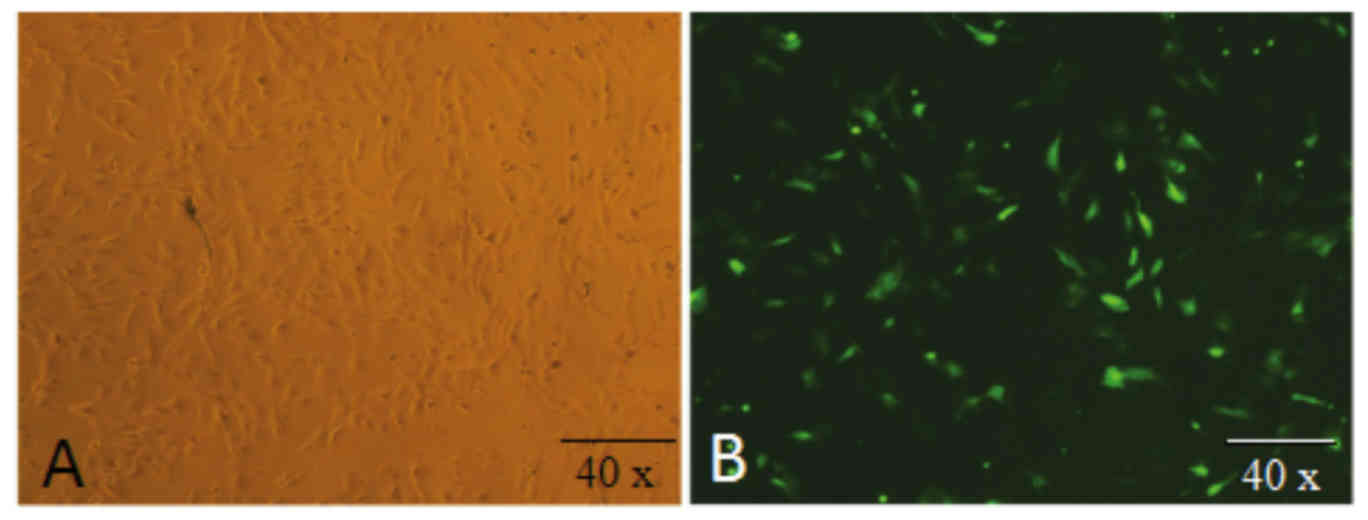
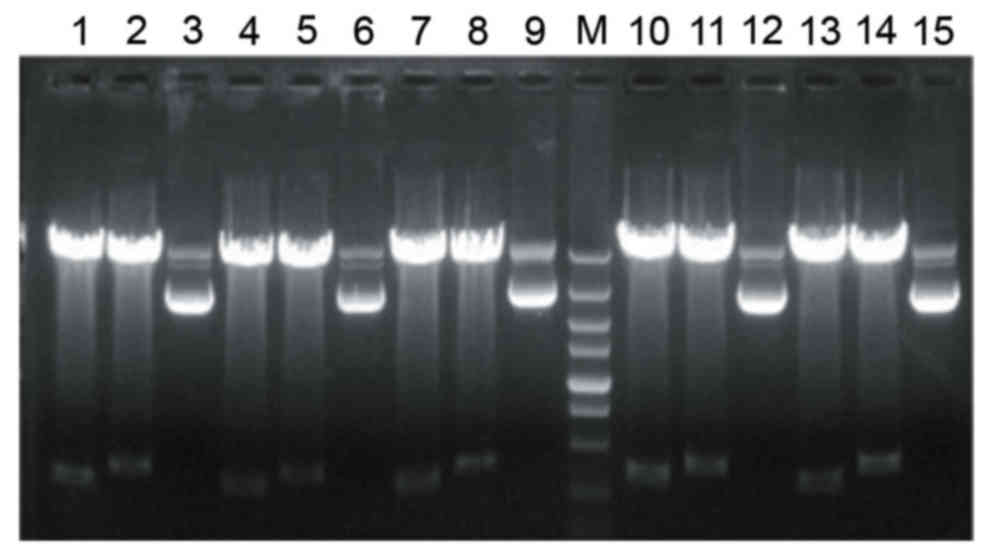
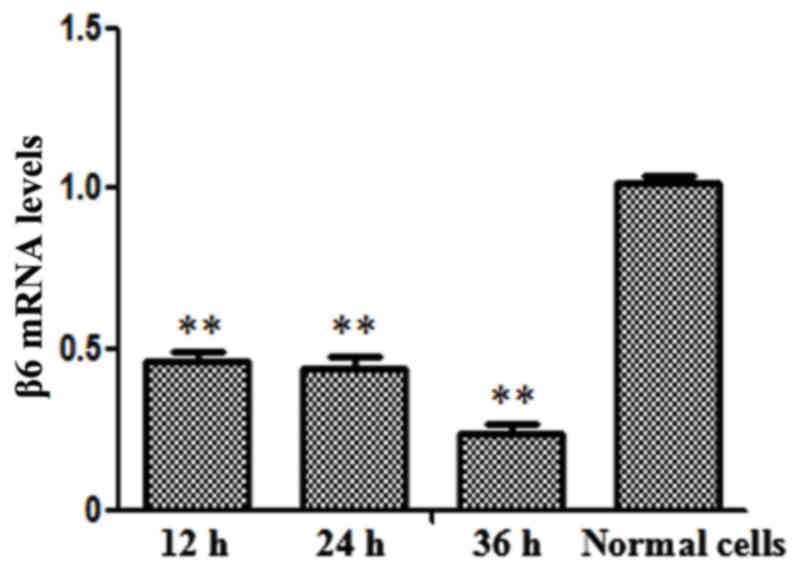
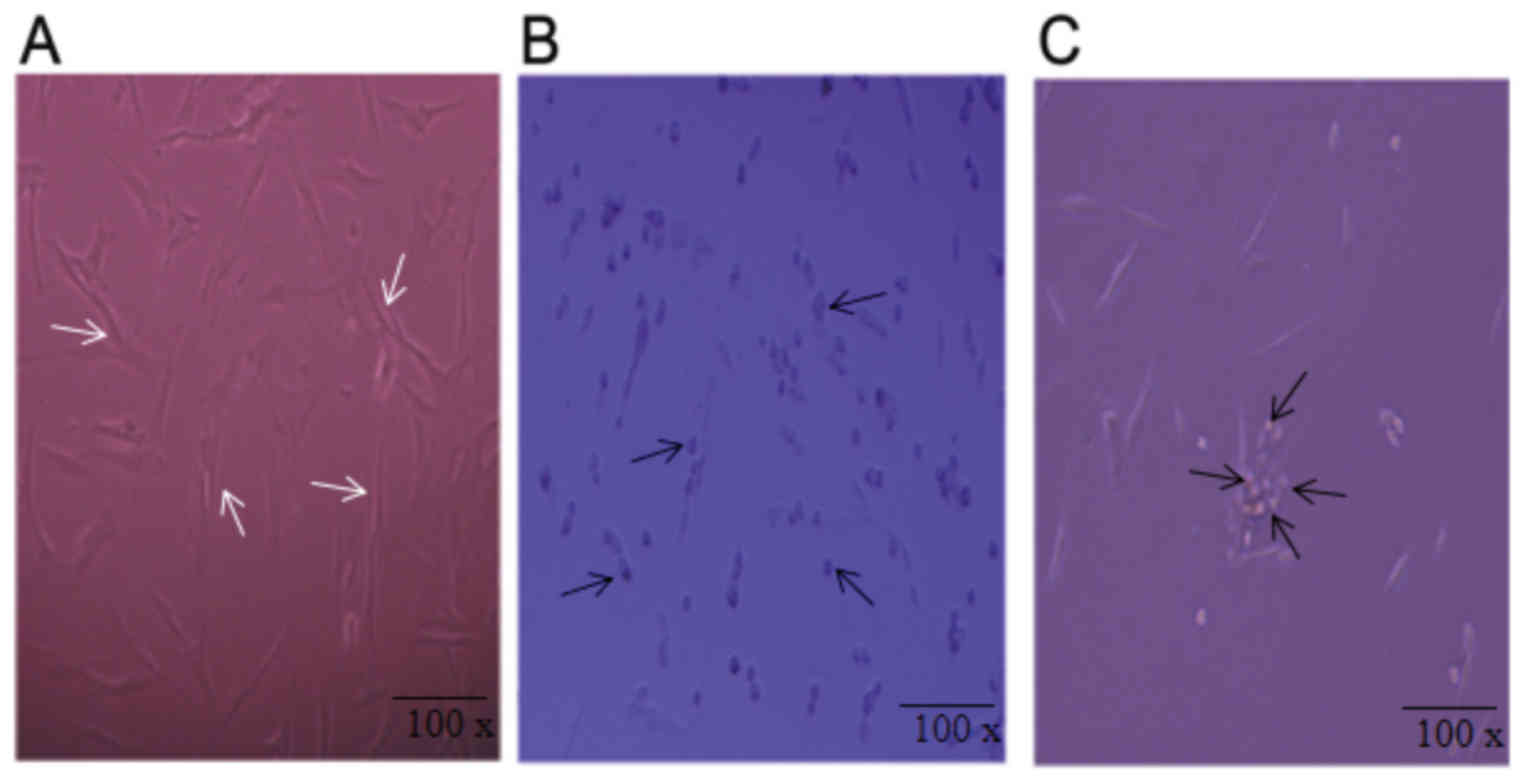
|
1
|
Li X, Wang J, Liu J, Li Z, Wang Y, Xue Y,
Li X, Cao H and Zheng SJ: Engagement of soluble resistance-related
calcium binding protein (sorcin) with foot-and-mouth disease virus
(FMDV) VP1 inhibits type I interferon response in cells. Vet
Microbiol. 166:35–46. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johns HL: Regulation of FMDV infection by
cellular rab GTPases. University of Surrey. uk.bl.ethos.486086.
2007
|
|
3
|
Shen XY, Chang HY, G Z Cong, Liu Y-S, Wang
JH and Xie QG: Advance in foot-and-mouth disease virus infectious
cycle. Progress in Veterinary Medicine. (6): 1–5. 2005.
|
|
4
|
Sekiguchi K, Franke AJ and Baxt B:
Competition for cellular receptor sites among selected
