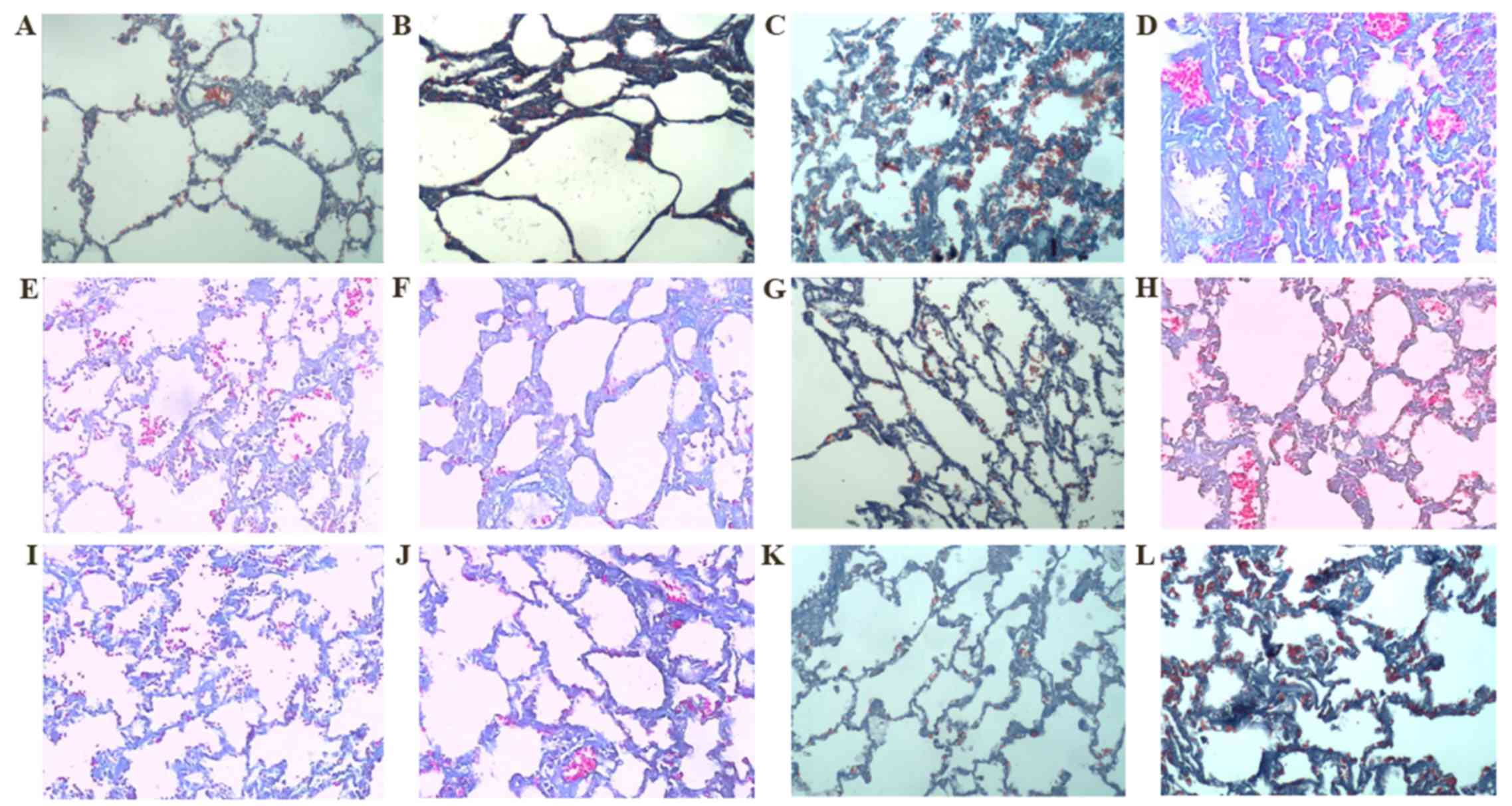
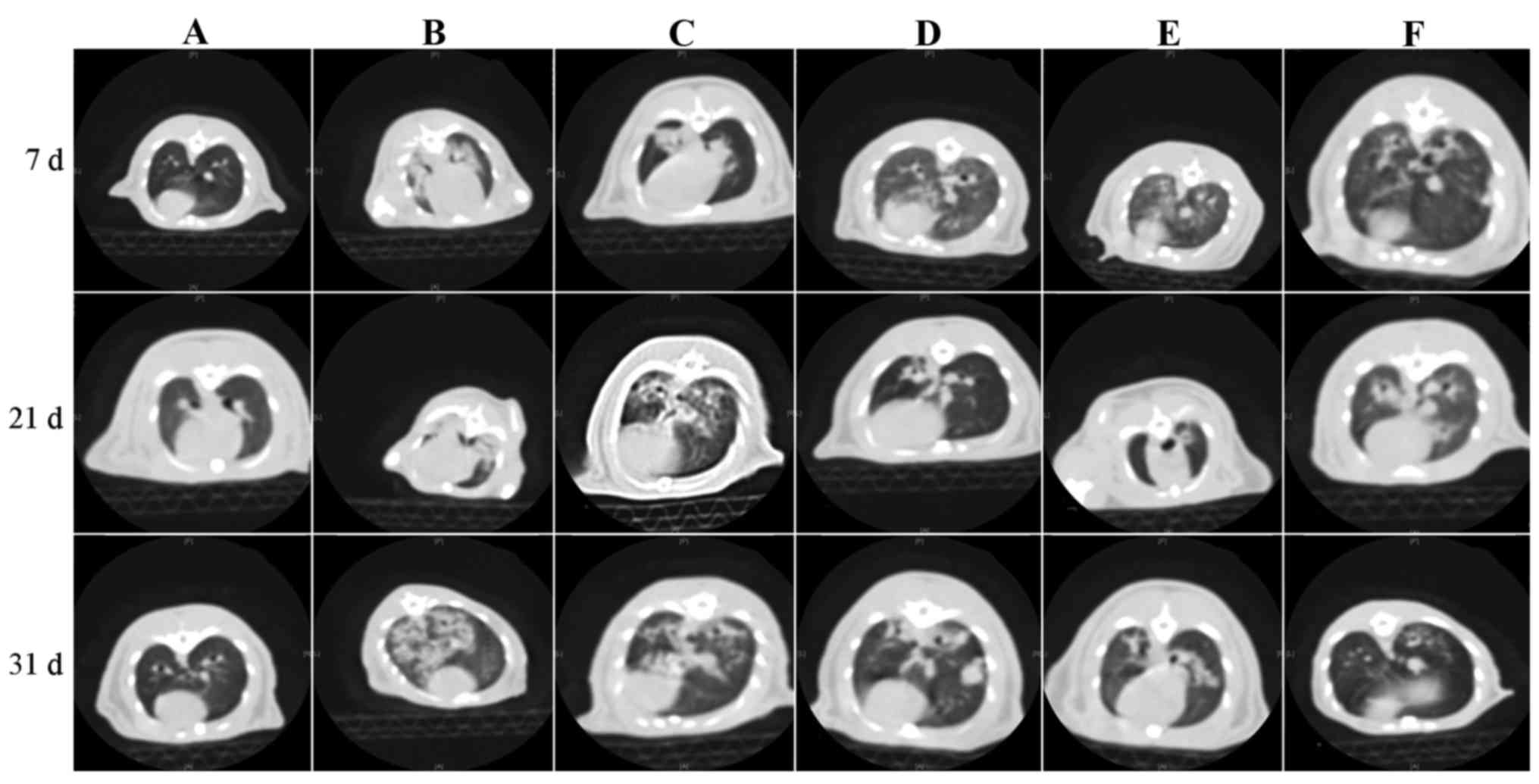
|
1
|
Ley B and Collard HR: Epidemiology of
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Epidemiol. 5:483–492. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ,
Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, et
al: An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: Idiopathic pulmonary
fibrosis: Evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 183:788–824. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, King TE
Jr, Lynch DA, Nicholson AG, Ryerson CJ, Ryu JH, Selman M, Wells AU,
et al: An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory
Society statement: Update of the international multidisciplinary
classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 188:733–748. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moua T, Martinez AC Zamora, Baqir M,
Vassallo R, Limper AH and Ryu JH: Predictors of diagnosis and
survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and connective tissue
disease-related usual interstitial pneumonia. Respir Res.
15:1542014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rafii R, Juarez MM, Albertson TE and Chan
AL: A review of current and novel therapies for idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. J Thorac Dis. 5:48–73. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical
Research Network, ; Raghu G, Anstrom KJ, King TE Jr, Lasky JA and
Martinez FJ: Prednisone, azathioprine, and N-acetylcysteine for
pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 366:1968–1977. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Clinical
Research Network, ; Martinez FJ, De Andrade JA, Anstrom KJ, King TE
Jr and Raghu G: Randomized trial of acetylcysteine in idiopathic
pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 370:2093–2101. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
King TE Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini
S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, Gorina E, Hopkins PM,
Kardatzke D, Lancaster L, et al: A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in
patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med.
