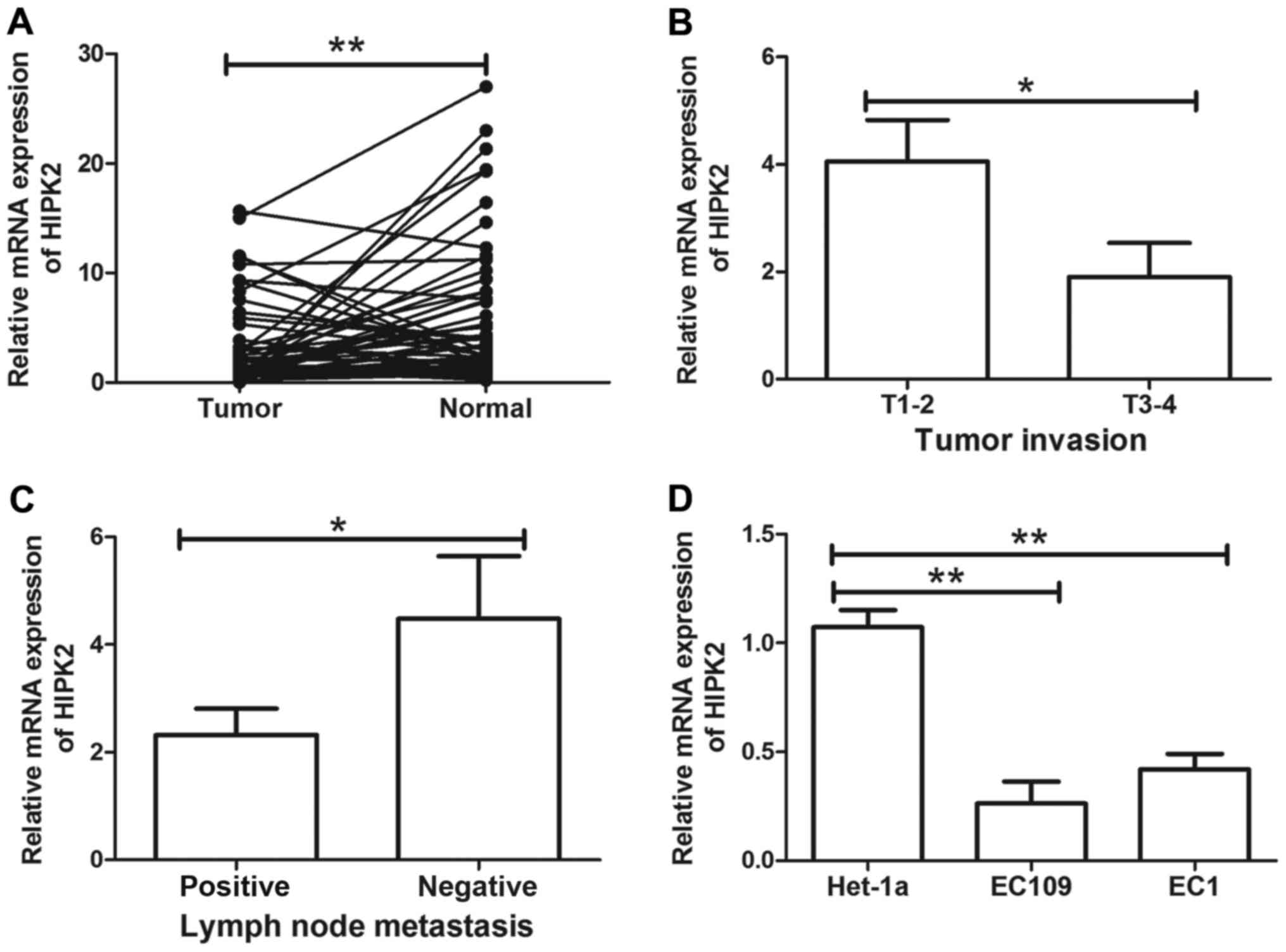
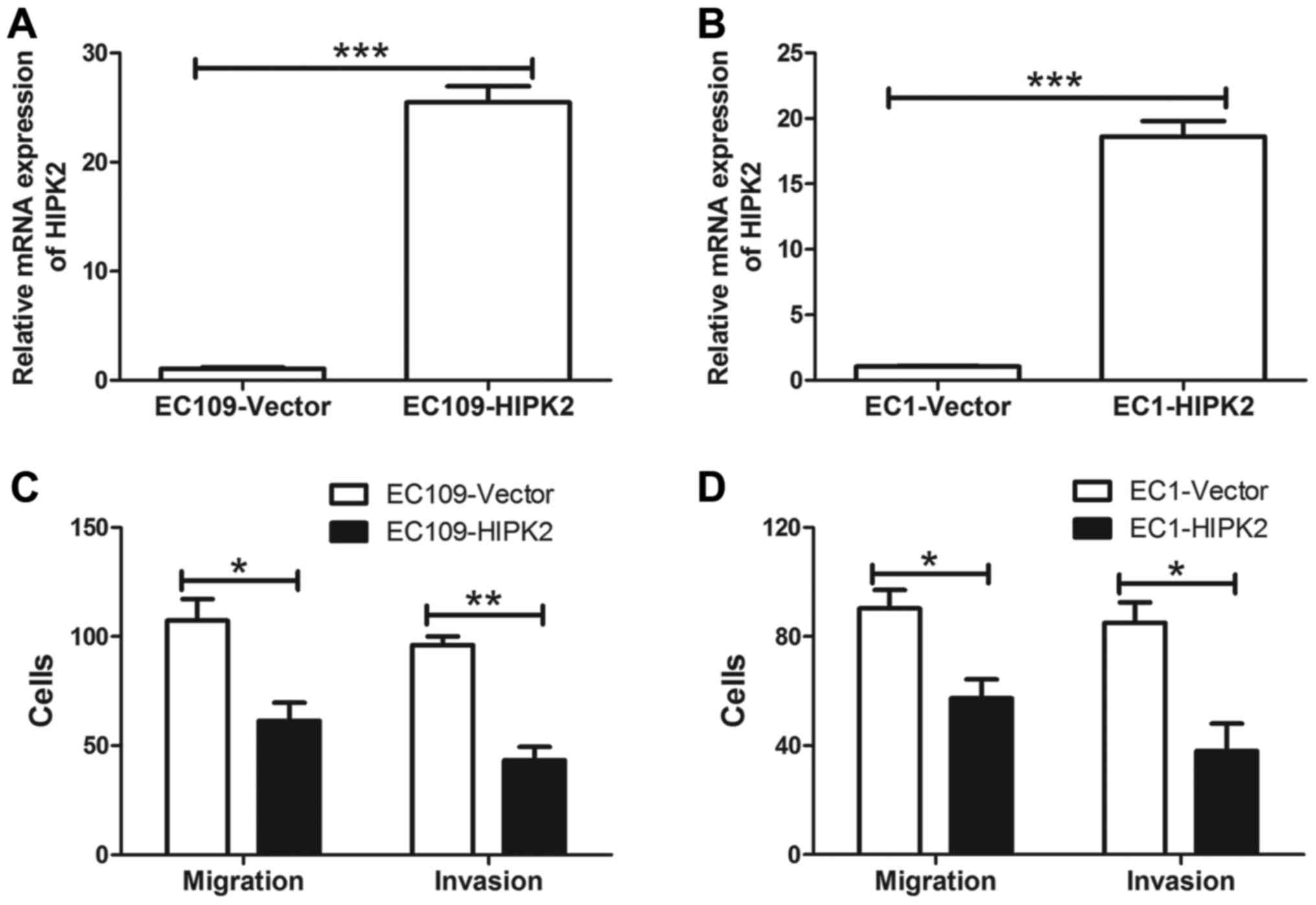
