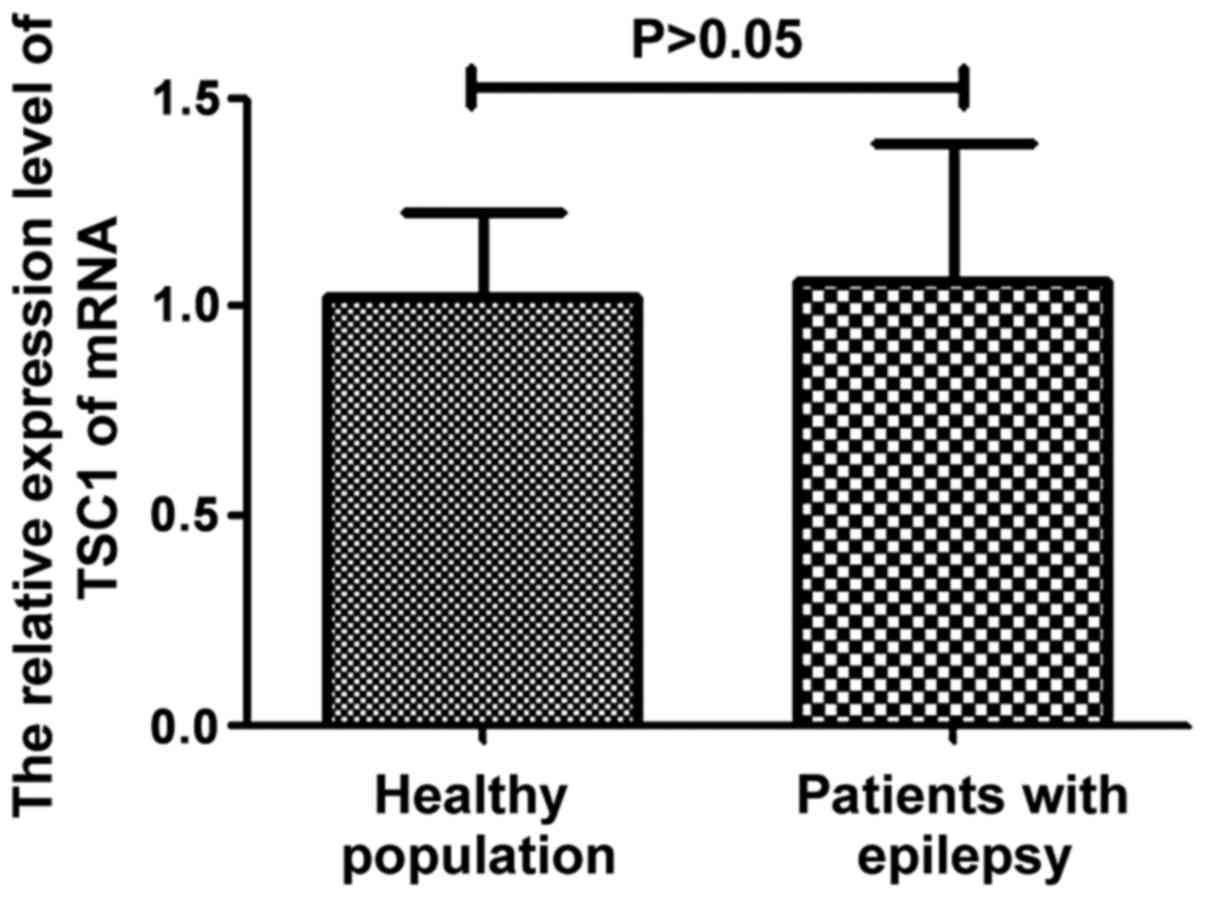
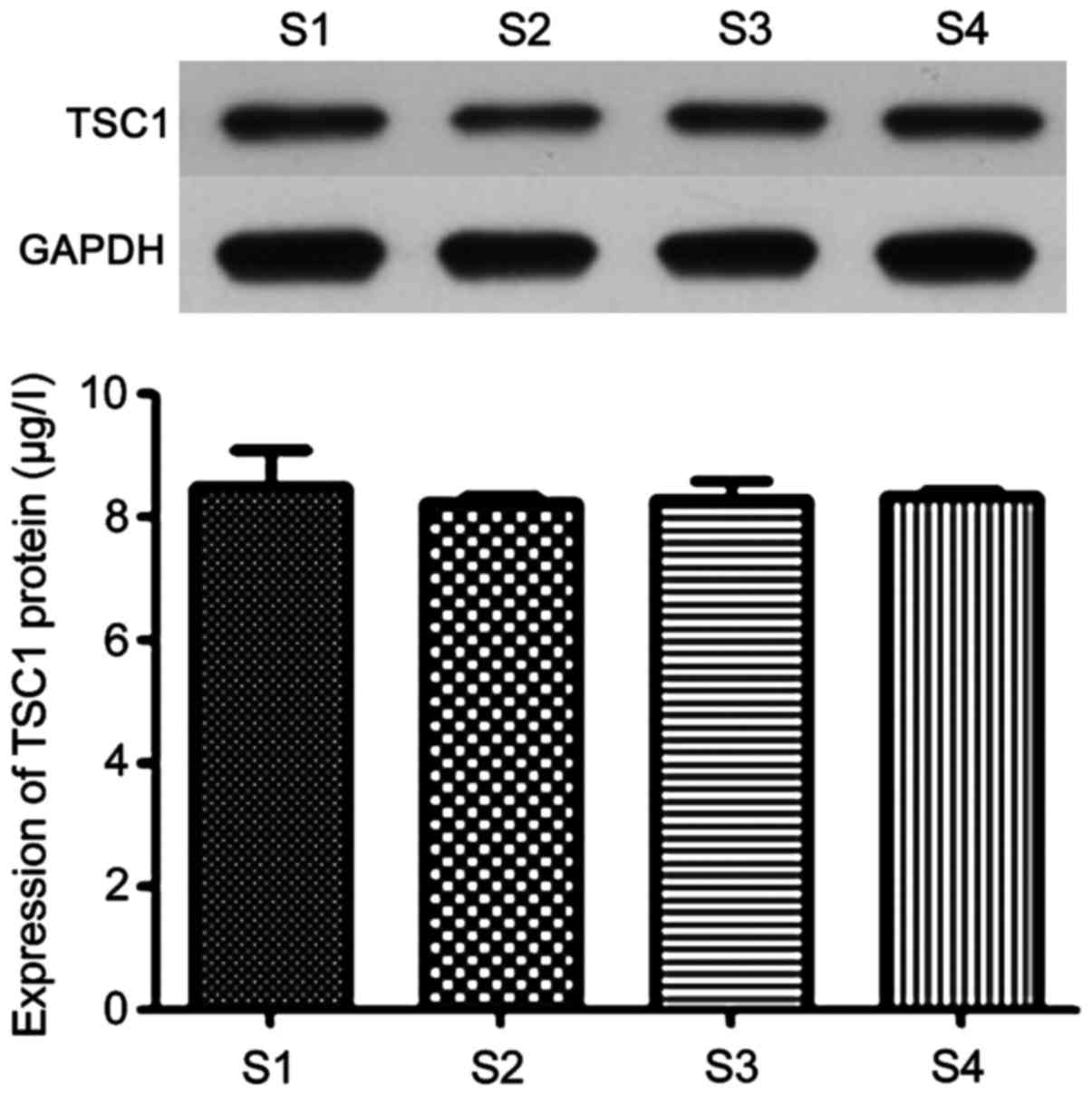
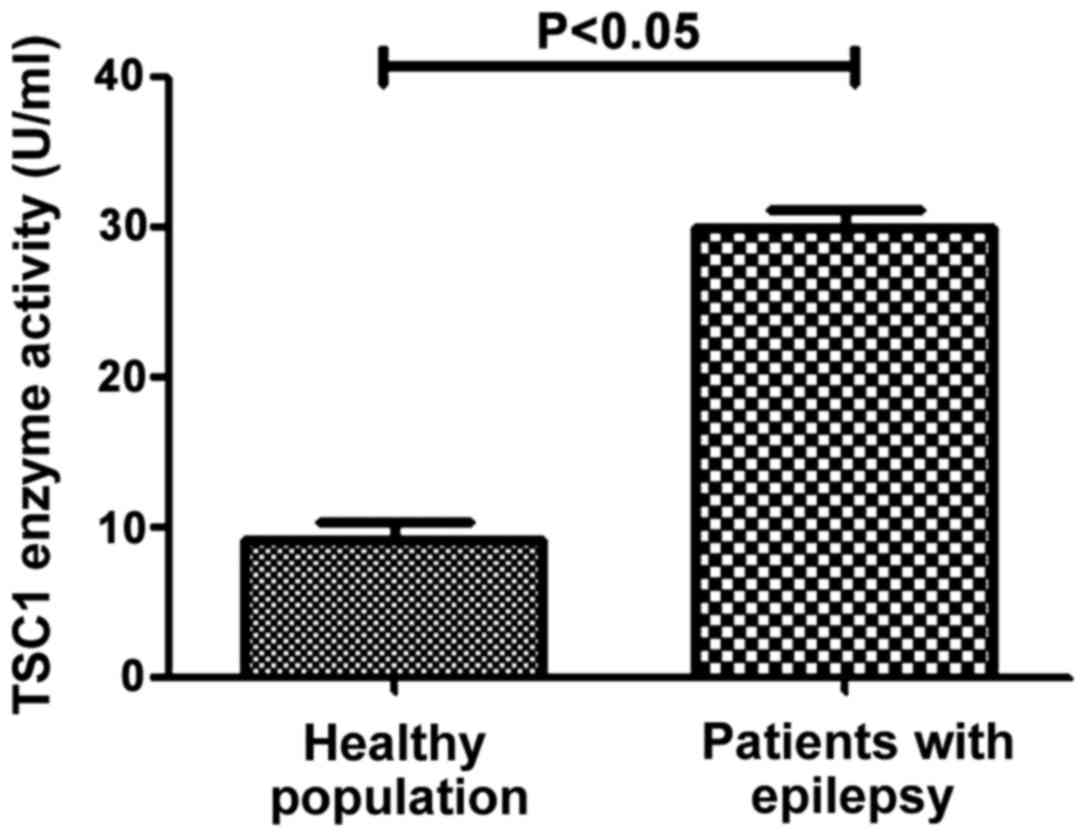
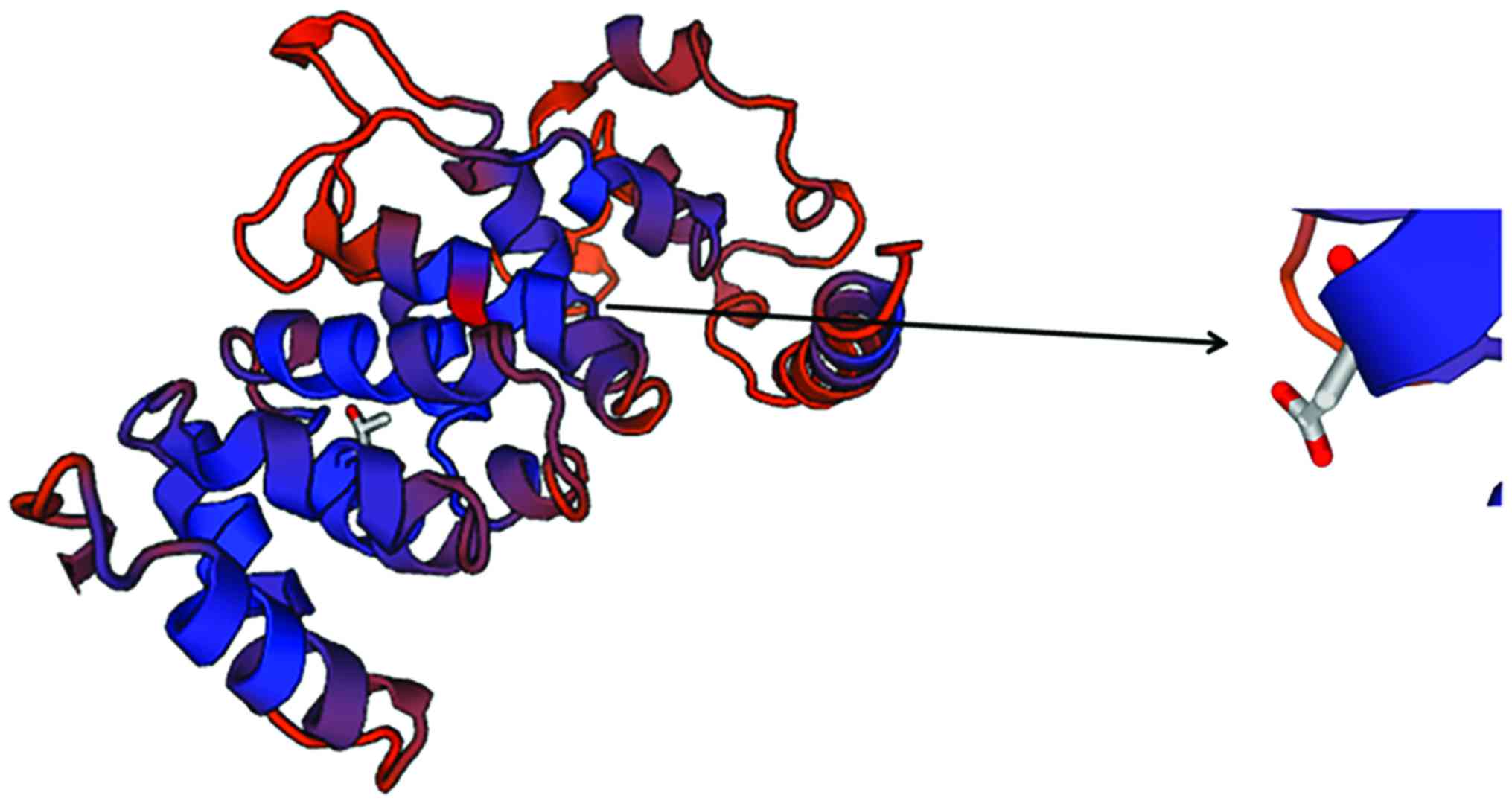
|
1
|
Faure JB, Marques-Carneiro JE, Akimana G,
Cosquer B, Ferrandon A, Herbeaux K, Koning E, Bar-belivien A,
Nehlig A and Cassel JC: Attention and executive functions in a rat
model of chronic epilepsy. Epilepsia. 55:644–653. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fernández-Gajardo R, Matamala JM, Carrasco
R, Gutiérrez R, Melo R and Rodrigo R: Novel therapeutic strategies
for traumatic brain injury: Acute antioxidant reinforcement. CNS
Drugs. 28:229–248. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rowley S and Patel M: Mitochondrial
involvement and oxidative stress in temporal lobe epilepsy. Free
Radic Biol Med. 62:121–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Korczyn AD, Schachter SC, Brodie MJ, Dalal
SS, Engel J Jr, Guekht A, Hecimovic H, Jerbi K, Kanner AM,
Johannessen Landmark C, et al: Epilepsy, cognition, and
neuropsychiatry (Epilepsy, Brain, and Mind, part 2). Epilepsy