370:2083–2092. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calkin AC, Giunti S, Jandeleit-Dahm KA,
Allen TJ, Cooper ME and Thomas MC: PPAR-alpha and -gamma agonists
attenuate diabetic kidney disease in the apolipoprotein E knockout
mouse. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 21:2399–2405. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iglarz M, Touyz RM, Viel EC, Paradis P,
Amiri F, Diep QN and Schiffrin EL: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and receptor-gamma activators
prevent cardiac fibrosis in mineralocorticoid-dependent
hypertension. Hypertension. 42:737–743. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Leclercq IA, Sempoux C, Stärkel P and
Horsmans Y: Limited therapeutic efficacy of pioglitazone on
progression of hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut. 55:1020–1029. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kayalar O and Oztay F: Retinoin induced
repair in the lung of adult hyperoxic mice, reducing transforming
growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) mediated abnormal alterations. Acta
Histochem. 116:810–819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Davis BH, Kramer RT and Davidson NO:
Retinoin modulates rat Ito cell proliferation, collagen, and
transforming growth factor beta production. J Clin Invest.
86:2062–2070. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chua F, Gauldie J and Laurent GJ:
Pulmonary fibrosis: Searching for model answers. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 33:9–13. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Limjunyawong N, Mitzner W and Horton MR: A
mouse model of chronic idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Physiol Rep.
2:e002492014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee CG, Cho SJ, Kang MJ, Chapoval SP, Lee
PJ, Noble PW, Yehualaeshet T, Lu B, Flavell RA, Milbrandt J, et al:
Early growth response gene 1-mediated apoptosis is essential for
transforming growth factor beta1-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Exp
Med. 200:377–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim KK, Wei Y, Szekeres C, Kugler MC,
Wolters PJ, Hill ML, Frank JA, Brumwell AN, Wheeler SE, Kreidberg
JA and Chapman HA: Epithelial cell alpha3beta1 integrin links
beta-catenin and Smad signaling to promote myofibroblast formation
and pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 119:213–224. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Asada K, Sasaki S, Suda T, Chida K and
Nakamura H: Antiinflammatory roles of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human alveolar
macrophages. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 169:195–200. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Burgess HA, Daugherty LE, Thatcher TH,
Lakatos HF, Ray DM, Redonnet M, Phipps RP and Sime PJ: PPARgamma
agonists inhibit TGF-beta induced pulmonary myofibroblast
differentiation and collagen production: Implications for therapy
of lung fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
288:L1146–L1153. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Genovese T, Cuzzocrea S, Di Paola R,
Mazzon E, Mastruzzo C, Catalano P, Sortino M, Crimi N, Caputi AP,
Thiemermann C and Vancheri C: Effect of rosiglitazone and
15-deoxy-Delta12,14-prostaglandin J2 on bleomycin-induced lung
injury. Eur Respir J. 25:225–234. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Milam JE, Keshamouni VG, Phan SH, Hu B,
Gangireddy SR, Hogaboam CM, Standiford TJ, Thannickal VJ and Reddy
RC: PPAR-gamma agonists inhibit profibrotic phenotypes in human
lung fibroblasts and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 294:L891–L901. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cifelli CJ and Ross AC: All-trans-retinoin
distribution and metabolism in vitamin A-marginal rats. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 291:G195–G202. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang L, Potter JJ, Rennie-Tankersley L,
Novitskiy G, Sipes J and Mezey E: Effects of retinoic acid on the
development of liver fibrosis produced by carbon tetrachloride in
mice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1772:66–71. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fleissner D, Frede A, Knott M, Knuschke T,
Geffers R, Hansen W, Dobos G, Langhorst J, Buer J and Westendorf
AM: Generation and function of immunosuppressive human and murine
CD8+ T cells by transforming growth factor-β and retinoic acid.
Immunology. 134:82–92. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Redlich CA, Delisser HM and Elias JA:
Retinoin inhibition of transforming growth factor-beta-induced
collagen production by human lung fibroblasts. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 12:287–295. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Massaro GD, Massaro D and Chambon P:
Retinoin receptor-alpha regulates pulmonary alveolus formation in
mice after, but not during, perinatal period. Am J Physiol Lung
Cell Mol Physiol. 284:L431–L433. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schüle R, Rangarajan P, Yang N, Kliewer S,
Ransone LJ, Bolado J, Verma IM and Evans RM: Retinoin is a negative
regulator of AP-1-responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 88:pp.
6092–6096. 1991; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|