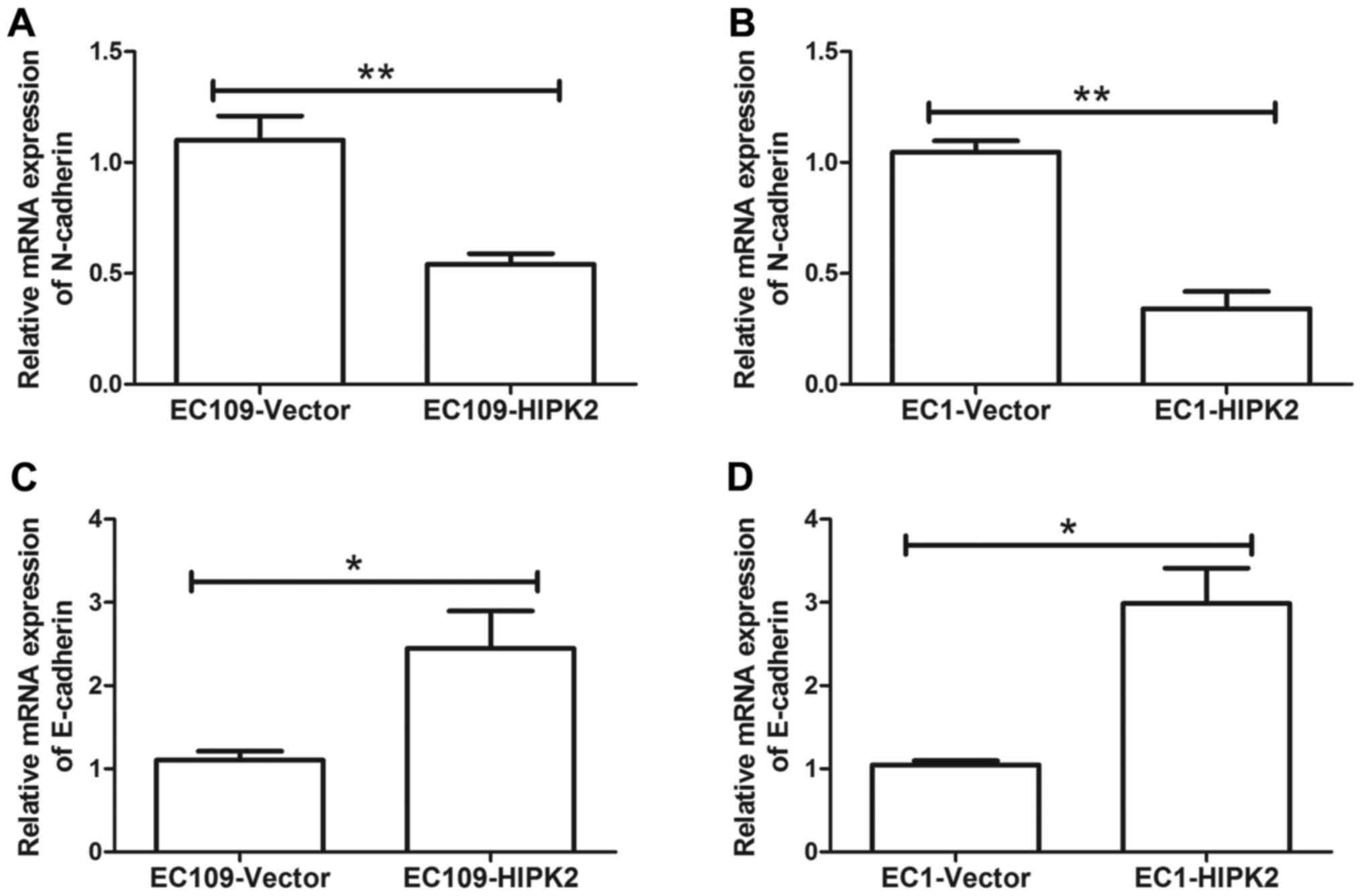
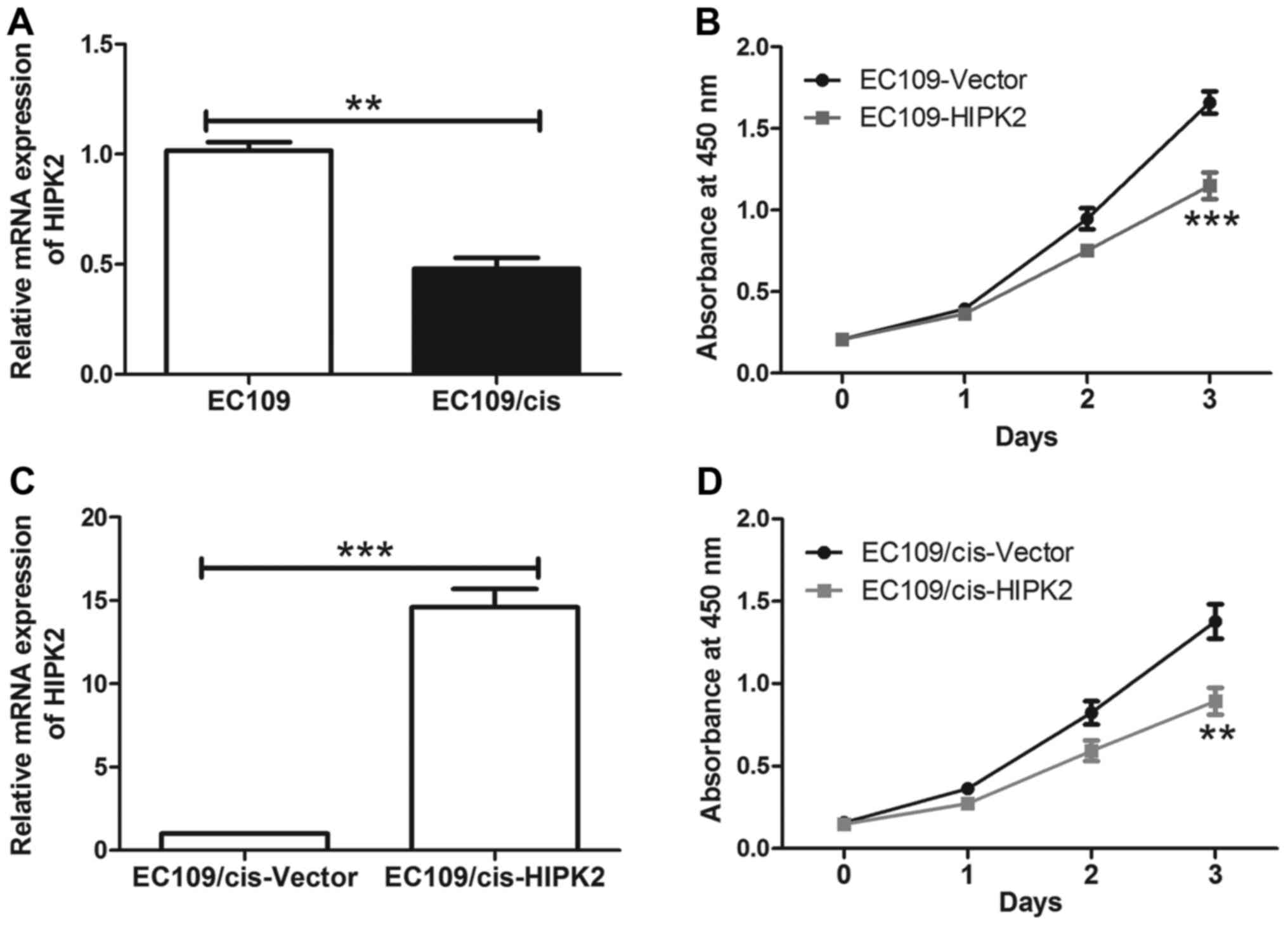
|
1
|
Wang LD, Zhou FY, Li XM, Sun LD, Song X,
Jin Y, Li JM, Kong GQ, Qi H, Cui J, et al: Genome-wide association
study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54. Nat Genet.