Behav. 28:283–302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
de Figueiredo SM, Filho SA,
Nogueira-Machado JA and Caligiorne RB: The anti-oxidant properties
of isothiocyanates: A review. Recent Pat Endocr Metab Immune Drug
Discov. 7:213–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kan MC, Wang WP, Yao GD, Li JT, Xie T,
Wang W and Ma WQ: Anticonvulsant effect of dexmedetomidine in a rat
model of self-sustaining status epilepticus with prolonged amygdala
stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 543:17–21. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Howard BA and Lu P: Stromal regulation of
embryonic and postnatal mammary epithelial development and
differentiation. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 25–26:43–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu X, Ory V, Chapman S, Yuan H, Albanese
C, Kallakury B, Timofeeva OA, Nealon C, Dakic A, Simic V, et al:
ROCK inhibitor and feeder cells induce the conditional
reprogramming of epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 180:599–607. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Düvel K, Yecies JL, Menon S, Raman P,
Lipovsky AI, Souza AL, Triantafellow E, Ma Q, Gorski R, Cleaver S,
et al: Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream
of mTOR complex 1. Mol Cell. 39:171–183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bissler JJ, Kingswood JC, Radzikowska E,
Zonnenberg BA, Frost M, Belousova E, Sauter M, Nonomura N,
Brakemeier S, de Vries PJ, et al: Everolimus for angiomyolipoma
associated with tuberous sclerosis complex or sporadic
lymphangioleiomyomatosis (EXIST-2): A multicentre, randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 381:817–824. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu NK and Xu XM: Neuroprotection and its
molecular mechanism following spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res.
7:2051–2062. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Colín-González AL, Orozco-Ibarra M,
Chánez-Cárdenas ME, Rangel-López E, Santamaría A, Pedraza-Chaverri
J, Barrera-Oviedo D and Maldonado PD: Heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1)
upregulation delays morphological and oxidative damage induced in
