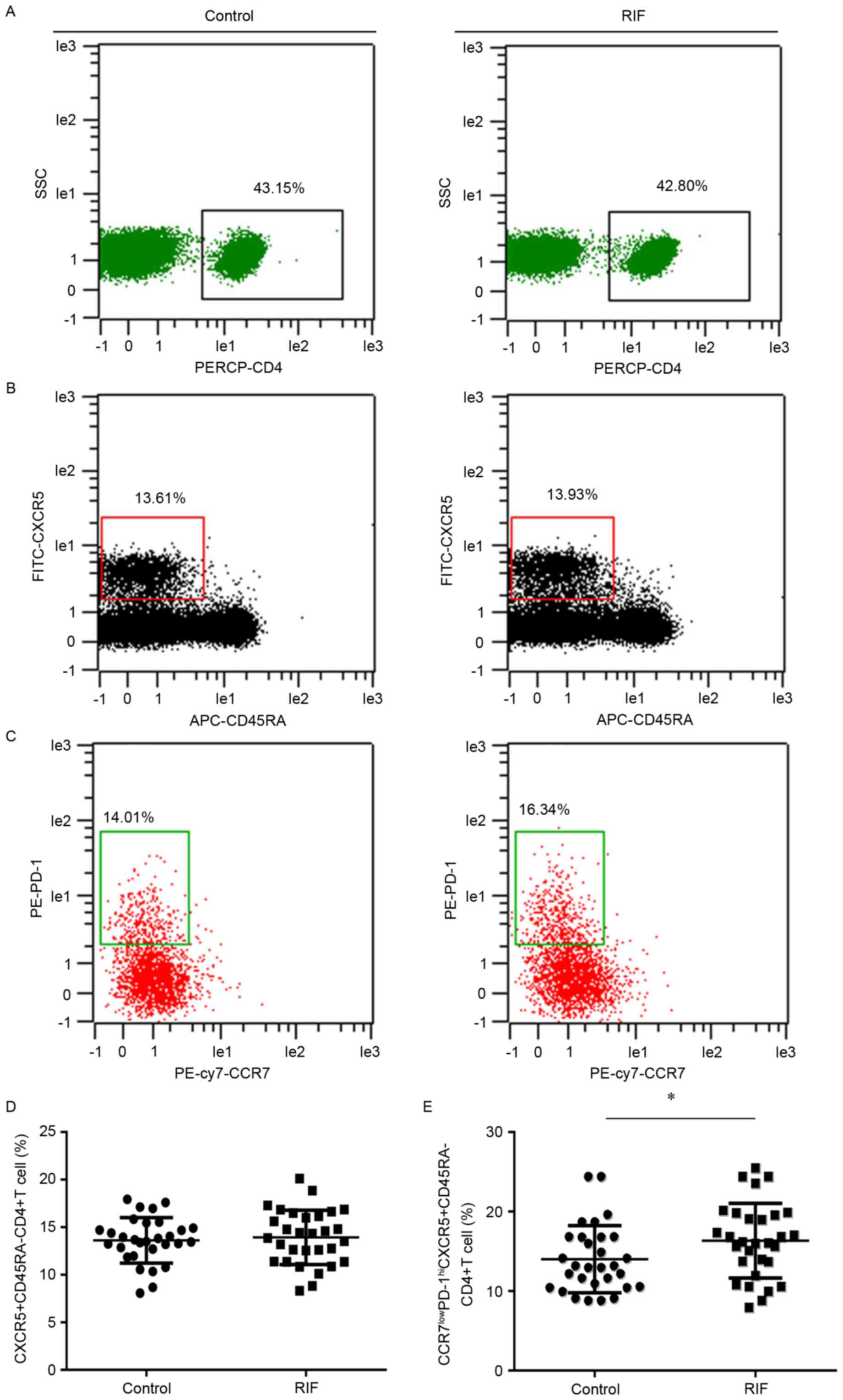
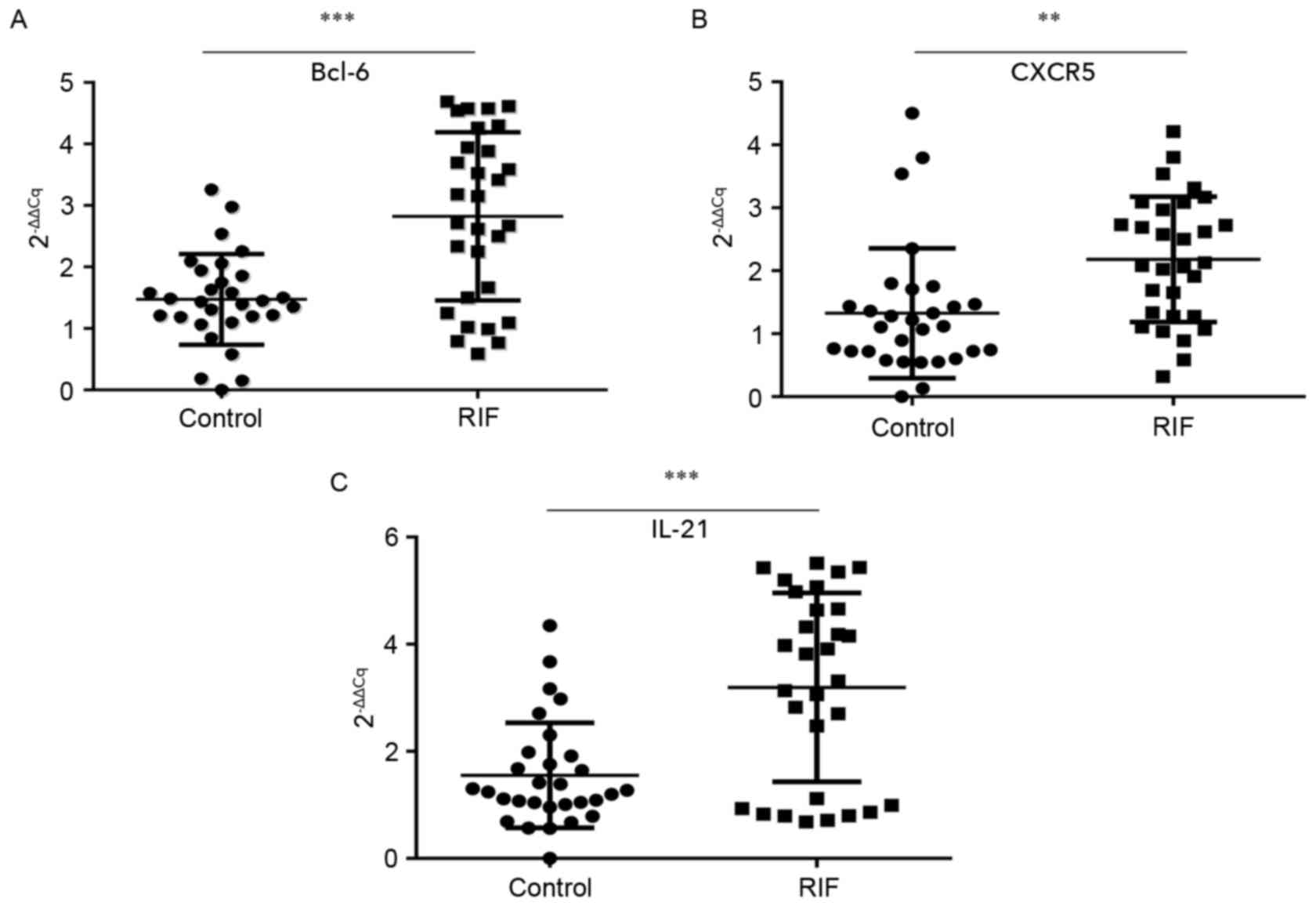
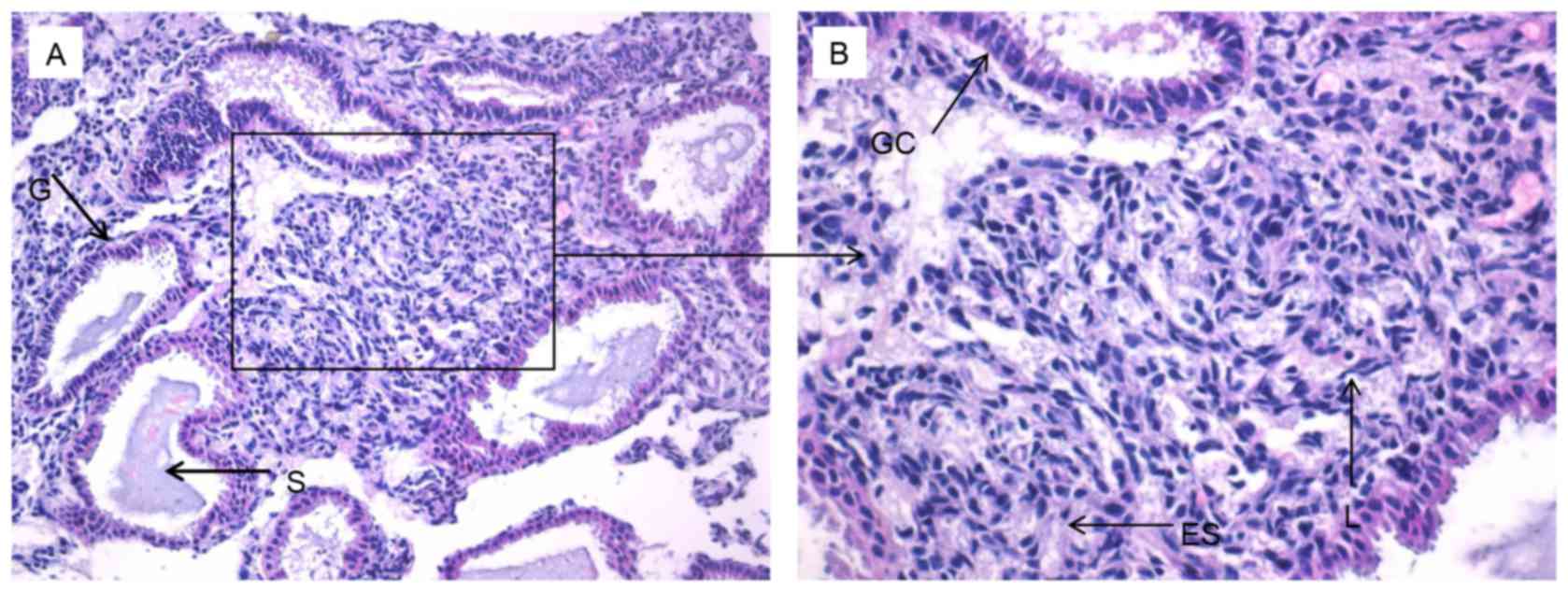
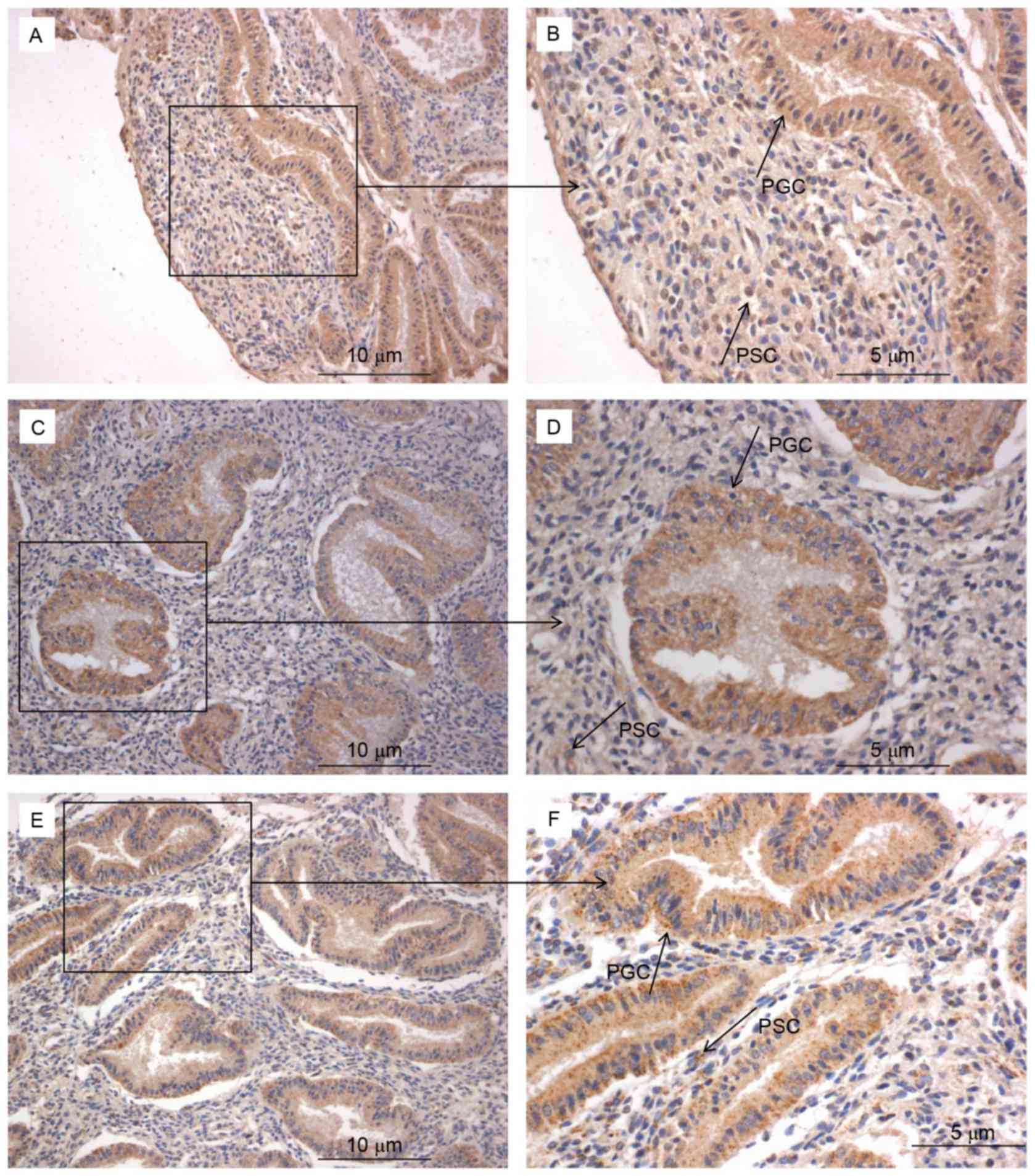
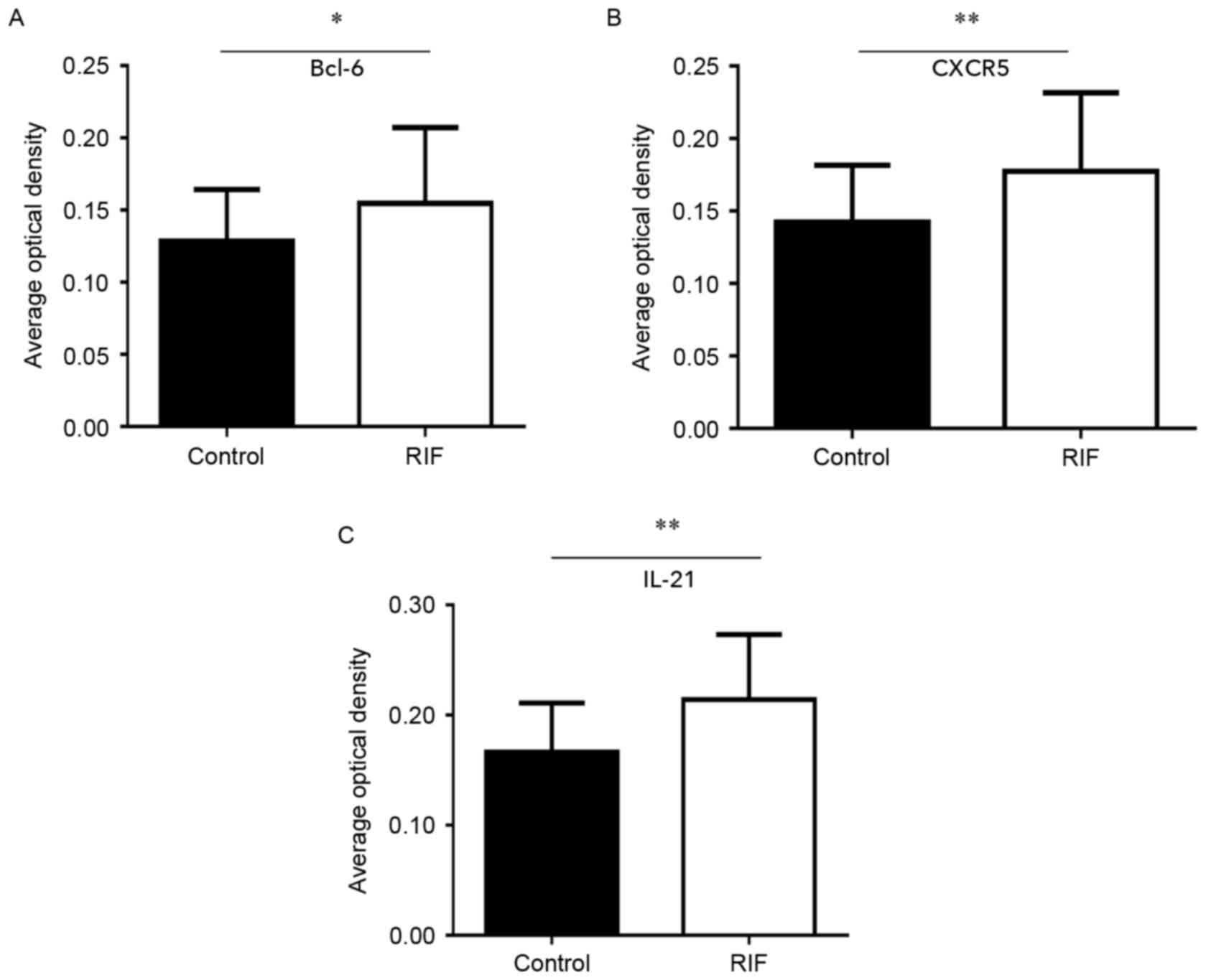
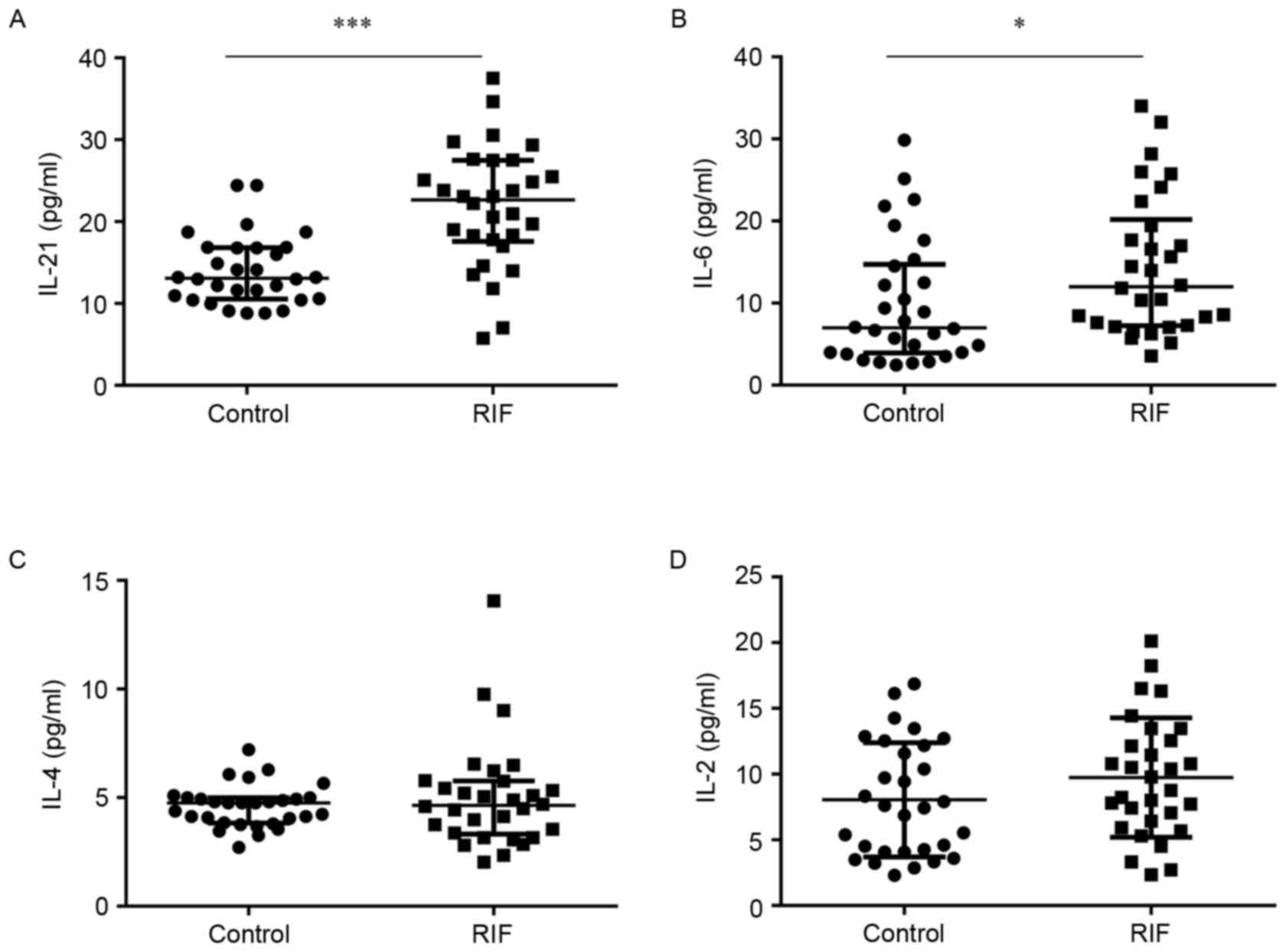
|
1
|
Valenzuela OA, Couturier-Tarrade A, Choi
YH, Aubrière MC, Ritthaler J, Chavatte-Palmer P and Hinrichs K:
Impact of equine assisted reproductive technologies (standard
embryo transfer or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) with in
vitro culture and embryo transfer) on placenta and foal morphometry
and placental gene expression. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dekel N, Gnainsky Y, Granot I, Racicot K
and Mor G: The role of inflammation for a successful implantation.
Am J Reprod Immunol. 72:141–147. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ledee N, Petitbarat M, Chevrier L, Vitoux
D, Vezmar K, Rahmati M, Dubanchet S, Gahéry H, Bensussan A and
Chaouat G: The uterine immune profile may help women with repeated
unexplained embryo implantation failure after in vitro
fertilization. Am J Reprod Immunol. 75:388–401. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crawford G, Ray A, Gudi A, Shah A and
Homburg R: The role of seminal plasma for improved outcomes during
in vitro fertilization treatment: Review of the literature and
meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update. 21:275–284. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tan BK, Vandekerckhove P, Kennedy R and
Keay SD: Investigation and current management of recurrent IVF
treatment failure in the UK. BJOG. 112:773–780. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Margalioth EJ, Ben-Chetrit A, Gal M and
Eldar-Geva T: Investigation and treatment of repeated implantation
failure following IVF-ET. Hum Reprod. 21:3036–3043. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Simon A and Laufer N: Repeated
implantation failure: Clinical approach. Fertil Steril.