42:759–763. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hongo M, Nagasaki Y and Shoji T:
Epidemiology of esophageal cancer: Orient to Occident. Effects of
chronology, geography and ethnicity. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
24:729–735. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morita M, Kumashiro R, Kubo N, Nakashima
Y, Yoshida R, Yoshinaga K, Saeki H, Emi Y, Kakeji Y, Sakaguchi Y,
et al: Alcohol drinking, cigarette smoking, and the development of
squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus: Epidemiology, clinical
findings, and prevention. Int J Clin Oncol. 15:126–134. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown LM, Hoover R, Silverman D, Baris D,
Hayes R, Swanson GM, Schoenberg J, Greenberg R, Liff J, Schwartz A,
et al: Excess incidence of squamous cell esophageal cancer among US
Black men: Role of social class and other risk factors. Am J
Epidemiol. 153:114–122. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nardinocchi L, Puca R, Sacchi A, Rechavi
G, Givol D and D'Orazi G: Targeting hypoxia in cancer cells by
restoring homeodomain interacting protein-kinase 2 and p53 activity
and suppressing HIF-1alpha. PLoS One. 4:e68192009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Di Stefano V, Blandino G, Sacchi A, Soddu
S and D'Orazi G: HIPK2 neutralizes MDM2 inhibition rescuing p53
transcriptional activity and apoptotic function. Oncogene.
23:5185–5192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bon G, Di Carlo SE, Folgiero V, Avetrani
P, Lazzari C, D'Orazi G, Brizzi MF, Sacchi A, Soddu S, Blandino G,
et al: Negative regulation of beta4 integrin transcription by
homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 2 and p53 impairs tumor
progression. Cancer Res. 69:5978–5986. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ann EJ, Kim MY, Yoon JH, Ahn JS, Jo EH,
Lee HJ, Lee HW, Kang HG, Choi DW, Chun KH, et al: Tumor suppressor
HIPK2 regulates malignant growth via phosphorylation of Notch1.
Cancer Res. 76:4728–4740. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin Y, Ratnam K, Chuang PY, Fan Y, Zhong
Y, Dai Y, Mazloom AR, Chen EY, D'Agati V, Xiong H, et al: A systems
approach identifies HIPK2 as a key regulator of kidney fibrosis.
Nat Med. 18:580–588. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pistritto G, Puca R, Nardinocchi L, Sacchi
A and D'Orazi G: HIPK2-induced p53Ser46 phosphorylation activates
the KILLER/DR5-mediated caspase-8 extrinsic apoptotic pathway. Cell
Death Differ. 14:1837–1839. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Puca R, Nardinocchi L, Pistritto G and
D'Orazi G: Overexpression of HIPK2 circumvents the blockade of
apoptosis in chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol.
109:403–410. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lazzari C, Prodosmo A, Siepi F, Rinaldo C,
Galli F, Gentileschi M, Bartolazzi A, Costanzo A, Sacchi A,
Guerrini L and Soddu S: HIPK2 phosphorylates ΔNp63α and promotes
its degradation in response to DNA damage. Oncogene. 30:4802–4813.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nodale C, Sheffer M, Jacob-Hirsch J,
Folgiero V, Falcioni R, Aiello A, Garufi A, Rechavi G, Givol D and
D'Orazi G: HIPK2 downregulates vimentin and inhibits breast cancer
cell invasion. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:198–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tan M, Gong H, Zeng Y, Tao L, Wang J,
Jiang J, Xu D, Bao E, Qiu J and Liu Z: Downregulation of
homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 contributes to bladder
cancer metastasis by regulating Wnt signaling. J Cell Biochem.