aphthoviruses. Arch Virol. 74:53–64. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lea S, Hernández J, Blakemore W, Brocchi
E, Curry S, Domingo E, Fry E, Abu-Ghazaleh R, King A, Newman J, et
al: The structure and antigenicity of a type C foot-and-mouth
disease virus. Structure. 2:123–139. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
O'Donnell V, Pacheco JM, Gregg D and Baxt
B: Analysis of foot-and-mouth disease virus integrin receptor
expression in tissues from naïve and infected cattle. J Comp
Pathol. 141:98–112. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jackson T, F M Ellard, Ghazaleh RA,
Brookes SM, Blakemore WE, Corteyn AH, Stuart DI, Newman JW and King
AM: Efficient infection of cells in culture by type O
foot-and-mouth disease virus requires binding to cell surface
heparan sulfate. J Virol. 70:5282–5287. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fox G, Parry NR, Barnett PV, McGinn B,
Rowlands DJ and Brown F: The cell attachment site on foot-and-mouth
disease virus includes the amino acid sequence RGD
(arginine-glycine-aspartic acid). Gen Virol. 70:625–637. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mason PW, Baxt B, Brown F, Harber J,
Murdin A and Wimmer E: Antibody-complexed foot-and-mouth disease
virus, but not poliovirus, can infect normally insusceptible cells
via the Fc receptor. Virology. 192:568–577. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cai K J, Ma SW, Qiao J, Meng WL, Chen CF,
Huang J, Zhang ZC and Yang HB: Anti-viral activity of cells from
foot-and-mouth disease virus shRNA transgenic pig. Chinese Journal
of Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 1:5–9. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Ma SW, Chen CF and Qiao J: The shRNA
screen and test of high effective inhibition from type O FMDV.