97:1039–1043. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakagawa K, Kwak-Kim J, Ota K, Kuroda K,
Hisano M, Sugiyama R and Yamaguchi K: Immunosuppression with
tacrolimus improved reproductive outcome of women with repeated
implantation failure and elevated peripheral blood TH1/TH2 cell
ratios. Am J Reprod Immunol. 73:353–361. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Persson M, Ekerfelt C, Jablonowska B,
Jonsson Y, Ernerudh J, Jenmalm MC and Berg G: Immunological status
in patients undergoing in vitro fertilisation: Responses to hormone
treatment and relationship to outcome. J Reprod Immunol. 96:58–67.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schlossberger V, Schober L, Rehnitz J,
Schaier M, Zeier M, Meuer S, Schmitt E, Toth B, Strowitzki T and
Steinborn A: The success of assisted reproduction technologies in
relation to composition of the total regulatory T cell (Treg) pool
and different Treg subsets. Hum Reprod. 28:3062–3073. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou J, Wang Z, Zhao X, Wang J, Sun H and
Hu Y: An increase of Treg cells in the peripheral blood is
associated with a better in vitro fertilization treatment outcome.
Am J Reprod Immunol. 68:100–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Saifi B, Rezaee SA, Tajik N, Ahmadpour ME,
Ashrafi M, Vakili R, SoleimaniAsl S, Aflatoonian R and Mehdizadeh
M: Th17 cells and related cytokines in unexplained recurrent
spontaneous miscarriage at the implantation window. Reprod Biomed
Online. 29:481–489. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang PY, Diao LH, Huang CY, Lian RC, Chen
X, Li GG, Zhao J, Li YY, He XB and Zeng Y: The pro-inflammatory and
anti-inflammatory cytokine profile in peripheral blood of women
with recurrent implantation failure. Reprod Biomed Online.
31:823–826. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Figueiredo MM, Costa PAC, Diniz SQ,
Henriques PM, Kano FS, Tada MS, Pereira DB, Soares IS,
Martins-Filho OA, Jankovic D, et al: T follicular helper cells
regulate the activation of B lymphocytes and antibody production
during Plasmodium vivax infection. PLoS Pathog.
13:e10064842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Monteiro C, Kasahara TM, Castro JR,
Sacramento PM, Hygino J, Centurião N, Cassano T, Lopes LMF, Leite
S, Silva VG, et al: Pregnancy favors the expansion of circulating
functional follicular helper T Cells. J Reprod Immunol. 121:1–10.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tangye SG, Ma CS, Brink R and Deenick EK:
The good, the bad and the ugly-TFH cells in human health and
disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:412–426. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ueno H: Human circulating T follicular
helper cell subsets in health and disease. J Clin Immunol. 36 Suppl
1:S34–S39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Vinuesa CG, Linterman MA, Yu D and
MacLennan IC: Follicular helper T Cells. Annu Rev Immunol.
34:335–368. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weinstein JS, Herman EI, Lainez B,
Licona-Limón P, Esplugues E, Flavell R and Craft J: TFH cells
progressively differentiate to regulate the germinal center
response. Nat Immunol. 17:1197–1205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McGuire HM, Vogelzang A, Warren J, Loetsch
C, Natividad KD, Chan TD, Brink R, Batten M and King C: IL-21 and
IL-4 collaborate to shape T-dependent antibody responses. J
Immunol. 195:5123–5135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schmitt N, Bentebibel SE and Ueno H:
Phenotype and functions of memory Tfh cells in human blood. Trends
Immunol. 35:436–442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Crotty S: T follicular helper cell
differentiation, function and roles in disease. Immunity.