an excitotoxic/pro-oxidant model in the rat striatum. Neuroscience.
231:91–101. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morroni F, Tarozzi A, Sita G, Bolondi C,
Moraga Zolezzi JM, Cantelli-Forti G and Hrelia P: Neu-roprotective
effect of sulforaphane in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned mouse model of
Parkinson's disease. Neurotoxicology. 36:63–71. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou H, Wang N, Xu L, Huang HL and Yu CY:
Clinical study on anti-epileptic drug with B vitamins for the
treatment of epilepsy after stroke. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:3327–3331. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sanchez RM, Ribak CE and Shapiro LA:
Synaptic connections of hilar basal dendrites of dentate granule
cells in a neonatal hypoxia model of epilepsy. Epilepsia. 53 Suppl
1:98–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Vittos O, Toana B, Vittos A and Moldoveanu
E: Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2): A review of
its role and significance as a cardiovascular biomarker.
Biomarkers. 17:289–302. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao T, Li Y, Dai X, Wang J, Qi Y, Wang J
and Xu K: Effects of retrograde gene transfer of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor in the rostral spinal cord of a compression
model in rat. Mol Biol Rep. 39:8045–8051. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakano N, Nakai Y, Seo TB, Yamada Y, Ohno
T, Yamanaka A, Nagai Y, Fukushima M, Suzuki Y, Nakatani T, et al:
Characterization of conditioned medium of cultured bone marrow
stromal cells. Neurosci Lett. 483:57–61. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Uriarte G, Paternain L, Milagro FI,
Martínez JA and Campion J: Shifting to a control diet after a
high-fat, high-sucrose diet intake induces epigenetic changes in
retroperitoneal adipocytes of Wistar rats. J Physiol Biochem.
69:601–611. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lovinsky-Desir S and Miller RL:
Epigenetics, asthma, and allergic diseases: A review of the latest
advancements. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 12:211–220. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|