Chinese Journal of veterinary science. 113–17. (22)2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Zhang J, Guo S, Zhang W, Niu D and Gong J:
Large-pore mesoporous silica nanospheres as vehicles for delivering
TRAF3-shRNA plasmids to Kupffer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
469:196–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reed LJ and Muench H: A simple method of
estimating fifty per cent endpoints12. Am J Epidemiol. 27:493–497.
1938. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Dong W, Hu H, Feng G, Yang G and Wang Q:
Construction and identification of eukaryotic expression vector of
small interfering RNA specific for BACE. Journal of Xi‘an Jiaotong
University (Medical Sciences). 26:413–416, 423. 2005.
|
|
16
|
Pierschbacher MD and Ruoslahti E: Variants
of the cell recognition site of fibronectin that retain
attachment-promoting activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 81:pp.
5985–5988. 1984; View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fox G, Parry NR, Barnett PV, McGinn B,
Rowlands DJ and Brown F: The cell attachment site on foot-and-mouth
disease virus includes the amino acid sequence RGD
(arginine-glycine-aspartic acid). J Gen Virol. 70:625–637. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Whitton JL, Cornell CT and Feuer R: Host
and virus determinants of picornavirus pathogenesis and tropism.
Nat Rev Microbiol. 3:765–776. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barczyk M, Carracedo S and Gullberg D:
Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 339:269–280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu J, He X, Corbett SA, Lowry SF, Graham
AM, Fässler R and Li S: Integrins are required for the
differentiation of visceral endoderm. J Cell Sci. 122:233–242.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wegener KL, Partridge AW, Han J, Pickford
AR, Liddington RC, Ginsberg MH and Campbell ID: Structural basis of
integrin activation by talin. Cell. 128:171–182. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Luo J, Du J, Gao S, Zhang G, Sun J, Cong
G, Shao J, Lin T and Chang H: Lentviral-mediated RNAi to inhibit
target gene expression of the porcine integrin αv subunit, the FMDV
receptor, and against FMDV infection in PK-15 cells. Virol J.
8:4282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Monaghan P, Gold S, Simpson J, Zhang Z,
Weinreb PH, Violette SM, Alexandersen S and Jackson T: The alpha
(v)beta6 integrin receptor for Foot-and-mouth disease virus is
expressed constitutively on the epithelial cells targeted in
cattle. J Gen Virol. 86:2769–2780. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Monaghan P, Gold S, Simpson J, Zhang Z,
Weinrab PH, Violette SM, Alexandersen S and Jackson T: The
alpha(v)beta6 integrin receptor for Foot-and-mouth disease virus is
expressed constitutively on the epithelial cells targeted in
cattle. J Gen Virol. 86:2769–2780. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jackson T, Clark S, Berryman S, Burman A,
Cambier S, Mu D, Nishimura S and King AM: Integrin alphavbeta8
functions as a receptor for foot-and-mouth disease virus: role of
the beta-chain cytodomain in integrin-mediated infection. J Virol.
78:4533–4540. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jacobsen JN, Steffensen B, Häekkinen L,
Krogfelt KA and Larjava HS: Skin wound healing in diabetic ß6
integrin deficient mice. APMIS. 118:753–764. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sullivan BP, Weinreb PH, Violette SM and
Luyendyk JP: The coagulation system contributes to alphaVbeta6
integrin expression and liver fibrosis induced by cholestasis. Am J
Pathol. 177:2837–2849. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miller LC, Blakemore W, Sheppard D,
Atakilit A, King AM and Jackson T: Role of the cytoplasmic domain
of the beta-subunit of integrin alpha(v)beta6 in infection by
foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 75:4158–4164. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kahana R, Kuznetzova L, Rogel A, Shemesh
M, Hai D, Yadin H and Stram Y: Inhibition of foot-and-mouth disease
virus replication by small interfering RNA. J Gen Virol.
85:3213–3217. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mohapatra JK, Sanyal A, Hemadri D, Tosh C,
Kumar RM and Bandyopadhyay SK: Evaluation of in vitro inhibitory
potential of small interfering RNAs directed against various
regions of foot-and-mouth disease virus genome. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 329:1133–1138. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schneider-Schaulies J: Cellular receptors
for viruses: Links to tropism and pathogenesis. J Gen Virol.
81:1413–1429. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|