41:529–542. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Badell IR and Ford ML: T follicular helper
cells in the generation of alloantibody and graft rejection. Curr
Opin Organ Transplant. 21:1–6. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nurieva RI, Podd A, Chen Y, Alekseev AM,
Yu M, Qi X, Huang H, Wen R, Wang J, Li HS, et al: STAT5 protein
negatively regulates T follicular helper (Tfh) cell generation and
function. J Biol Chem. 287:11234–11239. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arroyo-Villa I, Bautista-Caro MB, Balsa A,
Aguado-Acín P, Bonilla-Hernán MG, Plasencia C, Villalba A, Nuño L,
Puig-Kröger A, Martín-Mola E and Miranda-Carús ME: Constitutively
altered frequencies of circulating follicullar helper T cell
counterparts and their subsets in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis
Res Ther. 16:5002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He J, Tsai LM, Leong YA, Hu X, Ma CS,
Chevalier N, Sun X, Vandenberg K, Rockman S, Ding Y, et al:
Circulating precursor CCR7(lo)PD-1(hi) CXCR5+
CD4+ T cells indicate Tfh cell activity and promote
antibody responses upon antigen reexposure. Immunity. 39:770–781.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang F, Pang N, Zhu Y, Zhou D, Zhao H, Hu
J, Ma X, Li J, Wen H, Samten B, et al: CCR7(lo)PD-1(hi) CXCR5(+)
CD4(+) T cells are positively correlated with levels of IL-21 in
active and transitional cystic echinococcosis patients. BMC Infect
Dis. 15:4572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu R, Li X, Zhang Z, Zhou M, Sun Y, Su D,
Feng X, Gao X, Shi S, Chen W and Sun L: Allogeneic mesenchymal stem
cells inhibited T follicular helper cell generation in rheumatoid
arthritis. Sci Rep. 5:127772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Blanco P, Ueno H and Schmitt N: T
follicular helper (Tfh) cells in lupus: Activation and involvement
in SLE pathogenesis. Eur J Immunol. 46:281–290. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Le Coz C, Joublin A, Pasquali JL, Korganow
AS, Dumortier H and Monneaux F: Circulating TFH subset distribution
is strongly affected in lupus patients with an active disease. PLoS
One. 8:e753192013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu H, Liu J, Cui X, Zuo Y, Zhang Z, Li Y,
Tao R, Li Y and Pang J: Increased frequency of circulating
follicular helper T cells in lupus patients is associated with
autoantibody production in a CD40L-dependent manner. Cell Immunol.
295:46–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park HJ, Kim DH, Lim SH, Kim WJ, Youn J,
Choi YS and Choi JM: Insights into the role of follicular helper T
cells in autoimmunity. Immune Netw. 14:21–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shi J, Luo F, Shi Q, Xu X, He X and Xia Y:
Increased circulating follicular helper T cells with decreased
programmed death-1 in chronic renal allograft rejection. BMC
Nephrol. 16:1822015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lu KH, Loose DS, Yates MS,
Nogueras-Gonzalez GM, Munsell MF, Chen LM, Lynch H, Cornelison T,
Boyd-Rogers S, Rubin M, et al: Prospective multicenter randomized
intermediate biomarker study of oral contraceptive versus
depo-provera for prevention of endometrial cancer in women with
Lynch syndrome. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 6:774–781. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jia L, Wang Y, Li J, Li S, Zhang Y, Shen
J, Tan W and Wu C: Detection of IL-9 producing T cells in the PBMCs
of allergic asthmatic patients. BMC immunology. 18:382017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Franasiak JM and Scott RT: Contribution of
immunology to implantation failure of euploid embryos. Fertil
Steril. 107:1279–1283. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang WJ, Liu FJ, Zhang X, Liu XM, Qu QL,
Li FH, Zhuang LL, Li XX and Hao CF: Periodic elevation of
regulatory T cells on the day of embryo transfer is associated with
better in vitro fertilization outcome. J Reprod Immunol. 119:49–53.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Akiyama M, Yasuoka H, Yamaoka K, Suzuki K,
Kaneko Y, Kondo H, Kassai Y, Koga K, Miyazaki T, Morita R, et al:
Enhanced IgG4 production by follicular helper 2 T cells and the
involvement of follicular helper 1 T cells in the pathogenesis of
IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 18:1672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
An LF, Zhang XH, Sun XT, Zhao LH, Li S and
Wang WH: Unexplained infertility patients have increased serum
IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, IL-21, TNFα, IFNgamma and increased Tfh/CD4
T cell ratio: Increased Tfh and IL-21 strongly correlate with
presence of autoantibodies. Immunol Invest. 44:164–173. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Perricone C, de Carolis C and Perricone R:
Pregnancy and autoimmunity: A common problem. Best Pract Res Clin
Rheumatol. 26:47–60. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen JL, Yang JM, Huang YZ and Li Y:
Clinical observation of lymphocyte active immunotherapy in 380
patients with unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion. Int
Immunopharmacol. 40:347–350. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ticconi C, Pietropolli A, Borelli B, Bruno
V, Piccione E, Bernardini S and Di Simone N: Antinuclear
autoantibodies and pregnancy outcome in women with unexplained
recurrent miscarriage. Am J Reprod Immunol. 76:396–399. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Breen KA, Sanchez K, Kirkman N, Seed PT,
Parmar K, Moore GW and Hunt BJ: Endothelial and platelet