115:1762–1767. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rice TW, Blackstone EH and Rusch VW: 7th
edition of the AJCC cancer staging Manual: Esophagus and
esophagogastric junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1721–1724. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han T, Zhu X, Wang J, Zhao H, Ma Q, Zhao
J, Qiu X and Fan Q: Establishment and characterization of a
cisplatin-resistant human osteosarcoma cell line. Oncol Rep.
32:1133–1139. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akita H, Doki Y, Miyata H, Hirao T, Yano
M, Takachi K, Miyashiro I, Sasaki Y, Ishikawa O, Ohigashi H and
Imaoka S: Clinical significance of the second cycle response to
cisplatin-based chemotherapy as preoperative treatment for
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 93:401–409. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu A, Zhu J, Wu G, Cao L, Tan Z, Zhang S,
Jiang L, Wu J, Li M, Song L and Li J: Antagonizing miR-455-3p
inhibits chemoresistance and aggressiveness in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 16:1062017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin J, Zhang Q, Lu Y, Xue W, Xu Y, Zhu Y
and Hu X: Downregulation of HIPK2 increases resistance of bladder
cancer cell to cisplatin by regulating Wip1. PLoS One.
9:e984182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng Y, Al-Beiti MA, Wang J, Wei G, Li J,
Liang S and Lu X: Correlation between homeodomain-interacting
protein kinase 2 and apoptosis in cervical cancer. Mol Med Rep.
5:1251–1255. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
D'Orazi G, Sciulli MG, Di Stefano V,
Riccioni S, Frattini M, Falcioni R, Bertario L, Sacchi A and
Patrignani P: Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 restrains
cytosolic phospholipase A2-dependent prostaglandin E2 generation in
human colorectal cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 12:735–741. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hsu WH, Hsu PK, Hsieh CC, Huang CS and Wu
YC: The metastatic lymph node number and ratio are independent
prognostic factors in esophageal cancer. J Gastrointest Surg.
13:1913–1920. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hosch SB, Stoecklein NH, Pichlmeier U,
Rehders A, Scheunemann P, Niendorf A, Knoefel WT and Izbicki JR:
Esophageal cancer: The mode of lymphatic tumor cell spread and its
prognostic significance. J Clin Oncol. 19:1970–1975. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Voulgari A and Pintzas A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis: Mechanisms,
markers and strategies to overcome drug resistance in the clinic.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1796:75–90. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chung S, Yao J, Suyama K, Bajaj S, Qian X,
Loudig OD, Eugenin EA, Phillips GR and Hazan RB: N-cadherin
regulates mammary tumor cell migration through Akt3 suppression.
Oncogene. 32:422–430. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qian X, Anzovino A, Kim S, Suyama K, Yao
J, Hulit J, Agiostratidou G, Chandiramani N, McDaid HM, Nagi C, et
al: N-cadherin/FGFR promotes metastasis through
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem/progenitor cell-like
properties. Oncogene. 33:3411–3421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mitra A, Mishra L and Li S: EMT, CTCs and
CSCs in tumor relapse and drug-resistance. Oncotarget.
6:10697–10711. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Jin YY, Chen QJ, Xu K, Ren HT, Bao X, Ma
YN, Wei Y and Ma HB: Involvement of microRNA-141-3p in
5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin chemo-resistance in esophageal
cancer cells via regulation of PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 422:161–170.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lagergren J, Smyth E, Cunningham D and
Lagergren P: Oesophageal cancer. Lancet. Jun 22–2017.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoshida T, Miyoshi T, Seike J, Yamai H,
Takechi H, Yuasa Y and Tangoku A: Gene expression changes in a
chemoresistant model with human esophageal cancer xenografts using
cDNA microarray. Anticancer Res. 29:1163–1168. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Puca R, Nardinocchi L, Givol D and D'Orazi
G: Regulation of p53 activity by HIPK2: MOlecular mechanisms and
therapeutical implications in human cancer cells. Oncogene.
29:4378–4387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|