microparticles in patients with antiphospholipid antibodies. Thromb
Res. 135:368–374. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kwak-Kim J, Skariah A, Wu L, Salazar D,
Sung N and Ota K: Humoral and cellular autoimmunity in women with
recurrent pregnancy losses and repeated implantation failures: A
possible role of vitamin D. Autoimmun Rev. 15:943–947. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Unuane D, Velkeniers B, Deridder S,
Bravenboer B, Tournaye H and De Brucker M: Impact of thyroid
autoimmunity on cumulative delivery rates in in vitro
fertilization/intracytoplasmic sperm injection patients. Fertil
Steril. 106:144–150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Valdes CT, Schutt A and Simon C:
Implantation failure of endometrial origin: It is not pathology,
but our failure to synchronize the developing embryo with a
receptive endometrium. Fertil Steril. 108:15–18. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Teh WT, McBain J and Rogers P: What is the
contribution of embryo-endometrial asynchrony to implantation
failure? J Assist Reprod Genet. 33:1419–1430. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kumar V, Soni UK, Maurya VK, Singh K and
Jha RK: Integrin beta8 (ITGB8) activates VAV-RAC1 signaling via FAK
in the acquisition of endometrial epithelial cell receptivity for
blastocyst implantation. Sci Rep. 7:18852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Salamonsen LA, Evans J, Nguyen HP and
Edgell TA: The microenvironment of human implantation: Determinant
of reproductive success. Am J Reprod Immunol. 75:218–225. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bidarimath M, Khalaj K, Kridli RT, Wessels
JM, Koti M and Tayade C: Altered expression of chemokines and their
receptors at porcine maternal-fetal interface during early and
mid-gestational fetal loss. Cell Tissue Res. 366:747–761. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Franasiak JM, Burns KA, Slayden O, Yuan L,
Fritz MA, Korach KS, Lessey BA and Young SL: Endometrial CXCL13
expression is cycle regulated in humans and aberrantly expressed in
humans and Rhesus macaques with endometriosis. Reprod Sci.
22:442–451. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Choi YS, Yang JA, Yusuf I, Johnston RJ,
Greenbaum J, Peters B and Crotty S: Bcl6 expressing follicular
helper CD4 T cells are fate committed early and have the capacity
to form memory. J Immunol. 190:4014–4026. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nurieva RI, Chung Y, Martinez GJ, Yang XO,
Tanaka S, Matskevitch TD, Wang YH and Dong C: Bcl6 mediates the
development of T follicular helper cells. Science. 325:1001–1005.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hatzi K, Nance JP, Kroenke MA, Bothwell M,
Haddad EK, Melnick A and Crotty S: BCL6 orchestrates Tfh cell
differentiation via multiple distinct mechanisms. J Exp Med.
212:539–553. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Vaeth M, Eckstein M, Shaw PJ, Kozhaya L,
Yang J, Berberich-Siebelt F, Clancy R, Unutmaz D and Feske S:
Store-operated Ca(2+) entry in follicular T cells controls humoral
immune responses and autoimmunity. Immunity. 44:1350–1364. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Belanger S and Crotty S: Dances with
cytokines, featuring TFH cells, IL-21, IL-4 and B cells. Nat
Immunol. 17:1135–1136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Spolski R and Leonard WJ: Interleukin-21:
A double-edged sword with therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 13:379–395. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tangye SG: Advances in IL-21
biology-enhancing our understanding of human disease. Curr Opin
Immunol. 34:107–115. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang J, Yin T, Wen Y, Tian F, He X, Zhou
D, Lin Y and Yang J: Potential effects of interferon regulatory
factor 4 in a murine model of polyinosinic-polycytidylic
acid-induced embryo resorption. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2015.
|
|
61
|
Messaoudi S, Al-Khateeb GM, Dendana M,
Sater MS, Jazia KB, Nouira M, Almawi WY and Mahjoub T: Genetic
variations in the interleukin-21 gene and the risk of recurrent
idiopathic spontaneous miscarriage. Eur Cytokine Netw. 22:123–126.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Harker JA, Lewis GM, Mack L and Zuniga EI:
Late interleukin-6 escalates T follicular helper cell responses and
controls a chronic viral infection. Science. 334:825–829. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chavele KM, Merry E and Ehrenstein MR:
Cutting edge: Circulating plasmablasts induce the differentiation
of human T follicular helper cells via IL-6 production. J Immunol.
194:2482–2485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Choi YS, Eto D, Yang JA, Lao C and Crotty
S: Cutting edge: STAT1 is required for IL-6-mediated Bcl6 induction
for early follicular helper cell differentiation. J Immunol.
190:3049–3053. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sahoo A, Wali S and Nurieva R: T helper 2
and T follicular helper cells: Regulation and function of
interleukin-4. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 30:29–37. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fairfax KC, Everts B, Amiel E, Smith AM,
Schramm G, Haas H, Randolph GJ, Taylor JJ and Pearce EJ:
IL-4-secreting secondary T follicular helper (Tfh) cells arise from
memory T cells, not persisting Tfh cells, through a B
cell-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 194:2999–3010. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|